Recent Posts
Local-part Semantics
An email address has two main parts. The local-part is the bit before the @-sign and the domain is the bit after it. Loosely, the domain part tells SMTP how to get an email to the destination mailserver while the local part tells that server whose mailbox to put it in.
I’m just looking at the local part today, the “steve” in “steve@example.com”.
Talkin’ ‘Bout a Specification
The original specification for SMTP email delivery, RFC 821, specifies a few things about the local-part. It can’t be more than 64 character ascii characters long, and it must be wrapped in double quotes if it includes any punctuation. But that’s just syntax, nothing to do with what it means. It does mention that it’s case-sensitive: “steve@example.com” is not the same recipient as “sTeve@example.com”.
The specification for the structure of email messages, RFC 822, tells us a little more. It clarifies that the local-part is case-sensitive, with the sole exception of the “postmaster” account, which is required to be deliverable as “postmaster”, “POSTMASTER”, “POSTmasTER” or any other variant you like.
August mini-recess
Blogging will be light through the end of the month. We’re headed to Wyoming to see the eclipse this weekend. As well, with all of the current political events happening it’s hard to focus on email right now.
So basically I’m giving myself permission to not blog daily through the end of August. I’ll blog as I have stuff to say. Some of those might be copies and pastes from comments I’ve made in other spaces. I seem to be on FB quite a bit these days – sometimes even email related.
I’ve also been asking questions and discussing stuff on some mailing lists. I had a flash of insight about how I think about deliverability differently from other people and am talking with some colleagues about it to make sure I can explain it well.
Email address as identity
A few months ago I was talking about different mailbox tools and mentioned email addresses are the keys to our online identity. They are, email addresses are the magic key that authenticates us and opens access to different accounts.
The bad guys know this too. The Justice department recently announced a plea deal related to compromised email accounts. The individual in question gained access to faculty, staff and student email accounts. They then used access to these accounts to access Facebook, iCloud, Google, LinkedIn and Yahoo accounts.
https://twitter.com/pwnallthethings/status/897930523120738304
https://twitter.com/pwnallthethings/status/897931383431061504
https://twitter.com/pwnallthethings/status/897932050111406081
Mediapost published an article this week referencing a survey performed at this year’s BlackHat conference.
Reengagement emails
By default I don’t load images in email. For one thing it lets me see who is using open / click data to measure engagement. This morning I got a reengagement email from my Senator. 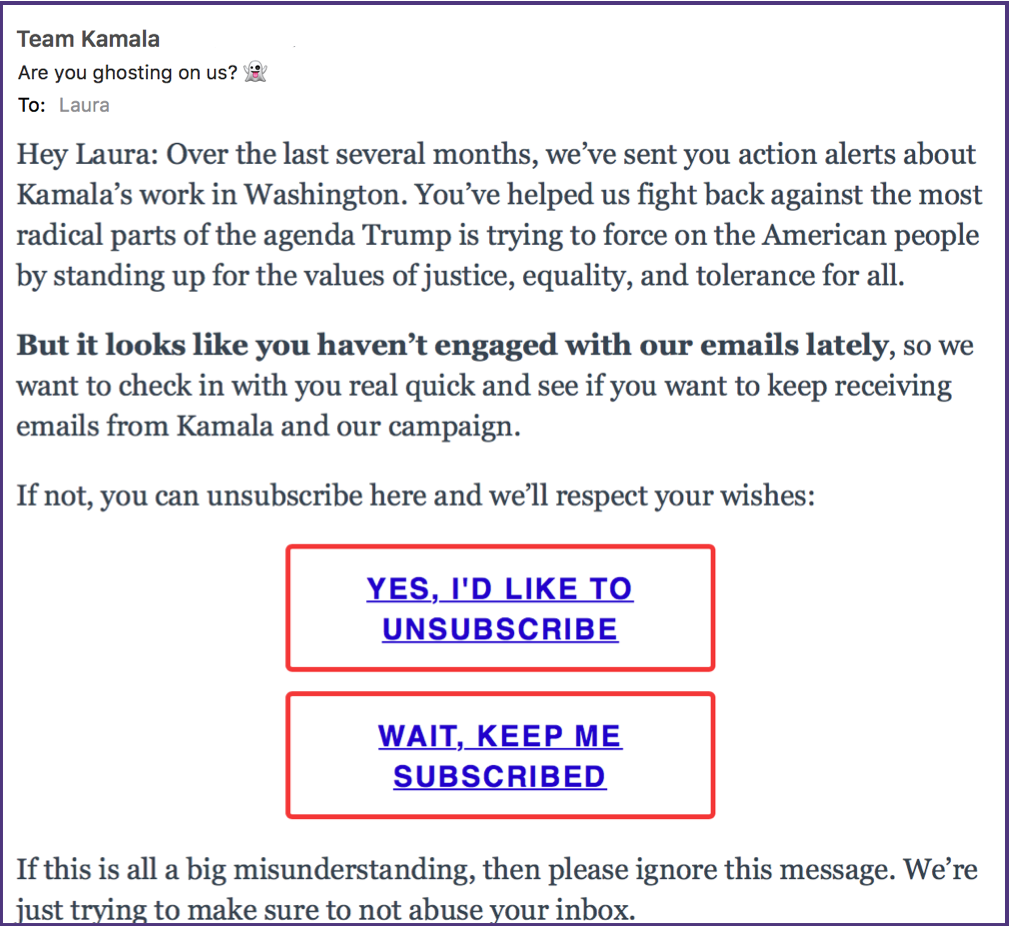
There are things I really like about this email and there are somethings I think they get a little wrong.
