What is the Mail From field?
- josh
- May 8, 2015
- Best practices , Technical
When emails are sent, there are two from fields, the Mail From and the Display From address. The Display From address (technically referred to as RFC.5322 from address) is the from address that is displayed to the end user within their email client. The Mail From (technically referred to as RFC.5321 from address) is the email address to which bounce messages are delivered. The Mail From field is sometimes referred to as the Return Path address, Envelope From address, or Bounce address.
It may seem confusing to have an email with two from fields, but knowing the difference is important to properly setup your SPF records.
Taking a look at this email I received from GoPro, the Return-Path (5321.From) goes back to @bounce.email.gopro.com. If I were to reply to the email, the message would go to @email.gopro.com. The Display From (5322.From) address is gopro@email.gopro.com.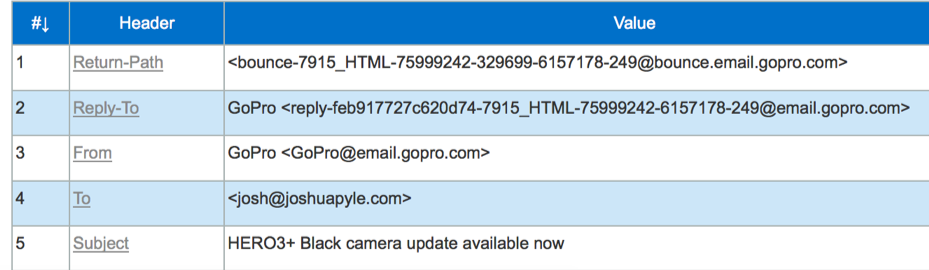
I would want to add the email address GoPro@email.gopro.com to my address book because that is the email address that is displayed in my email client. The reason why the Return-Path is different from the From address is because GoPro likely has an automated system that will process the bounce back messages (sent to @bounce.email.gopro.com) and automatically flag or unsubscribe those email addresses. This allows GoPro to setup automatic processing of the different mail streams sent to them, one stream being the bounce backs after a mailing and the second being an automated customer service system.
Where does SPF fit in?
SPF checks the Mail From (5321.From) address, not the Display From (5322.From) address. In the example above, there should be an SPF record for the subdomain of bounce.email.gopro.com. I can check the SPF record using our Authentication tools http://tools.wordtothewise.com/spf/check/bounce.email.gopro.com and I receive the following results: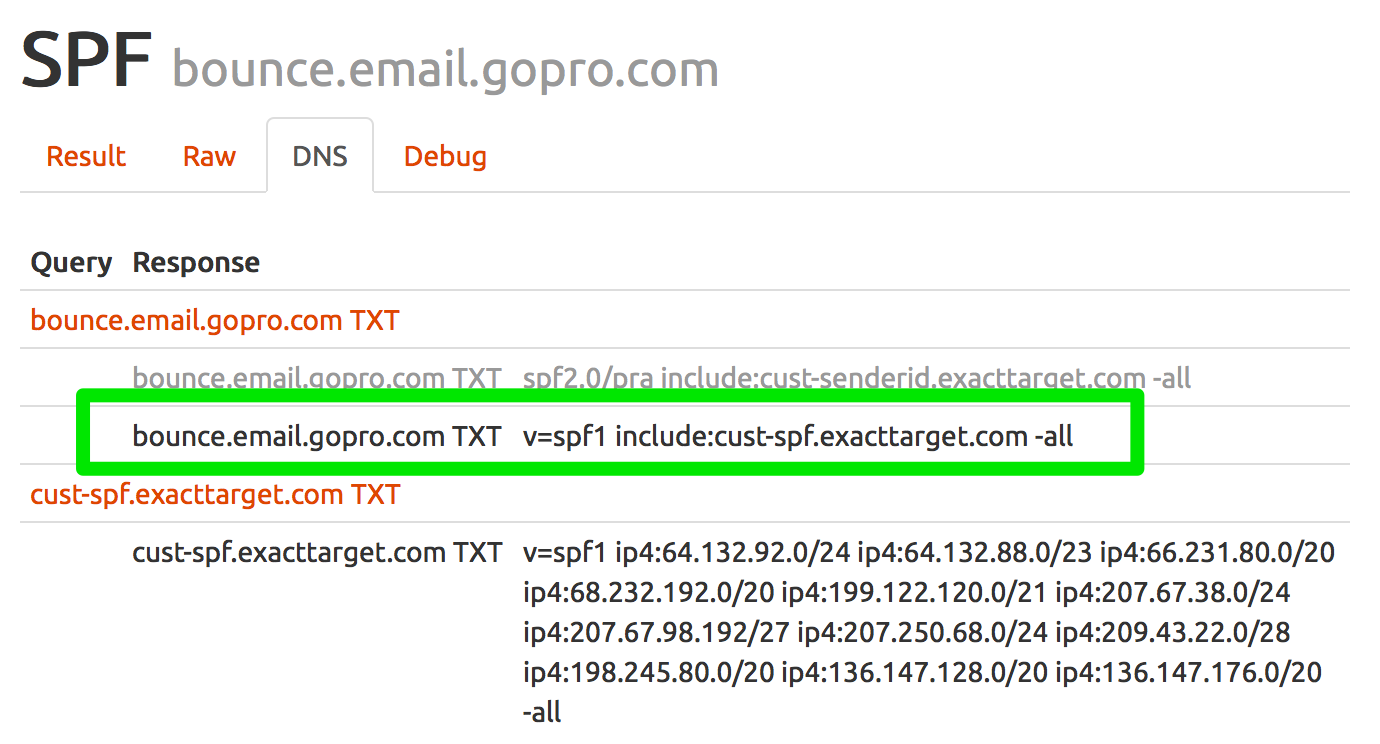
Checking the headers shows that GoPro does have a SPF record setup and the message was authenticated with SPF.![]()
For SPF records, make sure the SPF record matches the Mail From (From.5321)/Return-Path domain name. Have your recipients add the Display From (From.5322) email address to their address book so they will continue to receive your mailings.