Tools!
I just added a DMARC validation tool over on tools.wordtothewise.com.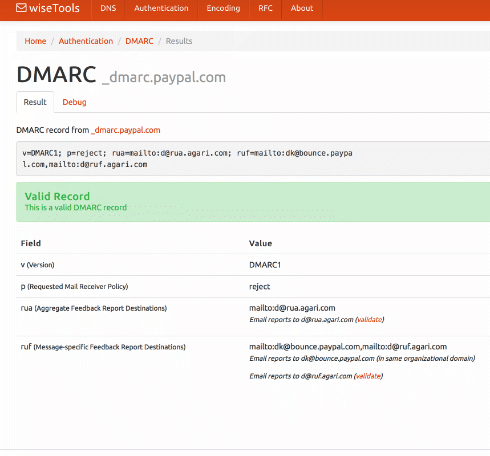
You can give it a domain – such as ebay.com – and it will fetch the DMARC record, then explain and validate it. Or you can paste the DMARC record you’re planning to publish into it, to validate it before you go live.
If you’ve not seen our tools page before, take a look. As well as DMARC we have a DKIM validator, SPF expander and optimizer, general DNS lookup tools, a bunch of RFCs covering all sorts of protocols, and base64 and quoted-printable decoders.
There’s also a widget that lets you add those little unicode pictures to your subject lines, whether you need a snowman ⛄, a forest ????, or a pig getting closer ???.
The results pages all have easily copyable URLs so they’re pretty good for sharing with co-workers or customers if you need that sort of thing.
(And if you need a cidr calculator, whois, or easy access to abuse.net & Microsoft SNDS check out Al’s xnnd.com.)