State of Email Deliverability
I had other posts in the pipeline, but saw a link to the Litmus 2017 State of Email Deliverability Report and decided that deserved a mention here.
There’s all sorts of interesting data there, and well worth a download and read. I was, of course, interested in the “most problematic subscriber acquisition sources.” Senders having blocking issues or blacklist problems in the past 12 months use list rental, co-reg and purchased lists more often than senders that didn’t have problems.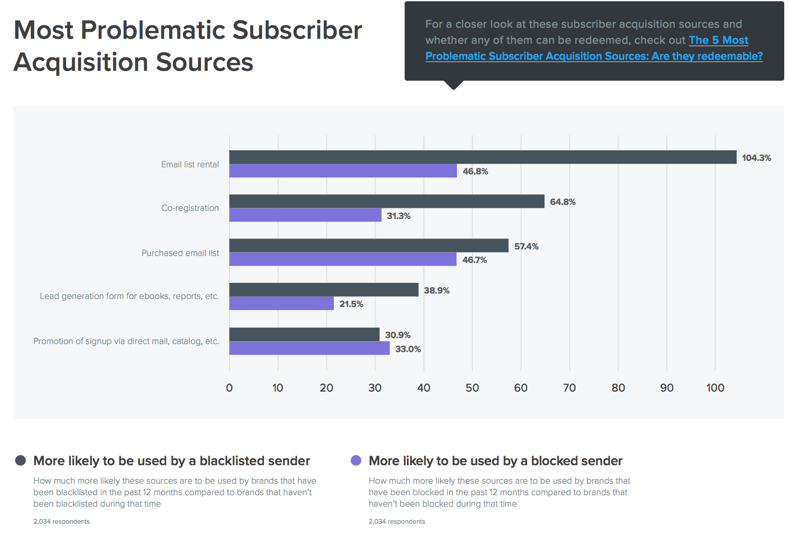
Senders acquiring addresses through list rental are 104% more likely to be blacklisted than senders not using list rental. And they’re 47% more likely to be blocked.
These stats are the primary reason that most ESPs don’t allow list rentals, purchased or co-reg lists. They cause blocking and blacklisting. The ESP ends up having to deal with lots of problems and clean up the mess.
I’m unsurprised that lead generation by giving something away (a report, ebook, whatever) is related to problems. Most of these forms do little to no data checking and accept any and all fake data. There are fairly simple ways to enforce better data, but that does limit the spread of the information.
I am surprised to see signup through direct mail and catalog sales is so bad. Unless maybe people don’t know how to say no when asked for an email address over the phone. I know it seems awkward to say no when asked for an email address. Maybe some folks are giving fake addresses. I sometimes say I don’t have email, or just tell them no, they don’t need one.
The white paper itself is well worth a read. Go download it yourself (but don’t give them a fake email address!).
Not a customer you want
Earlier this week one of my ESP clients contacted me. They have a new (potential?) customer dealing with some delivery challenges. Client was looking for advice on how to move the customer over and improve their delivery at the same time.
My advice was actually pretty simple: this isn’t a customer you want. Walk away.
