Best Practices
Google, Alignment and DMARC
- laura
- Mar 11, 2025
Google has been making a number of changes to their systems over the last few weeks. Folks are seeing a lot of changes in Google postmaster tools and they’re seeing changes in how Google is displaying headers in the “show original” tab.
Read MoreEffects of the Yahoo and Google Changes
- laura
- Jan 23, 2025
In October 2023, Yahoo and Google announced new standards for sending bulk mail to their systems. For bulk senders these changes included requiring aligned authentication and publishing a DMARC record and complying with the List-Unsubscribe RFC. The ISPs also formally announced complaints must stay below a threshold of 0.3%. At the time of the announcement, they said enforcement would start in February 2024. As with many things, this enforcement deadline was pushed as ESPs explained the challenges to meet the deadlines.
Read MoreThe Economics of Cold Outreach
- laura
- Aug 12, 2024
It’s time we talk about cold outreach mail. In the last 2 years the volume and aggressiveness of cold outreach mail seems to have exploded. There are dozens of companies out there who are selling services to companies to facilitate cold outreach. My own sales mailbox is full of requests from companies to help them solve their delivery problems.
Read MoreSending domains and hostnames
- steve
- Jul 12, 2024
Lots of times I see someone asking a question and they talk about their sending domain. And it’s sometimes not 100% clear which domain they mean by that – and when we’re talking about alignment and reputation it can make a difference. So here’s a list of (some of?) the different places a mailserver uses a domain.
Read MoreWho’s your Email Czar?
- steve
- Jun 21, 2024

The gentleman with the excellent hat is Иван IV Васильевич, The Great Sovereign, Tsar and Grand Prince of all Russia, Vladimir, Moscow, Novgorod, Tsar of Kazan, Tsar of Astrakhan, Sovereign of Pskov, Grand Prince of Smolensk, Tver, Yugorsk, Perm, Vyatka, Bolgar and others, Sovereign and Grand Prince of Novgorod of the Lower Land, Chernigov, Ryazan, Polotsk, Rostov, Yaroslavl, Beloozero, Livonia, Udoria, Obdoria, Kondia and Master of all the Siberian Lands and Northern Countries.
Read MoreWarmup is Communication
- steve
- Jun 19, 2024
During the war they saw airplanes land with lots of good materials, and they want the same thing to happen now. So they’ve arranged to make things like runways, to put fires along the sides of the runways, to make a wooden hut for a man to sit in, with two wooden pieces on his head like headphones and bars of bamboo sticking out like antennas—he’s the controller—and they wait for the airplanes to land. They’re doing everything right. The form is perfect. It looks exactly the way it looked before. But it doesn’t work. No airplanes land. — Richard Feynman
Read MoreFilter Evasion
- steve
- Jun 19, 2024

It’s deliverability week, so everyone is talking about deliverability. But I’d like to take a moment to mention deliverability’s evil twin from the mirror universe – filter evasion.
Read MoreDeliverability is Collaborative
- steve
- Jun 18, 2024
Mailbox providers want happy recipients

Mailbox providers want their users to be happy with the mail they receive and the service they get. That’s driven by stark business reasons: acquiring new users is costly, happy users bring in revenue – whether directly, or indirectly via advertising – and their word of mouth helps bring in more users, and hence more revenue. That’s still true when the email service is bundled as part of a larger package, such as broadband service or domain registration.
Read MoreNo, Google doesn’t hate responsive design
- steve
- Apr 19, 2024
I’ve seen a bunch of folks panic about some phrasing in Google’s Email sender guidelines.
Read MoreOne-click unsubscribe
- steve
- Jan 31, 2024
The worst thing about the yahoogle requirements has been their use of the term “one-click unsubscribe”. It’s an overloaded term that’s being used here to mean RFC 8058 in-app unsubscription. That’s a completely different thing to what one-click unsubscription has been used to mean for decades, often in the context of complying with legal requirements around unsubscription.
Read MoreAre you a grown-up sender?
- steve
- Jan 5, 2024
Yes, it’s another yahoogle best practices post.
Google divide their requirements for senders into those sending more than 5,000 messages a day, and those sending less.
Read MoreYahoogle FAQs
- steve
- Jan 4, 2024
Just a very, very short post with links to the Yahoo and Google requirements FAQs. Given I can’t ever remember them I’m guessing lots of y’all can’t either.
Read MoreAbout My Email
- steve
- Jan 2, 2024
Happy 2024, everyone!
We’ve released a shiny new tool to let folks self-check a lot of common questions we see about email requirements.
Read MoreYahoogle Requirements Update
- steve
- Nov 9, 2023
Since I wrote about it last month the requirements for bulk senders to Yahoo and Google have changed a little.
Read MoreUnsubscribe vs Suppress
- steve
- Aug 4, 2023
When someone sends a complaint to your compliance desk there are a range of things you want to do, but one thing you always want to do is ensure that the recipient doesn’t receive any more unwanted email from your customer. Or, at least, not from your network.
Read MoreWant a link on WttW?
- laura
- May 9, 2023
There is an ever increasing amount of spam I am getting from various companies asking for links here on WttW.
Read MoreWhen best practices don’t work
- laura
- Jul 6, 2022
I started out with the best intentions to get back into the swing of things with blogging more regularly. But between MAAWG recovery, COVID recovery and life it’s not worked out that way.
Read MoreESPs need to step up their compliance game
- laura
- Jun 6, 2022
I don’t send a lot of spam complaints generally. Mostly I block and move on. There are some companies, though, that I offer the professional courtesy of sending a complaint or a report to their abuse@ address. Former clients, friends and colleagues generally get that courtesy.
Read MoreCleaning old lists
- laura
- May 11, 2022
There comes a time in many marketers’ lives where they are faced with and old, stale database and a management chain that wants to mail those addresses. Smart marketers know that delivery problems will arise if they just reactivate all those users. They also know that mailing older addresses can affect current and engaged addresses as well. Still, many executives think there is no downside to mailing old addresses.
Read MoreApple MPP reporting and geolocation
- steve
- Sep 27, 2021
A while back I wrote about Apple Mail Privacy Protection, what it does and how it works. Since MPP was first announced I’d assumed that it would be built on the same infrastructure as iCloud Private Relay, Apple’s VPN product, but hadn’t seen anything from Apple to explicitly connect the two and didn’t have access to enough data to confirm it independently.
Read MoreTerminology
- laura
- Jun 11, 2020
There is a lot more to say here, and I’m working on a longer post to really talk about the underlying racism in tech and how we as an industry have failed.
Read MoreAdvice on coronavirus emails
- laura
- Mar 16, 2020
Gartner has some really good recommendations for companies considering mailing about the coronavirus pandemic.
Read MoreThe key to improving deliverability
- laura
- Feb 18, 2020
According to the UK DMA, marketers report improvements in deliverability after GDPR went into effect.
Read MoreStop obsessing about open rates
- laura
- Feb 12, 2020
In 2020:
- 250OK says open rates were much lower than ESPs report.
- The Only Influencers list hosts a discussion about the value and use of open rates.
- A potential client contacts me asking if I can get their open rates to a certain percentage.
- A client shows me evidence of 100% inboxing but wants to improve their open rate.
- An industry group runs sessions at multiple meetings discussing how inaccurate open rates are.
The industry needs to stop obsessing over open rates.
Read MoreUsing Reply-To:
- laura
- Jan 29, 2020
Yesterday I learned that some ESPs don’t support the reply to: address. I asked around to discover which ESPs did. Here’s what I learned.
Read MoreThe variables are not independent
- laura
- Jan 15, 2020
In my previous career I was a molecular biologist. Much of my work was done on bacteria but after I left grad school, I ended up working in a developmental biology lab. Bacteria were (mostly) simple: just about every trait was controlled by a single gene. We could study what that gene did by removing it from the bacteria or adding it to a well characterised bacteria.
Read MoreAlt-text and phishing warnings
- steve
- Nov 22, 2019
For a long time one of the “best practices” for links in html content has been to avoid having anything that looks like a URL or hostname in the visible content of the link, as ISP phishing filters are very, very suspicious of links that seem to mislead recipients about where the link goes to. They’re a very common pattern in phishing emails.
Read MoreForget about engagement, think inboxing
- laura
- Oct 17, 2019
While answering a question about how to improve IP reputation at Gmail I realized that I no longer treat Gmail opens as anything about how a user is interacting with email. There are so many cases and ways that a pixel load can be triggered, without the user actually caring about the mail that it’s not a measure of the user at all.
Read MoreOpting out of “service” messages
- laura
- Oct 16, 2019
A frequent question in a number of deliverability spaces is how to tell if a message is transactional or marketing. In most cases the decision is related to whether or not to respect an unsubscribe request. All too often companies decide that their messages are too important to allow someone to opt-out of. The problem is, in some cases, there is no longer a customer relationship to send notices about.
Read MoreAn open is not permission
- laura
- Sep 26, 2019
A decade or so ago I was helping a client troubleshoot a Spamhaus listing. They, as many companies do, had a database with addresses from a number of different sources. Spamhaus was asking for them to reconfirm the entire database, which they didn’t want to do. I came up with the idea that if we had some sign of activity on the email address, like an open or a click and some other corresponding activity related to that open or click then we could assume that the address was likely a real user and was interested in the emails.
Read Mored= for data
- laura
- Aug 26, 2019
A few ISPs use the d= value in the DKIM signature as a way to provide FBL and reputation data to senders. This has some good bits, in that senders can get FBLs and other information regardless of the IP address they’re using and whether or not they have sole access to it.
Read MoreLink tracking redirectors
- steve
- Aug 22, 2019
Almost every bulk mail sent includes some sort of instrumentation to track which users click on which links and when. That’s usually done by the ESP rewriting links in the content so they point at the ESP’s tracking server, and include information about the customer, campaign and recipient. The recipient clicks on the link in the email, their web browser fetches the link from the tracking server, the tracking server records the details of that click and tells the browser to immediately open the original destination page.
Read MoreNew laptop, old reminder
- steve
- Jun 24, 2019
I have a new laptop.
New OS (maybe this year will be the year of Linux on the Desktop?1Yes, the hardware problems did show up as crashes in Xorg). New hardware problems. New applications. New keyboard layout.
Read MoreLow bounce rates don’t mean a list is good
- laura
- Apr 9, 2019
Many people believe that if they remove non-existent addresses from their mailing lists that their lists will make it to the inbox without a problem. In fact, an entire industry has grown up around the idea that sending mail to valid addresses can never be spam. This isn’t true, of course, spammers use many of the same techniques legitimate mailers do to clean their lists.
Delivery is not dependent on authentication
- laura
- Apr 4, 2019
All too often folks come to me with delivery problems and lead off with all of the things they’ve done to send mail right. They assure me they’re using SPF and DKIM and DMARC and they can’t understand why things are bad. There is this pervasive belief that if you do all the technical things right then you will reach the inbox.
Read MoreEconomics of spam
- laura
- Mar 1, 2019
There was a discussion on Slack about the economics of email. It’s probably not a surprise that I have opinions (Who owns the inbox? Ownership of the Inbox). There was a discussion about this that was useful enough I’d share it.
Read MoreIt’s not marketing, it’s spam
- laura
- Feb 27, 2019
There are times when I hesitate to call what marketers do “spam.” I can use the euphemisms with the best of ’em. “Cold emails” “Targeted Marketing” “B2B marketing.”
Read MoreRe-adding subscribers after reputation repair
- laura
- Feb 26, 2019
A comment came in on Engagement and Deliverability and I thought it was a good question and deserved a discussion.
Read MoreCousin domains
- laura
- Feb 7, 2019
When I checked in on Facebook this morning there was a discussion from a couple people frustrated by cousin domains. I share their frustration.
Read MoreRecycled spamtraps
- laura
- Jan 29, 2019
Spamtraps strike fear into the heart of senders. They’ve turned into this monster metric that can make or break a marketing program. They’ve become a measure and a goal and I think some senders put way too much emphasis on spamtraps instead of worrying about their overall data accuracy.
Read MoreB2B mail and compliance failures
- laura
- Jan 24, 2019
This morning I got an email to a tagged address. The tag matched the company so it’s very likely I did actually sign up. Digging back through my mailbox, I see one previous email to that account – back in 2008.
Read MoreYeah… don’t do that
- laura
- Jan 15, 2019
Never add someone to a mailing list without giving them a heads up that you’re doing it. It’s just uncool and rude. For example, I have been contacting some vendors about some work we need done. One of them has yet to answer my inquiry, but has already added me to their newsletter. Even worse, I had no idea submitting a form asking about their services would get me on their mailing list.
Read MoreIt’s a new year, do you know what your filters are doing?
- laura
- Jan 3, 2019
Yesterday the NJABL domain expired. The list was disabled back in 2013 but the domain continued to be maintained as a live domain. With the expiration, it was picked up by domain squatters and is now listing everything. Steve wrote about how and why expired blocklist domains list the world last year.
Read MoreThinking about the concept of best practices
- laura
- Nov 29, 2018
In 2010 Chad White declared best practices dead.
Frankly, the term has always been too “big tent” to be truly useful. When “don’t buy email lists” and “use buttons for primary calls-to-action” are both best practices, it’s no wonder there’s confusion. What we need is new language that differentiates those practices that are a litmus test for legitimate email marketers vs. spammers, from practices that are simply wise.
Read More
Send Actual SMTP
- laura
- Nov 19, 2018
It’s rare I find mail that violates the SMTP spec (rfc5321 and rfc5322). I’ve even considered removing “send mail from a correctly configured mail server” from my standard Best Practices litany.
Read MoreDedicated IPs, pros and cons
- laura
- Nov 8, 2018
There’s a whole belief system built around the idea that the best way to get good deliverability is to have your own dedicated IPs. In fact, senders regularly approach me to ask when is the right time for them to get a dedicated IP. They assume all their deliverability problems will disappear if they get a dedicated IP.
Read MoreTools aren’t a luxury
- laura
- Nov 5, 2018
I was on the phone with a colleague recently. They were talking about collecting a bit of data over the weekend and mentioned how great it was they had the tools to be able to do this. Coincidentally, another colleague mentioned that when the subscription bombing happened they were able to react quickly because they had a decent tool chain. I’ve also been working with some clients who are dealing with compliance issues but don’t have the tools they need.
Read MoreSaaS systems are spammer targets
- laura
- Oct 30, 2018
There are probably hundreds of thousands of really awesome SaaS products out there. They provide a framework to do all sorts of stuff that used to be really hard to do. Almost all of them include some email component. They dutifully build the email piece into their platform and, because they’re smart, they outsource the actual sending to one of SMTP providers. They’re happy, their customers are happy, and spammers are happy.
Read MoreJane! Stop this crazy thing!
- laura
- Oct 18, 2018
One of the consequences of moving to Ireland is I’m unsubscribing from most commercial mail, including some lists I’ve been on for a decade or more. Sadly, many of the companies don’t ship to Ireland, or their shipping costs are prohibitively expensive. Even if I wanted to purchase from them, I couldn’t.
Read MoreCompany responsibility and compliance
- laura
- Oct 12, 2018
I blogged a few times recently about Zoho and their issues with malicious actors abusing their platform. They asked me to post the following statement from their CEO Sridhar Vembu.
Read MoreUnsubscribe means unsubscribe
- laura
- Jul 19, 2018
But, unfortunately, some senders don’t actually think unsubscribe means stop sending mail.
Today, for instance, the nice folks at The Container Store sent me an email with an “important update to my POP! account”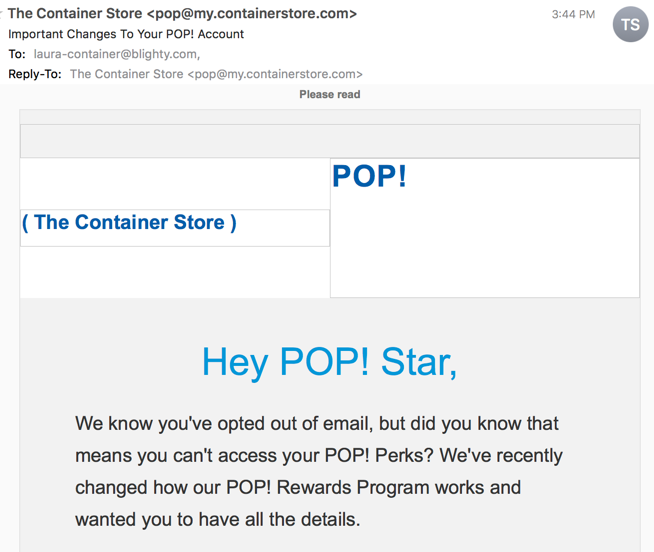
Yes, that’s an address I gave them. But I don’t have any record of setting up an account. I was on their mailing list for all of 4 emails back in November 2016 before unsubscribing. But, they’ve decided they can email me despite my unsubscribe request.
They’ve cloaked this as an “Important Account Update” about some account I don’t have. In fact, when I go to their website and try and see what this oh so important account is about they tell me: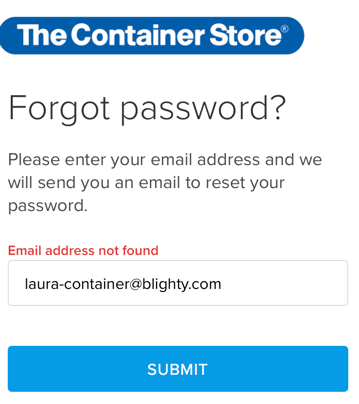
I understand legitimate account notifications might be an acceptable excuse to send mail even after the recipient opted out. This, however, was done extremely poorly. There is no record of the account that they are sending me information about. Neither the company nor I have any record of this account of mine.
At a minimum the emails should have only be sent to the folks that actually had an account. But, they weren’t.
I also have some issues with a company requiring recipients to accept email in order to continue using reward points. As a recipient, if I wanted what they were offering I might go ahead and continue receiving emails. But, I might not. It would all depend on how aggressive their email program is and how good the rewards are. As a deliverability consultant, this strikes me as a great way to create a mailing list full of unengaged users. Unengaged users lead to spam foldering and eventual failure of an email marketing program.
Whatever some executives think, and having been in this industry for a decade and I half I’m sure this is coming from the top down, this is not a good way to build an email program. You really can’t force folks to accept your email. ISPs are too protective of their users to make that a viable strategy.
Why is my cold email going to the spam folder?
- laura
- May 19, 2018
Because that’s what the spam folder is for unsolicited email.
Read MoreGDPR and the EU and Opt-in Confirmation
- steve
- Apr 17, 2018
There’s a lot of discussion going on about just what GDPR requires, and of who, and in which jurisdictions. German organizations in particular have been more aggressive than most about wanting to see opt-in confirmation for years and now seem to be adding “because GDPR” to their arguments.
I’m still not sure how this is going to shake out, but I’m beginning to see list owners take externally visible action.
I’ve been a subscriber for four or five years – it’s a good mailing list, run well, and I doubt it has any delivery issues beyond the unavoidable.
So this is a permission pass solely because they’re not sure whether I’m an EU resident, and aren’t 100% sure their opt-in confirmation data is squeaky clean (I subscribed as part of downloading an app of theirs, but after five years I couldn’t tell you whether that was technically confirmed opt-in or not, and I’m sure they can’t either).
Zoomdata aren’t taking any chances on confirmation. This isn’t a single “click to confirm you want to stay on the list” permission pass, rather it goes to a form that asks whether I’m an EU resident and if I am requires me to check an “Opt-in to email communications” checkbox and then click on a link in a confirmation email.
I’m not an EU resident today but may be an EU resident in the near future – yet my email address won’t change and nor will my mailing list subscriptions. That does make me wonder how valid it is to be capturing opt-in permission solely for recipients who are EU residents today.
Also are non-EU residents likely to claim they live in the EU because they’ll be treated better as far as their privacy is concerned, much the same as telling Facebook or Twitter you live in Germany provides you with better content filters?
I guess I’ll be seeing more of this in my inbox over the next few weeks. How are all y’all handling GDPR compliance?
Collecting email addresses
- laura
- Jan 26, 2018
One of the primary ways to collect email addresses is from website visitors, and it’s actually a pretty good way to collect addresses. One of the more popular, and effective, techniques is through a pop-up window, asking for an address. Users need to provide an address or click a “no thanks” link or close the window. I’ve noticed, though, that many companies drop something passive aggressive in their “no thanks” button. “No, thanks, I don’t want to save money.” “I don’t need workout advice.”
Read MoreSocial media connections are not opt-ins
- laura
- Jan 25, 2018
It seems silly to have to say this, but connecting on social media is not permission to add an address to your newsletter or mailing list or prospecting list or spam list. Back in 2016, I wrote:
Read MoreThat's not how you do it…
- laura
- Jan 11, 2018
Got an email this morning from a company advertising their newest webinar “The Two Pillars of Effective Large-Scale Email: Security and Deliverability.” The message came to a tagged address, so clearly I’d given them one at some point. But I didn’t recognize the name or company or anything. I did a search to seen when I may have interacted with this company in the past.
Looking through my old emails, it appears I contacted this company through their support form back in 2007. They were blocking a client’s newsletter. This is what I sent:
What … is your name?
- steve
- Jan 6, 2018
For some reason otherwise legitimate ESPs have over the years picked up a habit of obfuscating who they are.
I don’t mean those cases where they use a customers subdomain for their infrastructure or bounce address. If the customer is Harper Collins then mail “from” @bounce.e.harpercollins.com sent from a server claiming to be mail3871.e.harpercollins.com isn’t unreasonable. (Though something in the headers that identified the ESP would be nice).
No, I mean random garbage domains created by an ESP to avoid using their real domains in the mail they send and in their network infrastructure. This isn’t exactly snowshoe behaviour. They’re not really hiding anything terribly effectively from someone determined to identify them – the domains are registered with real contact information, and the IP addresses the mail is sent from are mostly SWIPped accurately – but they do prevent a casual observer from identifying the sender.
Silverpop has registered over 9,000 domains in .com that are just “mkt” followed by some random digits that they use for infrastructure hostnames, bounce addresses and click-tracking links. Apart from anything else, it’s a terrible waste of domain name space to use links.mkt1572.com where they could just as well use links1572.silverpop.com or links.mkt1572.silverpop.com.
For what they’re paying just for domain name registration and management they could probably hire multiple full time employees.
And Marketo has registered over 17,000 domains in .com that are just “mkto-” followed by what looks like a location code.
(I’m not picking on Marketo and Silverpop in particular – several other notable ESPs do the exact same thing – they’re just relevant to the end of the story).
Using garbage domains like this makes you look more like a snowshoe spammer at first glance than a legitimate ESP.
It also makes it much harder for a human glancing at your headers to correctly identify a responsible party …
… which is probably why abuse@marketo are rather tired of receiving misdirected complaints about spam sent by Silverpop from machines called something like mkt1572.com.
Not fooling anyone…
- laura
- Nov 30, 2017
A question came up on the Women of Email Facebook page about sending cold B2B emails. This is one of those areas I have strong opinions about, mostly because I am so tired of getting deceptive and unending messages from folks.
Realistically, cold emailing isn’t going to stop just because recipients hate receiving it. We haven’t wiped out spam in 20+ years, we’re not going to manage it for this one tiny piece. But I do think there are things senders can do to minimize the amount of frustration their spam creates.
Interacting in professional fora
- steve
- Nov 8, 2017
There are a bunch of online communities – mailing lists, Slack channels, etc. – where “people who do email” interact.
Some of them are open to anyone to subscribe, some of them are semi-private and require an invitation, others are closed and only available by invitation and yet others are associated with trade associations and only open to their members.
Many of them include representatives from ISPs, ESPs, reputation providers and technical specialists. They also – especially the open lists – have participants with no particular role in the industry, but very strong opinions on what others should do.
They’re a useful place to keep up to date on current issues and industry trends, and to get help when you need it. But … quite a lot of people reduce their chance of getting timely help by the way they behave there. Don’t be like those people.
Some of the things you should and shouldn’t do are specific to mailing lists. Some are specific to professional fora. Some are specific to entreating others for help. Here, in no particular order, are some suggestions:
DO: Be friendly. Be patient. Be welcoming. Be considerate. Be respectful.
DO: Be careful in the words that you choose.
DON’T: Be a dick.
DON’T: Be wildly unprofessional. If you think sexist or racist behaviour isn’t wildly unprofessional, leave the email industry. Ditto for unwanted sexual attention, personal insults, sexualized language or imagery.
DON’T: Harass people. If someone wants you to stop, then stop.
DO: Follow the community norms. Different communities have different styles and traditions – try and pick up on what they are, and avoid violating them.
DO: Follow the community norms for replying to messages, quoting them and trimming threads. If you’re not sure what they are then snipping out parts that aren’t relevant and replying in-line isn’t likely to offend anyone.
DO: Follow the level of formality of the community. Some are very formal, and should be treated much the same as a business meeting. Others much less so, and blend professional discussion with blowing off steam, ranting about idiot clients and social banter between friends.
DO: Lurk on the list for a day or three before posting to get a feel for how the community works (unless there’s a “welcome to the new person” thread). If you’ve joined because you have an immediate emergency you’re looking for help on, say so and be polite – maybe even a little apologetic – about it. Maybe spend five minutes checking the list archives first.
DON’T: Lurk except when you have a problem. Interacting with others when you’re not asking for help builds up relationships and karma. If you only appear when you’re looking for help, people are less likely to be helpful.
DO: Be clear about what company or organization, you’re affiliated with. That might mean using a corporate email address, mentioning it in a sig file or in a “Hi, I’ve just joined the group” message. Or it might mean including the relevant company name when asking for help. If, for political reasons, you absolutely cannot admit to your affiliations it’s still useful to know that you work for an unnamed major US cable company or an email provider based in Switzerland – particularly when you’re offering help or advice where your insight is coming from your experience in that role.
DO: Remember that the vast majority of the people you’re interacting with aren’t being paid to be there. They’re sharing their time and expertise in return for benefiting from others. Try to both give and take.
DO: Remember that a representative from a large ISP probably doesn’t have answering your questions or helping with your problem in their job description.
DON’T: Aggressively demand help. Nobody owes you anything.
DO: Read responses carefully. Someone may not be able to publicly join the dots on an issue for you, but may point out which dots you might want to look at.
DO: Understand limits. If someone says “our lawyers say this is the process you must follow” then follow that process. And don’t push that person to do things that their lawyers say they can’t do.
DO: Be aware that you’re interacting with people, not company representatives. They almost certainly have opinions that don’t reflect those of their organizations.
DO: Remember that nobody owes you support. Be nice. And if someone doesn’t volunteer help or stops responding, don’t badger them.
DO: Follow the community style for how you present your message. But … in general, mostly plain text won’t offend anyone, heavy use of rich text will annoy some people.
DON’T: Rely on rich text for meaning. It may not be visible to some people or not visible when quoted. “Look at the log lines highlighted in yellow” isn’t a good approach.
DON’T: Warlord. There’s no need for long legal disclaimers on your mail. Nor for more than four lines of signature – we don’t need to know your life history. Graphics are cheesy, even if they’re your employers professionally drawn logo. Even colour can be distracting if it’s not used carefully.
DON’T: Assume that you’re the best representative of your organization to interact with a community. If you’re a senior manager and you have a smart employee who is actively working in the area – they may be a better rep than you are.
DO: Be aware of how public a community is. Does it have a public archive that’s indexed by Google? Is it open subscription? Be aware of how public things you say are.
DO: Be aware of what is expected from you in terms of information distribution. Can things you learn from the community be shared elsewhere? With attribution, or not? If you’re not sure, don’t share information unless the person providing it OKs that – it’s always OK to ask if you’re not sure. Terms you might see are Traffic Light Protocol or Chatham House Rule.
DO: Assume good faith.
DO: Provide relevant information when looking for help or asking “has anyone else seen this?”.
DO: Check unread mail to a list before posting. If someone else is already talking about an issue, join that thread rather than starting your own.
DO: Check the archives first, if you can. The answer to your problem might be in there. And if it’s not, including a mention of “this looks similar to what Yahoo was doing in October” signals that you’ve done a little work before asking for help and might trigger someone’s memory of what happened last time.
DO: Include relevant IP addresses and hostnames, if you’re asking about a delivery issue.
DO: Include exact error or rejection messages – “blocked at AOL” isn’t particularly useful, “554 RLY:B1” is much more so.
DO: Mention what sort of email it is, especially if you think the problems may be content related.
DON’T: Obfuscate.
DO: If you’re asking about a problem, say how long it’s been going on and what you’ve already tried to fix it.
DO: Respond promptly if someone asks for more details.
DON’T: Expect help if you’re not prepared to share data.
DON’T: Vanish once you resolve the problem. Share what you did, even if it’s just “it cleared up around 3pm”.
DO: Be prepared to take conversations that only you and one other person, out of hundreds, are interested in to direct message or private email.
DO: Stick around and help others. Share what you know.
DON’T: Post off-topic stuff people aren’t going to be interested in. It’s great that your kid is selling girl scout cookies or you’re doing a charity 5k, but unless you’re absolutely sure that this is a good place to fundraise, it almost certainly isn’t.
DO: Keep conversation on a mailing list, on the mailing list. There’s no need to Cc everyone involved – they’re on the mailing list too.
DON’T: Email angry. If someone has made you mad, wait before responding.
The Blighty Flag
- laura
- Nov 3, 2017
Back in the dark ages (the late ’90s) most people used dialup to connect to the internet. Those people who had broadband could run all sorts of services off them, including websites and mail servers and such. We had a cable modem for a while handling mail for blighty.com.
At that time blighty.com had an actual website. This site hosted some of the very first online tools for fighting abuse and tracking spam. At the same time, both of us were fairly active on USENET and in other anti-spam fora. This meant there were more than a few spammers who went out of their way to make our lives difficult. Sometimes by filing false complaints, other times by actually causing problems through the website.
At one point, they managed to get a complaint to our cable provider and we were shut off. Steve contacted their postmaster, someone we knew and who knew us, who realized the complaint was bogus and got us turned back on. Postmaster also said he was flagging our account with “the blighty flag” that meant he had to review the account before it would be turned off in the future.
I keep imagining the blighty flag looking like this in somebody’s database.
That is to say, sometimes folks disable accounts they really shouldn’t be disabling. Say, for instance:
This was an accident by a twitter employee, according to a post by @TwitterGov
The feds are deploying DMARC
- steve
- Oct 19, 2017
The US National Cybersecurity Assessments & Technical Services Team have issued a mandate on web and email security, including TLS+HSTS for web servers, and STARTTLS+SPF+DKIM+DMARC for email.
It’s … pretty decent for a brief, public requirements doc. It’s compatible with a prudent rollout of email authentication.
Warmup advice for Gmail
- laura
- Sep 28, 2017
Getting to the Gmail inbox in concept is simple: send mail people want to receive. For a well established mail program with warm IPs and domains, getting to the inbox in practice is simple. Gmail uses recipient interaction with email to determine if an email is wanted or not. These interactions are easy when mail is delivered to the inbox, even if the user has tabs enabled.
When mail is in the bulk folder, even if it’s wanted, users are less likely to interact with the mail. Senders trying to change their reputation to get back to the inbox face an uphill battle. This doesn’t mean it’s impossible to get out of the bulk folder at Gmail, it’s absolutely possible. I have many clients who followed my advice and did it. Some of these clients were simply warming up new IPs and domains and needed to establish a reputation. Others were trying to repair a reputation. In both cases, the fixes are similar.
When I asked colleagues how they handled warmup at Gmail their answers were surprisingly similar to one another. They’re also very consistent with what I’ve seen work for clients.
Sometimes less is more
- steve
- Sep 26, 2017
We just bought some new desks, to replace the old ones that date back to the days of CRT monitors.
The supplier we bought them from, Autonomous, did a nice set of triggered sends throughout the sales process – “we’ve received your order”, “we’ve shipped your order”, “your order has been delivered”.
