Is email dead?
These last few years have been something, huh? Something had to give and, in my case, that something was blogging. There were a number of reasons I stopped writing here, many of them personal, some of them more global. I will admit, I was (and still am a little) burned out as it seemed I was saying and writing the same things I’d been saying and writing for more than a decade. Taking time off has helped a little bit, as much to focus on what I really want to talk about.
It helps, too, there are a lot more deliverability resources out there than when I started. I don’t have to say it all, there are other voices (and perspectives!) that are adding to the collective understanding of delivery. That’s taken some of my (admittedly internal) pressure off from having to write about specific things to explain, educate and clarify. Other folks are doing that admirably. Instead I can move back to using writing blog posts to explore concepts and work through better ways to model and explain email and deliverability.
What are some of these bigger issues I’ve been thinking about?
Bounce Handling
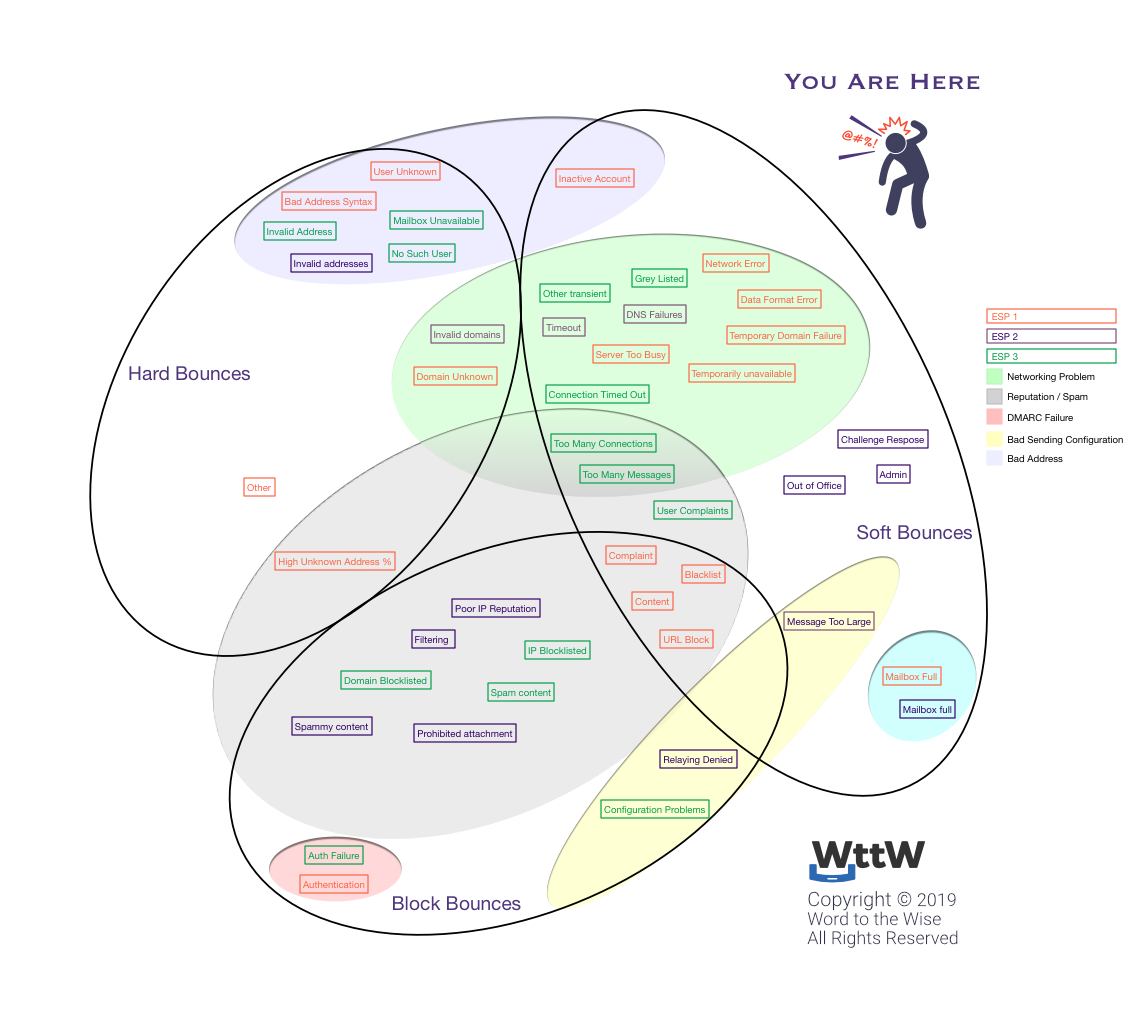
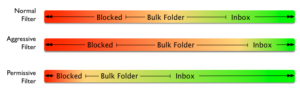
This is a problem that’s been on my mind for a while. The industry is very bad at managing undeliverable emails. Almost every organization has different definitions for the same terms. Mailbox providers send bounces that work for them but are unique to that provider. ESPs make up their own classification sets which I tried to classify a long time ago in a massive Venn diagram that still doesn’t capture it all. Filtering organizations say follow the RFCs. ESPs hide information about bounces from their customers.