I reached that conclusion about 10 seconds after I loaded the customer’s website. Because I know sometimes initial impressions are wrong, I did spend about 10 more minutes poking around. What I found did nothing to change my mind or convince me my initial impression was wrong. In fact, everything I found reinforced the belief that this was not a good customer for my client.
I sent my client an email explaining what I’d found and they agreed. Future deliverability problem averted!
Some of what I found inspired the conversations with spammers blog post from earlier this week. For instance, the website had two different signup forms, each pointing to a different ESP. Both links were dead.
Then I looked at the company’s whois record and found a bunch of cookie cutter websites, all with different domain names, all with the same broken subscription links.
I do this manually and I can’t fathom how you would automate this kind of checking. For me, it seems there absolutely needs to be a human in the loop. But I suspect that there are ways to automate these types of checks.
In any case, there’s a spammer looking for an email service provider. He’s having problems with IP reputation at his current ESP. He sends content and will even share with you the domain he’s using to collect email addresses. Pro tip: try and sign up for his mail before he signs your contract.
Conversations with spammers
It’s amazing how many spammers try and fool deliverability into accepting a questionable list. All too often they fall back on a story. The basic points: a company you’ve never heard of collected millions of email addresses on a website hosted on a low end VPS.
I’ve never heard of your company. We’re just that much better at marketing. This list is guaranteed 100% opt in. Subscribers are desperate to hear from us. The mail is vital and important. We had some problems at our last ESP, but that’s just because they don’t understand our business model. And we had a brief problem with complaints. But they weren’t real complaints. Our competitors are signing up for the list and complaining to hurt out business. It’s not a list problem, it’s that we’re so dominant they have to subvert us. That’s just because we’re that much better at their jobs than anyone else.
You’re looking for deliverability help. Well, yeah, sometimes Gmail delivery is bad, but that’s simply because we won’t pay Google money for advertising. Google is so afraid of us they deliberately filter all this spectacularly wanted email into the bulk folder. They have problems with us as a business. Oh, and we might, sometimes, occasionally have a minor problem with Yahoo. But, again, it’s because we threaten them and they don’t want to have to compete on a level playing field.
If they’re a potential customer, I tell them about our services and offer a proposal. Once some company I’ve never heard of tells me their bad delivery is because global companies are afraid of them, there’s really nothing I can do. They’re unlikely to listen to me explain reality to them.
Sometimes, though, this conversation happens because I’m consulting for an ESP or an Agency. They’ve brought me in to discuss deliverability with a customer or vendor. In those cases, it’s my job to keep going.
Your site doesn’t actually have a signup form. That’s because we’re in the middle of an upgrade cycle and had some problems with the back end. [Alternative: We stopped collecting new email addresses because of their deliverability problems and removed the form.]
Your site has a signup form, and I signed up, but never got any mail from you. We disconnected the signup form while we handle our deliverability problems. [Alternative: That shouldn’t happen. We can forward you some messages instead.]
I have received spam advertising your company. We had a rogue affiliate that we discovered was spamming and we cut them off.
No, this is direct from your IP space. Oh, well, you must have opted in and forgotten about it. [Alternative: We had a rogue sales guy, but we fired him for spamming.]
Your company has only been in business for 3 years, this is an address I haven’t used since the ’90s. Oh, we probably bought a company that you opted into and so have permission that way.
That’s not really permission. Of course it is!
OK…. How can I help you. We want you to call Google / Yahoo / Hotmail and tell them we’re really a legitimate company that’s sending content and we shouldn’t be in the bulk folder.
What have you changed? Nothing! Why would we change anything? We’re great marketers. We have all these plans but need to get back to the inbox before we can implement them.
Um… there’s no filter setting for “laura says they’re a good sender.” They’re going to look for new sending patterns so let’s change a few things. Well, we recently removed 2/3 of our database, but it made no difference so we don’t know what else you think we can do.
Let’s talk about your technical setup.
July 2017: The month in email
August is here, and as usual, we’re discussing spam, permissions, bots, filters, delivery challenges, and best practices.
One of the things we see over and over again, both with marketers and with companies that send us email, is that permission is rarely binary — companies want a fair amount of wiggle room, or “implied permission” to send. There are plenty of examples of how companies try to dance around clear permissions, such as this opt form from a company we used to do business with. But there are lots of questions here: can you legitimately mail to addresses you haven’t interacted with in 5 years? 10 years? What’s the best way to re-engage, if at all?