That’s not rocket science – you plug your ordering system and your FedEx shipping API into your SendGrid API and you’re done.
I’d normally expect glossy, rich-text branded emails with logos and images, but Autonomous went in the opposite direction.
The mail is “From:” Mark@Autonomous, not a generic role account. It’s signed off by Mark, and has his contact info at the end of the email – but in a “I typed my email and phone number here for you” sort of way rather than a fancy signature block. It’s HTML, but it’s not using any images (other than a single tracking image) and is using the mail clients default font.
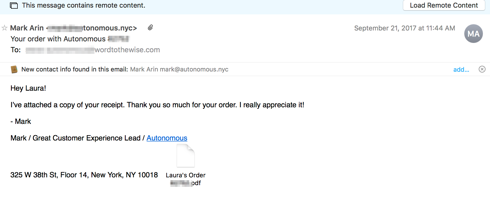
The first mail has an invoice attached, with a nice customized name (“Laura’s Order.pdf”).
The second one says that the warehouse manager, Eddie, has shipped the order and includes four fedex tracking numbers, all linked to the fedex tracking site, and a soft upsell for an assembly service.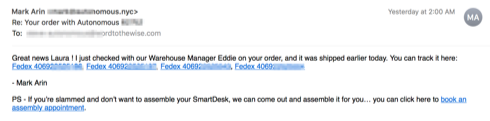
The third links to a youtube video about how to put the desks together, and pulls in Justin, the customer experience manager.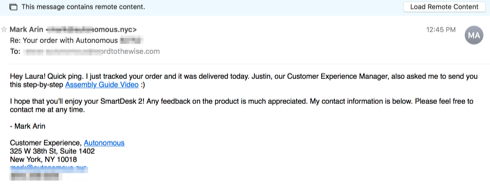
It feels very small company and individual service. But looking at the way the emails are put together, and the times they were sent, I’m fairly sure it’s automatic, templated triggered sends. But I’m not entirely sure, and that’s part of the charm.
Sometimes less is more.
10 things every mailer must do
- laura
- Sep 26, 2017
A bit of a refresh of a post from 2011: Six best practices for every mailer. I still think best practices are primarily technical and that how senders present themselves to recipients is more about messaging and branding than best practices. These 6 best practices from 2011 are no longer best, these days, they’re the absolute minimum practices for senders.
If you can’t manage to do these, then find someone who can.
A DMARC warning
- laura
- Sep 22, 2017
One challenge when implementing DMARC is to ensure that all mail, and I do mean ALL mail is authenticated correctly, before switching to a p=reject notice. The easiest way to do this is to set up a p=none record and check reports to see what mail isn’t authenticated. At least some of this mail is actually going to be valid but unauthenticated email.
I regularly recommend monitoring for 6 – 12 months in order to catch some irregular emails. Even then, someone should regularly monitor DMARC reports in order to identify systems that need authentication added.
One of the cases I worry about is system monitoring emails. These are emails intended to notify sys admins about problems and errors. They often don’t go through the main SMTP server. They usually don’t have an external facing IP and there are security arguments against putting internal IPs into external SPF records. These emails are important and are, usually, not authenticated.
Overall, I could imagine cases where a DMARC record would lead to some problems. And, well, it can. Reading through the postmortem of a significant system failure, one of the problems was no one knew backups weren’t running because notification emails were failing DMARC.
Maybe they're just not that into you?
- steve
- Aug 28, 2017
In April of last year I created a new twitter account. I can’t remember exactly why, but it was a throwaway created to look at some aspect of how twitter interacts with new accounts.
As part of the account creation process I gave Twitter an email address. They sent me a confirmation message right away: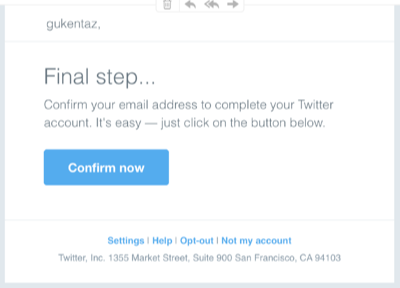
I didn’t click the button.
Four months later they sent me another confirmation email. I didn’t click the button.
It’s now sixteen months later. Nobody has logged in to or interacted with that twitter account since the day it was created. Twitter are sending me confirmation messages for that account about once a month.
They’re doing quite a lot of things right – they have not just an “Opt-out” link but also a “Not my account” link, which is great!
But after sixteen months of not returning your messages, maybe they’re just not that in to you?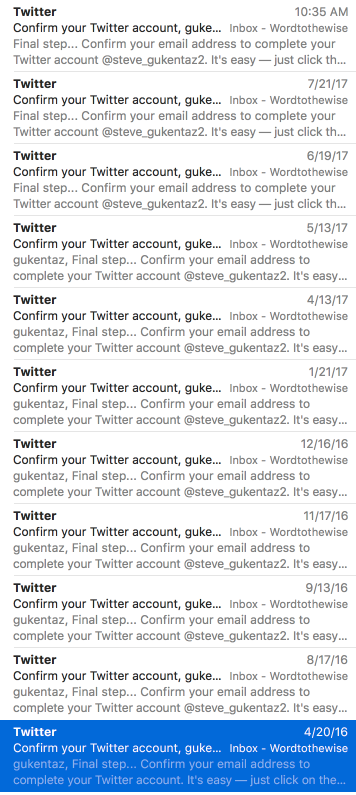
Reengagement emails
- laura
- Aug 15, 2017
By default I don’t load images in email. For one thing it lets me see who is using open / click data to measure engagement. This morning I got a reengagement email from my Senator. 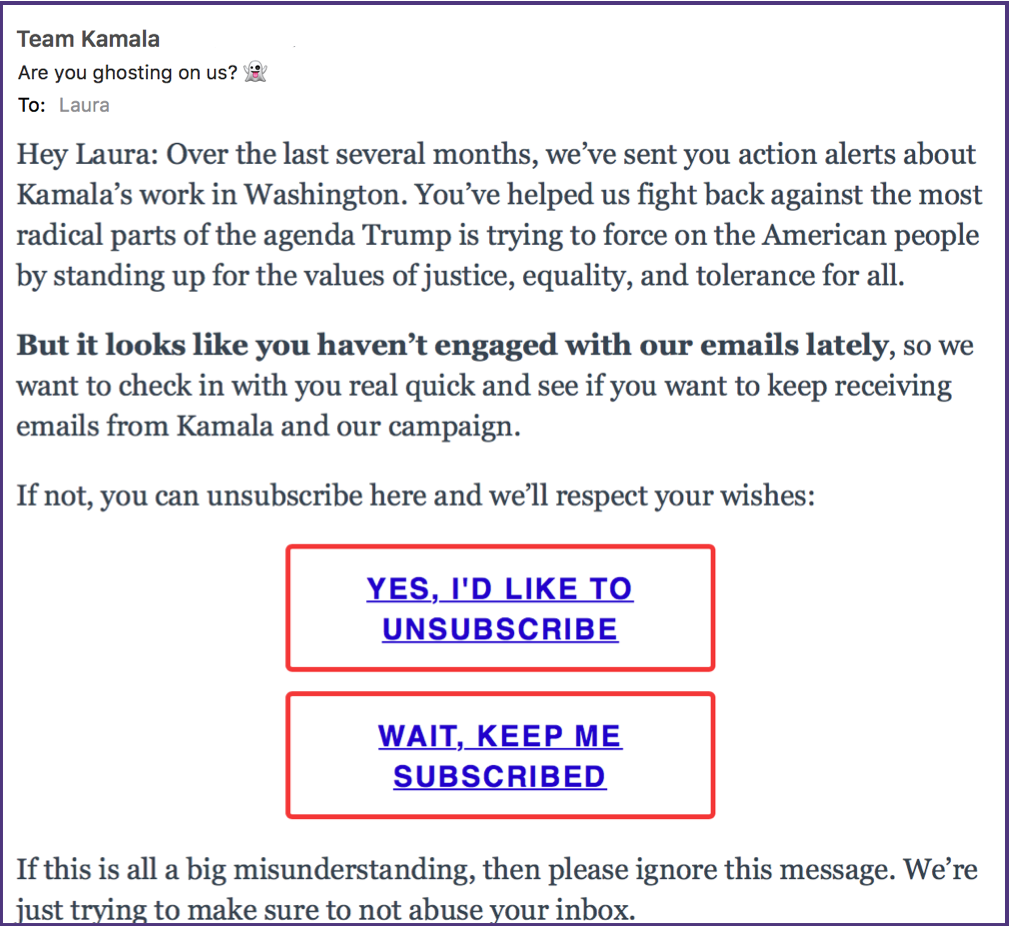
There are things I really like about this email and there are somethings I think they get a little wrong.
Implied permission
- laura
- Jul 24, 2017
Codified into law in CASL, implied permission describes the situation where a company can legally mail someone. The law includes caveats and restrictions about when this is a legitimate assumption on the part of the company. It is, in fact, a kludge. There isn’t such a thing as implied permission. Someone either gives you permission to send them email or they don’t.
We use the term implied permission to describe a situation where the recipient didn’t actually ask for the mail, but isn’t that bothered about receiving it. The mail is there. If it has a particularly good deal the recipient might buy something. The flip side of not being bothered about receiving mail, is not being bothered about not receiving mail. If it’s not there, eh, no biggie.
Implied permission isn’t real permission, no matter what the law says.
Now, many deliverability folks, including myself, understand that there are recipients who don’t mind getting mail from vendors. We know this is a valid and effective way of marketing. Implied permission is a thing and doesn’t always hurt delivery.
However, that does not mean that implied permission is identical to explicit permission. It’s one of the things I think CASL gets very right. Implied permission has a shelf life and expires. Explicit permission doesn’t have a shelf life.
Implied permission is real, but not a guarantee that the recipient really wants a particular email from a sender, even if they want other emails from that sender.
I'm not a customer any more
- laura
- Jul 21, 2017
We recently moved co-working spaces, after 8 or 9 years in the same place. I’ll be up front here, we left Space A because I was annoyed with them. I’ve been increasingly unhappy with them for a while, but moving is a pain so just put up with them. But their most recent rent increase along with the lost packages, increasing deposit requirements and revolving door of incompetent staff finally drove us to find a new co-working space.
On the 15th of the last month of our contract, I started receiving marketing emails from Space A. I just deleted a couple of them but finally decided I didn’t want to ever see their name again. I tried to unsubscribe.
Gotta give them credit. Checkboxes for everything, except some of them are to opt-in and some of them are to opt-out. This is the kind of interface marketers use to confuse folks and limit the actual number of opt-outs. I’ll admit, the first time I tried to opt-out, I probably did it wrong. But, I know CAN SPAM says they have 10 days, and I know many marketers take advantage of that so I wait a while and keep deleting the messages that show up in my mailbox.
That was late June. By early July I realize it’s been more than 10 days and I’m still getting mail from them. So I click another opt-out link. This time I notice I need to uncheck most boxes, but check the bottom one. OK, fine, you got me, I didn’t read and didn’t correctly opt-out the first time. This time I will.
I continue to receive email. I continue to delete the email. We run our own mail system so I don’t have the benefit of a this-is-spam button, but you can bet if I did I would have used it, on every message I received after my first attempt to opt-out.
This week, after getting yet more mail, I start digging. What ESP are they using that’s bungling the opt-out process? Ah. I know that ESP. So I send in a complaint to abuse@ESP asking them to please make their customer stop mailing me. I also go, once again, to the preference page and submit an opt-out request. Because, hey, maybe third time is a charm?
12 hours later I get yet another mail from them. Really? REALLY? OK. Now I’m moving from annoyed to irate. First step: figure out if I know anyone working at said ESP. Ah, right, them. I have a lot of respect for this colleague, so I send a heads up pointing out that their customer isn’t honoring unsubscribes and can they take a look at what might have broken in their unsubscribe process.
This morning they tell me they looked into my subscription and have not registered any opt-out request until the one this week. The other two? Not recorded in their system. “Does this match your recollection of what happened?” No. No it doesn’t. I know I clicked on unsub links at least 3 times and only one of those clicks is recorded.
At this point, I’m pretty sure I’ll be suppressed by the ESP so I won’t have to get mail from Space A any longer. That fixes the annoyance on my end. But I can’t help thinking about how horrible this interaction was, both from a deliverability perspective and from a customer perspective.
People are the weakest link
- laura
- Jul 17, 2017
All of the technical security in the world won’t fix the biggest security problem: people. Let’s face it, we are the weakest link. Adding more security doesn’t work, it only causes people to figure out ways to get around the security.
Read MoreActive buttons in the subject line
- laura
- Jul 7, 2017
This morning I waded into a twitter discussion with a bunch of folks about some issues they were having with delivery to gmail. The discussion started with a blog post at detailed.com describing how some senders are seeing significant drops in open rates. I thought I’d take a look and see if I can help, because, hey, this is an interesting problem.
I signed up for a bunch of the mail that was seeing gmail problems and discovered that one of them had the confirmation link in the subject line. How cool is that?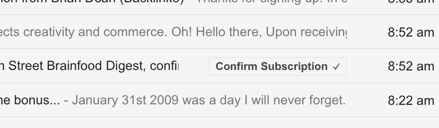
I’ve known about the Gmail subscription line functionality for a while, but this is the first time I’ve seen it in the wild.
The action is in a <div> tag at the bottom of the email. Gmail has been allowing actions in subject lines for a while, this is just the first time I’ve seen it used for subscriptions. It’s so cool.
Want to add one to your post? Instructions are available from Google on their Email Markup pages.
Help! We're on Spamhaus' list
- laura
- Jun 28, 2017
While trying to figure out what to write today, I checked Facebook. Where I saw a post on the Women of Email group asking for help with a Spamhaus listing. I answered the question. Then realized that was probably useable on the blog. So it’s an impromptu Ask Laura question.
We’re listed on Spamhaus’ list, any advice on how to get off? Our email provider has a plan, just looking for more input.
If you’re on the SBL, there’s a problem (somewhere) with your data collection process. You’re getting addresses that don’t actually belong to your customers / subscribers / whatever.
The fastest way off it to cut WAY back on who you are mailing to. Mail only to addresses you know, for sure, based on activity in the email, want your mail. Then you can start to go through the other addresses and make decisions about how to verify that those addresses belong to the people you think they do.
If you’re at an ESP, do what they tell you to do. Most ESPs have dealt with this before.
One thing to think about, once you get past the crisis stage, is that if you’re on the SBL, it’s likely your delivery is overall pretty bad. These aren’t folks that dramatically list for a single mistake, there’s a pattern. ISPs look at different patterns, but will often find the same answers and delivery will be bad.
It’s important to realize that Spamhaus has 4 or 5 different lists that have different listing criteria. This is for the SBL, there’s also CSS, CBL, PBL, DBL and XBL. They address different problems and have different listing and delisting criteria.
Delete or read?
- laura
- Jun 23, 2017
This week I attended a Data Visualization workshop presented by the Advanced Media Center at UC Berkeley. Every year I set at least one professional development goal; this year it’s learning how to better communicate visually.
Part of the class included other resources, which led me to Nathan Yau’s website. One of the articles on the front page of his site is titled “Email Deletion Flow Chart.” Well, of course I had to read the post.
The cycle goes on
- laura
- Jun 15, 2017
Monday I published a blog post about the ongoing B2B spam and how annoying it is. I get so many of these they’re becoming an actual problem. 3, 4, 5 a day. And then there’s the ongoing “drip” messages at 4, 6, 8, 12 days. It is getting out of control. It’s spam. It’s annoying. And most of it’s breaking the law.
But, I can also use it as blog (and twitter!) fodder.
Appending in a nutshell
- laura
- Jun 1, 2017
A few months ago a colleague sent me, and every other person on his overly large LinkedIn list, an email looking for some help hiring. It starts off with “Greetings LinkedI Connections” and ends with… an unsubscribe link.
Read MorePurchased lists aren't always purchased
- laura
- May 31, 2017
Spamhaus has listed a number of domains belonging to French politicians recently. In their blog post about it, they mention that the listings are directly related to address lists provided to candidates by the French government.
Read MoreYou're kidding me
- steve
- May 17, 2017
All the authentication and DMARC in the world can’t save you from stupid.
I just got a survey request from my bank. Or, at least, it claimed to be from my bank.
… and bad acquisition practices
- steve
- May 2, 2017
I talked last week about how incentivizing people to sign up for your mailing list could be effective when it’s done well.
This week I’m staying at a Large International Hotel Chain and I’ve got a great example of what happens when it’s done poorly.
The “free” wifi requires you to join the hotel’s loyalty programme. I’ve done that in the past, so I login with my email address and password. Nope, the email address isn’t what you log in with, it’s an obscure nine digit number (but I only discover this after assuming I’d forgotten my password and attempting the password recovery dance, which doesn’t work).
OK, new loyalty programme account time. I create a new throwaway^W tagged email address and cough up some contact information. I get a welcome email. It has a Reply-To: address of, literally, “REPLYTOADDR”.
The newly created account also doesn’t actually get me in to the hotel wifi. I’m probably not going to be a terribly receptive recipient when they start emailing me at that address about what a great hotel they are. I’ll just unsubscribe. Any reasonable recipient not in the email industry will probably hammer the “this is spam” button until the mail goes to their spam folder and doesn’t come back.
On a somewhat related note, I have line-of-sight to a nearby discount mall. They have free public wifi and “me@privacy.net” already has an account on it in the name of “Eric”. I wonder how much email they send Eric?
Every Download a Confirmation
- steve
- Apr 26, 2017
We often talk about confirmed opt-in (aka “closed-loop opt-in” or “double opt-in”) as the gold standard for address acquisition for permission-based mail.
It’s not the only way to gather permission, and in some ways it’s a rather blunt tool that can discourage people from completing a sign-up process if it’s done badly – the confirmation email isn’t sent immediately, it goes to the recipients spam folder, they don’t have any reason to go and look for it, …
When it’s done well, though, it’s excellent.
Tor.com, the site for science-fiction and fantasy operated by publisher Macmillan, just did it very well with an ebook giveaway.
Last year they published Every Heart a Doorway, a novella that won several awards and caused quite a bit of buzz in the SFF community, partly because it’s very good and partly because it’s author, Seanan McGuire, has some serious social media chops. The sequel, Down among the Sticks and Bones, is being released in the next month or two.
Perfect timing for a time-limited giveaway of the first book, tied to signing up for their mailing list.
The signup form is on a page dedicated to the giveaway that talks about the book and sets some expectations about the mailing list. The form itself makes it very clear that you’ll need to enter a real email address to get the ebook download, so me@privacy.net is less likely to subscribe.
People aren’t required to sign up for the mailing lists to get the download. This isn’t a barter, a mailing list signup for a book, rather it’s putting the opportunity to sign up for the mailing lists in front of people who are self-selected to be interested in the content. That probably reduces the “how many people signed up” metric somewhat, but I bet the “how many new subscribers are still signed up in a month” numbers will look very healthy.
It provides some options. Do you want weekly content? Monthly? Both? You know that you’re not going to end up on a thrice-daily list from Macmillan and all their affiliates.
The confirmation email landed in my inbox within a few seconds after I clicked the “Sign Me Up” button. That’s important. If it takes even a few minutes I might have moved on, and wouldn’t be looking for the confirmation mail if it had ended up in my bulk folder.
And the confirmation mail isn’t a “click here to confirm your subscription” yawnfest. The subject line is “Download EVERY HEART A DOORWAY by Seanan McGuire Now” and the body content is on-brand and includes the front cover of the book.
Way more compelling.
It’s still solid informed consent from me, and confirmation that I, the owner of the email address, want on the list. (And, yes, the download link has 56 bytes of opaque hex-encoded data in it, so I know they’re tracking that.)
This is how it should be done.
(And, if you like fantasy you should head over to Tor and sign up for their promo. Seanan writes some amazing things, and I’m not just saying that because she’s a friend.)
Why is bounce handling so hard
- laura
- Apr 3, 2017
It should be easy, right? Except it’s not. So why is it so hard?
With one-on-one or one-to-few email it’s pretty simple. The rejections typically go back to a human who reads the text part of the rejection message and adapt and makes the decision about future messages. The software handles what to do with the undeliverable message based on the SMTP response code.
In the case of a 5xy response the server stops attempting delivery and alerts the original sender the mail failed. One example from helping a client troubleshoot a delivery problem recently.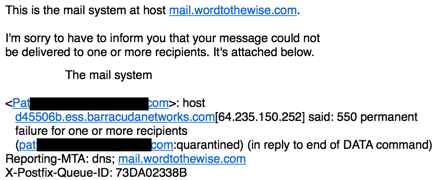
There’s useful information in the text portion of this email from my mail server. It says there was a permanent failure (550) and that my message won’t be delivered. It also says the email is quarantined in reply to the end of DATA. That’s actually a critical piece of information. It means Barracuda saw the entire message before deciding to reject it. It’s likely a problem with the content of the email and so I need to look at links in the message.
This type of plain text explanation is great for a human to read and act on. But it’s not that simple for list handling software to identify the relevant information in the text message and act on future emails to that recipient. Different MTA vendors and ESPs have done a lot of work to try and correctly parse bounce messages to pull out relevant information.
ISPs have tried to help the situation by giving more descriptive rejection messages. They’re still using the SMTP required 3 digit numbers, but they include short, parseable codes in the text portion of the message. In many cases they also include URLs and links that open up webpages explaining the meaning of the code. They even post a list of the most common codes on their postmaster webpages.
All of these things make it somewhat easier to handle bounces automatically. Kinda.
I’ve been working on some bounce handling recommendations for a client using a few different ESPs. I spent a good few days digging into the bounces returned by their different ESPs. It was an interesting exercise as it demonstrated how very differently ESPs handle bounces. But it also clarified for me that there are a lot of different kinds of bounces.
It's not fair
- laura
- Mar 23, 2017
In the delivery space, stuff comes in cycles. We’re currently in a cycle where people are unhappy with spam filters. There are two reasons they’re unhappy: false positives and false negatives.
False positives are emails that the user doesn’t think is spam but goes into the bulk folder anyway.
Fales negatives are emails that the user does thing is spam but is delivered to the inbox.
I’ve sat on multiple calls over the course of my career, with clients and potential clients, where the question I cannot answer comes up. “Why do I still get spam?”
I have a lot of thoughts about this question and what it means for a discussion, how it should be answered and what the next steps are. But it’s important to understand that I, and most of my deliverability colleagues, hate this question. Yet we get it all the time. ISPs get it, too.
A big part of the answer is because spammers spend inordinate amounts of time and money trying to figure out how to break filters. In fact, back in 2006 the FTC fined a company almost a million dollars for using deceptive techniques to try and get into filters. One of the things this company did would be to have folks manually create emails to test filters. Once they found a piece of text that would get into the inbox, they’d spam until the filters caught up. Then, they’d start testing content again to see what would get past the filters. Repeat.
This wasn’t some fly by night company. They had beautiful offices in San Francisco with conference rooms overlooking Treasure Island. They were profitable. They were spammers. Of course, not long after the FTC fined them, they filed bankruptcy and disappeared.
Other spammers create and cultivate vast networks of IP addresses and domains to be used in snowshoeing operations. Still other spammers create criminal acts to hijack reputation of legitimate senders to make it to the inbox.
Why do you still get spam? That’s a bit like asking why people speed or run red lights. You still get spam because spammers invest a lot of money and time into sending you spam. They’re OK with only a small percentage of emails getting through filters, they’ll just make it up in volume.
Spam still exists because spammers still exist.
Relaying Denied
- laura
- Mar 20, 2017
I’ve got multiple clients right now looking for insights about bounce handling. This means I’m doing a lot of thought work about bounces and what they mean and how they match up and how different ISPs manage delivery and how different ESPs manage delivery and how it all fits together. One thing I’ve been trying to do is contextualize bounces based on what the reason is.
Despite what people may thing, spam filtering isn’t the only reason an email fails to deliver. There are lots of other reasons, too. There is a whole category of network problems like routing issues, TCP failures, DNS failures and such. There are address issues where a recipient simply doesn’t exist, or is blocking a particular sender. There are spam and authentication issues. The discussion of all these issues is way longer than a blog post, and I’m working on that.
One of the interesting bounces that is so rare most people, including me, never talk about is “Relaying Denied.” This is, however, one of the easier bounces to explain.
Relaying Denied means the mail server you’re talking to does not handle mail for the domain you’re sending to.
Well, OK, but how does that happen?
There are a couple reasons you might get a “Relaying Denied” message, most of them having to do with a misconfiguration somewhere. For whatever reasons, the receiving server doesn’t handle mail for a domain.
DNS records are incorrect. These can be due to a number of things
End of an era
- laura
- Mar 2, 2017
A few moments ago, I cancelled one of my email addresses. This is an address that has been mine since somewhere around 1993 or 4. It was old enough to vote. And now it’s no more.
I am not even sure why I kept it for so long. It was my dialup account back when I was in grad school in Delaware. When I moved to Madison to work at the university, I kept it as a shell account and email address. I gave it up as my primary email address about the time it was bought by a giant networking company. By then I had my own domain and a mail server living behind the futon in the living room. That was back when we started WttW, somewhere around 2002.
15 years the address has mostly laid dormant. I used it for a couple yahoo groups accounts, but just lists that I lurked on.
I did use it as research for some past clients, typically the ones using affiliate marketers. “Our affiliates only ever send opt in mail!” Yeah, no. See, look, your affiliate is spamming me. My favorite was when said customer put me on the phone with the affiliate.
Confirmed Opt-In: An Old Topic Resurrected
- laura
- Mar 1, 2017
Looking back through my archives it’s been about 4 years or so since I wrote about confirmed opt in. The last post was how COI wasn’t important, but making sure you were reaching the right person was important. Of course, I’ve also written about confirmed opt-in in general and how it was a tool somewhat akin to a sledgehammer. I’m inspired to write about it today because it’s been a topic of discussion on multiple mailing lists today and I’ve already written a bunch about it (cut-n-paste-n-edit blog post! win!).
Confirmed opt-in is the process where you send an email to a recipient and ask them to click on a link to confirm they want the mail. It’s also called double opt-in, although there are some folks who think that’s “spammer” terminology. It’s not, but that’s a story for another day. The question we were discussing was what to do with the addresses that don’t click. Can you email them? Should you email them? Is there still value in them?
We have to treat the addresses as a non-homogenous pool. There are a lot of reasons confirmation links don’t get clicked.
From the archives: Taking Permission
- laura
- Feb 17, 2017
From February 2010, Taking Permission.
Permission is always a hot topic in email marketing. Permission is key! the experts tell us. Get permission to send email! the ISPs tell us.
Marketers have responded by setting up processes to “get” permission from recipients before adding them to mailing lists. They point to their privacy polices and signup forms and say “Look! the recipient gave us permission.”
In many cases, though, the permission isn’t given to the sender, permission is taken from the recipient.
Yes, permission is being TAKEN by the sender. At the point of address collection many senders set the default to be the recipient gets mail. These processes take any notion of giving permission out of the equation. The recipient doesn’t have to give permission, permission is assumed.
This isn’t real permission. No process that requires the user to take action to stop themselves from being opted in is real permission. A default state of yes takes the actual opt-in step away from the recipient.
Permission just isn’t about saying “well, we told the user if they gave us an email address we’d send them mail and they gave us an email address anyway.” Permission is about giving the recipients a choice in what they want to receive. All too often senders take permission from recipients instead of asking for permission to be given.
Since that post was originally written, some things have changed.
CASL has come into effect. CASL prevents marketers from taking permission as egregiously as what prompted this post. Under CASL, pre-checked opt-in boxes do not count as explicit permission. The law does have a category of implicit permission, which consists of an active consumer / vendor relationship. This implicit permission is limited in scope and senders have to stop mailing 2 years after the last activity.
The other change is in Gmail filters. Whatever they’re doing these days seems to really pick out mail that doesn’t have great permission. Business models that would work a few years ago are now struggling to get to the inbox at Gmail. Many of these are non-relationship emails – one off confirmations, tickets, receipts. There isn’t much of a relationship between the sender and the recipient, so the filters are biased against the mail.
Permission is still key, but these days I’m not sure even informed permission is enough.
Are seed lists still relevant?
- laura
- Feb 16, 2017
Those of you who have seen some of my talks have seen this model of email delivery before. The concept is that there are a host of factors that contribute to the reputation of a particular email, but that at many ISPs the email reputation is only one factor in email delivery. Recipient preferences drive whether an email ends up in the bulk folder or the inbox.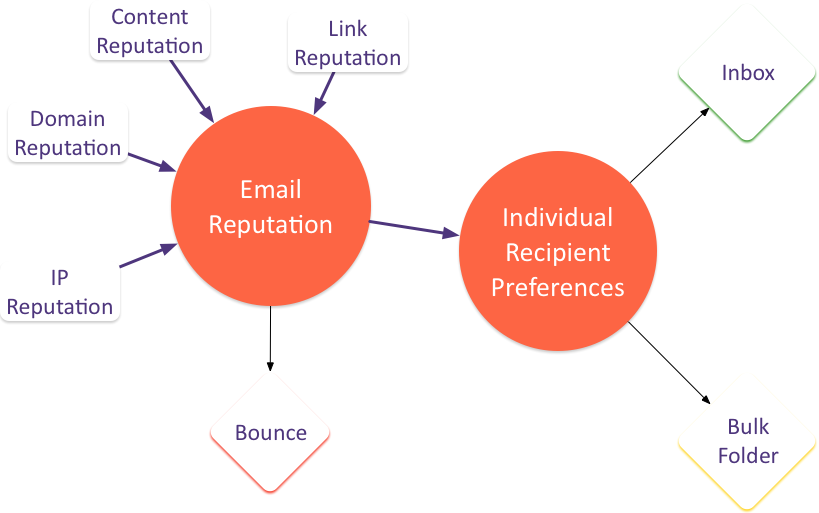
The individual recipient preferences can be explicit or implicit. Users who add a sender to their address book, or block a sender, or create a specific filter for an email are stating an explicit preference. Additionally, ISPs monitor some user behavior to determine how wanted an email is. A recipient who moves an email from the bulk folder to the inbox is stating a preference. A person who hits “this-is-spam” is stating a preference. Other actions are also measured to give a user specific reputation for a mail.
Seed accounts aren’t like normal accounts. They don’t send mail ever. They only download it. They don’t ever dig anything out of the junk folder, they never hit this is spam. They are different than a user account – and ISPs can track this.
This tells us we have to take inbox monitoring tools with a grain of salt. I believe, though, they’re still valuable tools in the deliverability arsenal. The best use of these tools is monitoring for changes. If seed lists show less than 100% inbox, but response rates are good, then it’s unlikely the seed boxes are correctly reporting delivery to actual recipients. But if seed lists show 100% inbox and then change and go down, then that’s the time to start looking harder at the overall program.
The other time seed lists are useful is when troubleshooting delivery. It’s nice to be able to see if changes are making a difference in delivery. Again, the results aren’t 100% accurate but they are the best we have right now.
Subscription transparency
- laura
- Feb 10, 2017
I regularly tell clients to be transparent with their sends. With email, permission is better than forgiveness. A surprise change in mail frequency or type leads to complaints. Complaints lead to bulk foldering. Once mail is in the bulk folder, it’s hard to get out of there, particularly at some webmail providers.
The permission is better than forgiveness is hard for a lot of senders to understand. Much of marketing is about assuming the yes in the absence of a no. Sure, they’ll back off when there’s a no, in DMA terms it’s the “one bite at the apple rule.” Unfortunately for senders the one bite rule doesn’t work in the email space.
