Are you ready for DMARC?
 The next step in email authentication is DMARC. I wrote a Brief DMARC primer a few years ago to help clear up some of the questions about DMARC and alignment. But I didn’t talk much about where DMARC was going. Part of the reason was I didn’t know where things were going and too much was unclear to even speculate.
The next step in email authentication is DMARC. I wrote a Brief DMARC primer a few years ago to help clear up some of the questions about DMARC and alignment. But I didn’t talk much about where DMARC was going. Part of the reason was I didn’t know where things were going and too much was unclear to even speculate.
We’re almost 2 years down the line from the security issues that prompted Yahoo to turn on p=reject in their DMARC record. This broke a lot of common uses of email. A lot of the damage created by this has been mitigated and efforts to fix it continue. There’s even an IETF draft looking at ways to transfer authentication through mailing lists and third parties.
For 2016, DMARC alignment is going to be a major factor in deliverability for bulk email, even in the absence of a published DMARC record.
What’s DMARC alignment?
DMARC alignment is where either the Return Path (5321.From, Envelope From, Bounce String) or the DKIM d= value is in the same domain space as the visible from address (5322.From, sender).
Why do you think so?
I’m already seeing some delivery issues for certain domains that are unaligned, particularly at ISPs like AOL and Yahoo.
What do I do?
If you’re an ESP customer, ask your ESP about using a custom bounce string / return path so your domain aligns. You just need to add a MX record for that domain that points to the ESPs bounce handler.
If you’re an ESP customer and can’t add a MX, ask them about signing your mail with a custom DKIM key that is at your domain. You will need to do a little DNS work – either publishing your public key yourself or publishing a DNS record that points to their public key server.
If you’re an ESP, and you can’t sign with custom keys or handle custom 5321.From addresses, you need to look at your development path and figure out how fast you can do either.
I’m not publishing DMARC, so this doesn’t affect me.
ISPs are already evaluating DMARC alignment on all incoming mail.
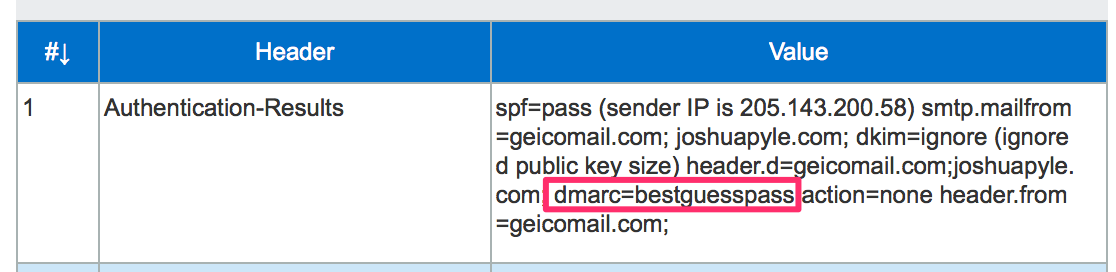
dmarc=pass (aol.com: the domain example.com reports that SPF aligns in relaxed mode, DKIM is unaligned.) header.from=test.example.com;
It’s a short step to use that as part of their delivery decisions, particularly when there is no alignment.
My unaligned mail is delivering just fine.
I’m sure it is. I also don’t think that’s a given for the future. I think it’s wise to be looking to have as much of your mail as possible aligned sooner rather than later.