We frequently get questions about how to address deliverability challenges, and I wrote up a post about some of the steps we take as we help our clients with this. These are short-term fixes; for long-term success, the most effective strategy is sending email that people want and expect. Engagement is always at the core of a sustainable email program.
We’ve also discussed the rise of B2B spam, and the ways in which marketing technologies contribute to the problem. B2B marketers struggle to use social and email channels appropriately to reach customers and prospects, but still need to be thoughtful about how they do it. I also wrote about some of the ways that marketing automation plugins facilitate spam and how companies should step up to address the problem. Here’s an example of what happens when the automation plugins go awry.
I wrote a few posts about domain management and the implications for security and fraud. The first was about how cousin domain names can set users up for phishing and fraud, and the second was a useful checklist for looking at your company’s domain management. We also looked at abuse across online communities, which is an increasing problem and one we’re very committed to fighting.
I also highlighted a few best practices this month: guidelines for choosing a new ESP and active buttons in the subject line for Gmail.
And finally, we celebrated the 80th birthday of the original SPAM. If you’re a regular reader of this blog, you probably already know why unwanted email is called SPAM, but just in case, here’s a refresher….
TLS certificates and CAA records
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is what gives you the little padlock in your browser bar. Some people still call it SSL, but TLS has been around for 18 years – it’s time to move on.
TLS provides two things. One is encryption of traffic as it goes across the wire, the other is a cryptographic proof that you’re talking to the domain you think you’re talking to.
The second bit is important, as if you can’t prove you’re talking to, for example, your bank you could really be talking to a malicious third party who has convinced your browser to talk to their server instead of your bank which makes the encryption of the traffic much less useful. They could even act as a man-in-the-middle and pass your traffic through to your bank, so that you wouldn’t notice anything wrong.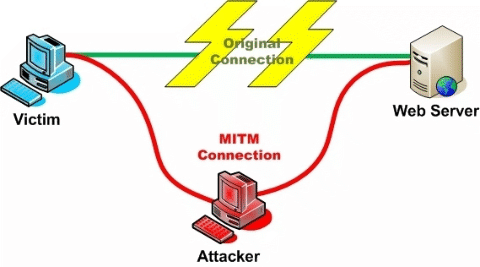
When your browser connects to a website over TLS it, as part of setting up the connection, fetches a “TLS certificate” from the server. That certificate includes the hostname of the server, so the browser can be sure that it’s talking to the server it thinks it is.
How does the browser know to trust the certificate, though? There’s not really a great way to do that, yet. There’s a protocol called DANE that stores information in DNS to validate the certificate, much the same as we do with DKIM. It’s a promising approach, but not widely supported.
What we have today are “Certificate Authorities” (CAs). These are companies that will confirm that you own a domain, issue you a certificate for that domain where they vouch for it’s authenticity (and usually charge you for the privilege). Anyone can set themselves up as a CA (really – it’s pretty trivial, and you can download scripts to do the hard stuff), but web browsers keep a list of “trusted” CAs, and only certificates from those authorities count. Checking my mac, I see 169 trusted root certificate authorities in the pre-installed list. Many of those root certificates “cross-sign” with other certificate authorities, so the actual number of companies who are trusted to issue TLS Certificates is much, much higher.
If any of those trusted CAs issue a certificate for your domain name to someone, they can pretend to be you, secure connection padlock and all.
Some of those trusted CAs are trustworthy, honest and competent. Others aren’t. If a CA is persistently, provably dishonest enough then they may, eventually, be removed from the list of trusted Certificate Authorities, as StartCom and WoSign were last year. More often, they don’t: Trustwave, MCS Holdings/CNNIC, ANSSI, National Informatics Center of India (who are currently operating a large spam operation, so …).
In 2011 attackers compromised a Dutch CA, DigiNotar, and issued themselves TLS Certificates for over 500 high-profile domains – Skype, Mozilla, Microsoft, Gmail, … – and used them as part of man-in-the-middle attacks to compromise hundreds of thousands of users in Iran. Coverage at the time blamed it on “DigiNotar’s shocking ineptness“.
In 2015 Symantec/Thawte issued 30,000 certificates without authorization of the domain owners, and even when they issued extended validation (“green bar”) certificates for “google.com” they weren’t removed from the trusted list.
So many CAs are incompetent, many are dishonest, and any of them can issue a certificate for your domain. Even if you choose to use a competent, reputable CA – something that’s not trivial in itself – that doesn’t stop an attacker getting certificates for your domain from somewhere else.