There are a couple reasons that permission is better than forgiveness in the email space. The biggest is that the ISPs own the mailbox and as the owners they make decisions about who gets access. They prioritize the wants and needs of their customers / users over the wants and needs of advertisers. It’s easy for users to give feedback; in many cases they just have to hit a button. But that’s another whole blog post.
Today I get an email from The Guardian. They’re modifying and expanding their newsletter program, so they sent subscribers an update about it.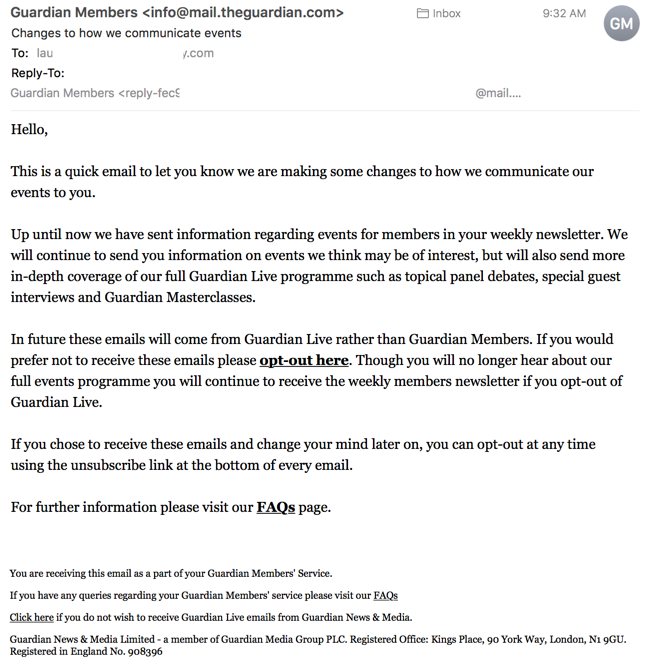
Asking for help with a blocklist
- laura
- Jan 12, 2017
There are often questions arising about how to go about getting off a particular blocklist. A few years ago I led the MAAWG effort to document what to if if you were On a Blocklist (pdf link). That document was aimed primarily at MAAWG members and deliverability experts with working knowledge of blocklists. I think, even now, it’s a good background on how to deal with a listing and mail being blocked.
There have been discussions on multiple mailing lists over the last week or so about how to deal with listings at different blocklists. Many folks on these lists have extensive experience, so these are good places to ask. With that being said, a lot of the requests lack sufficient details to help.
So, if you’re ever on a blocklist and want some help from a mailing list about the problem, here’s a short guide for how to ask for help.
Ask Laura: Should we confirm unsubscribes?
- laura
- Dec 9, 2016
Dear Laura,
We have some questions about best practices for unsubscribes. Our ESP uses the List-Unsubscribe header by default on every email. I’m not familiar with this, and I have some questions for you.
First, do you think this is a good idea? Should we always use it, or just for certain emails? Should we use the mailto:link or link to a web site to unsubscribe?
We were also asked about double opt-out and if we should do it. We’re thinking that if someone clicks on the unsubscribe link they would be directed to a site displaying a message such as “Sorry to see you go. We have sent an email out for you to fully unsubscribe from the mailing list”. They then have to open the email and click on the link. Do you recommend doing this? Are there anti-spam regulations that this might violate?
And then, once someone unsubscribes (either with double opt-out or not), should we send out some sort of email confirmation? We currently do not, but we’re thinking of sending something like “Sorry to see you go. If you unsubscribed accidentally please click here to re-subscribe.” What do you think?
Thanks,
Breaking Up Is Hard to Do
Outreach or spam?
- laura
- Dec 6, 2016
This showed up in my mailbox earlier today: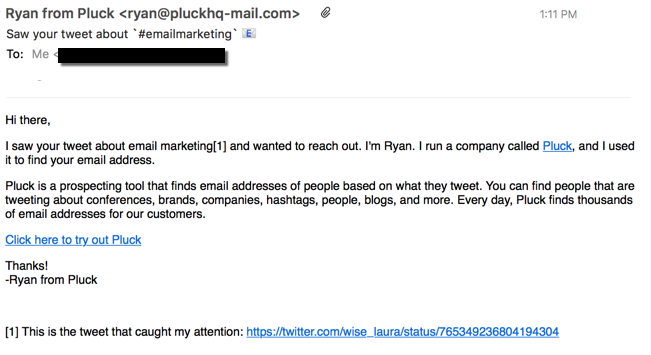
The tweet in question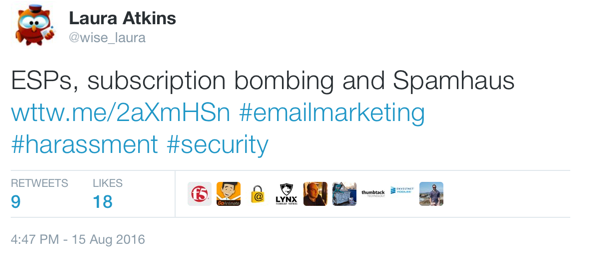
From Crunchbase: “Pluck is an email prospecting tool that gives you the email addresses of the people tweeting about subjects related to your business.”
Prospecting: another name for spamming. Look, I know that you want to sell you’re newest, greatest product to the world. But just because I tweet something with a # that you think is relevant to your product doesn’t mean that I want to get your spam. I also know it’s hard to get attention and find prospects; I’m a small business owner, too and I need to market my own services. But spamming isn’t a good idea. Ever.
There’s been a significant increase in this kind of spam “to help your business” lately. It’s a rare day I don’t get something from some company I’ve never heard of trying to sell me their newest product. It might be something if they tried a contact or two and then went away. But they’ll send mail for weeks or months without getting an answer. Look, silence IS an answer and it means you need to go away and leave your prospects alone.
Unfortunately, there are services out there that sell a product that let you “automatically follow up” with your prospects. Pluck up there uses one of them, as that’s who’s handling all the links in the message. In fact, if you go to the bare domain (qcml.io) they talk a good anti-spam game. “Die, spammers, die.” I reported the message to them. I’m not expecting them to actually do anything, and I’m not expecting a response.
It’s just spam under another name. There’s no pretense that it’s anything else. Even if it’s sent in a way that makes it look like a real person typed the message, like QuickMail offers. “All emails will come straight out of your personal inbox as though you typed them yourself.” As if you typed them yourself.
The worst part is there’s no real way to stop the mail. I can’t unsubscribe. The companies selling the software don’t provide any guidance to their customers about what the law requires. Take the message from Pluck that started the post. It violates CAN SPAM in multiple ways. Moreover, the address they used is not publicly associated with my twitter handle, which means they’re doing some harvesting somewhere. That means treble penalties under CAN SPAM.
I could reply and ask them to stop mailing me. I’ve done that a couple times with a message that says, “Please don’t email me any more.” I’ve got to tell you, some people get really mad when you ask them not to email you. Some just say yes, but others are really offended that you asked them to stop and get abusive. It’s gotten to the point where I don’t ask any more because of that one person who decides to harass, threaten and scream at me. Sure, it’s maybe 1 in 5, but I don’t have the time or energy to figure out who is going to be receptive and who isn’t. I don’t have time for that. No one has time for that.
I’m expecting that filters are going to catch up eventually and these types of mail will be easier to filter out. Until then, though, small business owners like myself are stuck in a place where we have to deal with spam distracting us from our business. At least I get blog content out of it.
DNSBLs, wildcards and domain expiration
- laura
- Nov 29, 2016
Last week the megarbl.net domain name expired. Normally this would have no affect on anyone, but their domain registrar put in a wildcard DNS entry. Because of how DNSBLs work, this had the effect of causing every IP to be listed on the blocklist. The domain is now active and the listings due to the DNS wildcard are removed.
Read MoreZombies are real but less of a problem
- laura
- Oct 31, 2016
A few years ago I wrote a series of blog posts about zombie email addresses. Zombie addresses are those that someone owned and used and interacted with, but for whatever reason stopped logging into and checking. This series started with the time before the zombies, and moved on to the zombie uprising. Then discussed how they don’t eat brains, but they do love to take a bite out of deliverability. Smart marketers, however, can defeat zombies by the judicious application of the double tap.
Since that series of blog posts a few things have changed. The biggest thing is that the webmail providers are being much more aggressive about disabling email reception at addresses where folks don’t log in. I have a few addresses on different providers I use for testing purposes. I have to remember, though, that I need to log into them before sending test messages. If I don’t, they generally bounce.
This doesn’t completely remove the challenge of zombie addresses but it does make it easier for regular senders to purge their lists of zombies just through their normal bounce handling. No double-taps needed.
Global Suppression Lists
- steve
- Sep 23, 2016
Global Suppression List.
Pander File.
Screamers List.
Whatever you call it, it’s the list of email addresses you suppress from every mailing.
If you’re an ESP, this is the list of people who you never, ever want to send email to – and I’m talking about ESP-wide global suppression lists here, not the suppression lists maintained per-customer.
Global suppression lists are a vital tool to have, as it’s the only way you can comply with requests like “Never mail me again.” – and failing to comply with those will lead to, at best, irritation, yelling and blocking, and at worst legal action.
But it’s only the right tool for suppressing mail in a few cases. One obvious one is when someone specifically requests no more mail, ever, through your system. Another is when there’s a technical reason (you never want to send mail to autoresponders, for instance), or a legal reason (pending litigation, or an incompatibility between the mail you send and a specific jurisdiction).
And there are a very few people who just cause way too much support overhead when you send them email – that’s the origin of the term screamer list, I’m sure.
But it’s not what you should be reaching for in response to spam complaints, even heated ones, or feedback loop hits. A spam complaint is a sign that your customer is probably doing something wrong, and that this recipient doesn’t want that customers mail. A feedback loop hit says that this recipient doesn’t want that customers mail (and, statistically may indicate that your customer has a problem).
Neither of them is a sign that the recipient doesn’t want mail from any of your customers. You definitely wouldn’t want one of your customers sending spam to cause mail from all of your customers to be blocked – so why would you let a complaint about one of your customers block mail to that recipient from all your customers?
(We’ve occasionally come across ESPs who have preemptively blocked all mail to addresses @wordtothewise.com, for no clear reason. When our clients discover that their ESPs are silently discarding our attempts to subscribe to their mailing lists it doesn’t do much for that ESPs reputation in our clients’ eyes.)
And whatever you do, don’t respond to a spam complaint telling them you’ve added them to a global suppression list. That says several things, to an already annoyed person. It tells them that you’ve just broken their subscriptions, past or future, to your other customers. And by “fixing” the spam problem for this one recipent in this way it suggests that you’re not actually going to do anything to deal with the customer they’re complaining about. Nothing about this can end well.
Instead, tell them that you’ll make sure they don’t receive any further mail from that customer, and that you’ll talk with the customer and take action that you deem appropriate. (And then do that).
P.S. Does anyone know the origin or etymology of the term “pander file”?
Use the form…
- laura
- Sep 21, 2016
A lot of senders get frustrated with the time it can take to get a response from some ISPs. It’s totally understandable, for a lot of companies delivery problems are all hands on deck level problems. They want them fixed and they want them fixed IMMEDIATELY. They want feedback that their issue is being addressed. They want to know someone at the ISP knows there is a problem.
I’ve talked before about visiting my friend Anna and watching her laptop screen explode with IMs from senders who wanted help with an AOL issue. She’s awesome and conscientious and tried to address all of those issues as fast as she could. She did want senders to feel like their issues were important and that someone inside AOL cared about the mail blocks.
I was always a strong advocate for following the official pathways for addressing problems. That was the whole point of the 2009 blog post. These days it’s easier to do than it ever was. Many ISPs have forms and process around handling delivery issues. This is good! In the past getting an answer to “why is my mail blocked” required knowing the right people. Now, it’s not about who you know. The ISPs and filtering companies who are open to senders have postmaster pages, unblock forms and official request channels. Those that don’t have those channels have made certain business decisions to not provide support for senders.
Despite the availability of webforms and knowledge bases and detailed information, a lot of people still think that the only way to get attention or get an issue addressed is to get someone on the phone. It’s not, though.
ISPs have their processes. If you want things handled quickly use those processes. Even in the places where very helpful reps are, they can’t (on order of lawyers and executives) help people unless there is a ticket already open.
Always, always use the recommended processes before trying to find “a real person.” Most of the time your issue can be solved faster if you fill out the form than if you hunt around for a person. In the worst case, all that time will be wasted as the person in question will tell you to fill out the form.
Incentivizing incites fraud
- laura
- Sep 8, 2016
There are few address acquisition processes that make me cringe as badly as incentivized point of sale collection. Companies have tried many different ways to incentivize address collection at the point of sale. Some offer the benefit to the shopper, like offering discounts if they supply an email address. Some offer the benefits to the employee. Some offer punishments to the employee if they don’t collect addresses from a certain percentage of customers.
All of these types of incentive programs are problematic for email collection.
On the shopper side, if they want mail from a retailer, they’ll give an address simply because they want that mail. In fact, asking for an address without offering any incentive is way more likely to get their real address. If they don’t want mail but there is a financial incentive, they’re likely to give a made up address. Sometimes it will be deliverable, but belong to another person. Sometimes it will be undeliverable. And sometimes it will be a spamtrap. One of my delivery colleagues occasionally shares addresses she’s found in customer lists over on her FB page. It’s mostly fun stuff like “dont@wantyourmail.com” and “notonyour@life.com” and many addresses consisting of NSFW type words.
On the employee side there can also be abuses. Retailers have tried to tie employee evaluations, raises and promotions to the number of email addresses collected. Other retailers will actively demote or fire employees who don’t collect a certain number of addresses. In either case, the progression is the same. Employees know that most customers don’t want the mail, and they feel bad asking. But they’re expected to ask, so they do. But they don’t push, so they don’t get enough addresses. Eventually, to protect their jobs, they start putting in addresses they make up.
Either way, incentivizing point of sale collection of information leads to fraud. In a case I read about in the NY Times, it can lead to fraud much more serious than a little spam. In fact, Wells Fargo employees committed bank fraud because of the incentives related to selling additional banking products at the teller.
Arguing against the anti-spam policy
- laura
- Sep 7, 2016
Not long ago I was talking with a colleague who works for an ESP. She was telling me about this new client who is in the process of negotiating a contract. Normally she doesn’t get involved in negotiations, but the sales group brought her. It seems this new client is attempting to remove all mention of the anti-spam policy from the contract. As she is the deliverability and compliance person, the sales people won’t agree unless compliance does.
Her sales team needs props for bringing her in to negotiate a contract where the anti-spam clause is removed.
This isn’t that unusual situation. Many well managed ESPs will include deliverability and compliance personnel in negotiations if the customer indicates they want changes to the language of the anti spam clause.
On the face of thing it seems reasonable for customers to want to negotiate compliance terms. They want to protect themselves from unexpected outages. It seems irresponsible to allow a service provider to have the ability to made such a business affecting decision.
Many folks try to negotiate their way out of anti-spam clauses. Just asking for changes isn’t a big deal. However, some companies push the issue with sales and contract folks to an extreme. They threaten to not sign if the anti-spam clauses are removed completely. 
Threatening a contract over compliance issues can poison an entire working relationship. The fact is that most people who argue about anti-spam clauses and compliance issues are people who have had problems with other ESPs in the past. For better or worse, prospects that try and remove anti-spam clauses from contracts are often problem customers.
On the compliance side, if someone is pushing hard to get the spam clause removed, they think a few different things:
Subscription bombing, ESPs and Spamhaus
- laura
- Aug 16, 2016
A number of ESPs woke up to a more-than-usually-bad Monday morning. Last night Spamhaus listed 10s of networks, including ESPs, on the SBL. The listings all contained the following note:
Read MoreSPF ?all
- laura
- Jul 21, 2016
The most read post on the blog is Authenticating with SPF: -all or ~all. In fact, it’s in the top 5 posts every single day. We still get comments on it, too. Usually from folks who disagree with my recommendations.
I still stand by my recommendations, though. It doesn’t really matter if you choose ~all or -all in your SPF records. Why? No major provider is rejecting mail solely because of a SPF fail. They may bulk the mail, but they won’t reject it. That’s why, in a deliverability context, it doesn’t matter which one you choose.
My one rule for SPF is never use ?all. Just. No. In the spec, ?all is “testing” mode. But it really is a signifier that the person who put the SPF record together doesn’t know what they’re doing. Unless they really are testing, but even then you shouldn’t see ?all on records for weeks or months.
~ or – never ?
Bad data drives delivery problems
- laura
- Jun 29, 2016
It’s a wild election season here in the US. In the past few presidential elections, email has played a bigger and bigger role in messaging and fundraising. President Obama’s campaign used email effectively, but sent huge volumes. In fact, the volume was so heavy, it led to a joke on the Daily Show.
Read MoreBounce handling is hard
- laura
- Jun 28, 2016
Sometimes I find it hard to find a new topic to write about. I decide I’m going to write about X and then realize I did, often more than once. Other times I think I can blog about some issue only to realize that it’s too complex to handle in a quick post. There are concepts or issues that need background or I have to work a little harder to explain them.
One thing I haven’t blogged about before is bounce handling. That particular topic falls into the other category of posts that take a lot of time to write and need a significant amount of work to make sense. I was even joking with my fellow panel members at EEC a few months ago about how that’s a post that so needs to be written but I’m avoiding it because it’s so hard. There’s so much to be conceptualized and explained and I realize it’s not a blog post but multiple blog posts, or a white paper or even a book.
So let’s start with some simple definitions. Those of you who work at ISPs are probably thinking of bounces in terms of accept than reject, that’s not exactly what I’m talking about here. I’m writing these for senders, who usually call rejects during the SMTP transaction bounces.
Domain transparency
- steve
- Jun 22, 2016
An email I received this morning got me thinking about how your domain name is one of the main ways you identify yourself if you’re sending email.
We talk about domain reputation quite a lot – DKIM and SPF let a sender volunteer a domain name as a unique identifier for recipients to use to track reputation, DMARC allows them to tie that domain to the domain visible to the user in the From: field. And most ISPs use the domains in links in the body of the message to track reputation, either internally or through third-party reputation providers.
But there’s also a human side. We expect people and companies to be honest in how they identify themselves – and we’re suspicious when they aren’t. We’ve been trained to be wary of messages that claim to be from a company we know but which, for whatever reason, don’t look quite right. Rightly so – a lot of phishing and credential theft is based on bad people using branding and domains that look like legitimate ones.
Here are some header snippets from this morning’s (legitimate) email:
Permission: Let’s Talk Facts
- laura
- Jun 8, 2016
I’ve commented in the past about how I can usually tell when an ISP makes filtering changes because all my calls relate to that ISP. The more recent contender is Gmail. They made changes a few months ago and a lot of folks are struggling to reach the inbox now. What I’m seeing, working with clients, is that there are two critical pieces to getting to the gmail inbox: permission and engagement.
Read MoreCan we put the FREE!!! Myth to bed?
- laura
- Jun 1, 2016
Really. Single words in the subject line don’t hurt your delivery, despite many, many, many blog posts out there saying they do. Filters just don’t work that way. They maybe, sorta, kinda used to, but we’ve gotten way past that now.
In fact, I can prove it. Recently I received an email from Blizzard. The subject line:
Laura — Last Chance to Claim Your FREE Copy of Warlords of Draenor — Including Level 90 Boost! Offer Expires Monday! Last Chance to Claim Your FREE Copy of Warlords of Draenor — Including Level 90 Boost! Offer Ends Monday!
We have an email with
Necessary but not sufficient
- laura
- May 27, 2016
With all the emphasis on getting the technical right, there seem to be people who think their mail will be delivered as long as the technical is right.
Getting the technical right is necessary for good inbox delivery, but it’s not sufficient.
The most important part of getting mail to the inbox is sending mail users want. In fact, if you’re sending mail folks want, interact with and enjoy then you can get away with sloppy technical bits. Look, major players (eBay and Intuit) have invalid SPF records, but we’re all still getting mail from them.
There are also a lot of folks who are doing everything technically perfectly, but their mail is still going to bulk. Why? Because their recipients don’t want their mail.
Permission is still the key to getting mail to the inbox. In fact, permission is more important than getting all the technical bits right. If you have permission you can play a little fast and loose with the technical stuff. If you have the technical stuff right you still need permission.
I cannot feel the Bern.
- meri
- May 24, 2016
On a lark (and to do my best to stay as informed as possible via primary sources) I decided to sign up for the official mailing lists of the Trump, Clinton, and Sanders campaigns.
Both Trump and Clinton were happy to take my email address and add it to their distribution lists, no confirmation required. Not terribly surprising, since they need to make it as easy as possible to get their messages out to anyone who will listen.
On to the Sanders campaign.
I… couldn’t figure out how to subscribe to Sanders’ mailing list.
I feel I must have missed something obvious. I’m certainly not saying that I’m a super-genius or anything… but, at the same time, if I can’t figure out how to get your mail, then it might just be that others are having similar problems.
The first obvious place to sign up for updates was the big blue “This is your movement” box. That route requires a donation to proceed. Back to the main page.
The next option would sign me up for mobile alerts. No thanks.
All the way at the bottom of the page, a final big blue box asks, “Are you ready?” Somewhat beyond ready, I entered my information, clicked “Join us” and held my breath.
The “Form submission limit reached” error is likely indicative of the use of outsourced product or service being used to collect and manage contact information on behalf of the campaign. My actually seeing this error is indicative of insufficient testing of the site by the campaign.
I’m sure the developer promised a bulletproof site, and it seems the campaign took this on faith. But at least one thing fell through cracks, resulting in the campaign not just losing an avenue of communication with someone who has self-selected as interested, but also potentially diminishing that person’s opinion of how the campaign manages the finer points, and wondering how that ultimately reflects on the candidate. Ultimately, it doesn’t matter whether or not the campaign developed the site themselves or hired someone else to do it on their behalf. All that matters is that they put their name on it, and let it speak for their brand.
Campaigning is sales. Whether you’re selling a candidate or a stock portfolio or a hand-made product, when you invite your audience to interact with you online, they must find the experience to have been worth their time, otherwise they’re unlikely to take you up on any future invitations. In business, as in politics, there’s a lot on the line, communication is vital, and mastering digital interaction with the public is no longer optional.
And while I was writing this post, I started receiving mail from the Sanders’ campaign. So I guess I could subscribe after all.
Ask Laura: What about Transactional Opt-Outs?
- laura
- May 20, 2016

Dear Laura,
We are having a bit of an internal struggle on our end as we launch our new quarterly account summaries. What are your views on including an unsubscribe link in these emails?
My personal opinion is that we should. Although the summaries can be classified as “transactional”, they are not tied to a specific recent transaction a customer made and can be viewed as a general reminder to shop again. As I gathered data to present my case, I reviewed several different account summaries and I found it split close to 50/50. Do you have any data or thoughts to support one way or another?
Thanks,
Summary Judgement
Your purchased list … is spam.
- laura
- May 13, 2016
This morning I got spam from someone selling email addresses. The mail starts:
Read MoreDon't just follow the HOWTO
- laura
- May 11, 2016
![]() There are so many moving parts to ensure good email deliverability. Email marketers need to know marketing, they need to know email and they need to know design. The technical bits of email can be a challenge to learn, and many folks who write tutorials and How-Tos write them for a different audience than marketers.
There are so many moving parts to ensure good email deliverability. Email marketers need to know marketing, they need to know email and they need to know design. The technical bits of email can be a challenge to learn, and many folks who write tutorials and How-Tos write them for a different audience than marketers.
One of the things I’m trying to do is demystify the technical end of email for marketers. Today I talked about authentication in the Only Influencers newsletter. Check it out!
Understanding the technical: Authentication
Authentication in general
It's still spam
- laura
- Apr 26, 2016
Companies are always trying to find new ways to use and abuse email. My mailbox has been rife with mail from companies trying to sell me stuff for my business. It’s been interesting to watch the new ways they’re trying to get attention, while not honoring the most important rule of email marketing.
Ugg, a spammer.
- laura
- Mar 21, 2016
I’ve written before about how there is some (I’m sure lovely) woman in the UK who has been connected to my email address. I get a lot of mail for her. Mostly spam. She doesn’t seem to be using the address, but I regularly get mail addressed to MRS. LAURA CORBISHLEY (all caps, always). Typically these messages are advertising various UK stores and products. Sometimes they’re mortgage offers. A few have been sweepstakes only open to UK residents.
I generally forward these spams off to various blocklists with the note it’s my “UK spamtrap” and they take whatever actions seem appropriate to them. Today, though, I got my first US spam to Mrs. Laura Corbishly. From a Yesmail customer called sanuk.com. I’m getting a website error (they get smacked for spamming already?) but a little research tells me this is shoe company that owns a bunch of brands, including Ugg.
Today, though, I got my first US spam to Mrs. Laura Corbishly. From a Yesmail customer called sanuk.com. I’m getting a website error (they get smacked for spamming already?) but a little research tells me this is shoe company that owns a bunch of brands, including Ugg.
Yes, Ugg a Spammer. They even even have a disclaimer at the bottom of the email telling me they’re a spammer!
Not so much, no. It appears, though, that the data brokers selling Mrs. Corbishley’s name connected to my email address have figured out that no one ever actually acts on any of their UK offers. So now they’re selling into the US market in hopes that they might entice a purchase?
On a purely nosy level, I’d love to know who was selling the address. First off, I’d love to know where they got this info in the first place. Secondly, what horrible database are they using that keeps name data in all caps? (When I get email to this trap I think they’re shouting at me, as if I’m the one who is wrong about my name. Maybe they think if they yell at me loud enough will I decide I really am the happy wife of Mr. Corbishley of Swindon, UK. )
I do tell clients that it’s useful to remind customers that they signed up for mail, especially if they haven’t mailed for a while. So I know not every email with a “you opted in” reminder is spam, but I only notice those things when I haven’t opted in. It’s something I mostly gloss over if I really did opt-in. I wonder if this is how other folks react to “you opted in” notices, too.
I do recommend the reminder be much more specific than “you opted in at our website.” Give the user a date, a time, something that isn’t just something any company can, and many do, make up.
Best practices or required practices
- laura
- Mar 9, 2016
What really are the best practices for email?
A year ago I wrote a post about best practices and how most of my best practices were different from what other people recommend. I don’t talk about rules for frequency or subject line length. I don’t focus on best practices for bounce processing or content length. My best practice recommendations are really about process.
My best practice recommendations are really about process.
This message has no content.
- steve
- Jan 22, 2016
This is what my mail client tells me about the latest mail Twitter sent me:
Criticism of Twitter’s copywriters?
Not exactly, no. Mail.app is looking for some textual content near the top of the mail to display to me as preview text. It can’t find any in this mail, so it’s telling me the message has no content.
Looking at the mail it’s a standard multipart mime message, with a text/plain part and a text/html part.
The text/plain part is entirely empty. Nothing in there at all.
Don’t do that. If you really can’t come up with a plain text version of your message just send simple text/html mail. (And think about why you’re employing talented copywriters if you’re not making good use of the copy they write).
With some messages the text/html part is also empty of text, containing nothing but images. That’s not the case here, though – the message is mostly text, and renders just fine without loading remote images (there are remotely hosted images, but loading them just enhances the message, they’re not essential).
But … there are nearly three hundred lines of HTML before we get to the first text. The mail client probably just gave up looking for content before it got there.
If you’re the sort of perfectionist who’ll A/B test subject lines to see which ones are most likely to get a recipient to open the message you should be paying just as much attention to the other content that is shown in the inbox – the friendly from and the message preview.
In an ideal world your message would have the most important text at the top, and mailbox previews would work perfectly. If your messages are slathered in so much CSS that the actual content is hidden, or if you rely on images for the headline, or if you put “View this email in web browser” at the top of all your messages then you’re likely not showing the content you’d like to recipients.
Try and craft your mails so the most important information is shown as text, and near the top of the mail. If you can’t do that, consider using explicit mailbox preview content. Litmus explain how to do that, and list the mail clients that support it in their article.
Hands off address books
- steve
- Jan 16, 2016
Germany’s highest court has ruled that Facebook’s practice of harvesting email addresses from their users contact lists in order to send invitations to them constitutes “advertising harassment” and violates German law on data protection and unfair trade practices. This in response to a suit filed by the Federation of German Consumer Organisations (VZBV)
Read MoreTriggered and transactional emails
- laura
- Jan 8, 2016
 Earlier this week I was talking on IRC with some colleagues. There was some kvetching about senders that think transactional emails are the same as triggered emails. This led to discussion about whether transactional and triggered emails are the same. I don’t think they are, but it took a while for me to come up with why I don’t think they’re the same. It took even longer to come up with definitions I liked.
Earlier this week I was talking on IRC with some colleagues. There was some kvetching about senders that think transactional emails are the same as triggered emails. This led to discussion about whether transactional and triggered emails are the same. I don’t think they are, but it took a while for me to come up with why I don’t think they’re the same. It took even longer to come up with definitions I liked.
Transactional Emails: Emails sent in response to direct request by the recipient. Transactional emails are usually one-off emails. Transactional emails probably don’t need an unsubscribe link, although it may be a good idea to include one just to make people feel comfortable receiving them. Examples: password reset emails, receipts, tickets.
Triggered Emails: Emails sent in response to an action by a recipient. Triggered emails can be one-off, but can also be series of emails. Triggered emails should have an unsubscribe link, so people can stop the emails if needed. Examples: cart abandonment emails, after purchase surveys, followups to software installation.
The key difference is that in a transactional email, the recipient has asked for that particular email. In a triggered email, the recipient may very well want and respond to the email, but they didn’t ask for it.
There are, as always, some grey areas here. Is a welcome message transactional or triggered? Probably transactional, but they should always have an unsubscribe link.
What about software installation followups? We’ve been looking at some alternatives to our current time tracking software which involved me setting up accounts at multiple different SaaS providers. A couple of them had triggered welcome series. These emails let me know things I could do with the software, things I still needed to set up, and led me through the process of trying out their system.
This was mostly good, but not completely. One of the series didn’t have an opt-out link, though. That was somewhat annoying because I’d already decided the tracker didn’t do what we needed. I couldn’t make the mail stop. I think if there is one thing I’d say about mail is that senders should never force someone to receive their mail.
It’s tempting for senders to define all triggered emails as transactional. Since it’s a user action that caused the mail to be sent, it must be a transactional email. But a lot of triggered emails are triggered by actions the user doesn’t know will trigger an email. Cart abandonment emails are a good example of this, not every retailer has them and so users aren’t yet expecting to get an email if they drop stuff in their carts and then leave the site.
Overall, both transactional and triggered emails have their place in a healthy email program. But they shouldn’t be confused for one another and should be treated as separate mail streams.
Doing it right
- steve
- Dec 29, 2015
It’s that time of the year – marketers send more email than usual, recipients unsubscribe from their lists.
Clicking on the unsubscription link in the email I just received took me to an unsubscription landing page. The box for my email address was prepopulated based on the cookie in the unsubscription link, the default setting is to unsubscribe me from all mail from the sender and just clicking the sole button on the page will unsubscribe me.
It offers me an alternative to unsubscribing from everything – letting me receive just the content I want. It does that immediately on the unsubscription landing page (rather than suggesting I go to a subscription center or, worse, requiring I click on a different link in the mail originally). And it tells me the important things about the newsletters I might want to subscribe to – what they’re about and how often they’re sent.
This isn’t anything particularly special, but sometimes it’s nice to highlight someone who is doing it right.
But my purchased list is TARGETED!!!
- laura
- Dec 9, 2015
 I hear this all the time. But, y’know what? It’s BS. Total BS.
I hear this all the time. But, y’know what? It’s BS. Total BS.
In the last month, I’ve gotten “targeted” messages (that escaped my filters) from the following companies who purchased lists.
Buying lists costs more than just money
- laura
- Dec 2, 2015
 I’ve been talking to a lot of companies recently who are dealing with some major delivery challenges probably related to their practice of purchasing lists and then sending advertising to every address on the list. They assure me that their businesses would be non-viable if they didn’t purchase lists and it has to be that way.
