DMARC=BestGuessPass
Looking at the headers within the mail received with my Office365 domain I see dmarc=bestguesspass. BestGuessPass? That’s a new.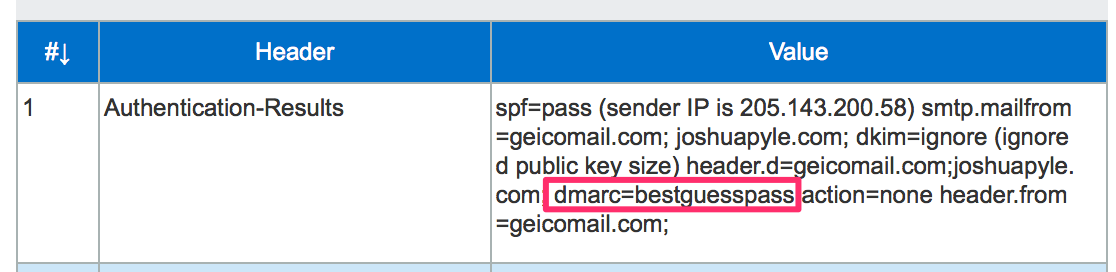
A few days after seeing dmarc=bestguesspass, Terry Zink at Microsoft posted an explanation. Exchange Online Protection, the filtering system for Office365, is analyzing the authentication of incoming emails and if the domain is not publishing a DMARC record, EOP attempts to determine what the results would be if they did. If an email is received that is not authenticated with either SPF or DKIM, the dmarc= results show none just as it always had. DMARC=BestGuessPass will appear if the message is authenticated and the matching authenticated domain does not have a DMARC record.
Having this information is helpful to see what the results would be before setting up a DMARC record. If you are seeing dmarc=bestguesspass when your mail is sent to an Office365 address and you are considering DMARC, the next step would be to publish a p=none DMARC policy and begin to document where your mail is being sent from. P=none will not have an impact on your delivery and asks the receiving mail server to take no action if a DMARC check fails. Once you have setup SPF and DKIM for your mail, p=none policy gives you the ability to begin receiving failure reports from receiving mail servers when unauthenticated mail is sent from your domain.