This is where CAA DNS records come in. They’re really simple and easy to explain, with no fancy crypto needed to set them up. If I publish this DNS record …
Categories
Tags
- 2010
- 2016
- 2fa
- 419
- 4xx
- 554
- 5xx
- @
- Aarp
- Abacus
- Abandoned
- Aboutmyemail
- Abuse
- Abuse Desk
- Abuse Enforcement
- Abuse Prevention
- Academia
- Accreditation
- Acme
- Acquisition
- Address Book
- Addresses
- Administrivia
- Adsp
- Advanced Delivery
- Advertiser
- Advertising
- Advice
- Affiliate
- Affiliates
- After the Email
- Alerts
- Algorithm
- Alice
- Alignment
- Allcaps
- Alt Text
- AMA
- Amazon
- Amp
- Amsterdam
- Analysis
- Anecdotes
- Anti-Spam
- Anti-Spam Laws
- Anti-Spammers
- Antwort
- AOL
- Appeals
- Appearances
- Appending
- Apple
- Arc
- Arf
- Arrest
- Arrests
- Ascii
- Asides
- Ask Laura
- Askwttw
- Assertion
- Assumptions
- ATT
- Attacks
- Attention
- Attrition
- Audit
- Authentication
- Authentication. BT
- Autonomous
- Award
- B2B
- B2C
- Backhoe
- Backscatter
- Banks
- Barracuda
- Barry
- Base64
- Base85
- Bcp
- Bear
- Bears
- Behaviour
- Benchmark
- BESS
- Best Practices
- Bgp
- Bimi
- Bit Rot
- Bitly
- Bizanga
- Black Friday
- Blackfriday
- Blacklist
- Blacklists
- Blast
- Blo
- Block
- Blockin
- Blocking
- Blocklist
- Blocklisting
- Blocklists
- Blocks
- Blog
- Blog Links
- Blogroll
- Blogs
- Bob
- Boca
- Bofa
- Book Review
- Bot
- Botnet
- Botnets
- Bots
- Bounce
- Bounce Handling
- Bounces
- Branding
- Brands
- Breach
- Breaches
- Breech
- Bronto
- Browser
- Bsi
- Bucket
- Bulk
- Bulk Folder
- Bulk Mail
- Business
- Business Filters
- Buying Leads
- Buying Lists
- C-28
- CA
- Caa
- Cache
- Cadence
- CAH
- California
- Campaign
- CAN SPAM
- Canada
- Candy
- Candycandycandy
- Canonicalization
- Canspam
- Captcha
- Career Developmnent
- Careers at WttW
- Cargo Cult
- Case Law
- Cases
- CASL
- Cat
- Cbl
- CDA
- Cert
- Certification
- CFL
- Change
- Charter
- Cheat
- Cheese
- Choicepoint
- Choochoo
- Christmas
- Chrome
- Cidr
- Cisco
- Civil
- Clear.net
- Clearwire.net
- Cli
- Click
- Click Through
- Click Tracking
- Clicks
- Clickthrough
- Client
- Cloudflare
- Cloudmark
- Cname
- Co-Reg
- Co-Registration
- Cocktail
- Code
- COI
- Comcast
- Comments
- Commercial
- Communication
- Community
- Comodo
- Comparison
- Competitor
- Complaint
- Complaint Rates
- Complaints
- Compliancce
- Compliance
- Compromise
- Conference
- Conferences
- Confirmation
- Confirmed (Double) Opt-In
- Confirmed Opt-In
- Congress
- Consent
- Conservatives
- Consistency
- Constant Contact
- Consultants
- Consulting
- Content
- Content Filters
- Contracts
- Cookie
- Cookie Monster
- COPL
- Corporate
- Cost
- Court Ruling
- Cox
- Cox.net
- Cpanel
- Crib
- Crime
- CRM
- Crowdsource
- Crtc
- Cryptography
- CS&M
- CSRIC
- CSS
- Curl
- Customer
- Cyber Monday
- Czar
- Data
- Data Hygiene
- Data Security
- Data Segmentation
- Data Verification
- DBL
- Dbp
- Ddos
- Dea
- Dead Addresses
- Dedicated
- Dedicated IPs
- Defamation
- Deferral
- Definitions
- Delays
- Delisting
- Deliverability
- Deliverability Experts
- Deliverability Improvement
- Deliverability Summit
