What’s the best opt-in method?
Kickbox interviewed a bunch of us to find out what methods of opt-in we recommend. Go check it out.
What’s your favourite method of opt-in?
Kickbox interviewed a bunch of us to find out what methods of opt-in we recommend. Go check it out.
What’s your favourite method of opt-in?
I regularly tell clients to be transparent with their sends. With email, permission is better than forgiveness. A surprise change in mail frequency or type leads to complaints. Complaints lead to bulk foldering. Once mail is in the bulk folder, it’s hard to get out of there, particularly at some webmail providers.
The permission is better than forgiveness is hard for a lot of senders to understand. Much of marketing is about assuming the yes in the absence of a no. Sure, they’ll back off when there’s a no, in DMA terms it’s the “one bite at the apple rule.” Unfortunately for senders the one bite rule doesn’t work in the email space.
There are a couple reasons that permission is better than forgiveness in the email space. The biggest is that the ISPs own the mailbox and as the owners they make decisions about who gets access. They prioritize the wants and needs of their customers / users over the wants and needs of advertisers. It’s easy for users to give feedback; in many cases they just have to hit a button. But that’s another whole blog post.
Today I get an email from The Guardian. They’re modifying and expanding their newsletter program, so they sent subscribers an update about it.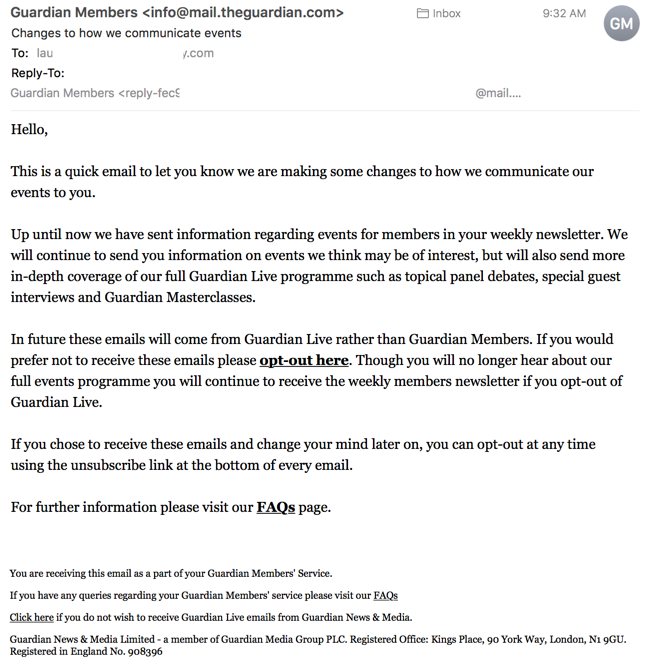
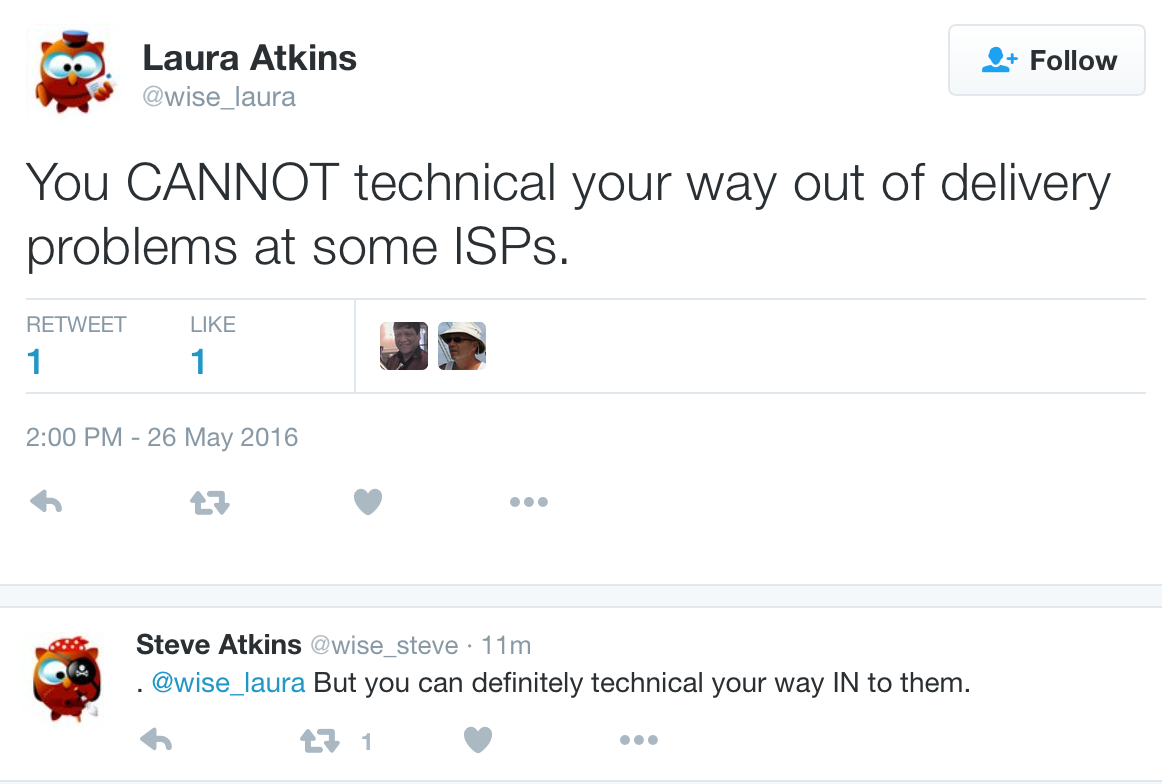
With all the emphasis on getting the technical right, there seem to be people who think their mail will be delivered as long as the technical is right.
Getting the technical right is necessary for good inbox delivery, but it’s not sufficient.
The most important part of getting mail to the inbox is sending mail users want. In fact, if you’re sending mail folks want, interact with and enjoy then you can get away with sloppy technical bits. Look, major players (eBay and Intuit) have invalid SPF records, but we’re all still getting mail from them.
There are also a lot of folks who are doing everything technically perfectly, but their mail is still going to bulk. Why? Because their recipients don’t want their mail.
Permission is still the key to getting mail to the inbox. In fact, permission is more important than getting all the technical bits right. If you have permission you can play a little fast and loose with the technical stuff. If you have the technical stuff right you still need permission.
Looking back through my archives it’s been about 4 years or so since I wrote about confirmed opt in. The last post was how COI wasn’t important, but making sure you were reaching the right person was important. Of course, I’ve also written about confirmed opt-in in general and how it was a tool somewhat akin to a sledgehammer. I’m inspired to write about it today because it’s been a topic of discussion on multiple mailing lists today and I’ve already written a bunch about it (cut-n-paste-n-edit blog post! win!).
Confirmed opt-in is the process where you send an email to a recipient and ask them to click on a link to confirm they want the mail. It’s also called double opt-in, although there are some folks who think that’s “spammer” terminology. It’s not, but that’s a story for another day. The question we were discussing was what to do with the addresses that don’t click. Can you email them? Should you email them? Is there still value in them?
We have to treat the addresses as a non-homogenous pool. There are a lot of reasons confirmation links don’t get clicked.