I’ve been talking to a lot of companies recently who are dealing with some major delivery challenges probably related to their practice of purchasing lists and then sending advertising to every address on the list. They assure me that their businesses would be non-viable if they didn’t purchase lists and it has to be that way.
Maybe that’s true, maybe it is more cost effective to purchase lists and send mail to them. I know, though, that their delivery is pretty bad. And that a lot of the addresses they buy never see their email. And that they risk losing their ESP, or they risk being SBLed, or they risk being blocked at Gmail, or they risk bulk foldering at Hotmail. There are a lot of risks to using purchased lists.
The reality is it’s only getting harder to mail to purchased lists and it’s getting more expensive to mail purchased lists. Paying for the list is a small part of the cost of using them.
Other costs incurred by companies using purchased lists include:
1) Having multiple ESPs. There are certainly legitimate reasons for companies to use different ESPs but there is a cost associated with it. Not only do they have to pay for duplicate services, but they spend a lot of employee time moving lists and recipients around to see who might have the better delivery today.
2) Multiple domains and brand new websites for every send. Landing pages are good marketing and are normal. But some ISPs track the IPs of the landing sites, and those IPs can get their own poor reputation. To get around it, senders using purchased lists often have to create new websites on new IPs for every send.
3) Complicated sending schedules. Sending schedules aren’t dictated by internal needs, they’re dictated by what ISP is blocking their IPs or domains (or even ESP) right now.
All of these costs are hidden, though. The only cost on the actual bottom line is the money they spend for the addresses themselves and that’s peanuts. Because, fundamentally, the folks selling addresses have no incentive to take any care in collecting or verifying the data. In fact, any verification they do only cuts into their profit, as buyers won’t actually pay for the verification and data hygiene and it also reduces the size of the lists they can sell.
And, no, data hygiene companies that look for traps and bounces and “bad addresses” don’t take a bad list and make it good. They just take a bad list and make it a little less bad. If the recipients don’t want the mail, all the hygiene in the world isn’t going to get that message into the inbox.
Outsourcing address collection to list selling companies is more expensive than it looks on paper. That doesn’t stop anyone from building a business around purchased lists, though.
Transactional mail
- laura
- Oct 1, 2015
 There are a lot of myths in the email space. Things that someone, somewhere said and another person repeated and then another person repeated and all of a sudden it is TRUTH. One of those things is the idea that there is a law defining what can be in a transactional email. Supposedly this law says that 80% of the message must be transactional content while 20% of the mail can be promotional content.
There are a lot of myths in the email space. Things that someone, somewhere said and another person repeated and then another person repeated and all of a sudden it is TRUTH. One of those things is the idea that there is a law defining what can be in a transactional email. Supposedly this law says that 80% of the message must be transactional content while 20% of the mail can be promotional content.
This isn’t really a law. I was even going to say it’s kinda a good idea, but then I stared thinking about it. It doesn’t even really make sense. 80% of what? Size? Space? Bytes? Layout? Do headers count in the 80% or just what’s visible? Does the HTML code count? What makes for “new” content?
Adding promotional content to receipts is great for conversions. It’s a great way to get someone to opt-in to mail. It’s a great way to upsell. It’s great for engagement; that makes it good for deliverability. Senders should include some level of promotional mail in receipts whenever possible.
There are some guidelines I suggest when looking at transactional mail.
Two factor authentication
- steve
- Sep 18, 2015
The drumbeat of “secure your accounts; help your customers secure their accounts with you” advice has faded away a bit, probably because we’ve not had a major ESP account compromise hit the media in the past few months.
The costs – customer support, security, reputation, executive focus – of customer account compromises are still significant, anything you can easily do to mitigate that in advance is still a good idea.
If two factor authentication isn’t available as an option on your platform, talk to your developers about getting it on their roadmap. If it is an option, maybe use it as a hook to hang a promotion on?
Good idea, Freddie!
Outrunning the Bear
- steve
- Sep 17, 2015

You’ve started to notice that your campaigns aren’t working as well as they used to. Your metrics suggest fewer people are clicking through, perhaps because more of your mail is ending up in junk folders. Maybe your outbound queues are bigger than they used to be.
You’ve not changed anything – you’re doing what’s worked well for years – and it’s not like you’ve suddenly had an influx of spamming customers (or, if you have, you’ve dealt with them much the same as you have in the past).
So what changed?
Everything else did. The email ecosystem is in a perpetual state of change.
There’s not a bright line that says “email must be this good to be delivered“. Instead, most email filtering practice is based on trying to identify mail that users want, or don’t want, and delivering based on that. There’s some easy stuff – mail that can be easily identified as unwanted (malware, phishing, botnet spew) and mail that can easily be identified as wanted (SPF/DKIM authenticated mail from senders with clean content and a consistent history of sending mail that customers interact with and never mark as spam).
Instead, most email filtering practice is based on trying to identify mail that users want, or don’t want, and delivering based on that. There’s some easy stuff – mail that can be easily identified as unwanted (malware, phishing, botnet spew) and mail that can easily be identified as wanted (SPF/DKIM authenticated mail from senders with clean content and a consistent history of sending mail that customers interact with and never mark as spam).
The hard bit is the greyer mail in the middle. Quite a lot of it may be wanted, but not easily identified as wanted mail. And a lot of it isn’t wanted, but not easily identified as spam. That’s where postmasters, filter vendors and reputation providers spend a lot of their effort on mitigation, monitoring recipient response to that mail and adapting their mail filtering to improve it.
Postmasters, and other filter operators, don’t really care about your political views or the products you’re trying to sell, nor do they make moral judgements about your legal content (some of the earliest adopters of best practices have been in the gambling and pornography space…). What they care about is making their recipients happy, making the best predictions they can about each incoming mail, based on the information they have. And one of the the most efficient ways to do that is to look at the grey area to see what mail is at the back of the pack, the least wanted, and focusing on blocking “mail like that”.
If you’re sending mail in that grey area – and as an ESP you probably are – you want to stay near the front or at least the middle of the grey area mailers, and definitely out of that “least wanted” back of the pack. Even if your mail isn’t great, competitors who are sending worse mail than you will probably feel more filtering pain and feel it sooner.
Some of those competitors are updating their practices for 2015, buying in to authentication, responding rapidly to complaints and feedback loop data, and preemptively terminating spammy customers – and by doing so they’re both sending mail that recipients want and making it easy for ISPs (and their postmasters and their machine learning systems) to recognize that they’re doing that.
Other competitors aren’t following this years best practices, have been lazy about providing customer-specific authentication, are letting new customers send spam with little oversight, and aren’t monitoring feedback and delivery to make sure they’re a good mail stream. They end up in the spam folder, their good customers migrate elsewhere because of “delivery issues” and bad actors move to them because they have a reputation for “not being picky about acquisition practices“. They risk spiraling into wholesale bulk foldering and becoming just a “bulletproof spam-friendly ESP”.
If you’re not improving your practices you’re probably being passed by your competitors who are, and you risk falling behind to the back of the pack.
And your competitors don’t need to outrun the bear, they just need to outrun you.
Organizational security and doxxing
- laura
- Sep 9, 2015
The security risks of organizational doxxing.
These are risks every email marketer needs to understand. As collectors of data they are a major target for hackers and other bad people. Even worse, many marketers don’t collect valid data and risk implicating the wrong people if their data is ever stolen. I have repeatedly talked about incidents where people get mail not intended for them. I’ve talked about this before, in a number of posts talking about misdirected email. Consumerist, as well, has documented many incidents of companies mailing the wrong person with PII. Many of these stories end with the company not allowing the recipient to remove the address on the account because the user can’t prove they own the account.
I generally focus on the benefits to the company to verify addresses. There are definite deliverability advantages to making sure email address belongs to the account owner. But there’s also the PR benefits of not revealing PII attached to the wrong email address. With Ashley Madison nearly every article mentioned that the email address was never confirmed. But how many other companies don’t verify email addresses and risk losing personally damaging data belonging to non customers.
Data verification is so important. So very, very important. We’ve gone beyond the point where any big sender should just believe that the addresses users give them are accurate. They need to do it for their own business reasons and they need to do it to prevent incorrect PII from being leaked and shared.
It's not about the spamtraps
- laura
- Sep 8, 2015
I’ve talked about spamtraps in the past but they keep coming up in so many different discussions I have with people about delivery that I feel the need to write another blog post about them.
Spamtraps are …
… addresses that did not or could not sign up to receive mail from a sender.
… often mistakenly entered into signup forms (typos or people who don’t know their email addresses).
… often found on older lists.
… sometimes scraped off websites and sold by list brokers.
… sometimes caused by terrible bounce management.
… only a symptom …
Deliverability advice to the DNC
- laura
- Aug 29, 2015
I was working on another post for this afternoon, but when I checked Facebook Autumn Tyr-Salvia had posted a link that’s much more interesting to talk about.
It seems the Democratic National Committee has acquired President Obama’s email list from the 2012 campaign.
Check your tech
- laura
- Aug 25, 2015
One of the things we do for just about every new client coming into WttW is have them send us an email from their bulk mail system. We then check it for technical correctness. This includes things like reviewing all the different From headers, rDNS of the connecting IP, List-Unsubscribe headers and authentication. This is always useful, IMO, because we often find things that were right when they were set up, but due to other changes at the customer they’re not 100% correct any more.
This happens to most of us. Even a company as small as Word to the Wise misses a rDNS update here or a hostname change update there when making infrastructure changes. That’s even when the same people know about email and are responsible for the infrastructure.
One of the most common problems we see is a SPF record that has accumulated include: files from previous providers. There are a couple reasons for this. One is the fact that SPF is set up while still at the old provider in anticipation of moving to the new provider. Once the move is made no one goes back to clean up the SPF record and remove the old entries. The other reason is that a lot of tech folks don’t like to delete things. Deleting things can lead to problems, and there’s no harm in a little extra in the SPF record. Except, eventually, there are so many include files that the lookup fails.
Every mailer should schedule a regular tech audit for their mail. Things change and sometimes in the midst of chance we don’t always catch some of the little details.
Utilizing all of your data
- josh
- Aug 21, 2015
Email marketing continues to be a great way to reach out to prospects and customers and many companies utilize multiple mail streams. Companies often have the following systems sending mail:
Read MoreLinking identities to email addresses
- laura
- Aug 19, 2015
As I predicted yesterday, a bunch of sites have popped up where you can input email addresses and find out if the address was part of the Ashley Madison hack. My spam trap address isn’t on it, which makes me wonder if unsubscribe data was kept elsewhere or if they just never bothered to save the requests.
One of the things I’m seeing in most articles about the hack is reassurance that Ashley Madison doesn’t verify addresses, so the accounts may not belong to the email address in question. We can’t say that the email address owner is the cheater, because Ashley Madison didn’t care who owned the email address.
The warnings have been published in security blogs.
LinkedIn addresses frequency issues
- laura
- Jul 28, 2015
Yesterday LinkedIn announced they’re decreasing the amount of mail they’re sending to users.
Read MoreData is the key to deliverability
- laura
- Jul 21, 2015
Last week I had the pleasure of speaking to the Sendgrid Customer Advisory Board about email and deliverability. As usually happens when I give talks, I learned a bunch of new things that I’m now integrating into my mental model of email.
One thing that bubbled up to take over a lot of my thought processes is how important data collection and data maintenance is to deliverability. In fact, I’m reaching the conclusion that the vast majority of deliverability problems stem from data issues. How data is collected, how data is managed, how data is maintained all impact how well email is delivered.
Collecting Data
There are many pathways used to collect data for email: online purchases, in-store purchases, signups on websites, registration cards, trade shows, fishbowl drops, purchases, co-reg… the list goes on and on. In today’s world there is a big push to make data collection as frictionless as possible. Making collection processes frictionless (or low friction) often means limiting data checking and correction. In email this can result in mail going to people who never signed up. Filters are actually really good at identifying mail streams going to the wrong people.
The end result of poor data collection processes is poor delivery.
There are lots of way to collect data that incorporates some level of data checking and verifying the customer’s identity. There are ways to do this without adding any friction, even. About 8 years ago I was working with a major retailer that was dealing with a SBL listing due to bad addresses in their store signup program. What they ended up implementing was tagged coupons emailed to the user. When the user went to the store to redeem the coupons, the email address was confirmed as associated with the account. We took what the customers were doing anyway, and turned it into a way to do closed loop confirmation of their email address.
Managing Data
Data management is a major challenge for lots of senders. Data gets pulled out of the database of record and then put into silos for different marketing efforts. If the data flow isn’t managed well, the different streams can have different bounce or activity data. In a worst case scenario, bad addressees like spamtraps, can be reactivated and lead to blocking.
This isn’t theoretical. Last year I worked with a major political group that was dealing with a SBL issue directly related to poor data management. Multiple databases were used to store data and there was no central database. Because of this, unsubscribed and inactivated addresses were reactivated. This included a set of data that was inactivated to deal with a previous SBL listing. Eventually, spamtraps were mailed again and they were blocked. Working with the client data team, we clarified and improved the data flow so that inactive addresses could not get accidentally or unknowingly reactivated.
Maintaining Data
A dozen years ago few companies needed to think about any data maintenance processes other than “it bounces and we remove it.” Most mailbox accounts were tied into dialup or broadband accounts. Accounts lasted until the user stopped paying and then mail started bouncing. Additionally, mailbox accounts often had small limits on how much data they could hold. My first ISP account was limited to 10MB, and that included anything I published on my website. I would archive mail monthly to keep mail from bouncing due to a full mailbox.
But that’s not how email works today. Many people have migrated to free webmail providers for email. This means they can create (and abandon) addresses at any time. Free webmail providers have their own rules for bouncing mail, but generally accounts last for months or even years after the user has stopped logging into them. With the advent of multi gigabyte storage limits, accounts almost never fill up.
These days, companies need to address what they’re going to do with data if there’s no interaction with the recipient in a certain time period. Otherwise, bad data just keeps accumulating and lowering deliverability.
Deliverability is all about the data. Good data collection and good data management and good data maintenance results in good email delivery. Doing the wrong thing with data leads to delivery problems.
Gmail Postmaster Tools for Senders
- josh
- Jul 13, 2015
 Google announced new postmaster tools for senders sending to Gmail. The Gmail Postmaster Tools are to help “qualified high-volume senders analyze their email, including data on delivery errors, spam reports, and reputation.” The updated postmaster pages also include Gmail’s best practices for bulk senders.
Google announced new postmaster tools for senders sending to Gmail. The Gmail Postmaster Tools are to help “qualified high-volume senders analyze their email, including data on delivery errors, spam reports, and reputation.” The updated postmaster pages also include Gmail’s best practices for bulk senders.
Postmaster Tools by Gmail http://gmail.com/postmaster
Update: ReturnPath has a blog post that includes data and definitions for each of the data points.
Set expectations for new subscribers
- josh
- Jul 10, 2015
A common way to build your email address list is to provide a free resource such as an eBook or PDF in return for contact information from the reader. While this is a good way to be mutually beneficial to the reader and the company, often the reader is providing their information only for the free resource and does not want to receive the emails. This leads to sending to an unengaged recipient or worst, sending to a bad email address.
Another way to build your email address list is to pre-check the “subscribe to the mailing list” when a user creates an account on your site. The same problem with the free resource offer, the user may not want the emails.
You can combat both of these types of unengaged users by providing them with an example of what they will be receiving from you via email. Displaying the most recent mailing or providing them with how often you send out monthly will not only help you collect accurate information but also helps set the expectations of what the recipient will be receiving. Examples of sending expectations would be to inform the recipient that you only send once a month but then allow them to select an onboarding program that may send daily for 10 days. Providing the end user with information about your mailings encourages them to provide accurate information and helps build your mailing list with recipients who want to engage with your emails. If you offer a free resource such as a whitepaper or ebook behind a signup form, send the download link within the email so that it encourages readers to provide accurate information. By sending the email with a link the recipient clicks, it shows ISPs that this mail is wanted and helps boost your sending reputation.
Providing the end user with information about your mailings encourages them to provide accurate information and helps build your mailing list with recipients who want to engage with your emails. If you offer a free resource such as a whitepaper or ebook behind a signup form, send the download link within the email so that it encourages readers to provide accurate information. By sending the email with a link the recipient clicks, it shows ISPs that this mail is wanted and helps boost your sending reputation.
When to include a physical address
- josh
- Jun 26, 2015
One of the requirements to be CAN-SPAM compliant is to include a physical address within every promotional email that is sent. If your company hires a third party to send email on your behalf, your physical address should be clearly visible within the message when the message is selling your products and services. There is a stipulation that if your message is transactional or a relationship message, then it does not need to adhere to the CAN-SPAM requirements by including your physical address or unsubscribe link.
Examples of transactional mail would be welcome emails, password resets, auto-responders, shipment notifications, or account alerts. While you and I may know that these emails aren’t required to include this information most users would not know. The CAN-SPAM Act has been in effect going on 12 years and recipients look for unsubscribe links and physical addresses within the messages. Emails that are missing this bit of information leads the recipient to believing the message is spam. While including the physical address and unsubscribe link are not required for your transactional emails, it’s better to be safe than sorry and include them anyways.
The CAN-SPAM Act has been in effect going on 12 years and recipients look for unsubscribe links and physical addresses within the messages. Emails that are missing this bit of information leads the recipient to believing the message is spam. While including the physical address and unsubscribe link are not required for your transactional emails, it’s better to be safe than sorry and include them anyways.
The recipient may have recently received a series of marketing emails from you and when they receive a transactional mail message, they may want to adjust the frequency of the mail they are receiving. By not including an unsubscribe link and physical address, the user may resort to marking the message as spam.
When sending marketing and transactional emails, you want to adhere to the law and then take the user behavior and expectations into consideration. There is no harm in including your physical address in both your marketing emails and transactional emails.
Whois privacy protection
- laura
- Jun 25, 2015
I’ve talked about using privacy protection on domains in the past (here, here, here, here, and here). Short version (if you don’t want to check all the old links) is that privacy protection for commercial domains is bad, that’s what spammers do and legitimate email marketers should not hide domains behind privacy protection services. I still believe all of these things.
What I’ve never really addressed is that I think privacy protection services are appropriate in some cases and are a reasonable protective measure for individuals. Over on Spamresource, Al wrote up a great post today about whois privacy protection.
Sometimes people do need anonymity and privacy online. Trusting a registrar’s privacy protection service is probably not your best bet for that. Like Al, we’ve stood in as a “privacy service” for friends and colleagues. It was our name on the domain registrations, and we could contact the appropriate people as needed. They trusted us to forward only the important stuff and we trusted them not to do bad things. This trust doesn’t scale.
Privacy protection services are used by a lot of bad actors to hide their involvement. Companies and commercial entities are tarring their own reputations using privacy protection services.
No real pull quote here, all of Al’s points are too good. So go read the whole thing.
Testing your opt-out process
- josh
- Jun 19, 2015
When was the last time you tested your opt-out process? Did you just click the unsubscribe link to see if the page loaded? How did you confirm the email address was unsubscribed?
If you have a Gmail account, Gmail allows you to use unlimited aliases. For example, if your Gmail email address is josh@gmail.com, you can add the + symbol to your email address to create an alias. An example of an alias would be josh+test1@gmail.com. Sending an email to josh+test1@gmail.com gets delivered to the mailbox for josh@gmail.com.
On your next mailing add a Gmail alias email address like josh+unsubtest06192015@gmail.com to be included with the mailing. After sending the mailing, find the email sent to the alias address and go through the unsubscribe process. After unsubscribing, log into your ESP or mailing software to confirm that the alias email address was successfully unsubscribed. Testing the unsubscribe process ensures that the landing page for the unsubscribe is working and that your ESP is registering the unsubscribe request.
A few reminders about your unsubscribe page:
On Father's Day
- steve
- Jun 18, 2015

I’m on quite a few mailing lists for companies whose main product is sending gifts: food hampers, jewelry, flowers, overpriced desk toys and so on. They tend to ramp up their volume before appropriate holidays such as Christmas, Mother’s Day, Thanksgiving, Valentine’s Day or Father’s Day and target their promotions to those particular holidays.
One recipient may have a toxic relationship with their Mother and not want to be reminded of Mother’s Day, another may have recently lost their Father and not want to revisit that distress every time they open their mail client in June, yet another may be recently divorced and really not want to see diamonds and roses in their inbox right now.
You should try and avoid sending mail that will distress your recipients. You should do that because you’re a compassionate human and you want to treat your recipients as humans. But if you need an ROI argument to justify the effort needed to do so… those recipients will associate your brand with that distress and then they’ll buy less or they’ll unsubscribe and you’ll lose their business entirely – even if they are interested in and responsive to your offers for the rest of the year.
How do you identify those recipients? Maybe just ask them. Or add an “Unsubscribe from Father’s Day promotions” link next to the “Unsubscribe” link – it’s not hard to do. Help your customers segment your list for you.
Image Blocking
- josh
- Jun 12, 2015
I received this email earlier this week, an email that I wanted but this is how it arrived.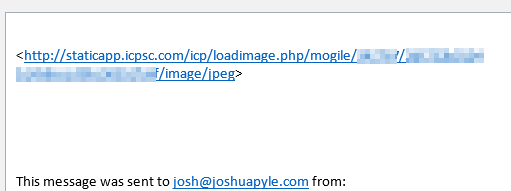
The email contained a single image link, a text line of who the message was sent to, the senders name, address, and finally an unsubscribe link.
Good news, the email is CAN-SPAM compliant! Bad news, I have no idea what the content of the message is and it looks somewhat spammy. The email was sent to my Junk Folder and all images were blocked. As a good netcitizen, we’re trained not to click links if we’re not sure what they are.
Here is another message I received around that same time and also had the images blocked. I immediately recognize the domain name, bowling.com and there is text that mentions bowling shoes, balls, and bags. Being an avid bowler, I wanted this message and I will be adding them to my safe senders list in Outlook.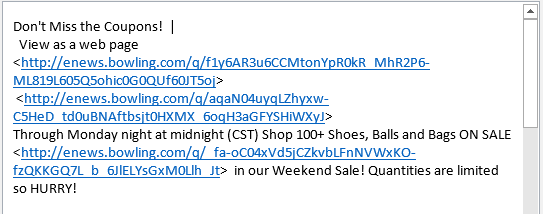
The good news for marketers who rely on image based emails is Gmail and many mobile mail clients will auto-load images but there are still many clients that will only display images if the user sets the sender as a trusted sender. If you are sending a Welcome Message, it’s best to include text along with your images so the recipient can recognize your email and will then add you as a trusted sender. You can also segment your list by users who are opening the images. The recipients who have not loaded the images would get a different version of the message that includes more text.
PTR Records
- josh
- Jun 5, 2015
PTR records are easy to over look and they have a significant impact on your ability to deliver mail without them. Some ISP and mailbox providers will reject mail from IP addresses that do not have a PTR record created. PTR records are a type of DNS record that resolves an IP address to a fully qualified domain name or FQDN. The PTR records are also called Reverse DNS records. If you are sending mail on a shared IP address, you’ll want to check to make sure the PTR record is setup, however you most likely will not be able to change it. If you are on a dedicated IP address or using a hosting provider like Rackspace or Amazon AWS, you’ll want to create or change the PTR records to reflect your domain name.
We usually think about DNS records resolving a domain name such as www.wordtothewise.com to an IP address. A query for www.wordtothewise.com is sent to a DNS server and the server checks for a matching record and returns the IP address of 184.105.179.167. The A record for www is stored within the zone file for wordtothewise.com. PTR records are not stored within your domain zonefile, they are stored in a zonefile usually managed by your service provider or network provider.
Some service providers provide an interface where you can create the PTR record yourself, others require you to submit a support request to create or change the PTR record.
If you know what IP address you are sending mail from, use our web based DNS tool to check if you have a PTR record created.
http://tools.wordtothewise.com/dns
Checking for a PTR record for 184.105.179.167 returns167.128-25.179.105.184.in-addr.arpa 3600 PTR webprod.wordtothewise.com.
If you received Response: NXDOMAIN (There is no record of any type for x.x.x.x.in-addr.arpa), this means you’re missing the PTR record and need to create one ASAP if you are sending mail from that IP address!
Yahoo Mail Deliverability FAQ Updated
- josh
- May 22, 2015
Yahoo has updated their FAQ and listed out a number of factors they use to determine if a mail message is spam.
Read MoreWhat about Tom?
- laura
- May 21, 2015
I use tom@hotmail.com as my default bogus email address. Tom has subscribed to so many things because of me.
Read More
Alternate contact when mail bounces
- laura
- May 20, 2015
We received an invite from a local company recently. At the top of the invite there was a sticker. We attempted to send email, but your address bounced. Please contact either me or the tasting room to update. Thanks!
We attempted to send email, but your address bounced. Please contact either me or the tasting room to update. Thanks!
Purchased Lists and ESPs
- laura
- May 14, 2015
After some thought, I’ve decided to remove a few ESPs from this list based on personal experience with them allowing customers to send to purchased lists. If your company has disappeared and you want to come back, you’ll need to actually stop the spam coming from your network. Every company that’s been removed has received a complaint from me specifically mentioning the address was purchased and allowed that same customer to continue spamming the same address. Deal with your spam and we can talk about reinstatement.
Read MoreWhat is the Mail From field?
- josh
- May 8, 2015
When emails are sent, there are two from fields, the Mail From and the Display From address. The Display From address (technically referred to as RFC.5322 from address) is the from address that is displayed to the end user within their email client. The Mail From (technically referred to as RFC.5321 from address) is the email address to which bounce messages are delivered. The Mail From field is sometimes referred to as the Return Path address, Envelope From address, or Bounce address.
It may seem confusing to have an email with two from fields, but knowing the difference is important to properly setup your SPF records.
Taking a look at this email I received from GoPro, the Return-Path (5321.From) goes back to @bounce.email.gopro.com. If I were to reply to the email, the message would go to @email.gopro.com. The Display From (5322.From) address is gopro@email.gopro.com.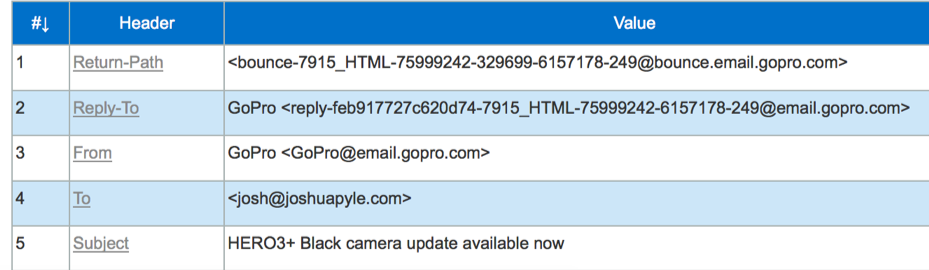
I would want to add the email address GoPro@email.gopro.com to my address book because that is the email address that is displayed in my email client. The reason why the Return-Path is different from the From address is because GoPro likely has an automated system that will process the bounce back messages (sent to @bounce.email.gopro.com) and automatically flag or unsubscribe those email addresses. This allows GoPro to setup automatic processing of the different mail streams sent to them, one stream being the bounce backs after a mailing and the second being an automated customer service system.
Where does SPF fit in?
SPF checks the Mail From (5321.From) address, not the Display From (5322.From) address. In the example above, there should be an SPF record for the subdomain of bounce.email.gopro.com. I can check the SPF record using our Authentication tools http://tools.wordtothewise.com/spf/check/bounce.email.gopro.com and I receive the following results: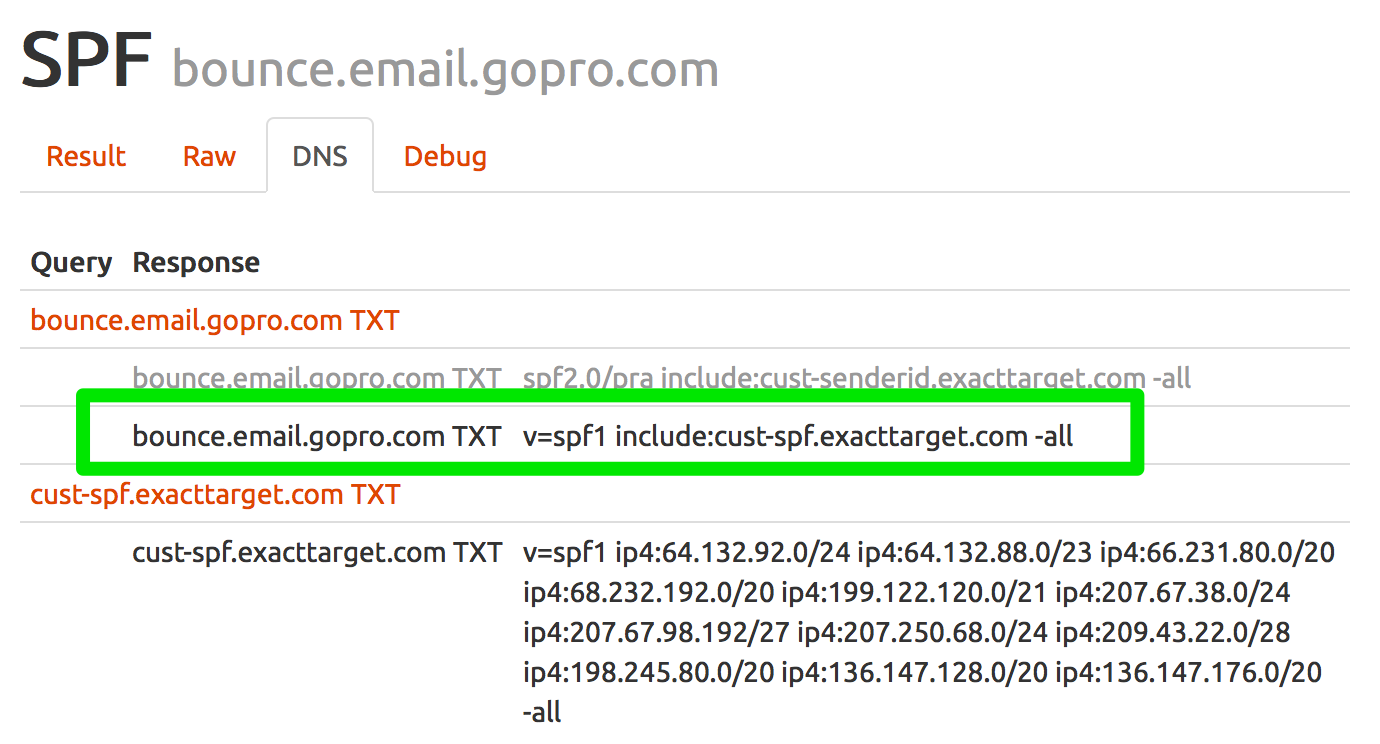
Checking the headers shows that GoPro does have a SPF record setup and the message was authenticated with SPF.![]()
For SPF records, make sure the SPF record matches the Mail From (From.5321)/Return-Path domain name. Have your recipients add the Display From (From.5322) email address to their address book so they will continue to receive your mailings.
4 things spammers do legitimate marketers don't
- laura
- May 7, 2015
I’ve never met a spammer that claims to be a spammer. Most that I’ve met claim to be legitimate marketers (or high volume email deployers). But there are things spammers do that I never expect to see a legitimate marketer doing.
I’ve written about these things throughout the blog (tag: TWSD), but it’s probably time to actually pull them together into a single post.
Four things to check before your next mailing
- laura
- May 5, 2015
Like many bits of technology, email is often set-and-forget. Everything is checked and rechecked during setup, and then no one goes back and looks at it again. But mail programs are not static, and people make changes. These changes don’t really break things, but over time they can create their own set of problems.