- Deliverability Week
- Deliverability Week 2024
- Deliverabiltiy
- DeliverabiltyWeek
- Delivery Blog Carnival
- Delivery Discussion
- Delivery Emergency
- Delivery Experts
- Delivery Improvement
- Delivery Lore
- Delivery News
- Delivery Problems
- Dell
- Design
- Desks
- Dhs
- Diagnosis
- Diff
- Dig
- Direct Mag
- Direct Mail
- Directives
- Discounts
- Discovery
- Discussion Question
- Disposable
- Dk
- DKIM
- Dkimcore
- DMA
- Dmarc
- Dns
- Dnsbl
- Dnssec
- Docs
- Doingitright
- Domain
- Domain Keys
- Domain Reputation
- DomainKeys
- Domains
- Domains by Proxy
- Dontpanic
- Dot Stuffing
- Dotcom
- Double Opt-In
- Dublin
- Dyn
- Dynamic Email
- E360
- Earthlink
- Ec2
- Ecoa
- Economics
- ECPA
- Edatasource
- Edns0
- Eec
- Efail
- Efax
- Eff
- Election
- Email Address
- Email Addresses
- Email Change of Address
- Email Client
- Email Design
- Email Formats
- Email Marketing
- Email Verification
- Emailappenders
- Emailgeeks
- Emails
- Emailstuff
- Emoji
- Emoticon
- Encert
- Encryption
- End User
- Endusers
- Enforcement
- Engagement
- Enhanced Status Code
- Ennui
- Entrust
- Eol
- EOP
- Epsilon
- Esp
- ESPC
- ESPs
- EU
- Ev Ssl
- Evaluating
- Events
- EWL
- Exchange
- Excite
- Expectations
- Experience
- Expires
- Expiring
- False Positives
- FAQ
- Fathers Day
- Fbl
- FBL Microsoft
- FBLs
- Fbox
- FCC
- Fcrdns
- Featured
- Fedex
- Feds
- Feedback
- Feedback Loop
- Feedback Loops
- Fiction
- Filter
- Filter Evasion
- Filtering
- Filterings
- Filters
- Fingerprinting
- Firefox3
- First Amendment
- FISA
- Flag Day
- Forensics
- Format
- Formatting
- Forms
- Forwarding
- Fraud
- Freddy
- Frequency
- Friday
- Friday Spam
- Friendly From
- From
- From Address
- FTC
- Fussp
- Gabbard
- Gdpr
- Geoip
- Gevalia
- Gfi
- Git
- Giveaway
- Giving Up
- Global Delivery
- Glossary
- Glyph
- Gmail
- Gmails
- Go
- Godaddy
- Godzilla
- Good Email Practices
- Good Emails in the Wild
- Goodmail
- Google Buzz
- Google Postmaster Tools
- Graphic
- GreenArrow
- Greylisting
- Greymail
- Groupon
- GT&U
- Guarantee
- Guest Post
- Guide
- Habeas
- Hack
- Hacking
- Hacks
- Hall of Shame
- Harassment
- Hard Bounce
- Harvesting
- Harvey
- Hash
- Hashbusters
- Headers
- Heartbleed
- Hearts
- HELO
- Help
- Henet
- Highspeedinternet
- Hijack
- History
- Holiday
- Holidays
- Holomaxx
- Hostdns4u
- Hostile
- Hostname
- Hotmail
- How To
- Howto
- Hrc
- Hsts
- HTML
- HTML Email
- Http
- Huey
- Humanity
- Humor
- Humour
- Hygiene
- Hypertouch
- I18n
- ICANN
- Icloud
- IContact
- Identity
- Idiots
- Idn
- Ietf
- Image Blocking
- Images
- Imap
- Inbox
- Inbox Delivery
- Inboxing
- Index
- India
- Indiegogo
- Industry
- Infection
- Infographic
- Information
- Inky
- Inline
- Innovation
- Insight2015
- Integration
- Internationalization
- Internet
- Intuit
- IP
- IP Address
- Ip Addresses
- IP Repuation
- IP Reputation
- IPhone
- IPO
- Ipv4
- Ipv6
- Ironport
- Ironport Cisco
- ISIPP
- ISP
- ISPs
- J.D. Falk Award
- Jail
- Jaynes
- JD
- Jobs
- Json
- Junk
- Juno/Netzero/UOL
- Key Rotation
- Keybase
- Keynote
- Kickstarter
- Kraft
- Laposte
- Lavabit
- Law
- Laws
