Well, we mostly survived 2016�. A year ago I was making predictions about how 2016 would be the year of email security. I was thinking of things like TLS and authentication and access to the inbox. It wasn’t out of the question, Gmail said they’d be turning on p=reject sometime mid-year. They also were suggesting that they would be putting more value on messages that aligned, even in the absence of a DMARC signature. The first still hasn’t happened, and the second doesn’t appear to be in place, either.

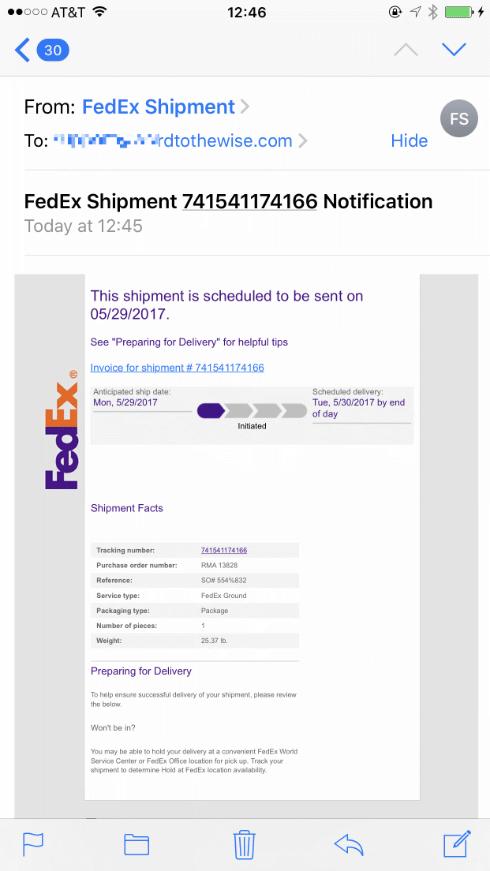
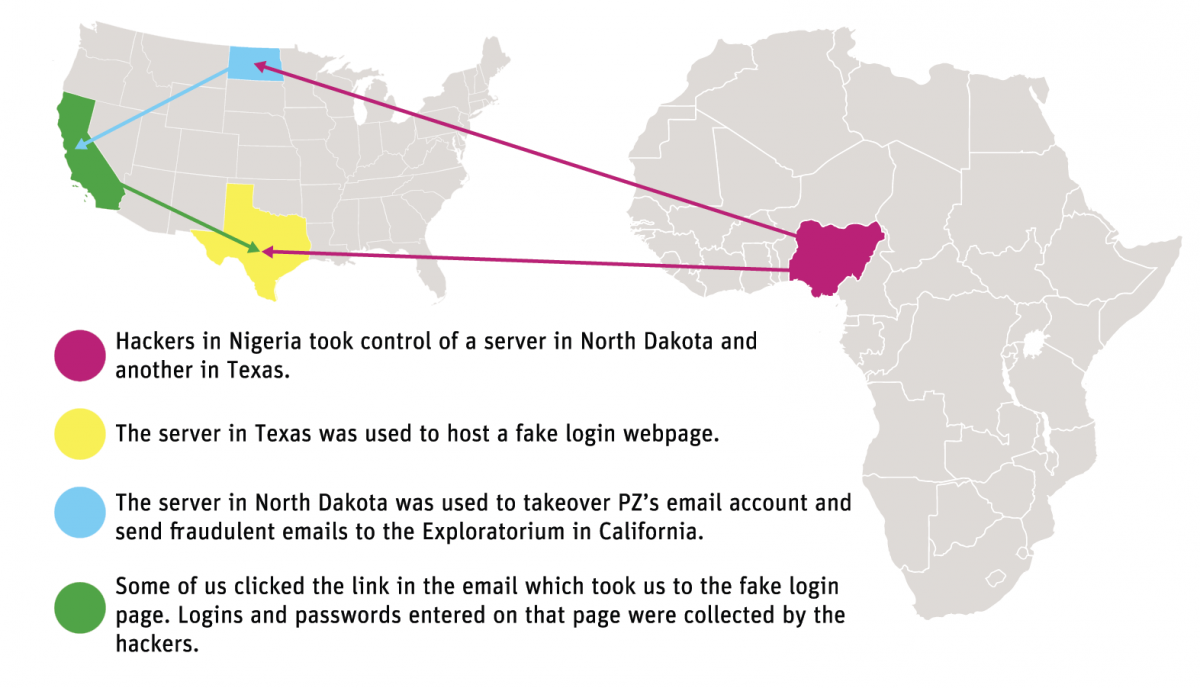
That doesn’t mean email security wasn’t a hot topic in 2016. In fact, the use of a private email server was a major topic during the US elections. We also had spear-phishing play a major role in the compromise of campaign systems. I didn’t talk much about that here when it happened, but news reports make it clear that Chairman Podesta and others were targeted for compromise. The NY Times has a more in depth article with broader context around the attacks and how emails were used to infiltrate a major political party.
The irony is with all the time spent talking about how insecure the private server was, that server wasn’t compromised. Instead, the compromise was at Gmail.
We all need to pay attention to our email and how we use it. It also means when we’re sending bulk and marketing email we need to consider the private and personal information we’re putting in messages. Do you send PII? Is there a way you don’t have to? What can we do to protect our brand and our users?
It’s not just bulk email we need to think about, either. Personal email can contain PII, or personal information. A common saying among some of my security friends is “never put in email anything you wouldn’t want to see on the front page of the Washington Post or NY Times.” That’s an easy thing to say, but the convenience of email makes it easy to share information that we may not want on the front page of either paper. Many of us aren’t actually targets of malicious activity so we don’t have to worry about being targeted the way elected and other officials are. But that doesn’t mean we are not at risk. It just means we’re at less risk than others.
Email is a frequent vector for malicious actors to access computers. Most, if not all of the major breeches in the last few years have started with a phishing attack of some sort. The attacks are planned out and sophisticated. This is not going to get better. The phishers are smart and plan the attacks. We also need to be more personally aware of security given the current political climate. We need to take steps to protect ourselves more than we have in the past.
Security is more important than ever and we all need to protect ourselves.
Read More