Setting aside some time every quarter or even every year to check and make sure all the bits of mail are configured correctly is a good idea.
Don't like opt-outs? Target your program better.
- laura
- Apr 9, 2015
I get a LOT of spam here. Most of it is marked and trivial to get rid of. Some of it is what I would call semi-legitimate. It’s a real product, but I never asked to receive any information from this company and am not actually part of their demographic. For one time things I just hit delete and move on. Life is too short to complain or opt out of every spam I get. (Tried that, got more mail)
But sometimes if the same sender keeps bothering me, I will send back an email asking them to cease contact. I recently had an occasion where someone sent an initial email trying to sell me bulk SMS, online video and other services. I ignored it because we’re not in the market for any of these services. A week later I get a followup asking why I hadn’t provided feedback to them and if there was a better person to talk to at the company. I looked for a way to opt-out of this message stream, but there wasn’t one. I send a reply telling them we were not interested in speaking to them and to please cease all communication. (“You didn’t receive feedback because I have no interest in talking to you. Please cease all future contact.” Admittedly that was terse, but it was polite.)
My request to cease communication was not well received, nor was it honored. Mind you, they first contacted me trying to sell me services that are totally off what we offer. When I asked them not to contact me, they turned it around that we’d lost business.
Best practices … what are they?
- laura
- Apr 9, 2015
“We follow all the best practices!” is a common refrain from many senders. But what does best practices really mean?
To me the bulk of best practices are related to permission, technical setup and identity.
Old Lists and RadioShack
- josh
- Apr 3, 2015
RadioShack is putting their assets up for sale including more than 65 million customer records and 13 million email addresses. Many are up in arms about the sale of personal data including the Texas Attorney General and AT&T who both want the data destroyed.
Part of the controversy is that RadioShack’s privacy policy states the collected data will be only used by RadioShack and its affiliates and that they will not “sell or rent your personally identifiable information to anyone at any time”. Company acquisitions happen all the time and data like this is often sold to the new owner and the sale of customer data is common. The problem with RadioShack selling the customer data is that their privacy policy states they will never sell the information.
RadioShack was one of the first companies to ask for personal information at checkout, sometimes refusing a sale without providing it and the collection of data during checkout caught on quickly. Having demographic information for retargeting of customers is extremely valuable to marketers, but only if it’s valid data. With RadioShack, people often lie about their zip code and if they are giving incorrect zip codes I’m pretty sure their email address isn’t going to be valid either. Even Kramer asks why does RadioShack ask for your phone number…
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WgfaYKoQxzQ
If a client asked if this was a good investment and if the list had value, I would tell them no. Sending to this list will have poor delivery because the data is dirty and the lack of a clear opt-in is going to be problematic especially since a RadioShack customer is not expecting to receive mail from you. Many ESPs have policies prohibiting sending to a purchased list and doing so will hurt your relationship with the ESP.
If a client had already purchased the list and wanted to send to it, I would tell them their reputation is going to take a significant hit and I would discourage them from sending. The list is going to be full of domains that no longer exist and contain abandoned email addresses including ones that have been turned into spam traps.
When preparing to send to a new list of email addresses, I go through this process:
What to do when an important email bounces
- laura
- Apr 2, 2015
Some emails are more important than others. I know, I know, all emails are important, but really, some are more important than others.
I’ve recently been decluttering by the simple expedient of enrolling in paperless statements for some of our accounts. We have a 1TB NAS, I’m not going to run out of storage space and I will have so much less paper to deal with. Plus, electronic searches are easier than digging through a file I’ve just shoved statements in for the whole year.
Some companies just let you sign up for statements online and don’t take any extra steps to verify your email address or tell you what happens if your email breaks. But at least one company has gone the extra mile to establish how they handle email bounces.
First, to sign up for paperless notifications I have to give my consent to receive docs. Even better, when I look at the important information it expressly details what happens if my email address bounces.
Bad SPF can hurt your reputation
- laura
- Mar 31, 2015
Can a bad SPF record ruin your delivery, even though all your mail still passes SPF?
Yes, it can.
One of our clients had issues with poor delivery rates to the inbox at gmail and came to us with the theory that it was due to other people using their domain to send spam to gmail. This theory was based on ReturnPath instrumentation showing mail “from” their domain coming from other IP addresses, and a plausible looking correlation between that mail being sent and their problems at gmail.
Checking their bounce handler, we see a lot of bounces coming in suggesting that someone is sending poor quality mail using their bounce domain from quite a few IP addresses, including a suspicious number scattered in small blocks across 69.64.0.0/8.
Their question they had was whether they should publish DMARC records to fix the problem, and whether they should use a DMARC policy of p=reject or p=none. They’re a good candidate for DMARC – their domains are used purely for bulk or transactional mail, they have a tightly controlled mail infrastructure for their marketing domains, and they’re already publishing SPF records and signing all the mail they send with DKIM.
I was half way through writing up my normal answer about DMARC deployment for customers with this sort of mail infrastructure – “It won’t help with delivery problems directly, but publishing with p=none and analyzing the reports you get back will give you insight into your mail flows, and provide the data you need to decide whether using DMARC p=reject is appropriate for your business model and mail flows.” – when I realized that something just didn’t make sense.
Gmail, perhaps more than most other mailbox providers, base their delivery decisions on data they gather mechanically from all their mailboxes. And they really understand domain-based reputation and the difference between authenticated and non-authenticated email. Why on earth would non-authenticated email from an unrelated IP address be damaging the domain reputation, and hence the delivery of authenticated legitimate email? That makes no sense.
Meanwhile, over in our slack channel, Josh was double-checking their infrastructure…
Oops. They have a small block of 8 IP addresses from which they send most of their email. When setting up their SPF records they inadvertently used ip4:69.20.20.48/8 instead of ip4:69.20.20.48/29 for that block of addresses. A /8 isn’t eight IP addresses – it’s every one of the 16,777,216 IP addresses that begins with “69.”.
Suddenly everything makes sense.
The SPF thinko means that all mail claiming to be from the client domain that’s sent from any IP address beginning with “69.” passes SPF – including the deluge of spam coming from the snowshoe spammers in 69.64.*.
Gmail (and other ISPs) don’t see a difference between the legitimate email and the SPF authenticated spam – they’re just seeing a high volume of authenticated email from the client domain, a large fraction of which is spam. That’s damaged the reputation of the client domain, causing their legitimate email to end up in the spam folder.
(The reality of filtering is more than just domain reputation, of course, but a terrible domain reputation is definitely going to cause you problems.)
The immediate action to take is simple – fix the SPF record so only legitimate mail will be authenticated. That’ll take effect within a couple of hours, as the old SPF record has a short TTL, and ISPs will start seeing the correct SPF record and begin rejigging their reputation.
We’ll keep monitoring delivery rates, check how long ISPs take to notice reputation changes, potentially reach out to some ISPs to see if it’s appropriate for them to do a one-time reputation reset for the affected domains, but we’re hoping things will begin to improve in the next few days.
What can you do to avoid or mitigate this sort of problem?
Updated M3AAWG Best Practices for Senders
- josh
- Mar 11, 2015
M3AAWG has published a new version of the Senders Best Common Practices document and the contains a lot of new information since the original publication in 2008. The new document covers how to vet ESP customers, considerations when selecting a dedicated or share IP to send mail, and includes best practices on a number of technical processes.
The Senders Best Common Practices document is targeted at deliverability teams and email marketers. Any company that is sending marketing emails, using an Email Service Provider, or provides an email enabled platform, it’s always good to go back and periodically review your system to ensure nothing was missed and to stay up-to-date on all new recommendations.
A few of the recommendations include the use of the List-Unsubscribe header, publishing a clear WHOIS for domains used for sending mail, and how to process non-delivery report messages.
The List-Unsubscribe header provides an additional way for users to opt-out of email messages. Gmail and Outlook.com both use the presence of the list-unsubscribe header to provide a one-click button to allow the user to unsubscribe from the mailing list. Often enough, if a user cannot find an opt-out link, they’re marking the message as spam. Allowing a recipient to unsubscribe easily is critical to maintaining good delivery reputation.
A WHOIS is query to determine who is the registered user or assignee of a domain name. During a session at the most recent M3AAWG meeting, it was announced that spammers throw away 19 million domains per year. When a postmaster or abuse desk receive a complaint, they’ll often query to see who owns the domain the email was sent from or who owns the domains used in the hyperlinks. If the WHOIS record is out of date or set to private, this limits the ability for the postmaster or abuse desk to reach out to the owner of the domain.
Processing non-deliver reports is critical to maintaining a high delivery reputation. Many ESPs have an acceptable-use-policy that includes a bounce rate. Mailjet recommends a bounce rate of less than 8% and Mandrill recommends less than 5%. If a system is not in place to remove the hard bounces from your mailing list, the sender’s reputation will quickly deteriorate.
The Senders Best Common Practices document can be downloaded at M3AAWG.org.
'Tis the season
- steve
- Feb 13, 2015

It’s the time of the year, when we celebrate a holiday by telling you about email.
Content marketing
- laura
- Jan 15, 2015
 There are a lot of mailing lists I’m on simply because I can’t be bothered to unsubscribe. Every week or every few days mail shows up in my inbox. I may look at the subject line, I may even open the message. But most of it is not interesting. It’s yet another sale at Sur La Table. It’s another promo from Macheist. Virgin America wants me to book a flight. All of these messages are useful and all, particularly if I’m trying to book a flight or looking to replace the dish I broke last week. But many of these companies send content that’s so close to the same, it’s not worth a whole lot of my attention.
There are a lot of mailing lists I’m on simply because I can’t be bothered to unsubscribe. Every week or every few days mail shows up in my inbox. I may look at the subject line, I may even open the message. But most of it is not interesting. It’s yet another sale at Sur La Table. It’s another promo from Macheist. Virgin America wants me to book a flight. All of these messages are useful and all, particularly if I’m trying to book a flight or looking to replace the dish I broke last week. But many of these companies send content that’s so close to the same, it’s not worth a whole lot of my attention.
I don’t think I’m that unusual in this respect. People are used to getting offers and so they know they can sit back and wait until they’re ready to shop and they’re ready to buy.
This is why content marketing can be such a win. It’s different, it’s new. It’s worth my time to dig into the email and read it. We recently bought some sheets from a company and they added me to their mailing list. Every week now, I get an email with lovely pictures of relaxing bedrooms and articles on how best to sleep and wash my sheets and replace my pillow cases.
From a consumer perspective, it makes me want to have a showroom bedroom with lots of comfy linens. From a marketing perspective I appreciate the hard work and dedication that goes into generating both the lovely pictures and the useful content. But I wonder if the effort put into the content generation provides a decent return on investment.
Dodging filters makes for effective spamming
- laura
- Jan 7, 2015
Spam is still 80 – 90% of global email volume, depending on which study look at. Most of that spam doesn’t make it to the inbox; ISPs reject a lot of it during the SMTP transaction and put much of rest of it in the bulk folder. But as the volumes of spam have grown, ISPs and filters are relying more and more on automation. Gone are the days when a team of people could manually review spam and tune filters. There’s just too much of it out there for it to be cost effective to manually review filters.
In some ways, though, automatic filters are easier to avoid than manual filters. Take a spam that I received at multiple addresses today. It’s an advertisement for lists to “meet my marketing needs.” I started out looking at this mail to walk readers through all of the reasons I distrusted this mail. But some testing, the same sorts of testing I do for client mails, told me that this mail was making it to the inbox at major ISPs.
What told me this mail was spam? Let’s look at the evidence.
M3AAWG Recommends TLS
- josh
- Dec 24, 2014
SSL or Secure Sockets Layer is protocol designed to provide a secure way of transmitting information between computer systems. Originally created by Netscape and released publicly as SSLv2 in 1995 and updated to SSLv3 in 1996. TLS or Transport Layer Security was created in 1999 as a replacement for SSLv3. TLS and SSL are most commonly used to create a secure (encrypted) connection between your web browser and websites so that you can transmit sensitive information like login credentials, passwords, and credit card numbers.
M3AAWG published a initial recommendation that urges the disabling of all versions of SSL. It has been a rough year for encryption security, first with Heartbleed vulnerability with the OpenSSL library, and again with POODLE which stands for “Padding Oracle on Downgraded Legacy Encryption” that was discovered by Google security researchers in October of 2014. On December 8, 2014 it was reported that TLS implementations are also vulnerable to POODLE attack, however unlike SSLv3, TLS can be patched where as SSL 3.0 has a fundamental issue with the protocol.
Brief DBL false positive
- steve
- Dec 17, 2014
A code glitch in a new DBL sub-zone known as 'Abused-Legit' caused the new Abused-Legit zone to list ".net." for 60 minutes from 08:35 UTC.
Read More
Spam is about invading other people's space
- laura
- Dec 9, 2014
At the recent Sendgrid Emailmatter’s conference Sally Lehman advised attendees to “Treat someone’s inbox like it was their home.” This is advice I’ve been giving clients for a long time. I think it’s even more relevant now as so many people have data enabled phones and are checking email so frequently. It’s not just their home, it’s their personal space they can take with them.
Seanan McGuire, a friend and NY Times bestselling author, wrote a blog post today about how she views promotion and marketing as an artist and someone who is expected to promote her work. She also talks about what it feels like to be a target of promotion and offers some advice about how to promote your products online. She talks about how she, as an author and creative type, is expected to do some level of self promotion and how that promotion is done in her space – whether that space be on twitter or her blog.
The long tail of domains
- laura
- Nov 4, 2014
I frequently get clients telling me that they have about 15 (20, 30) major domains on their list, and then a long tail of domains with only a couple of recipients. If you sort simply by the left hand side of the @, that’s true.
When you’re sending email, it’s not just the domain in the email address that is important. Of equal importance is the MX. The MX is what actually handles the mail and where many filters are applied. Sorting by MX, instead of simply recipient domain, can identify that most of your small business clients are hosted at a particular provider. The number of subscribers behind that filter may be enough to push that filter into your top 10 or even top 5 recipient domains.
There’s a much smaller tail when grouping recipients by MX domain. It makes it much easier to understand where blocks are happening. I have even seen cases where clients didn’t realize they were blocked at a commercial provider because they only saw the “onesie twosie” domains as undeliverable. They missed a real problem with blocking because they were looking at the wrong data.
I sometimes get the side eye from some ISP folks if I use the term receiver (because, well, they’re senders as much as they are receivers). But I use receiver to help distinguish between the recipient domain and the actual domain handling the email.
When was the last time you looked at your delivery by filter or MX rather than by recipient domain? What did you find?
Unsubscribing is hard
- laura
- Aug 20, 2014
A comment came through on my post about unsubscribing that helpfully told me that the problem was I didn’t unsubscribe correctly.
As you know, there are usually two unsubscribe options in many of the bulk senders emails. Are you unsubscribing from the global or the offer unsub? Unless you are unsubscribing from both, you will still be on the lists.
To address the underlying question, I did unsubscribe from both links for those very few mails in my mailbox that had double unsubscribe links. I know that some spammers use multiple unsubscribe links in their emails. We routinely recommend clients not use 3rd party mailers with double unsubscribes because it’s a clear sign the 3rd party mailer is a spammer.
Given the presence of double unsubscribes I generally assume the point is to confuse recipients. By having multiple unsubscribe links the spammers can ignore unsubscribe requests with the excuse that “you unsubscribed from the wrong link.” Plausible deniability at its finest. The best part for the spammer is that it doesn’t matter which unsubscribe link the recipient picks, it will always be the Wrong One.
I’ve been dealing with spam since the late 90s, and have been professionally consulting on delivery for over 14 years. If I can’t figure out what link to use to unsubscribe, how is anyone supposed to figure out how to make mail stop?
In some cases, the unsubscribe links admitted that the address I was trying to unsubscribe was already removed from the list. They helpfully refused to let me unsubscribe again through their form. But they offered a second way to unsubscribe.
The address I was unsubscribing was the same one I was unsubscribing. Some of the emails even helpfully told me “this email was sent to trapaddress@” which is the address in the above screenshot.
I’m sure my friend will come back and comment with “why didn’t you unsubscribe by forwarding the email?” Because I was spending enough time unsubscribing as it was, and I didn’t want to have to try and navigate yet another unsubscribe process. I knew they weren’t going to stop mailing me, no matter what hoops I jumped through.
I’m not saying that all unsubscribe processes are broken, there are millions and millions of emails sent every day with simple and effective unsubscribe links. What I am saying is that there is a lot of mail getting to inboxes that users never requested nor wanted. “Just unsubscribing” from this mail Does Not Work. It just keeps coming and coming and coming.
But of course, the mail still coming is my fault, as I was unable to correctly unsubscribe. 
Unsubscribing from spam, part 3
- laura
- Aug 9, 2014
At the end of last year, I talked a little bit about a project I was working on to see if unsubscribing from spam would actually work. The address I picked was my first non-work/school related email address. It’s been mine since 2004 or so. I stopped using it for anything commerce related back in the late 90s. But it is on a lot of address lists (as it was used to post to Usenet), and a lot of affiliate mailers have it and it gets spam, despite being behind commercial spam filters.
During the month of November, I unsubscribed from every commercial email that came into the account. In total I unsubscribed from 312 messages. We’re now 8 full months after that, and my spam load on that account is only increasing, it was almost triple that amount in April (908 messages).
Unsubscribing from spam does not work. Here’s what 6 months of spam looks like after unsubscribing from every message received in an inbox on an address that is not currently given to anyone (and hasn’t been for more than 10 years). This is also after it’s gone through my ISP spam filters, which do seem to do a decent job of weeding out the botnet spam and phishing.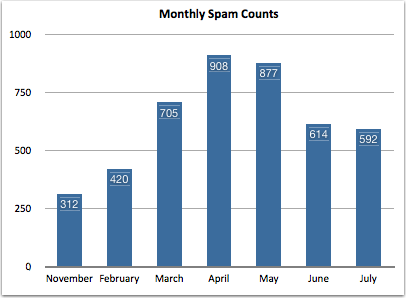
This isn’t, of course, any sort of controlled study and I’ve left a lot of details out of this blog post about the address and about how I handled the project. I do want to write it up and publish it, but it’s a back burner project right now.
One relevant note is about 5 or 6 years ago one of my clients wanted me to look at their affiliates and I was able to pull mail out of this box to show them their affiliates were spamming. They put me on the phone with the affiliate. I explained this was an address I hadn’t used since the late 90’s, before their company existed. They insisted I had given it to them or some company they bought. Even after I used the phrase “spam trap” they still insisted I’d opted in and they didn’t have to stop mailing me.
Another note is that while a lot of these are semi-scammy products, a number of them are legitimate businesses and have broad advertising campaigns in multiple mediums, including television.
For all those people that say “just unsubscribe” it doesn’t always work, at least not for addresses that were on the “millions CD” and the “flamers list” from the “Millions CD.”
Why don't users want that mail?
- laura
- Jul 22, 2014
Things are extremely busy here and blogging is going to be light for a few weeks. I’ll be reposting some older blog posts that are still relevant for today’s email senders.
Today’s post is a repost from July 2009. I discuss why recipients complain about mail and how senders can lower the complaint rates. While this addresses complaint rates directly, the same series of questions can be used to investigate almost any change in performance.
Typo traps
- laura
- Jul 16, 2014
People make all sorts of claims about typo traps. One claim that showed up recently was that Spamhaus has just started using typo traps. I asked my Facebook network when people started using typos to detect incoming spam.
Two different colleagues mentioned using typos, both on the left hand side and the right hand side, back in ’98 and ’99.
The point is, typo traps are absolutely nothing new. They are, in fact, as old as spam filtering itself. And as one of trap maintainers remind me, not all of them even look like typos. It’s not as simple as hotmial.com or gmial.com.
I really think that focusing on traps is paying attention to the wrong thing.
The traps are not the issue. The underlying issue is that people are signing up addresses that don’t belong to them. Sometimes those are addresses that are spamtraps. Sometimes those are simply addresses that belong to someone else. Those addresses don’t belong to customers, they belong to random people who may never have heard of the sender. Sending mail to those people is sending spam.
Just trying to remove traps from your address lists isn’t going to solve the underlying problem. Instead, focus on improving your data process to keep from sending mail to random strangers.
Have fun storming the CASL!
- steve
- Jul 3, 2014
I’ve given Humble Bundle my (tagged) email address a bunch of times – as part of purchases, as my username on their website, to download games and books I’ve bought.
And, naturally, they’ve sent me newsletters announcing when they have new sales. Did I check a checkbox or uncheck a checkbox? I don’t remember, and don’t really care. It’s a company I have a real relationship with and have purchased from, they’re sending content I want to see, and I trust them not to misuse my address and to honour an unsubscription request.
So … probably opt-in, and I’m fairly sure they’ve confirmed that it’s my email address. But did they explicitly tell me they’d use my email address for a newsletter? I and my email archive don’t remember that far back, and it’s quite possible that Humble Bundle’s current staff and records don’t either.
In todays newsletter, right above their talking about their summer sales, they had this:
They’re confirming that I want to keep getting newsletters, and stressing why I want to keep getting them. Their database probably dates back to the iron age, or at least 2010, and my clicking on the big, friendly green button both lets them know that I’m an engaged subscriber and lets them record in their database that “Yes! This subscriber has explicitly said they want our newsletters!”.
Gradually adding that information to their subscriber database will let them better make decisions in the future about what content to send, how often, whether to try and reengage with a subset of their subscribers.
Oh, and there’s CASL, of course.
If you or your recipients have a Canadian presence you have a little less than eighteen months to make sure you have documented, explicit consent from any recipients for whom you only have implicit (e.g. business relationship) consent or for whom you’ve lost the original records.
Transactional advertising
- laura
- Jun 17, 2014
 One of the things our bank does that I really like is send ATM receipts directly to the email address associated with the ATM card. No more random pieces of paper I have to track down, it’s all there in my mailbox. This week I noticed that the bank is leveraging the transactional mail to tell me about new services they provide.
One of the things our bank does that I really like is send ATM receipts directly to the email address associated with the ATM card. No more random pieces of paper I have to track down, it’s all there in my mailbox. This week I noticed that the bank is leveraging the transactional mail to tell me about new services they provide.
I think this is awesome. I get my receipt and I get to learn about bank services I didn’t know about previously.
I don’t remember if the bank made me confirm my address when I signed up for online banking, it was a long time ago. But if they did, then they have a dedicated, confirmed advertising channel right to my mailbox. Good for them, convenient for me.
A win-win.
Affiliate mailers struggling
- laura
- Jun 12, 2014
What are affiliate mailers?
Affiliate mailers collect email addresses and then rent access to those addresses out to 3rd parties. There are a wide range of vendors that fall into the affiliate category. Some vendors compile lists through co-registration, others compile lists themselves through website opt-ins and some affiliate vendors fulfill mailing requests by hiring affiliates. There are, of course, some senders in the affiliate space that don’t even pretend to send opt-in mail, they just buy, compile or harvest addresses and blast mail to those addresses.
Read MoreA good example of a privacy change notification
- laura
- Jun 6, 2014

A friendly reader sent me this example of the notice Coldwater Creek sent out to subscribers this week.
Coldwater Creek was a major retailer that recently filed for bankruptcy. As part of that, they’re transferring assets, including customer lists, to a holding company for potential use when the company is re-launched. That holding company is also the parent company of Talbots, another clothing retailer.
The thing I really like about this notice is that it’s clear what the company is doing with customer information. Not only that, the customer gets to control their information and with whom it gets shared.
Spot the unsub
- laura
- May 27, 2014
A new game! Spot the unsub! Our first challenge is the footer from a major software company. How long does it take for you to to find the unsub link?
What’s even more annoying is that I never actually subscribed to mail from this company. A few years ago I was doing some work for them and they required I set up an account on their cloud service so they could share docs with me. Last month, they started emailing me as “a customer.” Yeah. No.
Spam is not a valid marketing strategy
- laura
- May 13, 2014
This seems like an attempt to create the next big viral marketing campaign. It’s just spam, though, and not even good spam. There’s nothing about a random “click here” that will entice me to click on it.
Scammers? Spammers? Whoever Ryann Rasmussen at HighSpeedInternet is, she might want to rethink her marketing strategy. It looks more like an infection attempt than anything else.
I guess we can say that their mail made an impression, a very negative impression. There is no website at http://highspeedinternet.com. The whois record for highspeedinternet.com is behind domains by proxy. The mail violates CAN SPAM. The address was scraped off our website.
Not all spammers are dodgy Russians. Some spammers are from Utah.
Why do we "warmup" IP addresses
- laura
- Apr 24, 2014
IP address warmup is a big issue for anyone moving to a new IP address for sending.
I’m constantly being asked how to warm up an IP. My answer is always the same. There’s no right way to warm up an IP nor is there a specific formula that everyone should follow.
What warming up is about is introducing mail traffic to receiving spam filters in a way that lets the filter know this is a legitimate email stream. This means sending small but regular amounts of mail that recipients interact with. As the filters adjust to the amount of mail from that IP, more mail can be sent over that IP. Increase the mail volume over the next few weeks until the desired volume is reached.
There are a couple things to remember about warming up.
A good example of 3rd party email
- laura
- Apr 16, 2014
This morning I received a great example of a 3rd party email that I thought I’d share with all of you.
What’s so great about it?
Ignoring opt-outs
- laura
- Apr 15, 2014
One of the marketing solutions to the spam problem is just to have recipients opt out.
Read MorePeople are your weakest link
- laura
- Mar 27, 2014
Social engineering is a long standing way to compromise security. Chunkhost reports today that they discovered accounts being compromised through social engineering of Sendgrid support. While the compromise did not work it was a close call. The only thing that saved the targeted customers was their implementation of 2 factor authentication.
We know many of our customers individually and personally, and are still careful about changing contact addresses and passwords. With larger customer bases, it’s vital that every person in the change follow security processes.
Get an email address, by any means possible
- laura
- Feb 28, 2014
Neil has a post up about the “opt-in” form that we were all confronted with when logging into the hotel wifi at M3AAWG last week. They aren’t the only hotel asking for email addresses, I’ve seen other folks comment about how they were required to provide an email address AND opt-in to receive email offers before they were allowed onto the hotel network. Mind you, they’re paying the outrageous fees for hotel internet and still being told they must provide an email address.
The addresses given by people who wouldn’t opt-in willingly aren’t going to be worth anything. These are not people who want your mail, they’re only giving you an address because they’re being forced to do so.
I know it is so tempting for marketers to use any methods to get an email address from customers. I recently was dealing with a very poorly delivering list that looked purchased. There were clear typos, invalid domains, non-existent domains, the whole nine yards. Over 20% of the mail was bouncing and what did get delivered wasn’t going to the inbox. I was working through the problem with the ESP before they went to talk to the customer. To my eye, the list looked purchased. Most times lists just don’t look that bad when they are actually opt-in lists. The ESP insisted that the addresses were being collected at their brick and mortar stores at point of sale. I asked if the company was incentivizing address collection, but the ESP didn’t know.
Eventually, we discovered that the retailer in question had set performance indicators such that associates were expected to collect email addresses from 90% of their customers. No wonder the lists looked purchased. I have no doubt that the pressure to give an email address caused some customers to just make up random addresses on the fly. I also wouldn’t be surprised if some associates, after failing to meet the 90% goal, would just enter random addresses in “on behalf of” the customer.
Email is a great way to stay in touch with customers. It is an extremely cost effective and profitable way to market. The caveat is that customers have to want that mail. Coercing a customer to give you an address doesn’t make your marketing better. It just makes your delivery harder. That lowers your overall revenue and decreases profits.
Quantity is not the be all and end all of marketing. This company? They have a great email marketing program, but their address collection is so bad hardly anyone gets to see the mail in the inbox, even the people who would be happy to receive the mail.
For email delivery quality trumps quantity every time.
Target acquires email addresses, exposing more customers to data breaches
- laura
- Jan 16, 2014
As most folks now know hackers broke into Target systems last December and stole financial and other data from 110 million customers. Target has been responding to this breach reasonably well. They’ve been notifying customers that were affected and they’re providing credit monitoring for affected individuals. They seem to be totally on top of protecting their customer’s data and privacy.
Mostly.
They seem to be purchasing or otherwise acquiring email addresses from at least one major retailer in order to send out notifications about the breach to customers that never gave them email addresses. Yes, even those of us who chose not to give Target email addresses are receiving email from them.
I understand Target’s drive to contact affected users. I even appreciate that. What I don’t appreciate is that Target appears to be compromising my security in order to notify me my security was compromised. The data of mine that was compromised at Target would be credit card and possibly address information. My email address was not part of the compromise. So what does Target do? They go and acquire my email address from a third party.
Their solution to the compromise is collecting more data that is vulnerable to compromise from unrelated third parties? I’m not sure this is the most consumer friendly thing Target could do. In my case, Target sent mail to an address I’ve only given to Amazon. That means I now need to worry about my Amazon account security, on top of everything else.
Ironically, the email sent by Target tells me that I can click a link and get free credit monitoring. Then the email goes on to tell me the following:
- Never share information with anyone over the phone, email or text, even if they claim to be someone you know or do business with. Instead, ask for a call-back number.
- Delete texts immediately from numbers or names you don’t recognize.
- Be wary of emails that ask for money or send you to suspicious websites. Don’t click links within emails you don’t recognize.
Don’t click links within emails I don’t recognize? You mean like the one you just sent me? With a link to a credit monitoring website?
I appreciate the notice. I don’t appreciate is that Target went out of their way to collect more information about me than I actually gave them. I am now worried about Amazon’s security as well. How did Target get an address only provided to Amazon? I don’t appreciate that my efforts to keep my information secure (not providing email address to Target) was undermined by Target themselves.
The full text of the email, with the relevant headers (munged slightly for privacy) is under the cut, if anyone is interested.
Images, again
- steve
- Jan 8, 2014
It’s a new year, but an old problem. Email with unloaded images.
Sure, you should be including critical content as text, and/or including alt-text as a normal part of your creative design process, but at the bare minimum you should look at what your mail looks like without images.
The last thing you want to do is send out email with just one strong call to action – the unsubscribe link.
Holiday mailing advice from mailbox providers
- laura
- Nov 20, 2013
Christine Borgia has a post on the Return Path blog where she interviews a number of different groups (spamfilters, DNSBLs, mailbox providers) about their filtering strategy for the holidays. Overall, no one changes their filtering during the Holiday Mailing Season. On the other hand, many marketers do change their marketing strategies in ways that trigger more filtering and blocking.
The take home message? Pay attention to what is being sent and who it is being sent to. This is nothing new, but many marketers seem to forget it in the effort to get into their customers’ inboxes.
Don't unsubscribe from spam!!
- laura
- Nov 19, 2013
Having been around the email and anti-spam industry for a while, I’ve just about seen and heard it all. In fact, sometimes I’ve been around for the beginning of the myth.
One myth that seems to never actually go away is “unsubscribing just confirms you’re a real address and your address will get sold and your spam load will explode.” This is related but orthogonal to “spammers harvest addresses out of unsubscribe forms.” The reality is that both of these things used to be true. Unsubscribing would confirm your email address and increase your spam load. Spammers would harvest addresses out of unsubscribe forms.
But neither of these things have really been true for the last decade.
I have had clients over the years that are spammers. Some of the are names that you probably would recognize. Some of them are companies we could probably all agree are spammers. Some of them are buying addresses from companies that are spammers. Some of them are companies that have a good mailing program here and then hire snowshoers over there. Sometimes they come to me claiming to be real mailers “with minor delivery problems.” Sometimes they come to me saying that a blocklist has recommended they talk to me about repairing their processes. Sometimes they even actually want to fix things. Sometimes they’re just looking to say that I’ve given them a clean bill of health (which is not something I do).