- Lawsuit
- Lawsuits
- Lawyer
- Layout
- Lead Gen
- Leak
- Leaking
- Leaks
- Legal
- Legality
- Legitimate Email Marketer
- Letsencrypt
- Letstalk
- Linked In
- Links
- List Hygiene
- List Management
- List Purchases
- List the World
- List Usage
- List-Unsubscribe
- Listing
- Listmus
- Lists
- Litmus
- Live
- Livingsocial
- London
- Lookup
- Lorem Ipsum
- Lycos
- Lyris
- M3AAWG
- Maawg
- MAAWG2007
- Maawg2008
- MAAWG2012
- MAAWGSF
- Machine Learning
- Magill
- Magilla
- Mail Chimp
- Mail Client
- MAIL FROM
- Mail Privacy Protection
- Mail Problems
- Mail.app
- Mail.ru
- Mailboxes
- Mailchimp
- Mailgun
- Mailing Lists
- Mailman
- Mailop
- Mainsleaze
- Maitai
- Malicious
- Malicious Mail
- Malware
- Mandrill
- Maps
- Marketer
- Marketers
- Marketing
- Marketo
- Markters
- Maths
- Mcafee
- Mccain
- Me@privacy.net
- Measurements
- Media
- Meh
- Meltdown
- Meme
- Mentor
- Merry
- Messagelabs
- MessageSystems
- Meta
- Metric
- Metrics
- Micdrop
- Microsoft
- Milter
- Mime
- Minimal
- Minshare
- Minute
- Mit
- Mitm
- Mobile
- Models
- Monitoring
- Monkey
- Monthly Review
- Mpp
- MSN/Hotmail
- MSN/Hotmail
- MTA
- Mua
- Mutt
- Mx
- Myths
- Myvzw
- Netcat
- Netsol
- Netsuite
- Network
- Networking
- New Year
- News
- News Articles
- Nhi
- NJABL
- Now Hiring
- NTP
- Nxdomain
- Oath
- Obituary
- Office 365
- Office365
- One-Click
- Only Influencers
- Oops
- Opaque Cookie
- Open
- Open Detection
- Open Rate
- Open Rates
- Open Relay
- Open Tracking
- Opendkim
- Opens
- Openssl
- Opt-In
- Opt-Out
- Optonline
- Oracle
- Outage
- Outages
- Outblaze
- Outlook
- Outlook.com
- Outrage
- Outreach
- Outsource
- Ownership
- Owning the Channel
- P=reject
- Pacer
- Pander
- Panel
- Password
- Patent
- Paypal
- PBL
- Penkava
- Permission
- Personalities
- Personalization
- Personalized
- Pgp
- Phi
- Philosophy
- Phish
- Phishers
- Phishing
- Phising
- Photos
- Pii
- PIPA
- PivotalVeracity
- Pix
- Pluscachange
- Podcast
- Policies
- Policy
- Political Mail
- Political Spam
- Politics
- Porn
- Port25 Blocking
- Postfix
- Postmaster
- Power MTA
- Practices
- Predictions
- Preferences
- Prefetch
- Preview
- Primers
- Privacy
- Privacy Policy
- Privacy Protection
- Private Relay
- Productive Mail
- Promotions
- Promotions Tab
- Proofpoint
- Prospect
- Prospecting
- Protocols
- Proxy
- Psa
- PTR
- Public Suffix List
- Purchased
- Purchased Lists
- Purchases
- Purchasing Lists
- Questions
- Quoted Printable
- Rakuten
- Ralsky
- Rant
- Rate Limiting
- Ray Tomlinson
- Rc4
- RDNS
- Read
- Ready to Post
- Readytopost
- Real People
- Realtime Address Verification
- Recaptcha
- Received
- Receivers
- Recipient
- Recipients
- Redirect
- Redsnapper
- Reference
- Registrar
- Registration
- Rejection
- Rejections
- Rejective
- Relationship
- Relevance
- Relevancy
- Removals
- Render Rate
- Rendering
- Repost
- Repudiation
- Reputation
- Requirements
- Research
- Resources
- Responsive
- Responsive Design
- Responsys
- Retail
- Retired Domains
- Retro
- Return Path
- Return Path Certified
- ReturnPath
- Reunion.com
- Reverse Dns
- Rfc
- RFC2047
- RFC2821/2822
- RFC5321/5322
