Microsoft deprecating SmartScreen filters
At the beginning of the month Microsoft announced that they were deprecating the SmartScreen filters used by the desktop Microsoft mail clients. These are the filters used in Exchange and various version of Outlook mail. This is yet further consolidation of spam filtering between the Microsoft free webmail domains, Office365 hosted domains and self hosted Exchange servers. The online services (hotmail.com, outlook.com, Office365, live.com, etc) have been using these filters for a while. The big change now is that they’re being pushed down to Exchange and Outlook users not hosted on the Microsoft site.
EOP was developed for Outlook.com (and friends) as well as Office365 users. From Microsoft’s description, it sounds like the type of machine learning engine that many providers are moving to.
Microsoft has published quite a bit of information about these filters and how they work on their website. One of the best places to start is the Anti-spam Protection FAQ. Something senders should pay attention to is the final question on that page: “What are a set of best outbound mailing practices that will ensure that my mail is delivered?” Those are all things deliverability folks recommend for good inbox delivery.
Poking around looking at the links and descriptions, there is a host of great information about spam filtering at Microsoft and how it works.
A page of note is their Exchange Online Protection Overview. This describes the EOP process and how the filters work.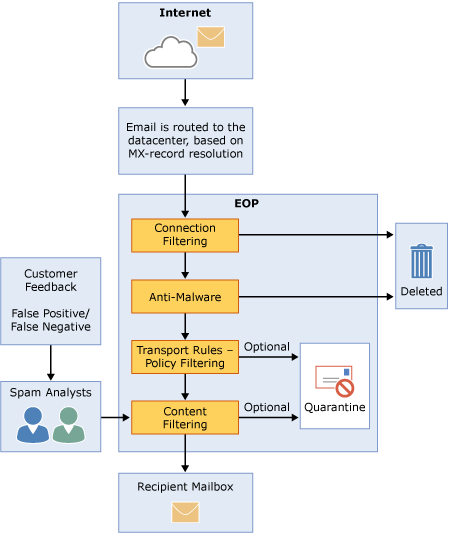
An incoming message initially passes through connection filtering, which checks the sender’s reputation and inspects the message for malware. The majority of spam is stopped at this point and deleted by EOP. Messages continue through policy filtering, where messages are evaluated against custom transport rules that you create or enforce from a template. For example, you can have a rule that sends a notification to a manager when mail arrives from a specific sender. (Data loss prevention checks also occur at this point, if you have that feature; for information about feature availability, see the Exchange Online Protection Service Description.) Next, messages pass through content filtering, where content is checked for terminology or properties common to spam. A message determined to be spam by the content filter can be sent to a user’s Junk Email folder or to the quarantine, among other options, based on your settings. After a message passes all of these protection layers successfully, it is delivered to the recipient.
Well, if you ever wanted to know how Microsoft filters mail, now you do.
I’m also pleased to read that MS is continuing to support SNDS. I know it’s been problematic for folks lately and was somewhat concerned as the person who created SNDS recently moved to a new position. However, their FAQs still recommend SNDS so I think we can expect it to be maintained by new folks.