What that means is that I have lots of addresses on lots of spammer lists. Not just the ones they’ve found, but ones I’ve used to test their systems. I use tagged or disposable addresses for everything. Some of my disposable accounts are only marginally connected to me as I want to see what senders really do for their subscribers rather than what they want me to think they do. The ones I add to their system I use to test their subscription process as well as their unsubscription process.
I have never encountered a situation where unsubscribing one of those addresses caused a “multiplication” (to quote one anti-spammer) of my spam load.
I’ve had cases where my clients have ignored unsubscribes. I’ve had cases where my clients have decided years later to add me to their list again. I’ve had cases where they’ve been bought out and my address has been reactivated by the new owners. I’ve had cases where months or even years of 5xx responses was ignored. I’ve seen just about every bad bit of behavior on behalf of spammers. But I’ve never actually had unsubscribing increase my spam load.
It doesn’t matter how often people demonstrate unsubscribing doesn’t result in more spam in the current email ecosystem. (Ken Magill 2013, NYTimes 2011, dayah.com 2009). It doesn’t matter that many mailers treat “this is spam” button hits the same way they handle unsubscribe requests. The myth still persists.
Yahoo now auctioning domain names
- laura
- Nov 13, 2013
This summer Yahoo shook up the email ecosystem by publicly announcing they were recycling usernames. The shakeup wasn’t so much that they were recycling usernames, but that they did it in a way that compromised user information and account security. Any user that had an account tied to a recycled Yahoo account is at risk for having their PII leaked. Folks are still dealing with the fallout, both Yahoo and the companies who are trying to meet customer needs by sending emails and protect customer emails by not sending emails.
On top of that, Yahoo announced they’re selling off a number of domains that they’ve accumulated over the years. Some of these are pretty high value domains like webserver.com, sandwich.com and other real words.
I don’t think Yahoo used any of these domains for email, and even if they did any addresses should have bounced off years ago. Still, it does bring up some broader policy issues.
Many, many things online, from bank accounts to social media accounts to blog commenting systems treat email addresses as a unique identifier for that account. Many of these databases were developed with the underlying assumption that people wouldn’t change their email addresses and that it was a static value. This wasn’t a true assumption 10 years ago and it’s certainly not true now. This mistaken assumption is a problem, and one that more and more companies are going to have to address moving forward. This isn’t about email and it isn’t about delivery, it’s about simple data accuracy and hygiene.
Companies must start thinking and addressing email address impermanence. These issues are not going away.
Tor cleans up their lists
- laura
- Nov 5, 2013
Recently I got an email from Tor. Apparently they’re watching their opens and clicks and they noticed I hadn’t loaded any images recently.
Read MoreWhat not to do when buying lists
- laura
- Oct 28, 2013
Saturday morning I check my mail and notice multiple emails from the DMA. Yes, I got three copies of an email from the US Direct Marketing Association with the subject line Kick It Up A Notch With The DMA Career Center. It seems the DMA are buying addresses from various companies. Because I use tagged email addresses, this means their naive de-duping doesn’t realize that laura-x and laura-y are the same email address. Of course, they’ve also managed to send to an untagged email address, too. I have no idea where they got that particular address; I’m sure I’ve never handed that address over to the DMA for any reason.
Saturday afternoon, I check one of the professional filtering / anti-spam mailing list. Some subscribers are asking for copies of spam from 97.107.23.191 to .194. They’d seen a lot of mail to non-existent email addresses from that range and were looking to see what was going on and who was sending such bad mail. Multiple people on the list popped up with examples of the DMA mail.
Sunday morning, I checked the discussions wherein I discovered the DMA was added to the SBL (SBL 202218, SBL 202217, SBL 202216). It seems not only did they hit over a hundred Spamhaus spamtraps, they spammed Steve Linford himself.
… until it stops moving
- steve
- Oct 25, 2013
Nothing is impossible to kill. It’s just that sometimes after you kill something you have to keep shooting it until it stops moving.Mira Grant, Feed
Read More
Is it real or is it spam?
- laura
- Oct 15, 2013
The wanted but unexpected email is one of the major challenges facing ISPs and filter developers. If there was never any need or desire for people to receive email from someone they don’t know, then mail clients could be locked down to only accept mail from addresses on a whitelist. It wouldn’t completely solve the spam problem, for a number of reasons, but it would lessen the problem, particularly for average email users.
But, we don’t live in a world where we know beforehand who will be sending us mail, so we can’t just whitelist correspondents and reject everything else. I think this is a good thing. Email can be used to meet new people, develop new relationships and introduce new opportunities.
While the “cold call” email isn’t much talked about I think it’s worth some discussion. What makes a good cold email? What makes a bad one? We can use two recent emails I received as examples.
Example 1:
On Discovery and Email
- steve
- Oct 9, 2013
If you’re involved in any sort of civil legal action in the US Courts – whether that be claims of patent violation, defamation, sexual harassment or anything else – there’s a point in the pre-trial process where the opposing lawyers can request information from you, and also from any third-parties they believe may have useful information. This phase is called Discovery.
US civil discovery has very few limits: you can demand, backed by the power of the court, any material or information that might be reasonably believed to lead to admissible evidence in the case. That’s much, much broader than just relevance, and it allows fairly prolonged fishing expeditions not just for admissible evidence, but also for background information that will allow the opposing legal team to better understand both the case and the people and companies involved in it. Often the discovery phase leads to both sides agreeing on how strong a case it is, and deciding to settle or drop it rather than taking it to trial.
One aspect of discovery is interrogatories and depositions – asking someone a list of questions, and having them reply in writing or in person. While most people will be honest in their replies in that situation, they’re under no obligation to be helpful or cooperative beyond answering, minimally, the questions they are posed. (In a spam case I was involved in as an expert many years ago one of the lawyers was explaining what the oppositions lawyers might ask and told me “If they ask ‘What do you recall was said about <X>?’ you can tell them that I said he was an asshole.”). The information from these can be vital, but it’s a lot of effort to acquire, and unless you already know enough to ask the right questions you might not discover anything useful.
Asking someone to provide documents is another aspect. That might be a literal paper document, or I’d guess more commonly nowadays, electronic data. “Provide copies of any email your employees sent or received that mentioned <plaintiff’s company>.”, “From what IP addresses at what times did this user log in to your system?” …
As someone who does data analysis I love electronic documents. It’s relatively easy to mechanically grovel through thousands of pages of data and crunch it into summaries that you can use to make decisions, or to focus on a useful subset. Give me someones mailbox and I can do the easy stuff, like find any mention of a company, or any link to a companies website. But I can also find the messages they sent while they weren’t in the office. I can do semantic analysis and find the emails that use angry language. I can find all the attachments that were used, open them up and analyze the contents. I can sometimes find where in the world they were when the email was sent – down to which hotel bar, or which office in a building. I can crunch the routing data of their mailbox (and other peoples) and see who they communicated with – and make recommendations as to whether it would be worthwhile to subpoena those people. I can build relationship graphs. And all this applies not just to their work mailbox, but also their private gmail addresses, if it’s a reasonable assumption that any communication there might lead to any relevant evidence – and, well, it’s always a reasonable assumption. (And that’s just email – I can often pull similarly useful data out of web logs and forum posts and so on too).
The discovery process can be long, and can consume a lot of resources (time, legal fees) and work focus from the people targeted by it. Making analysis easier (and hence cheaper) makes it reasonably possible to expand and extend the discovery process to find additional data. Whether that’s good for you or not depends on the details of the case and whether you are the one doing the discovery.
None of this is intended to be legal advice, nor even a description of the process by someone with any legal training – it’s just some aspects I’ve noticed from my limited experience of the process as an expert working with some very good lawyers.
Finally, another piece of advice a lawyer I was working with gave me some years ago was “Always assume that anything you write anywhere may be made available to opposing counsel. And when it comes to legally sensitive matters, use email just for sending copies of documents that will be provided to opposing counsel and for scheduling ‘phone calls where you’ll discuss other details. Nothing else.”.
Losing friends and influencing people
- laura
- Oct 2, 2013
I download a lot of ESP white papers. Not because I’m looking for an ESP, but because I think it’s important to know what’s happening in the industry and what topics people think are important. I understand fully that white papers are a lead generation tool and I can expect followup from sales people at the places I download papers from. This is all well and good.
Generally the emails I get are polite, introduce the company to me, and ask if I have any questions or would like to talk. I tend to respond that I’m not looking for an ESP, and that I appreciate their contact. If I’ve blogged about said white paper, I will mention that and give a link to the post. I don’t want to waste a sales person’s time when said person can be working with potential customers.
Overall, these interactions have been pleasant and cordial. That makes the unpleasant few stand out even more.
There’s one memorable case where the first email from the sales rep had the subject line, “Meeting Time Tomorrow at 10am.” Wait. What? As I was checking email from bed before getting up, that subject line had me dashing out of bed to figure out what I had forgotten and work out how badly my schedule was messed up. Thankfully, my schedule wasn’t messed up, this was just an aggressive sales person optimistically claiming we had a meeting set. The email assured me that said sales person would continue to follow up with me until “we were able to connect.”
There is a place for aggressive selling techniques. This is the kind of sales drive that will work in certain situations. But I’m not sure it’s the appropriate opening when nothing is known about the target. In this case it certainly wasn’t a good opening. A number of companies ask me for ESP recommendations, and I tend to recommend those I know. I don’t think I’ll be recommending the above ESP to any customer. Their sales process was just that off putting.
Not quite the result Mr. Over Eager Sales Person expected.
Insights on how to improve email marketing
- laura
- Aug 23, 2013
I can’t do anything except say +1 to this list of ineffective habits of email marketers from Loren McDonald.
Read More"Blocked for Bot-like Behavior"
- laura
- Aug 20, 2013
An ESP asked about this error message from Hotmail and what to do about it.
“Bot-like” behaviour usually means the sending server is doing something that bots also do. It’s not always that they’re spamming, often it’s a technical issue. But the technical problems make the sending server look like a bot, so the ISP is not taking any chances and they’re going to stop accepting mail from that server.
If you’re an ESP what should you look for when tracking down what the problem is?
First make sure your server isn’t infected with anything and that you’re not running an open relay or proxy. Second, make sure your customers aren’t compromised or have had their accounts hijacked.
Then start looking at your configuration.
HELO/EHLO values
TWSD: Don't honor opt-outs
- laura
- Aug 13, 2013
One of the big arguments various mailers make is that they make it easy for users to opt-out of mail, so it’s not a big deal. Users who don’t want to receive the mail, can make it stop. This was one of the guiding principles of CAN SPAM. The sender can make the decision to send mail to any recipient but they have to offer an opt-out.
The problem is there are a lot of major companies out there that don’t honor opt-outs. Since earlier this year I’ve been tracking when I opt-out of mail. Why? Because I kept getting the feeling that I’d opted out of mail before, but kept getting it.
The good(?) news is that it wasn’t my imagination, some of these companies aren’t honoring their opt-outs. The bad news is that major companies are not honoring opt-outs.
Delivery implications of Yahoo releasing usernames
- laura
- Jul 24, 2013
Yahoo announced a few weeks ago it would be releasing account names back into the general pool. This, understandably, caused a lot of concern among marketers about how this would affect email delivery at Yahoo. I had the opportunity to talk with a Yahoo employee last week, and ask some questions about how this might affect delivery.
Q: How many email addresses are affected?
The death of IP based reputation
- laura
- Jul 12, 2013
Back in the dark ages of email delivery the only thing that really mattered to get your email into the inbox was having a good IP reputation. If your IP sent good mail most of the time, then that mail got into the inbox and all was well with the world. All that mattered was that good IP reputation. Even better for the people who wanted to game the system and get their spam into the inbox, there were many ways to get around IP reputation.
Every time the ISPs and spam filtering companies would work out a way to block spam using IP addresses, spammers would figure out a way around the problem. ISPs started blocking IPs so spammers moved to open relays. Filters started blocking open relays, so spammers moved to open proxies. Filters started blocking mail open proxies so spammers created botnets. Filters started blocking botnets, so spammers started stealing IP reputation by compromising ESP and ISP user accounts. Filters were constantly playing catchup with the next new method of getting a good IP reputation, while still sending spam.
While spammers were adapting and subverting IP based filtering a number of other things were happening. Many smart people in the email space were looking at improving authentication technology. SPF was the beginning, but problems with SPF led to Domains Keys and DKIM. Now we’re even seeing protocols (DMARC) layered on top of DKIM. Additionally, the price of data storage and processing got cheaper and data mining software got better.
The improvement in processing power, data mining and data storage made it actually feasible for ISPs and filtering companies to analyze content at standard email delivery speeds. Since all IPv4 addresses are now allocated, most companies are planning for mail services to migrate to IPv6. There are too many IPv6 IPss to rely on IP reputation for delivery decisions.
What this means is that in the modern email filtering system, IPs are only a portion of the information filters look at when making delivery decisions. Now, filters look at the overall content of the email, including images and URLs. Many filters are even following URLs to confirm the landing pages aren’t hosting malicious software, or isn’t content that’s been blocked before. Some filters are looking at DNS entries like nameservers and seeing if those nameservers are associated with bad mail. That’s even before we get to the user feedback, in the form of “this is spam” or “this is not spam” clicks, which now seem to affect both content, domain and IP reputation.
I don’t expect IP reputation to become a complete non-issue. I think it’s still valuable data for ISPs and filters to evaluate as part of the delivery decision process. That being said, IP reputation is so much less a guiding factor in good email delivery than it was 3 or 4 years ago. Just having an IP with a great reputation is not sufficient for inbox delivery. You have to have a good IP reputation and good content and good URLs.
Anyone who wants good email delivery should consider their IP reputation, but only as one piece of the delivery strategy. Focusing on a great IP reputation will not guarantee good inbox delivery. Look at the whole program, not just a small part of it.
Know what you're promising, and keep your promises
- steve
- Jul 10, 2013
Although we can’t always provide a personal response to your complaint, we do investigate all reports. Please don’t interpret a lack of response as a lack of action taken. If we find that a customer is violating our policies, we will take make sure they stop the violating activity.
Read More
Bad unsubscribe processes
- laura
- Jun 24, 2013
We recently renewed our support contract with VMWare. It’s a weirdly complicated system, in that we can’t buy directly from VMWare, but have to buy through one of their resellers. In this case, we purchased the original hardware from Dell, so we renewed our contract through Dell.
Dell sends my email address over to VMWare as part of the transaction.
My only role in this is as CFO. I approve the purchase and pay the bill. I don’t do anything technical with the license.
The email failures start when VMWare decides that I need to receive mail about some user group meetings they’re holding all over the US. First off, I’m not the right person to be sending this mail to inside our company. I’m the billing contact, not the user contact. Then, they send me mail about meetings all over the US, when they know exactly where I’m located. Would it be so hard to do a semi-personalized version that highlighted the meetings in my local area then pointing out the other locations? Apparently, yes, it is so hard.
The biggest failures, though are in the unsubscribe process.
The unsubscribe page is no big deal. I get to unsub from all VMWare communications, and submit that request without having to figure out what my VMWare password is or anything.
After I hit submit, I’m taken to this page.
Wait? What?
“Thank you for registering?” I didn’t register! I don’t want you to contact me. Plus, this is a HP co-branded page when I’m not a customer of HP. VMWare knows this, they know they got my address from Dell.
The biggest problem is that I’m not sure that my address was actually unsubscribed. I suspect that someone copied a form from elsewhere on the site to use as an unsubscribe form. This person forgot to change the link after the “submit” button was clicked. But what else did they forget to change? Is the unsubscribe actually registered in the database?
I suppose only time will tell if VMWare actually processed my unsubscribe. If they didn’t they’re technically in violation of CAN SPAM.
The lesson, though, is someone should check unsubscribe forms. Someone in marketing should own the unsubscribe process, and that includes confirming that unsubscribe pages work well enough.
Feedback from recipients
- laura
- Jun 21, 2013
Please Don’t Add Me to Your Email List
Email marketing wisdom from Forbes and someone who spends a lot of time networking and handing out business cards.
Handling SNDS requests
- laura
- Jun 6, 2013
I’ve been working with a new client on getting them signed up for FBLs, whitelists and other sorts of monitoring. One of the places I recommended to them was signing up for the Hotmail Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) program. It’s been a while since I’ve gone through the process, so I decided to sign up our network space to give up to date instructions from to clients.
As part of the process, Microsoft confirms the request with the network owner. This is smart, it prevents the wrong people from getting access to delivery data. They use public records (ARIN and IP Whois data) to figure out the “network owner” and send an email to that person. In my case, the mail was sent to a role account at Hurricane Electric (he.net).
I asked for access, filling in “this is Laura from Word to the Wise and I am looking for access to our space.” The email address in the request was my @hotmail.com address. A few minutes later I checked my inbox to find an email from he.net.
TWSD: avoid filters
- laura
- May 31, 2013
I was cleaning out one of my spamtraps. This is the one that gets a ton of “legitimate” spam. In the last 12 hours it’s gotten spam advertising: T.G.I.Fridays, KFC, Applebees, LendingTree, Lasix Vision Institute, Khols, Burger King, Match.com, and Vistaprint.
The footer of some of the mails are making me laugh, though. It’s clear they’re trying to comply with CAN SPAM, but are having problems with content filtering. Here’s a brief selection of the footers:
Ondemand Research, 1O5 E.[34th]-Street Ste 144, New Y0rk, NY 1OO16
Ondemand Research, 105 E. 34th Street St #144, New York, NY 10016
0ndemand=Research, 1O5/E/./34th Street Ste 144,New Y0rk,NY=1OO16
Poor OnDemand Research, they just can’t catch a break.
EDIT: Just got a spam for Ruby Tuesday’s using a .pw domain.
Do you have an abuse@ address?
- laura
- Apr 19, 2013
I’ve mentioned multiple times before that I really don’t like using personal contacts until and unless the published or official channels fail. I don’t hold this opinion just about resolving delivery issues, but also use official channels when reporting spam to one of my addresses or spam traps.
My usual complaints contain a plain text copy of the mail, including full headers and a short summary of the email address it was sent to. “This is an address that was part of a leak from…” or “This is an address scraped off my website. It’s been removed from the website since 2004” or “This address isn’t used to sign up for any mail.”
Sadly, there are a number of “legitimate” ESPs that don’t have or don’t monitor their abuse address. In some cases it’s an oversight or a break down of internal mail handling. But in most cases, it’s a sign that the ESP doesn’t actually handle abuse.
It’s frustrating to watch an ESP post long blog posts about “best practices” and “effective delivery” and “not spamming” and yet not be able to actually stop their own customers from spamming. It’s not even that I necessarily want them to disconnect their spamming customers (although that would be nice) but suppressing the address that I’ve told them was a spamtrap seems trivial. And yet, a month after my first complaint and weeks after escalating to a personal contact, I’m still getting spam.
The 5 things every ESP should do to handle spam complaints.
Increase in bounces at Y!
- laura
- Apr 5, 2013
I’ve been seeing reports over the last few days about an increase in bounces at Yahoo. Reliable people are telling me they’re seeing some increase in “invalid user” bounces.
You may remember Yahoo announced an overhaul of their mail product back in December. Reliable sources tell me that this is more than just interface revamp. In the back end, Yahoo! is removing older products with few users and security problems. This fits in with the changes CEO Mayer has been making with the company: slim down and stop supporting unprofitable products.
It makes sense that while engineers are looking at the guts of the email program and cleaning up the cruft, they will also disable long unused email addresses. This will result in higher unknown users for some senders.
What’s interesting to me is that the reports are somewhat sporadic. Some senders are seeing a huge percentage of bounces, some are seeing the normal percentage. I expect this difference isn’t anything more than how actively a sender purges based on engagement. Senders that purge unengaged addresses are going to have already removed a lot of the addresses Yahoo! is now purging from their database. Senders that keep sending to their whole list, are going to see a lot of unknown user bounces.
I’ve asked a few folks and people who’ve responded told me that spot checks showed all the addresses turning up as invalid had no engagement for long periods of time.
If you are seeing a lot of bounces at Yahoo! over the last few days, you need to remove those addresses from your lists. I also recommend looking at the engagement statistics of these newly purged recipients. This will tell you, approximately, what an abandoned address profile looks like. You can use that information to make good decisions about purging unengaged users at other ISPs as well. Not only does this lower costs, because you’ll be sending to less non-responsive email addresses, it will also improve delivery at many ISPs.
Questioning standards
- laura
- Mar 25, 2013
M3AAWG publishes documents summarizing and discussing current practices for stopping and preventing abuse. Some of these documents are focused on ISPs while others are focused on marketers. While M3AAWG is not directly nor officially a standards body, most of the documents have been written by members and reflect the best current practices for that document.
Members have been asked to leave the organization and some companies are denied membership because they are not in line with the organizational values. Some of these companies are ESPs or marketers, but some of these companies have been ISPs as well.
The standards written by M3AAWG are challenging for a lot of marketers to follow. These standards are written with the input of senders, but they all comply with the M3AAWG mission of stopping messaging abuse. Many ISPs believe that unsolicited email is abuse, thus M3AAWG standards say that all mail needs to be sent to recipients who request that mail. Purchasing lists, selling lists, and appending email addresses are all unacceptable activities for M3AAWG members.
I never really had much concern about the effectiveness of the M3AAWG process. Most of the big industry players are there and many of the ISPs have an aggressive anti-abuse attitude.
But last week I saw a blog post on a fairly major industry blog that listed a bunch of (made up, tasteless and sexist) things “overheard” at the recent M3AAWG conference (it’s been removed and I wouldn’t link to it anyway). The blog post made it look like no real work gets done at M3AAWG and that the attendees don’t work at the conference. I won’t claim that it’s a staid and quiet conference, but most attendees work very hard during the day.
The next day, the author tweeted:
Mail that looks good on desktop and mobile
- steve
- Mar 19, 2013
Over the weekend I noticed a new CSS framework aimed at email rather than web development, “Antwort“.
This isn’t the first or only framework for email content, but this one looks simple and robust, and it allows for content that doesn’t just adapt for different sized displays but looks good on all of them. The idea behind it is to divide your content into columns, magazine style, then display the columns side-by-side on desktop clients and top to bottom on mobile clients. That opens up much more interesting designs than the more common single fluid column approach.
It looks nice, it supports pretty much every interesting email client, but it also comes with some directions based on real world experience.
Social invading everything
- laura
- Mar 9, 2013
I discovered, inadvertently, that there is a business networking site modeled after dating site. If you’re selling something you go on the site and register as a seller. If you’re buying something you go on the site and register as a buyer. Buyers can post RFIs and sellers can respond.
Decent enough business model, they’ve even fleshed it out so the site itself acts as an invoicing and billing mechanism.
That’s how I discovered it, one of our very large international telco customers decided they wanted to use this site for billing. Many large telcos expect vendors to use their proprietary site, so I wasn’t that surprised when they asked. And, given they’re international being able to bill them electronically just means I don’t have to remember to use the international stamps.
At the behest of our customer, I signed up at the website. It’s like most social networking sites, create a profile, categorize yourself, make everything public. The thing is, I don’t want to use this site to find new customers. I am just using it because one of my current customers is expecting it. Don’t get me wrong, Abacus is a great product and our customers are extremely happy with it, but it’s pretty niche. It’s not something that’s going to be searched for on a generic website.
I thought that when I set my profile to private that would be some sort of signal to keep me out of the main directory of the site. This morning I realized that wasn’t true when I got a bunch of emails telling me about all these companies looking for “business software” (the closest category I could find).
Getting a bunch of irrelevant mail was annoying enough. Even worse, there was no unsub link in the email. Eventually, I discovered an entire page of email options that were not made clear to me up front. I also sent mail to support and suggested that they talk to their lawyers to clarify whether their opt-out option was consistent with CAN SPAM. I’m pretty sure it doesn’t, but I am not a lawyer.
To the company’s credit, they did have good support and my questions through support were answered in a timely fashion. One of their support reps even called me on the phone to clarify what it was that I wanted to happen and walk me through their email options. She was very upfront about yes, they opted everyone in to all the mail at the very beginning of the process. “We’re like match.com for businesses!”
I’m sure there are some businesses that will find this service to be great. But it’s not what I want or need. Despite the fact that their support was so helpful, I don’t have a great feeling about this company. It seems a bit dishonest that I thought I was signing up for a billing portal, but was actually joining “match.com for businesses. Why couldn’t they make that clear in the 7 emails in 2 days “inviting” me to sign up?
I know I’m a little more sensitive to bad mailing processes than most people, but this was quite an unpleasant experience from the multiple identical emails and reminders before I signed up to the irrelevant stuff I got afterwards.
Thoughts on bounce handling
- laura
- Feb 28, 2013
This week’s Wednesday question comes from D.
What are your thoughts on bounce handling
Read More
TWSD: Hiding the opt-out
- laura
- Feb 20, 2013
![]()
This is an actual opt-out link that came in a recent email. Sadly, this is a real company, listed on the NYSE sent by a major ESP.
Verifying addresses after POS collection
- laura
- Feb 19, 2013
Collecting email addresses at point of sale is a challenge. Some stores collect the addresses electronically, where the clerk or the customer types addresses directly into the register. Smaller stores, however, typically collect addresses on a sheet of paper at the cash register. Eventually someone takes the list and types it into whatever contact management system the store maintains.
There are all sorts of errors that can happen when someone types in an address, but those errors are only compounded when the addresses are written on a sheet of paper for later transcription. Not all of us have perfect, copperplate handwriting and many of us have barely legible scribbles. In one case I had a sender read the tag in my email address wrong causing all their mail to me to bounce.
One person found an interesting solution to the problem of illegible addresses: using Facebook’s lookup to clarify illegible addresses.
Mini Cooper and their email oops
- laura
- Jan 31, 2013
I haven’t been able to track down any information about what happened, but it seems MINI USA had a major oops in their email marketing recently. So much so that they’re sending out apologies by snail mail. Pictures of the apology package appeared on Reddit earlier this week, and include a chocolate rose, some duct tape and a SPAM can stress reliever.
It’s a great example of a win-back campaign that really focuses on the recipients rather than the sender.
8 things that make your mail look like spam
- laura
- Jan 30, 2013
In the comments of last week’s Wednesday question John B. asked
Read MoreFrequency and Relevance: Insight from Actual Recipients
- steve
- Jan 10, 2013
Last night, the email practices of Facebook, Verizon and LinkedIn sparked something of a discussion on IRC.
Rather than trying to summarize into a business language friendly post I thought I’d share the whole thing.
Warning: Includes strong language and graphic descriptions of human on salesman violence.
Increasing engagement for delivery?
- laura
- Jan 4, 2013
I’ve talked a lot about engagement here over the years and how increasing engagement can increase inbox delivery.
But does driving engagement always improve delivery?
Take LinkedIn as an example. LinkedIn has started to pop-up a link when users log in. This popup suggests that the user endorse a connection for a particular skill. When the user clicks on the popup, an email is sent to the connection. The endorsement encourages the recipient to visit the LinkedIn website and review endorsements. Once the user is on the site, they receive a popup asking for endorsement of a connection. Drives engagement both on the website and with email. Win for everyone, right?
I get lots of these endorsements, but I’ve had a few that have made me wonder what’s really going on. Are these people really endorsing my skills? If they are then why am I getting endorsements from people I’ve not seen in 15 years and why are some of the endorsed skills things I can’t do?
This morning I asked one of my connections if he really did endorse me for my abilities in Cloud Computing. His response was enlightening.
Meaningless metrics
- laura
- Dec 27, 2012
I’ve been having some conversations with fellow delivery folks about metrics and delivery and bad practices. Sometimes, a sender will have what appear to be good metrics, but really aren’t getting them through any good practices. They’re managing to avoid the clear indicators of bad practices (complaints, SBL listings, blocks, etc), but only because the metrics aren’t good.
This made me laugh when a friend posted a link to a Business Insider article about how many website metrics aren’t useful indicators of the business value of a website. Then I found the original blog post referenced in the article: Bullshit Metrics. It’s a great post, you should go read it.
I’d say the concluding paragraph has as much relevance to email marketing as to web marketing.
Confirmation Fails
- laura
- Dec 5, 2012
Yesterday I talked about registration confirmations. Today I’m going to talk about a couple recent experiences with websites and their registration failures.
The first experience was with Yelp. One of my readers decided I needed a Yelp account and created one using my laura-questions email address. Yelp understands that people will be jerks and so sent me an email to confirm the account.
DKIM and Gmail
- steve
- Nov 28, 2012
 After they were a a little embarrassed by their own DKIM keys being poorly managed a few months ago, Google seem to have been going through their inbound DKIM handling and tightening up on their validation so that badly signed mail that really shouldn’t be treated as DKIM signed, won’t be treated as signed by Gmail.
After they were a a little embarrassed by their own DKIM keys being poorly managed a few months ago, Google seem to have been going through their inbound DKIM handling and tightening up on their validation so that badly signed mail that really shouldn’t be treated as DKIM signed, won’t be treated as signed by Gmail.
This is a good thing, especially as things like DMARC start to be layered on top of DKIM, but it does mean that you really need to check your signing configuration and make sure you’re not doing anything silly.
Spammers are funny
- laura
- Nov 28, 2012
Dear Spammer,
If you are going to send me an email that claims it complies with the Federal CAN SPAM act of 2003, it would be helpful if the mail actually complies with CAN SPAM.
In this case, however, you are sending to an address you’ve harvested off my website. The mail you are sending does not contain a physical postal email address. You’re also forging headers. Both of those things are violations of CAN SPAM. Given you have also harvested the laura-questions@ email from this website, that is treble damages.
Oh, and while we’re at it, you might want to consider your current disclaimer.
Subject lines
- laura
- Oct 9, 2012
There has been a lot of discussion in various places recently about subject line length and how it affects email marketing. There have been multiple studies done on how the subject line affects opens and clicks. (Mailchimp, Alchemy Worx, Mailer Mailer, Adestra). The discussion has even spilled over into Ken Magill’s newsletter today.
I’ve had a couple people ask me my opinion on subject line over the years. My general response is that subject line length is not directly measured by spamfilters and so don’t fret about the length. It is true that consistently crafting poor subject lines can indirectly cause delivery problems. Send mail few people open and that will hurt your reputation over time.
I think Ken really said it best, though.
The naming of lists
- steve
- Sep 25, 2012
Any ESP that supports multiple mailing lists per customer lets you name your mailing lists. That’s useful for keeping track of where a list was from , but sometimes those list names are visible to the recipient:
Here the list name is visible on the opt-out / email preferences form, but you’ll also see them in (hidden) email headers or (visible) email footers.
“Last 10000” is pretty innocuous, but I’ve seen “Non responders”, “Vegas blast”, “Opt-outs 2010”, “Jigsaw 3”, “Purchased 2011-07-01″, Trade 2”, “Co-reg 4” as well as lists named after companies completely unrelated to the list owner.
You could check to see whether the list names are visible on every ESP and mail platform you use – or you could just assume they will be visible to end users eventually and be always careful in naming them.
Driving customers away
- steve
- Sep 20, 2012
I have a frequent flyer account with Virgin America. They want me to sign up for some new thing, and they’ve sent me two emails about it so far, with lots of good call-to-action language, and a big “Join Now” button.
But this is the start of the form that clicking on that button leads to:
(It goes on further, finally ending up with a captcha and a submit button.)
Virgin America already has all that information, and it’s all tied to the account they sent the email to. If they were to have pre-filled the form with that personal information I might have looked at it further. Quite apart from the annoyance of having to give information that they already know, I’ve no idea what my frequent flyer number is and I’d need to go and look it up before I could go any further. From a typical recipients point of view this makes it much less likely that I’d consider signing up for it. That barrier to entry drives people away.