Bounce handling is a mess. You can see this in Kickbox’s recent Email Deliverability Unfiltered: Understanding and Handling Bounces. A number of folks contributed content and we all went in completely different directions. I brought bounce handling as an open round table discussion at London M3AAWG meeting last June. The organization has been having ongoing discussions about it ever since, without getting to any conclusion.
I have long planned to write something about bounces, but struggle because I feel like I need to go back and start with defining all my terms. I mean, first off, we’re not talking bounces we’re talking rejections as they usually happen during the SMTP session and the SMTP RFC doesn’t talk about hard or soft bounces at all. I digress and this document is more about mapping out what I want to talk about – and making it public means I’m more likely to do it. I think I need to work a lot of that out in a long series of blog posts about bounces.
Spam is on the uptick again – for business users
The amount of B2B spam is getting out of control. It seems every small and medium business out there is purchasing lists and hiring an army of half literate sales folks who send out a bunch of cold email. They get really upset and angry when you call them spammers, but I’m not sure what else to label them. They’re certainly not permission based marketers.
They send unwanted, un-targeted and irrelevant email. They have adopted a host of techniques to avoid blocking and prevent people from filtering their mail. These include, but aren’t limited to: rotating domains regularly, using Google Workspace and O365 to prevent IP based blocking, using gmail.com addresses to prevent blocking, hiring lead generation companies to send on their behalf. They also violate CAN SPAM by not including a postal address and by not honoring unsubscribes.
In many ways it feels like the late 90s when we just didn’t have the tools to stop spam and were chasing spammers around. The techniques are modern versions of the techniques invented with Wallace and Rines and Ralsky and their competitors. Instead of open relays they use Google Workspace and O365 accounts. Instead of domain tasting they use gmail.com addresses. Instead of dictionary attacks they buy lists. Scraping still exists, but instead of badly written web crawlers, there’s browser plugins to harvest off LinkedIn.
Compliance is hard again
In the decade between about 2004 and 2014, compliance was important. ESPs were funding and staffing compliance desks. Bad customers were disconnected. FBLs were proliferating and anti-abuse was important. But that’s just not how it’s going these days.
ESPs actually have spam filters in front of their abuse desks and don’t even get complaints. If or when you can reach out in person, they generally only remove the address from lists and don’t actually disconnect the customer.
Many of the metrics compliance desks used to identify problem customers come with a host of problems that make them less useful now than in the past. Metrics like FBLs and bounce rates are not only gameable, customers can purchase services to game them. Open and click rates, are so noisy they’re useless for compliance purposes. In the B2B space, FBLs simply don’t exist; even providers that collect ‘this is spam’ metrics don’t share that information with the sender.
There was a big push by Spamhaus last year with “informational” listings. A lot of those listings were because so many ESPs (not you, you didn’t deserve it) have mostly stopped effectively policing their customer base. There are so many reasons for the build up of bad practices. Management has a lot of blame here for a host of reasons. Some decided if they weren’t blocked their customers weren’t spamming. Others failed to innovate on tools and reporting and didn’t adjust their compliance thresholds to address the metrics problems I talked about earlier. Others simply chased the income as long as their shared IPs had decent delivery. Dedicated IPs were left to fend for themselves and if they ruined their delivery that wasn’t the ESP’s problem.
Part of the issue is how good the ISPs have gotten at filtering off shared IPs. They can separate out and differentially filter mail from a single IP. This makes it easier for some ESPs to throw the problem back on the problem customer(s) and wash their hands of it.
Some good news
That was an awful lot of negativity to spew out. I think we’re all a little tired and burnt out from the last 6 years. I swear 2014 was yesterday. Have a palate cleanser of kittens.

But it’s not all bad and we shouldn’t despair. We’re just in the cycle where spammers caught up with the tools and abuse used by desk. The tools will catch up and all won’t be lost. I mean, when we started this back in the late 90s we spent a lot of time convincing folks spam was bad and harmful. Folks started building out tools and filters and blocklists and FBLs and all that. We’re about due for another round of investment and innovation.
We’ve already seen Google increasing their enforcement against the spammers abusing them to send B2B spam. They’ve also disconnected a couple of the spam support services that were using their own API to evade filters.
The overall industry is working hard to get a handle on the bounce issue. We’re talking about how better to address the bad customers, and also how to explain to management that enforcement is good for the business. Filters are protecting the majority of consumers from the bulk of the spam that’s sent.
I’ll be talking more about some of these issues over the coming months, along with some actual ideas about solutions and things that we in the email industry can do to improve the overall situation.