- RFC5322
- RFC8058
- RFC821/822
- RFCs
- Roadr
- RoadRunner
- Rodney Joffe
- ROKSO
- Role Accounts
- Rollout
- RPost
- RPZ
- Rule 34
- Rules
- Rum
- Rustock
- S.1618
- SaaS
- Sales
- Salesforce
- Sass
- SBCGlobal
- Sbl
- Scam
- Scammers
- Scams
- Scanning
- Scraping
- Screamer
- Screening
- Script
- Sec
- Secure
- Security
- Segmentation
- Selligent
- Send
- Sender
- Sender Score
- Sender Score Certified
- Senderbase
- Senderid
- Senders
- Senderscore
- Sendgrid
- Sending
- Sendy
- Seo
- Service
- Services
- Ses
- Seth Godin
- SFDC
- SFMAAWG2009
- SFMAAWG2010
- SFMAAWG2014
- Shared
- Shell
- Shouting
- Shovel
- Signing
- Signups
- Silly
- Single Opt-In
- Slack
- Slicing
- Smarthost
- Smiley
- Smime
- SMS
- SMTP
- Snds
- Snowshoe
- Soa
- Socia
- Social Media
- Social Networking
- Soft Bounce
- Software
- Sony
- SOPA
- Sorbs
- Spam
- Spam Blocking
- Spam Definition
- Spam Filtering
- Spam Filters
- Spam Folder
- Spam Law
- Spam Laws
- Spam Reports
- Spam Traps
- Spam. IMessage
- Spamarrest
- Spamassassin
- Spamblocking
- Spamcannibal
- Spamcon
- Spamcop
- Spamfiltering
- Spamfilters
- Spamfolder
- Spamhaus
- Spamhause
- Spammer
- Spammers
- Spammest
- Spamming
- Spamneverstops
- Spamresource
- Spamtrap
- Spamtraps
- Spamza
- Sparkpost
- Speaking
- Special Offers
- Spectre
- Spf
- Spoofing
- SproutDNS
- Ssl
- Standards
- Stanford
- Starttls
- Startup
- State Spam Laws
- Statistics
- Storm
- Strategy
- Stunt
- Subject
- Subject Lines
- Subscribe
- Subscriber
- Subscribers
- Subscription
- Subscription Process
- Success Stories
- Suing
- Suppression
- Surbl
- Sureclick
- Suretymail
- Survey
- Swaks
- Syle
- Symantec
- Tabbed Inbox
- Tabs
- Tagged
- Tagging
- Target
- Targeting
- Techincal
- Technical
- Telnet
- Template
- Tempo
- Temporary
- Temporary Failures
- Terminology
- Testing
- Text
- Thanks
- This Is Spam
- Throttling
- Time
- Timely
- TINS
- TLD
- Tlp
- TLS
- TMIE
- Tmobile
- Too Much Mail
- Tool
- Tools
- Toomuchemail
- Tor
- Trademark
- Traffic Light Protocol
- Tragedy of the Commons
- Transactional
- Transition
- Transparency
- Traps
- Travel
- Trend/MAPS
- Trend Micro
- Trend/MAPS
- Trigger
- Triggered
- Troubleshooting
- Trustedsource
- TWSD
- Txt
- Types of Email
- Typo
- Uce
- UCEprotect
- Unblocking
- Uncategorized
- Unexpected Email
- Unicode
- Unroll.me
- Unsolicited
- Unsubcribe
- Unsubscribe
- Unsubscribed
- Unsubscribes
- Unsubscribing
- Unsubscription
- Unwanted
- URIBL
- Url
- Url Shorteners
- Usenet
- User Education
- Utf8
- Valentine's Day
- Validation
- Validity
- Value
- Valueclick
- Verification
- Verizon
- Verizon Media
- VERP
- Verticalresponse
- Vetting
- Via
- Video
- Violence
- Virginia
- Virtumundo
- Virus
- Viruses
- Vmc
- Vocabulary
- Vodafone
- Volume
- Vzbv
- Wanted Mail
- Warmup
- Weasel
- Webinar
- Webmail
- Weekend Effect
- Welcome Emails
- White Space
- Whitelisting
- Whois
- Wiki
- Wildcard
- Wireless
- Wiretapping
- Wisewednesday
- Women of Email
- Woof
- Woot
- Wow
- Wtf
- Wttw in the Wild
- Xbl
- Xfinity
- Xkcd
- Yahoo
- Yahoogle
- Yogurt
- Zoidberg
- Zombie
- Zombies
- Zoominfo
- Zurb