From an email/privacy professionals point of view I know why they do it this way, though. This web form isn’t Virgin America’s form – it’s a third party that Virgin America is doing co-registration with (though neither party is as clear about that fact as they could be, of course). Virgin America are being paid by that third party for each new sign up they capture – but they don’t want to share their customers private information with the untrusted third party. Doing the information capture this way, by just using their mailing list to drive traffic to the third party’s website is very cheap to do, much cheaper (and so more profitable) than doing it “properly” by having Virgin America induct people into the third party program, and reducing the barrier to entry to just a simple disclosure and “Sign me up!” button.
But treating third-party co-registration signups as “free money for almost no investment” only works if you don’t consider the attention of your existing customers valuable. Of the past five emails I’ve received from Virgin America, only one has been talking about buying flights – the other four were, like this one, co-registration offers (credit card, car hire, vacation, online surveys), with varying degrees of Virgin branding. They don’t really bring much benefit to recipients, and they’re a bit intrusive.
I’m not sure how much Virgin America is paid for dropping this sort of co-reg and third-party advertising into their mail stream, but it can’t be that much (does anyone know?). Treating your existing customers as a resource of cheap, fungible eyeballs to be sold to random third parties, rather than as people you’re maintaining a relationship with, risks driving them away from your email program. Given the value of a loyal airline traveller that can’t be profitable in the longer term, and likely not the short term.
Check your unsubscribe process
- laura
- Sep 19, 2012
When was the last time you actually tried to unsubscribe from one of your mailing lists? Have you ever even checked to see that your process works?
For whatever reason, unsubscribe processes don’t always work. Sometimes the problem is on the client end. Sometimes the problem is on the ESP end. But in either case, continuing to mail recipients who have attempted to opt-out from your mail is a recipe for disaster.
I mentioned last week about our new mortgage company that can’t process my unsubscribe. Today I contacted their ESP and pointed out I’d tried to unsub a few times, but was still getting mail. The ESP thanked me, pointed out that was not an ESP managed unsubscribe page and did a little digging. A few hours later their delivery guy told me that he saw my multiple unsubscribe attempts (June, July, 2 in August…) and they were all marked as “trashed.” But he’s going to make sure I’m not mailed any more and follow up with his customer.
Now, there are a lot of reasons this unsub process could have failed. It could be that the website doesn’t handle my tagged addresses well and this is a bank, it’s very possible security is locked down. But that means they shouldn’t have accepted my tagged address in the first place.
There are a couple things to take away from this story.
Questions about CAN SPAM.
- laura
- Sep 11, 2012
In the US, the law governing the sending of commercial email is CAN SPAM. I’ve seen a number of questions about CAN SPAM recently.
One came from twitter, where someone was asking if just having an email address meant permission to send to it. Clearly, just being able to dig up an email address doesn’t imply permission to send marketing or commercial email to it. I can promise you April23@contact.wordtothewise.com did not sign up to receive information on increasing Facebook followers.
CAN SPAM doesn’t prohibit unsolicited email. All it says is that if you send unsolicited email you must do a few things.
Creative HTML Table Abuse
- steve
- Sep 1, 2012
There’s an old-school ’90s HTML design trick that dates back to the dim and distant past before we had decent layout control in CSS. That’s “slicing” – chopping a large image up into multiple parts, then reassembling them in an HTML table.
If you slice your images in an email and the end user hasn’t loaded images what will they see? They’ll see a rectangular box – either empty or with the image alt text in it. And, if you set the background colour for the table cell, they’ll see that – but only when images are turned off.
If you’re sneaky, you can do clever things with that.
Images off:
The same mail with images on:
Or like this, with images off:
And the same mail with images on:
(There’s more discussion in this reddit thread about it).
Emails that make you smile
- laura
- Aug 20, 2012
This summer’s non-work project for me has been training for a 5K run with Fleet Feet in Menlo Park. As part of the training programs we get weekly emails from the store on Monday. As I was reading through today’s email, I found myself smiling and happy. Lisa, who is one of the store owners and writes the emails, is just so happy and bouncy and thrilled to share her love of running and that comes through in the newsletter.
Our group’s primary coach is the other store owner. During runs we often talk about random stuff, and when I tell people I do email delivery, they always start talking about their experience with email and spam. One night I was running with Jim, and we were talking about Jim’s experiences with sending email. He mentioned their ESP and talked about how convenient it was. But then he mentioned he wasn’t sure that they were sending enough mail (which made me laugh hard enough I almost tripped on a curb).
I realized I am not just a delivery expert when I started thinking about all the ways they could increase the amount of email they send, while still maintaining the quality and the friendly feel of their bulk emails. What could they offer local runners that would increase the value of the store to them? The first very obvious thing was a race calendar. There are dozens of local races every week, telling folks about upcoming races and entry deadlines would be a way to contact folks regularly without it always being a “buy stuff from us!!”
What commercial emails have you gotten recently that have made you smile?
Mail.app outs lazy marketers
- steve
- Aug 17, 2012
The default mail client on OS X is Mail.app. In recent versions it does it’s best to bundle threads of email together to make it easier for you to keep track of conversations via email – they appear in the list of messages as a single entry with a badge showing the number of messages in that thread. There are standard ways to track mail threads, but they sometimes get broken by mailing list software, so Mail.app also bundles together messages with an identical sender and Subject line.
That has an unexpected side effect, when it comes to email marketing.
That little “4” badge on the right tells me that this is the fourth time Marriott have sent me this same email (over a period of several months) and there’s really no need for me to open it and read it again.
Asking smart questions
- steve
- Aug 10, 2012
Your mail is being blocked or deferred and you’d like to know why.
Before you ask someone “why?” you should have done these things:
Non marketers speak
- laura
- Aug 8, 2012
A couple quotes from different folks, who aren’t actually in marketing, but have insightful comments on marketing.
Read MoreCheck what now?
- laura
- Aug 3, 2012
A client sent me a shot of a page where they were attempting to change their preferences at a website. This is one of my long time clients, and someone who has been in email marketing for years. He tells me that he spent quite a long time staring at the screen trying to figure out what he was supposed to do to opt out.
Bounces, complaints and metrics
- laura
- Jul 31, 2012
In the email delivery space there are a lot of numbers we talk about including bounce rates, complaint rates, acceptance rates and inbox delivery rates. These are all good numbers to tell us about a particular campaign or mailing list. Usually these metrics all track together. Low bounce rates and low complaint rates correlate with high delivery rates and high inbox placement.
Letting people stop transactional mail
- laura
- Jul 24, 2012
The question of putting unsub links on transactional messages came up on multiple lists recently. As with any question that has to do with email and controlling it, there were a lot of different opinions.
A number of people believed that transactional mail should never, ever have an unsubscribe. Their argument was that transactional mail is too valuable to allow recipients to unsubscribe from it.
Other people argued that the recipient should always be able to stop mail and that an unsub link was important, even in transactional mail.
A third group pointed out that under CASL transactional mail to Canadian residents may have to have an unsub link, even if the sender doesn’t want to add one in.
As with most questions, I don’t think there is necessarily a single answer for every mailer or sender.
There are absolutely cases where transactional messages should have an unsubscribe. Twitter notifications and Facebook notifications are just some of the examples of mail a lot of people just want to stop.
But should companies allow recipients to unsubscribe from receipts? Some people feel very, very strongly that recipients should never be allowed to unsubscribe from receipts.
The problem with that stance is it ignores the fact that people don’t always correctly type their email addresses and end up giving the address of another person as part of a purchase. Al found a report at the Consumerist where someone is getting flooded with receipts for Nook books she’s never purchased.
This isn’t the first time this has happened, not by a long shot. In fact, in the past year I negotiated a Spamhaus delisting for a very large company that wasn’t confirming email addresses of their customers. This company sells a service that sends email alerts triggered when certain actions happen. Because they were not confirming their customer’s email addresses, they ended up sending alerts to spamtraps. The alerts triggered a SBL listing.
I don’t think that the Nook owner or the alert purchaser are actually malicious or that they purposely gave the wrong email address to their vendors. But it happens, and it happens not infrequently.
What do I recommend?
Transactional mail that is only ever a single event and where that address is not associated with an account don’t need to have an unsubscribe link. If it’s a one-time email, then it’s OK to not have an opt-out link. It’s OK to have an opt-out link, but not necessary.
Transactional mail that’s associated with some sort of account should have a process in place to make sure that mail is going to the right person and if it’s not, that the wrong person can make the mis-directed mail stop. There are multiple ways to do this. One is to confirm the email address associated with the account during the account creation process. Or you can allow anyone receiving the mail to click on a link and opt-out of receiving mail.
Whatever it is, it needs to be effective and protect everyone involved. Requiring the victim recipient to hand over a bunch of personal information, like Virgin Mobile does, helps no one. Continuing to send purchase receipts to an unrelated third party is poor business practice, particularly when you’ve been informed that this is the wrong person.
Leaving money on the table
- laura
- Jul 24, 2012
On August 1 two domains in the Netherlands are going away: wanadoo.nl and orange.nl. Current users of these domains are being transitioned to new addresses at online.nl. Mailchimp has more information and links.
This is a good time for all of us to consider how easy it is for a subscriber to change their address of record. Some senders just have the subscriber unsubscribe from one address and resubscribe for another. This sounds like the simplest way to do things, and it certainly doesn’t take much engineering effort.
But what information do you lose by simply asking subscribers to unsubscribe and resubscribe? It depends on what you’re tracking, but you do lose everything that you track. Preferences, interaction history, purchase history, it’s all gone. Providing a simple way to change an email address of record preserves the information related to that subscriber.
For some senders, keeping subscriber information through different ISPs and email addresses will pay for the development of a preference center. For others, there’s no real value there. How much money are companies leaving on the table by not providing a mechanism for recipients to change their email address?
How to make sure your mail is read
- laura
- Jul 10, 2012
ThinkGeek have a bit of a challenging audience to connect with. Many of their customers are, well, geeks. And many geeks have a reputation for being suspicious of marketing. I’d even go so far as to say that ThinkGeek has a bigger marketing challenge than other popular retailers.
One of the challenges all marketers face, though, is getting people to actually open and read an email carefully. ThinkGeek have addressed this challenge by turning reading email into a competitive game.
In June they sent out an email with a hidden coupon code in it. The first person to redeem the code received $100 off their order. What a creative way to get people to actually look through an email and make a purchase.
This, of course, is not a new marketing technique. I have at least 2 different Sigma t-shirts using the same style of marketing. This was in the dark ages and we didn’t have online forms, but the new catalog came with a postcard of questions to answer and return and the first 100 post cards got t-shirts. It was actually kinda nifty. As head tech, I got catalogs all the time. But answering the questions got me to look through the Sigma catalog and see their new products. Plus! T-shirt!
What new an interesting ways have you seen marketers use to engage recipients?
Targeting and Segmentation
- laura
- Jul 5, 2012
MarketingSherpa has a great case study of a retailer that got a 208% higher conversion (purchase) rate for a targeted email sent to a small segment (10%) of their list.
Read MoreWorking as intended
- laura
- Jun 28, 2012
There’s a certain type of sender that thinks every ISP block or email delivered to the bulk folder is a false positive. They’re so sure that the filters aren’t actually supposed to catch their mail that they’ll spend any amount of money and do every possible thing to get their mail to the inbox.
The problem for these senders, though, is that their mail is exactly the type of mail filters are designed to catch. They’re sending mail without recipient permission. I’m not talking about the lists that get a few typos or problem addresses on them. I’m talking about senders that buy and trade mailing lists. I’m talking about senders that don’t believe they have to have permission to send mail.
This mail getting filtered is a sign that the filters are working as intended. They’re keeping the unsolicited email out.
A lot of us take for granted that all commercial mail, at least that isn’t selling fake watches or herbal viagra, is always sent with permission. But there’s an awful lot of mail out there that doesn’t even have a minor fig leaf of permission. Filters stop that mail. And senders have very little recourse when they do.
Engagement in email
- laura
- Jun 25, 2012
From Tim Roe at eConsultancy.com: Is engagement email marketing finally here?
Tim lays out a number of factors for why engagement is important in email marketing and how to use engagement to improve ROI.
Internet fraud and private whois records
- laura
- Jun 15, 2012
The Verge has a long article about Internet Marketing and how much fraud is perpetrated by people who label themselves Internet Marketers.
It was interesting, but I didn’t think it was necessarily relevant to email marketers until I saw this quote from Roberto Anguizola at the FTC Bureau of Consumer Protection.
Training recipients
- laura
- Jun 14, 2012
Want to see a WWF style smackdown? Put a marketer and a delivery expert in a room and ask them to discuss frequency and whether or not more mail is better.
The marketer will point to the bottom line and how much more money they make when they increase frequency. The delivery expert will point to inbox rates and user engagement and point out that too much mail drives users to ignore the mail.
This isn’t actually unique to marketing mail. Send a lot of mail that doesn’t engage recipients and recipients are trained that they don’t have to actually pay attention to the mail. Some of them hit delete. Some may even report the mail as spam.
According to Cloudmark, this is exactly what happened when LinkedIn informed users of the recent data breach. They estimate that up to 4% of users who received the fully DKIM authenticated mail about the data breach deleted it immediately without reading it. This is higher than notification emails from other social networks.
Cloudmark suggests that part of the problem is that LinkedIn has an unclear opt-in process. Instead of asking users for preferences, LinkedIn assumes that all users want all the mail LinkedIn cares to send them. Then LinkedIn makes it difficult to find the page to change mail settings. This means recipients are very trained to ignore mail from LinkedIn. I know I ignore most of it. Anything that’s not a “want to connect” gets filed in the “I’ll read it when I’m bored” mailbox. So far I’ve not been bored enough to read any of it.
But I’m not sure it’s just about too much email. LinkedIn is a company that is heavily forged in phishing mail. Since May 1, just one of my email addresses has received over 50 messages purporting to be from LinkedIn.
Crowdsourced Investing and Spam
- steve
- Jun 11, 2012
Kickstarter’s success has made a lot of people pay attention to the concept of crowdfunding. At it’s best, crowdfunding investment allows fans of an artist to send her money to directly support her work, and get something special out of it. At it’s worst, it’s photoshopped fake products, dubious consumer electronics and videogame projects from the implausible to outright scams.
Crowdfunding sites provide a fairly simple service: they allow people to list products on their website, provide a discussion forum and allow people interested in the project to pay money (after the crowdfunding site skims 5-10% off the top) to the project backers. The project backers promise something in return for the payment – from one or more of the actual product being developed, if it’s every released, down to a simple “thanks!’ on a website. That’s something that makes perfect sense in the original KickStarter artist fan-club world, but also allows attempts to fund tech startups to avoid SEC requirements on both the startup and the crowdfunding company. Those SEC requirements were put in place many years ago to make it more difficult for scam-artists to swindle people in the guise of investing in a worthless company…
What does this have to do with spam? Well, if you’re going to set up a spam campaign of some sort – whether it’s for a real product, or an outright scam – there are several things that are very useful to have: A website that looks plausible, and won’t be taken down by the webhost. A way to accept money, ideally via online credit card payments. And a way to control discussion about your product, so that you can maintain an appearance of legitimacy and build buzz, while keeping naysayers from dissuading potential customers would be perfect.
That’s exactly what the crowdfunding sites offer. Some of them – KickStarter, for one – are very aware of the potential for abuse. Not only do they do some basic checks potential projects for legitimacy, but they have – and enforce – acceptable use policies to deter bad behaviour. Others, like IndieGoGo, don’t.
I got this spam out of the blue:
Leads, leads, leads!
- laura
- Jun 8, 2012
There are a number of places that will sell business leads from data they’ve compiled, crawled or crowd-sourced. How great is that? Anyone can buy a list of targeted business information to use to further their business goals! Awesome! Great! Step right up and get your lead here!
But how accurate is that information really?
One of the bigger companies, which allows for public searches, is Zoominfo. I did some lookups recently just to see what their data is like. My conclusion? If the data they have on me is any indication of the overall accuracy of their data, companies are way better off just setting light to a pile of money in their parking lot instead of giving it to Zoominfo.
Let’s look at the data they have on me. When you go to their homepage and enter my name in, you get about 2 dozen profiles. Looking through them, there are a number that describe me.
Laura Atkins; MCRS rep. Fair enough, I do mention MCRS on a few of my webpages and was recently on their board of directors. What I can’t figure out is why they think the Minnesota Companion Rabbit Society is run out the Chesterfield County Business Development office. The MCRS is neither a business nor is it located in the state of Virginia. It’s not even located in the same time zone as Virginia. Strike 1 for Zoominfo.
Laura T. Atkins; Founding Partner. This one is the reference that is most clearly me. Zoominfo claims this information was “community contributed.” OK, so someone uploaded their address book and my name and contact info was in it. But they have my company listed as simply “Word.” Sure, Zoominfo went and scraped a bunch of info off our website, but that isn’t reflected in the actual listing. Strike 2 for Zoominfo.
Laura Atkins; Spamtacular. This one is one of my favorites. I’m listed as associated with Spamtacular. Spamtacular is a blog run by my former co-worker Mickey Chandler. Mickey’s currently working for a major ESP, but he blogs about email, spam and delivery under the Spamtacular.com domain. And, in fact, the “association” is that he lists me as part of the Spamtacular blogroll. But Zoominfo claims they have an email address and phone number for me associated with Spamtacular. According to Mickey, Zoominfo have repeatedly attempted to mail laura at spamtacular. It’s not just my email address they’ve pulled out of nether orifices, though. The Spamtacular corporate information is, if anything, more inaccurate than the MCRS data. Spamtacular is not and has never been registered anywhere near the state of California. Strike 3 for Zoominfo.
But wait! Just because they’ve struck out doesn’t mean they’re going to stop swinging or walk off the field.
Laura Atkins; Context Magazine. I did an interview with Context Magazine back in 2002, and Zoominfo claims they have a phone number for me. I suspect this is not my phone number, but, rather, is the main number for Context Magazine.
There are a couple of other, less interesting profiles for me: Spamcon Foundation, Deliverability.com. All are demonstrably me, but with no real contact information it’s not going to help anyone get in touch with me.
I have to admit, I’m actually surprised at just how totally inaccurate the data about me is. I’m not that hard to find. Zoominfo has 6 listings I can clearly identify as me. In those 6 listings:
Relevant and timely marketing
- laura
- May 19, 2012
What better time to advertise pizza specials than at 2:30 pm on a Friday afternoon?
Either my local pizza joint is doing sophisticated tracking (hrmmm… these people often order pizza on the weekend, email on Friday) or I’m just smack dab in the middle of their average demographic.
In either case, advertising pizza on a Friday afternoon strikes me as the epitome of timely, relevant marketing.
Pizza for dinner, anyone?
Confirming addresses in the wild
- laura
- May 16, 2012
A lot of marketers tell me “no sender confirms addresses” or “confirming addresses is too hard for the average subscriber.” I find both these arguments difficult to accept. Just today I subscribed to a mailing list that had a confirmation step. The subscription form was pretty simple.
Happy Mailman Day!
- steve
- May 1, 2012
For people who are on many discussion mailing lists, the first of every month is “Mailman Day”, and has been for nearly a decade.
Mailman is the most widely used mailing list manager for discussion lists and, by default, it sends email to all subscribers on the first of the month reminding them that they’re still subscribed to the list and how to unsubscribe. This is really useful, as I’m on some mailing lists that haven’t had any traffic other than the reminders in a couple of years, but it does mean that my mailbox looks like this this morning:
Discussion lists sending reminders is a close parallel to our usual recommendations for bulk mailing lists to send something at least monthly, so that recipients remember who you are and that they’re subscribed – and so that recipients who have vanished bounce that mail, so you can eventually remove them from your mailing list. (We’re not suggesting that you send a “this is a reminder” mail monthly – create some real content and send that).
Mailman Day also means that if you’re sending mail to a technical/internet-savvy demographic and you choose to send it first thing in the morning of the first of the month, you’re competing with a lot of noise in your recipient inbox. Unless you’re mailing daily it might be worth shifting a day forward or backward to avoid that conflict.
First step in delivery
- laura
- Apr 23, 2012
Ever trawl through your logs and notice that there is a delivery problem somewhere? I’m sure everyone sending email in any volume has.
What’s the first thing you do when you discover a block?
Forcing those opens
- laura
- Apr 19, 2012
Most email marketers want to see their open rates go up. This particular marketer has come up with a new way to force recipients to load their mail.
Read MoreSpamtraps mean your list is bad
- steve
- Apr 11, 2012

Spamtraps on a list are a symptom, not the disease itself. They’re (usually) a sign of some serious underlying problem, whether it be with address capture, bounce management, list purchase or epending.
We’ve talked about this a lot in the past, but sometimes you need a short summary to refer someone to.
Best Practices: your mileage may vary
- laura
- Apr 3, 2012
YMMV. One of those abbreviations us old folks used ages ago before email had pictures and the closest we had to social networking was USENET and social gaming was in the form of MUDs. I rarely see it used any more. In a lot of ways that’s a sad thing. It was a very useful abbreviation. Using it at the end of a post full of advice was a sign that the author was providing information but knew that different situations may require different solutions. It acknowledged that what might be the best practice in one form may not be the best for another.
It’s not just the usage that seems to have declined, there seem to be a lot more people who just want to share The Answer! and not acknowledge their experience may not be universal. This seems particularly rampant in email marketing, at least to me (YMMV).
I’ve talked before about how I don’t believe there are any universal best practices for email.
Let’s be honest, the experience of a well known national retailer buying, or appending email addresses is not going to be the same as a local business doing the same thing. The national retailer acquiring email addresses and sending well targeted mail to their purchasers probably won’t cause too many delivery problems, and will generate revenue. The local pizza place probably won’t be so lucky.
A number of marketers have complained that they all too often hear “it depends” when they ask a question about email. But how well a particular email campaign perform does depend. Success depends on the audience and the offer. But more than just the specific offer, success also depends on how well known the brand is and what their real world reputation with customers is.
Customers are a lot more likely to give brands the benefit of the doubt if they like the product. That means poor practices don’t always result in poor results. It also means other companies may not have the same success with poor practices.
Your Mileage May Vary.
What email metrics do you use?
- laura
- Mar 27, 2012
Vertical Response talks about email metrics that are useful on a dashboard.
Metrics are an ongoing challenge for all marketers. The underlying need for metrics is to evaluate how effective a particular marketing program is. Picking metrics involves understanding what the goal is for a particular program. If your goal is brand recognition then perhaps sales and click-through figures aren’t a good metric. If your goal is sales then opens is not as good a metric as average order value or revenue per email.
Measuring email success is important. But how you choose to measure it is a critical decision. Too many marketers just use canned metrics and don’t think about what they really want to know.
Gmail and the bulk folder
- laura
- Mar 21, 2012
Earlier this week Gmail announced they were providing reasons for why they delivered a particular mail to the bulk folder. I’m sure a lot of senders are rejoicing over the clear feedback. After all this is exactly what they’ve been asking for “tell us why you’re filtering our mail and we’ll fix it.”
I am not sure, however, that this is going to help the majority of senders seeing mail going to the bulk folder. On the Gmail support pages, they list a number of the explanations they’re be providing.
Lasting effects from aggressive marketing
- laura
- Mar 16, 2012
Return Path has an interesting post on the lasting effects of aggressive holiday marketing.
Read MoreSo you want to start a company? (part 4)
- steve
- Feb 25, 2012
You’re setting up a company (or a new division or maybe even a new brand) and you’d like to use email to communicate with your customers. In this series of posts I’m going to touch on some of the things you can do today to make email life easier for you in the future. Today’s final post is on DNS hosting and setup.
Read MoreSo you want to start a company? (part 3)
- steve
- Feb 23, 2012
You’re setting up a company (or a new division or maybe even a new brand) and you’d like to use email to communicate with your customers. In this series of posts I’m going to touch on some of the things you can do today to make email life easier for you in the future. Today, domain registration.
Read MoreSo you want to start a company? (part 2)
- steve
- Feb 22, 2012
You’re setting up a company (or a new division or maybe even a new brand) and you’d like to use email to communicate with your customers. In this series of posts I’m going to touch on some of the things you can do today to make email life easier for you in the future. Today, choosing a domain name.
Read MoreSo you want to start a company? (part 1)
- steve
- Feb 22, 2012
You’re setting up a company (or a new division or maybe even a new brand) and you’d like to use email to communicate with your customers. In this series of posts I’m going to touch on some of the things you can do today to make email life easier for you in the future, starting with the naming of companies.
Read MoreBefore you build a list
- laura
- Feb 17, 2012
I can’t add much more to Steve Denner’s article about building list size.
Read MoreI know your customers' passwords
- steve
- Feb 14, 2012
Go to your ESP customer login page and use “View Source” to look at the HTML (under “Page” on Internet Explorer, “Tools->Web Developer” on Firefox, and “View” on Safari).
Go on, I’ll wait.
Search for the word autocomplete. If it says something like autocomplete=”off” then your web developers have already thought about this security issue. If it doesn’t, then you might have a serious security problem.
What’s going on here? You’ve probably noticed that when you’re filling in a web form your browser will often offer to fill in data for you once you start typing. This feature is supported by most modern browsers and it’s very convenient for users – but it works by recording the contents of the form in the browser, including the username and password.
As a bad guy that’s very interesting data. I can take some off-the-shelf malware and configure it with the URLs of a bunch of ESP login pages. Then I just need to get that malware installed on your customers desktops somehow. A targeted web drive-by malware attack, maybe based on targeted hostile banner ads is one approach, but sending email to people likely to be ESP customers is probably more effective. Maybe I’ll use hostile email that infects the machine automatically, or – most likely – I’ll use a phishing attack, sending a plausible looking email with an attachment I’m hoping recipients will open.
Once the malware is installed it can rummage through the users browser files, looking for any data that matches the list of login pages I gave it. I just need to sit back and wait for the malware to phone home and give me a nicely packaged list of ESPs, usernames and passwords. Then I can steal that customer’s email lists and send my next phishing run through that ESP.
This isn’t a new issue – it’s been discussed since browsers started implementing autocompletion over a decade ago, and it’s been a best practice to include autocomplete=”off” for password fields or login forms for years.
How serious a risk is this for ESPs? Well, I looked at the customer login pages at several ESPs that have a history of being compromised and none of them are using autocomplete=”off”. I looked at several that haven’t been compromised that I know of, and they’re all using either autocomplete=”off” or a complex (and reasonably secure-looking) javascript approach to login. Correlation isn’t causation, but it’s fairly strong circumstantial evidence.
ESPs should fix this hole if they haven’t already. If any customers are upset about having to actually type in their password (really?) they can take a look at secure password management tools (e.g. 1Password, LastPass or KeePass).
Thanks to Tim at Silverpop for reminding me that this is a serious security hole that many ESPs haven’t plugged yet and pointing me at some of these resources.
More on passwords and application security tomorrow.
Rancid Slime and Email Marketing
- steve
- Feb 10, 2012
Despite what some email marketers may tell you there are times when it’s really not appropriate to try and add someones email address to your list.
I just opened a pot of yogurt and instead of a smooth, creamy dessert there was a sticky brown slurry dotted with firm white chunks – looking like hot-and-sour soup, and not in a good way. No, this isn’t an email marketing metaphor, it’s just background to the story.
Food is a fairly delicate product, and supply-chain problems happen – it doesn’t take leaving yogurt out in the sun all day to turn it into something unpleasant. I’m not too concerned, but I thought I’d drop them a line and tell them that they had a problem (not because I want the traditional coupon for a free yogurt but because I want them to fix their problem and reduce the odds of the yogurt I buy next month trying to kill me).
They have a web site. I dodge past the full-screen pop-up “subscribe to our newsletter!” and go to their contact us link. Comment, complaint or question? Complaint, I guess.
They ask for a lot of information, almost all of it “required”. UPC Code, Plant Number, Production Line, Use By Date, Time Stamp, Store where it was purchased, city, state, comments. And my title, first name, last name, email address. And my email address again (no, people, that is *not* what double opt-in means). Phonenumber, Street Address, Building/Suite/Unit, City/Town, State, Zip Code, Country.
And whether I “Would you like to receive news, information and other offers from Brennan’s” – with the tempting options of “Accept” or “Not Accept”.
Skipping over the question of whether 23 fields ever makes sense for a subscription capture form, someone who’s contacting you to complain that your product looks like last months chinese take-out isn’t someone you have a close relationship with, someone who wants to receive your email. Odds are pretty good that they’re either going to decline your tempting offers and be slightly annoyed, or (accidentally?) sign up for them and hit the this-is-spam button when you mail them.
Neither is a good result, for you or them. Maybe you should wait to offer the opportunity to sign up for your yogurt mailing list until after you’ve resolved the complaint to their satisfaction, rather than when they’re making the complaint?
Unsolicited feedback
- laura
- Feb 10, 2012
Those of us in the email space often have opinions about volume and frequency and opt-in and everything involved in email marketing. What we don’t always have is the luxury of receiving unsolicited feedback from recipients.
Every once in a while I find a post online that is that unsolicited feedback from someone. Today a poster on reddit describes his experience with signing petitions and the resulting mail from political causes. After signing a number of petitions, he started getting huge amounts of email. The volume was so high, he started unsubscribing.
I’m not going to copy his whole article here, but there are some interesting points relevant to the email marketing end of things.
What not to do
- laura
- Feb 1, 2012
There’s a London concert promoter that’s been spamming our old sales address for 5 or 6 years now. I’ve sent in complaints, I’ve tried to unsubscribe, and the mail still keeps coming. They managed to get through my filters, again, this morning. In a fit of frustration I tweeted about how frustrated I was that they would not stop spamming me.
Well, that got someone’s attention. The person managing their twitter account tweeted at me with an email address and a suggestion to send him my address so he could take care of it. I sent the mail as asked and even got a reply.
Unfortunately, the reply was “I clicked the unsubscribe link at the bottom of the message for you.”
I dunno, maybe his mouse is a magic mouse and, somehow, the click from that magic mouse will be more effective than a click from my not-magic mouse. I’m not holding out much hope, though. I have no doubt that my sales address will keep getting invited to raves in London long after I retire.
Costs and accounting for email
- laura
- Jan 28, 2012
The decision by Cheetahmail to stop allowing customers to use email append caused a very long discussion on some of the marketing lists. One of the criticisms had to do with what a dumb “business decision” Cheetah was making.
I disagree. Appending, and other non-permission based sending cause a lot of costs to trickle down on the ESP. Many of the large ESPs have teams of 8 or 10 people working to manage delivery, deal with blocks and keep the mail flowing. In fact, I once had a client say “We want to be as clean as ExactTarget” only to choke when I told them how many people are on the compliance and delivery team at ET.
That’s not even looking at the cost of a SBL listing. One company estimated the cost of a slightly less than 24 hour block at over $1,000,000 in lost opportunity costs and in actual staff costs to deal with the listing. I know of one Fortune 20 company who had to re-engineer their entire customer and prospect databases due to a blocklist. And, yeah, that one was actually due to an append. They did an append and the append not only added a “new” address to a record where the person had previously opted out, but that person worked at a major spam filtering company. They experienced a whole world of very expensive pain.
Many ESPs are actually making a sound business decision by refusing to deal with non-permission mail, whether it be a purchased list or an appended list. The sender does not have permission to send to the addresses. That causes all sorts of delivery problems, which costs the ESPs lots of money and staff time to deal with. Most marketers won’t actually pay for the resources they use when appending or buying lists. Then they blame the ESP when their mail ends up in the bulk folder or is blocked outright.
I don’t think many marketers fully integrate the cost of dealing with a poor list into their decisions. My tweet from earlier today “If you have to “ignore all the costs associated with complaints” to find a positive ROI on opt-out mail, is there really a positive ROI? is a paraphrase of one of the things I heard.
ESPs can’t avoid those costs, they’re stuck with them. Lowering those costs by requiring senders to only send to recipients who have given permission is a smart business decision. Marketers don’t pay those costs, but if they even acknowledged them I suspect that there would be a whole lot less sloppy email marketing.
IP Address reputation primer
- laura
- Jan 27, 2012
There has been a lot of recent discussion and questions about reputation, content and delivery. I started to answer some of them, and then realized there weren’t any basic reference documents I could refer to when explaining the interaction. So I decided to write some.
This first post is about IP address reputation with some background on why IPs are so important and why ISPs focus so heavily on the sending IP.
Cheetahmail on appending
- laura
- Jan 19, 2012
Experian CheetahMail believes that opt-out email appending is no longer an acceptable practice, and that marketers should no longer use of this practice to acquire customer email addresses. EmailResponsibly
Read More
Don't spam filter your role accounts
- steve
- Dec 21, 2011
A variety of “amazon.com order confirmations” showed up in my inbox this morning. They were quite well done, looking pretty close to real Amazon branding, so quite a few people will click on them. And they funnel people who do click to websites that contain hostile flash apps that’ll compromise their machines (and steal their private data, login and banking credentials then add them to botnets to attack other sites and so on).
Not good. Just the sort of urgent, high-risk issue that ISP abuse desks really want to hear about. I sent email about it to the ISPs involved, including a copy of the original email. One of them went to iWeb, a big (tens of thousands of servers) hosting company.
This was the response:
Bounce handling simplified
- laura
- Dec 7, 2011
I am a strong believer that bounce handling should be designed to remove addresses that have no human on the other end while not removing addresses that have a real recipient on the other end.
Bounce handling should be designed to appropriately manage your subscriber base. Delivery problems are the consequence if you don’t do that. They shouldn’t be the reason you bounce handle, though.
Context matters.
My experience tells me that senders that think about the impact of their sends can do things that “break the rules” while still being respectful of their subscribers and still see good delivery.
Think before you mail
- laura
- Dec 1, 2011
I get quite a bit of unsolicited mail. I mean, sure, we all get a lot of spam, but that’s not the unsolicited mail I’m talking about. I’m talking about from people and companies in the email space. They want to make sure I’ve seen their new whitepaper or article about delivery. Or they have a question about something I’ve written here. Or they are looking to hire me.
All of these things are great. I love hearing from readers, either in comments or in email. We have a valid (unfiltered) contact address here on the blog. My email address(es) aren’t difficult to find. I want to talk to people.
Sometimes some of the people who contact me do actually send spam. It’s bulk, it’s impersonal, it’s not about me or my perspective it’s about them trying to sell something (themselves, their newest product, their company) to anyone who is buying.
If it’s clear it’s a one off I’ll generally just move the mail out of my inbox and forget about it. Sometimes, though, there are hints that this is more than just a one time mail. The email will have an unsubscribe link, or it’s the third or fourth time I’ve gotten mail from that sender or it will be from a PR company. I deal with them in different ways. Sometimes I’ll offer a different email address that I route better, or I’ll just filter the mail based on some unique bit of the header.
The ones that really get me, though, are when the senders argue with me that I should feel special to get their bulk mail. “It was individually sent to you!” “I sent it because you’re such a great resource and wanted to say thank you!” But it was bulk mail, mail dozens of other people got (hint: the email / delivery industry is very small. we talk to each other all the time, if you send mail to more than one of us, we’re going to talk about it).
I have no problem with you inviting me to your event. Or telling me about the latest or greatest thing you wrote. I don’t even mind the occasional one-off bulk mail. But if you are sending mail to a specific person, put in the 20 seconds to personalize it and make it feel like it’s special for me.
A few moments to think and personalize before you send that email will make your recipient much more open to your pitch. This is as applicable to one off mail as it is to bulk.
About that Junk Folder
- steve
- Nov 30, 2011
I use a pretty standard mail filtering setup – a fairly vanilla SpamAssassin setup on the front end, combined with naive bayesian content filters in my mail client. So I don’t reject any mail, it just ends up in one of my inboxes or a junk folder. And I have a mix of normal consumer mail – facebook, twitter, lots of commercial newsletters, mail from friends and colleagues and spam. (As well as that I have a lot of high traffic industry mailing lists, but overall it’s a fairly normal mix.)
My bayesian filter gets trained mostly by me hitting “this is spam” when spam makes it to my inbox. If I’m expecting an email “immediately” – something like a mailing list COI confirmation or email as part of buying something online – I’ll check my spam filter and move the mail to my inbox in the rare case it ended up there. Other than that I let it and spamassassin chug along with no tweaking.
I’m starting a data analysis project, based on my own inboxes, and as part of that I’m using some tools to look for false positives in my junk folders, and manually fixing anything that’s misclassified. I’ve been doing this for a couple of hours now, and I’ve found some interesting things.
Opt-in vs. opt-out
- laura
- Nov 28, 2011
Jeanne has a great post up at ClickZ comparing the performance of mail to an opt-in list to performance of mail to an opt-out list.
The article looks at opens, clicks and click through rates over 7 quarters (Q1 – Q4 2010; Q1 – Q3 2011) covering 330 million emails. I strongly suggest anyone interested go read the whole article.
The short version, though, is that the opt-in lists had more opens and more clicks than the opt-out lists. In some quarters it was double the number of opens and clicks.
This data is a strong indication that opt-in lists perform much better than even the best opt-out lists.
Vetting customers
- laura
- Nov 16, 2011
MAAWG has published a BCP for vetting new customers. This is the culmination of much work by a lot of people.
One of the best things about the document is the discussion of how spammers attempt to hide their identity. All too often I’ve been called in by ESPs to help them identify how a spammer got on their network and where their process failed. As filtering gets better at blocking spam, spammers are spending more and more time trying to steal good reputations to get their unwanted mail through.
Providers who follow these rules may still find themselves with spammers as customers, but the spammers will have to work harder to get on clean networks.
Does it look like you're spamming?
- steve
- Nov 8, 2011
There are lots of terribly complicated rules in email marketing and retention. “Only send email to people who opted-in”, “Never use a pink background”[1], “Have a working unsubscription link”, “Don’t put FREE in the subject line”[1].
Another one should be “How does what you’re doing look to a typical recipient?”.
I’ve received several pieces of spam recently from senders who were ticking quite a lot of the “email best practices” checkboxes, but who completely blew it by not looking at it from the recipients point of view. The mistakes they’ve made, and the things to learn from them, and much the same, so I’ll just give one example.
“Likes Music” is not the same as “Likes Groupon Clones”
I’ve been a subscriber to our local radio station’s mailing list for years – promos KFOG is running, local gigs, that sort of thing, all in a newsletter sort of format. They recently sent out an ad for a Groupon clone called “SweetJack” – on it’s own, not as part of a newsletter. I’m not interested, and I think it’s a fairly poor pitch and won’t work well for their demographic, but fair enough. A couple of weeks later I start getting spam from SweetJack, thanking me for signing up – to the tagged email address I’d only given to KFOG. And no mention of KFOG at all.
Most recipients are just going to see this as spam out of the blue from SweetJack, and hammer on the “This is Spam” button until it goes away. That’s dreadful for SweetJack’s reputation, and is going to hurt their delivery.
Recipients paying more attention are going to notice that the first they heard of SweetJack was an out of the ordinary promo by KFOG, and then they start getting spam from SweetJack. They’re likely to assume that KFOG sold their email addresses to SweetJack – and that they’re sending their spam to an email address that only KFOG has in my case confirms that. That’s going to be dreadful for SweetJack’s reputation and going to damage the relationship between KFOG and their existing subscribers. A dreadful idea.
Digging down deeper, it seems that while KFOG being bought out by media behemoth Cumulus Media a few years back didn’t damage their on-air content, it did change the amount of respect they have for their subscribers. SweetJack is a new Groupon clone started by Cumulus Media. They did have legitimate access to the KFOG mailing lists, sorta. It’s probably not an AUP or privacy violation. It’s just the sort of thing an eager marketing guy at the corporate owners would think was a great idea, to leverage the value of their existing subscribers.
But it would have been a pretty bad idea had they carried it out perfectly, with clear messaging and transparency to the recipients. And they blew their one opportunity to do it well, and I’m betting that most of the recipients have SweetJack categorized as “spammers”, both mentally and in their mail clients.
1. Not a real email marketing rule.
Spamtraps: should you care?
- laura
- Nov 4, 2011
I believe that spamtraps – for the professional marketer – are scare tactics that are no longer relevant. a professional marketer
Read More
Six best practices for every mailer
- laura
- Nov 1, 2011
People get into all sorts of details when talking about best practices. But so much of email depends on the type of email and the target market and the goals of the sender. It’s difficult to come up with universal best practices.
I’ve said in the past that I think that best practices are primarily technical. I don’t believe there is a best frequency or a best time to send mail or a best image to text ratio.
My top 6 best practices every marketer should be doing (and too few are).
Persistence of unsubscribes
- laura
- Oct 19, 2011
It’s really, really frustrating when an unsubscribe request doesn’t take. And it happens a lot more than many people expect.
Most of the culprits are marketing companies. United Business Media is a huge problem, for instance. I never even signed up for their mail, but they bought an address I’d used to register for a conference. I unsubscribed at least a dozen times, but the mail kept coming. Of course, it wasn’t actually mail I’d unsubscribed from. Every email was part of a different list.
There was no way to find out what lists I was on through their unsubscribe page and preemptively unsubscribe. I tried mailing their privacy department, but it took multiple emails to get any sort of response. Finally, someone responded that they had removed me from all their lists.
Illegal? Probably not. Annoying? Totally.
This is the reason I don’t unsubscribe from mail if I don’t recognize the sender. Too many people who “acquire” my email address without permission don’t actually pay any attention to the law, much less best practices.
The other time I see this problem is with some of the addresses I’ve used for testing customers and their vendors. I unsub from any lists I’ve signed up for when I’ve collected the information I need. It’s not totally unheard of, though, for those addresses to lay dormant for years and then start receiving mail again.
This is a problem. They’re “reactivating” addresses. Again, they’re probably different “lists” so it’s not a CAN SPAM violation, but I don’t really care. I unsubscribed. I don’t want any more of that mail. I really can’t figure out what possesses companies to just decide, after not having interaction with subscribers for years, that the right thing to do is just add those addresses to a new list.
It’s not even like they try and re-engage me. Or ask me to opt-in. All they do is start sending me copies of the Annoying Meme of the Hour newsletter. It’s even more frustrating because I know that the sender has been exposed to best practices. I have spent anywhere from weeks to months helping them create a email marketing program that shouldn’t do this kind of thing.
I’ve tried talking to some clients after this happens. Usually, the issue is the marketers or IT staff that I worked with are gone. A new, shiny marketing group has moved in and decided that they had this huge database and of COURSE they should mail it, all of it, opt-outs notwithstanding.
It happens to me as a consumer and subscriber, too. In those cases I don’t have much recourse beyond reporting it as spam and blocking the mail. I don’t trust that a new unsubscribe will work, since the last one didn’t. I have to take other steps to make the mail stop.
In this case, I am much less persistent than the sender is. I think it would be better if senders actually believed me when I said I didn’t want their mail. But I don’t expect that will ever happen. Too many senders think they know better.
Where do you accept reports?
- laura
- Oct 18, 2011
One of the things that is most frustrating to me about sending in spam reports is that many ESPs and senders don’t actively monitor their abuse address. A few months ago I talked about getting spam from Dell to multiple email addresses of mine.
What I didn’t talk about was how badly broken the ESP was in handling my complaint. The ESP was, like many ESPs, an organization that grew organically and also purchased several smaller ESPs over the course of a few years. This means they have at least 5 or 6 different domains.
The problem is, they don’t effectively monitor abuse@ for those different domains. In fact, it took me blogging about it to get any response from the ESP. Unfortunately, that initial response was “why didn’t you tell us about it?”
I pointed out I’d tried abuse@domain1, abuse@domain2, abuse@domain3, and abuse@domain4. Some of the addresses were in the mail headers, others were in the ESP record at abuse.net. Three of those addresses bounced with “no such user.” In other words, I’d tried to tell them, but they weren’t accepting reports in a way I could access.
Every ESP should have active abuse addresses at domains that show up in their mail. This means the bounce address domain should have an abuse address. The reverse DNS domain should have an abuse address. The d= domain should have an abuse address.
And those addresses should be monitored. In the Dell case, the ESP did have an active abuse@ address but it was handled by corporate. Corporate dropped the ball and never forwarded the complaint to the ESP reps who could act on the spam issue.
ESPs and all senders should have abuse@ addresses that are monitored. They should also be tested on a regular basis. In the above case, addresses that used to work were disabled during some upgrade or another. No one thought to test to see if they were working after the change.
You should also test your process. If you send in a complaint, how does it get handled? What happens? Do you even have a complaint handling process outside of “count and forward”?
All large scale senders should have appropriate abuse@ addresses that are monitored. If you don’t, well, you look like a spammer.
Not lazy, just annoyed
- laura
- Oct 18, 2011
I don’t usually send in spam reports, but I submitted a couple in the last few weeks. Somehow an address of mine is on a bunch of rave / club lists in London. You want to know what is happening at London clubs this week? It’s all there in my spam folder.
This mail finally hit my annoyance threshold, so I’ve been submitting reports and complaints to the senders the last few weeks. The mail, with full headers, goes with an explanation that the address that received it was harvested off a website more than 5 years ago and never opted in to receive any mail.
One of the ISPs I sent the report to has a web form where the complainant and the customer can see the report and both can comment on it. The customer replied to my complaint on it.
Recipients are the secret to good delivery
- laura
- Oct 12, 2011
Many, many people hire me to educate them on delivery and fix their email problems. This is good, it’s what I do. And I’m quite good at helping clients see where their email program isn’t meeting expectations. I can translate tech speak into marketing. I can explain things in a way that shifts a client’s perception of what the underlying issues are. I can help them find their own way into the inbox.
But…
Most of what I do is simply think about email delivery from the point of view of a recipient and help clients better meet their recipient’s expectations. This works. This works really well. If you send mail that your recipients want your mail gets to the inbox.
Here’s the secret: ISPs and most spam filters have a design goal to deliver mail their users want. They only want to block mail their users don’t want.
Filters are not designed to block wanted mail.
Sure there are complicated situations where senders have gotten behind the 8 ball and need some help cleaning up. There are situations where filters screw up and block mail they shouldn’t (and aren’t quite designed to). Spam filters are complicated bits of code and sometimes they do things unexpectedly. All of these things do happen.
But these situations happen a lot less than most senders think. Most of the time when mail is hitting the bulk folder, or is throttled at the MTA the issue is that recipients don’t care about the mail.
Recipients aren’t engaged with a particular sender or particular brand. So ISPs react accordingly and that mail ends up slowly delivered or bulked. This upsets the senders to no end, but the recipients? The recipients often don’t care that some mail shows up in bulk or arrives Wednesday afternoon instead of Tuesday evening.
When recipients are engaged with a particular sender or brand, though? Delivery is fast and reliable. Mail is rarely delayed or bulked. When recipients want mail, they interact with it. They look in the bulk folder. They miss it when it’s not there. They complain to the ISPs when they don’t get it. The ISPs react accordingly and prioritize or “red carpet” that email.
The secret to really good delivery is to get your recipients to handle your ISP relations for you. Send mail they miss when they don’t get it, and you’ll discover most of your delivery problems go away.
Six months or out
- laura
- Sep 28, 2011
Mickey Chandler has a great post up about Triage vs. Planning. Where he talks about the decisions you make differ depending on the context.
It’s a good read, and I strongly encourage everyone to go give it a look.
But his post led me to a post by Andrew Kordek at Trendline where he claims that there is an industry rule of thumb that says 6 months is the rule of thumb to define an inactive.
Wait, What?
I know there’s a huge amount of controversy in the email space about whether or not you should purge inactive addresses. I know there are some very vocal people who think that removing inactive addresses is tantamount to marketing suicide. But where did 6 months come from? Who made it an industry standard?
If we don’t know where the standard came from, if we don’t know why we’re doing it then what kind of mickey mouse industry are we running here?
There is a lot about email marketing that is empirical. You poke the black box on one side and see what happens on the other. The problem with that is, that we can “discover” a lot of effects that aren’t real, but somehow turn into “you must do this!”
I have no doubt there are times when a 6 month expiry is a good idea. A number of my clients over the last few years use a much, much shorter time because that’s what works for them. I also know there are times when longer expiry times are a good idea, too.
It’s really important that when you’re making decisions about your email marketing program that you don’t mindlessly apply “standards” to what you’re doing. Think about the practical effects of your decisions and put them in context with your overall business plan.
To do otherwise is to kneecap your email marketing program.
ESPs, complaints and spam
- laura
- Sep 13, 2011
Steve wrote a while back about how Mailchimp handled his complaint.
Sadly, I have a counter example from recently.
It's easy to be a sloppy marketer
- laura
- Sep 7, 2011
Sometimes marketers are just sloppy.
Take, for example, an email I received today from a company.
I wasn’t expecting it (sloppy #1).
I never consciously signed up for it (sloppy #2). Apparently I’d bought a package they sold through Appsumo and they claim I asked for future offers. If I did, I didn’t mean to.
The email itself used a template from the sender’s ESP, but whomever wrote the copy didn’t actually proof read it (sloppy #3).
How to respond to an abuse complaint
- steve
- Aug 26, 2011
There’s a lot of variation in how ESPs respond to a report of one of their customers sending spam. Almost all ESPs will suppress future email to the recipient. Most will also note that there was a complaint about the sender, and use a count of those complaints for reporting, triage and escalation of problems. Beyond that, though, there’s little consistency.
I sent a spam report to abuse@mailchimp last week. The spam was nothing special – it was an advert about bouncy castles from a small company local to me sent to a tagged address used to register a domain that expired several years ago, so I knew someone had purchased a “targeted” list. The mail I sent to mailchimp was just one line, mentioning where the email address had come from and a full copy of the email with headers – again, nothing special.
The response I got back from Meredith was particularly good, so I thought I’d share it.
When the inbox isn't the inbox
- laura
- Aug 26, 2011
There was a discussion today on the OI list about email filtering that brought up something I usually don’t mention in delivery discussions. Most email marketers treat the inbox as the holy grail of delivery. Everything about delivery is focused on getting to the magical inbox.
I think, though, that inbox is often just shorthand for “not landing in the bulk or spam folders.”
For some recipients, particularly those of us who get lots of mail, sometimes it’s better to land in a folder rather than the inbox. I have a folder set up, where most of my commercial mail goes. It’s labeled “commercial.” I check it once or twice a day.
This is beneficial to me and to the senders. Why? Because when I check that folder I’m ready to actually look at my commercial mail. I’m looking for those offers.
For someone like me, who does most of their work in their inbox, commercial interruptions are a problem. Commercial mail that ends up in my inbox, which can happen if I’ve been lazy about filters, interrupts me and usually doesn’t get read. But when it’s in my commercial folder? Well, then I can look at it, visit websites and make purchases.
So just remember, it’s not that you want mail in the inbox as much as you want mail somewhere that the recipient will notice it.
Uptick in botnet spam
- laura
- Aug 23, 2011
There’s been a heavy uptick in botnet spam over the last few days, judging by things I’m hearing and my own mailboxes. There are a few common subject lines, but all of them are trying to get recipients to either run programs or visit malicious web pages.
The first subject line I’m seeing a lot of is “<name> wants to be friends with you on facebook!” In my mailbox most of those names have not been common European names. The give away that this isn’t actually a Facebook invite is the Reply-To address pointing to Linkedin. The URLs in the message appear to be random strings of numbers, and may actually encode recipient information in them.
The second has a subject that that is a variation on “End of July Statement.” The spammers are mixing capitals, adding in “Re:” and “FWD:” and sometimes increasing the urgency by adding required or STAT!! to the mail. These mails contain a .zip file which probably contains some virus which will turn the recipient machine into the next spam spewing bot.
The third variation has the subject line “Uniform Traffic Ticket.” The content is a citation that tells the recipient they were speeding somewhere in New York (possibly other states, I have only done a spot check of the couple hundred copies I have). There is, however, a .zip attachment with a virus.
Most people probably aren’t seeing these. SpamAssassin is doing a reasonably good job here of catching the spam and filtering it. I’m sure that the bigger ISPs are also filtering it effectively. But one person did forward a copy of the spam to a mailing list and ask if anyone knew what was going on.
If you get any of these messages, you don’t need to ask. It’s virus spam. Don’t open it and don’t forward it.
Evil weasels and random monkeys
- steve
- Aug 11, 2011
I’m doing testing on a new release of Abacus at the moment, so I’m in a software QA (Quality Assurance) frame of mind.
One of the tenets of software QA is “Assume users are malicious”. That’s also one of the tenets of security engineering, but in a completely different way.
A security engineer treats users as malicious, as the users he or she is most concerned about are crackers trying to compromise their system, so they really are malicious. A QA engineer knows that if you have enough users in the field, making enough different mistakes or trying to do enough unusual things, they’ll find all the buggy little corners of your application eventually – and crash it or corrupt data more reliably than a genuinely malicious user.
As a QA engineer it’s easier to personify the forces of chaos you’re defending against as a single evil weasel than a million random monkeys.
In the bulk email world the main points where you interact with your users are signup, confirmation, unsubscription and click-throughs. Always think about what the evil weasel will do at that point.
Signup
Don't think bounce handling is important?
- laura
- Aug 11, 2011
James from Cloudmark has his own insight on spamtraps.
Read MoreHave you audited your program lately?
- laura
- Jul 28, 2011
A few months ago, I got spammed by a major brand. I know their ESP takes abuse seriously, so I sent a note into their abuse desk. It bounced with a 550 user unknown. I sent another note into a different abuse address, it bounced. I sent mail into their corporate HQ, it disappeared into a black hole. I eventually connected with their delivery person and he’d not seen hide nor hair of any complaint. Their entire abuse handling system had broken down and no one noticed.
In the recent past, I was dealing with a client’s SBL listing. We were talking about how their fairly clean subscription process ended up with multiple Spamhaus spamtraps on the list. They mentioned bounce handling, and that they’d not been correctly managing bounces for some period of time. Their bounce handling system was broken and no one noticed.
Last year, I was working with another client. They were looking at why some subscribers were complaining about unsubscribes not taking. A bit of poking at different forms and they realized that one of their old templates pointed to an old website. Their unsubscription form had broken and no one noticed.
Another client insisted that their engagement handling removed any addresses that didn’t open or click on mail. But after ignoring their mail for 6 months, they still hadn’t stopped mailing me. Their engagement handling was broken and no one noticed.
Periodic monitoring would have caught all of these things before they became a big enough problem to result in a Spamhaus listing, or recipient complaints, or lawsuits for failure to honor CAN SPAM. Unfortunately, many companies don’t check to make sure their internal processes are working very often.
Email marketing is not set and forget. You need to monitor what is happening. You need to make sure that your processes are still in place and things are still working.
Gmail and the via
- laura
- Jul 22, 2011
I was hoping to have a detailed post up today about the conditions where gmail presents the user with a “via” but time seems to have gotten away from me. But I can give you the conclusions.
Read MoreAuthentication Cheat Sheet
- steve
- Jul 20, 2011
There are a several approaches to authenticating email, and the different authentication methods have a lot of different settings to choose from (sometimes because they’re useful, other times just because they were designed by committee). It’s nice that they have that flexibility for the complex situations that might benefit from them, but almost all the time you just want to choose a good, default authentication approach.
So here’s some short prescriptive advice in no particular order for “how to do email authentication at an ESP well” without the long discussions of alternative approaches and justification of each piece of advice.
Charter hard bounces valid addresses
- laura
- Jul 18, 2011
Last week Charter had a technical problem that caused them to respond with “user unknown” to email sent to valid users.
I recommend re-activating any address to Charter that was disabled July 14 or 15.
TWSD: I can haz ethix marketing
- laura
- Jul 14, 2011
I’m getting slammed by spam advertising URLs at http://perfectdeliveries.com/ from
Ethix Marketing LLC
711 S. Carson Street Suite 4
Carson City, Nevada 89701
The kicker? They’re violating CAN SPAM while they’re doing it. Seriously, sending mail out through open relays and proxies with forged From: addresses is a violation of CAN SPAM. And they’re spamming for ambulance chasers.
Spammers, eh?
URL Shortening and Email
- steve
- Jun 29, 2011
Any time you put a URL in mail you send out, you’re sharing the reputation of everyone who uses URLs with that hostname. So if other people send unwanted email that has the same URL in it that can cause your mail to be blocked or sent to the bulk folder.
That has a bunch of implications. If you run an affiliate programme where your affiliates use your URLs then spam sent by your affiliates can cause your (clean, opt-in, transactional) email to be treated as spam. If you send a newsletter with advertisers URLs in it then bad behaviour by other senders with the same advertisers can cause your email to be spam foldered. And, as we discussed yesterday, if spammers use the same URL shortener you do, that can cause your mail to be marked as spam.
Even if the hostname you use for your URLs is unique to you, if it resolves to the same IP address as a URL that’s being used in spam, that can cause delivery problems for you.
What does this mean when it comes to using URL shorteners (such as bit.ly, tinyurl.com, etc.) in email you send out? That depends on why you’re using those URL shorteners.
The URLs in the text/html parts of my message are big and ugly
Unless the URL you’re using is, itself, part of your brand identity then you really don’t need to make the URL in the HTML part of the message visible at all. Instead of using ‘<a href=”long_ugly_url”> long_ugly_url </a>’ or ‘<a href=”shortened_url”> shortened_url </a>’ use ‘<a href=”long_ugly_url”> friendly phrase </a>’.
(Whatever you do, don’t use ‘<a href=”long_ugly_url”> different_url </a>’, though – that leads to you falling foul of phishing filters).
The URLs in the text/plain parts of my message are big and ugly
The best solution is to fix your web application so that the URLs are smaller and prettier. That will make you seem less dated and clunky both when you send email, and when your users copy and paste links to your site via email or IM or twitter or whatever. “Cool” or “friendly” URLs are great for a lot of reasons, and this is just one. Tim Berners-Lee has some good thoughts on this, and AListApart has two good articles on how to implement them.
If you can’t do that, then using your own, branded URL shortener is the next best thing. Your domain is part of your brand – you don’t want to hide it.
I want to use a catchy URL shortener to enhance my brand
That’s quite a good reason. But if you’re doing that, you’re probably planning to use your own domain for your URL shortener (Google uses goo.gl, Word to the Wise use wttw.me, etc). That will avoid many of the problems with using a generic URL shortener, whether you implement it yourself or use a third party service to run it.
I want to hide the destination URL from recipients and spam filters
Then you’re probably spamming. Stop doing that.
I want to be able to track clicks on the link, using bit.ly’s neat click track reporting
Bit.ly does have pretty slick reporting. But it’s very weak compared to even the most basic clickthrough reporting an ESP offers. An ESP can tell you not just how many clicks you got on a link, but also which recipients clicked and how many clicks there were for all the links in a particular email or email campaign, and how that correlates with “opens” (however you define that).
So bit.ly’s tracking is great if you’re doing ad-hoc posts to twitter, but if you’re sending bulk email you (or your ESP) can do so much better.
I want people to have a short URL to share on twitter
Almost all twitter clients will abbreviate a URL using some URL shortener automatically if it’s long. Unless you’re planning on using your own branded URL shortener, using someone else’s will just hide your brand. It’s all probably going to get rewritten as t.co/UgLy in the tweet itself anyway.
If your ESP offers their own URL shortener, integrating into their reporting system for URLs in email or on twitter that’s great – they’ll be policing users of that just the same as users of their email service, so you’re unlikely to be sharing it with bad spammers for long enough to matter.
All the cool kids are using bit.ly, so I need to to look cool
This one I can’t help with. You’ll need to decide whether bit.ly links really look cool to your recipient demographic (Spoiler: probably not) and, if so, whether it’s worth the delivery problems they risk causing.
And, remember, your domain is part of your brand. If you’re hiding your domain, you’re hiding your branding.
So… I really do need a URL shortener. Now what?
It’s cheap and easy to register a domain for just your own use as a URL shortener. Simply by having your own domain, you avoid most of the problems. You can run a URL shortener yourself – there are a bunch of freely available packages to do it, or it’s only a few hours work for a developer to create from scratch.
Or you can use a third-party provider to run it for you. (Using a third-party provider does mean that you’re sharing the same IP address as other URL shorteners – but everyone you’re sharing with are probably people like you, running a private URL shortener, so the risk is much, much smaller than using a freely available public URL shortener service.)
These are fairly simple fixes for a problem that’s here today, and is going to get worse in the future.
(9/18/17: Closing comments because this post attracts spam comments)
Well designed email program
- laura
- Jun 27, 2011
I so often talk about the failures of various email marketing programs that it’s only fair I mention when someone gets it right.
We spent the past week with family on the east coast. Our flight back to the west coast was very, very early Sunday morning so I booked a night at the airport hotel. That way we could just stumble to the shuttle at some horrible hour and not worry about trying to coordinate drivers and cars and all that other stuff.
As we were headed to the airport, I pulled out my phone to confirm directions. I found a new message in my mailbox offering me the opportunity to check-in online. I decided to see how it worked.
The frequency conundrum
- laura
- Jun 17, 2011
What is the perfect frequency to send mail? Is it daily, weekly, monthly, hourly, minutely (is that even a word?) or randomly? Any number of experts will give you a definitive answer to this question, but I don’t believe there is a single answer.
The frequency recipients will respond to depends on the type of mail, the recipient expectations, the sender and a host of other factors.
For one example look at the mail sent by social networks. Many people, myself included, will accept dozens of emails a day telling me someone wrote on my Facebook wall or retweeted something I said or wants to link to my network on LinkedIn. Another example is when I’m traveling or waiting to pick up someone who is, I am thrilled to receive multiple updates an hour from the airline.
This willingness to receive frequent commercial or bulk emails doesn’t necessarily translate to marketing emails. When Sur la Table started sending double digit amounts of email a week, I down-subscribed, and had they not let me pick an acceptable-to-me frequency I would have unsubscribed completely.
A lot of marketing experts insist that mailers don’t send frequently enough. That increasing frequency increases ROI. What a lot of people miss are all the caveats in the fine print. In their minds, increasing frequency goes hand in hand with increased segmentation, targeting and recipient specific emails.
The idea isn’t simply to mail the entire list more frequently but to mail those who are more open to increased frequency. This is an idea I wholeheartedly support.
Smart email
- laura
- Jun 16, 2011
This week I received an email from a vendor we purchased software from 6 months ago. And it was exactly 6 months to the day of our original purchase I received an email basically reminding me of what I purchased and asking me to update my contact information.
Read MoreMarketing or spamming?
- laura
- May 31, 2011
A friend of mine sent me a copy of an email she received, asking if I’d ever heard of this particular sender. It seems a B2B lead generation company was sending her an email telling her AOL was blocking their mail and they had stopped delivery. All she needed to do was click a link to reactivate her subscription.
The mail copy and the website spends an awful lot of time talking about how their mail is accidentally blocked by ISPs and businesses.
End of quarter spam
- laura
- May 27, 2011
There has been a plethora of big brand companies doing stupid stuff with marketing recently. I can only figure it’s end of quarter and everyone is looking to pump up their numbers as fast as possible.
I talked about Millenium hotels sending me with an utterly irrelevant ad earlier this week.
@Yahoomail direct message spammed all their twitter followers with an ad for something related to the new Yahoo mail product.
Anyone watching my twitter feed yesterday probably noticed me complaining about spam from Dell.
All of these things are just examples of sloppy marketing. In Dell’s case it’s even worse because they sent me multiple copies of the spam to different addresses. Two copies of the same “SHOP NOW!” email to different addresses, one of which has never been given to Dell.
Mail to the first address is unquestionably spam and I did send in a complaint to Dell’s ESP. That address is never used to sign up for anything. I did try clicking on the “update your subscription” link in the footer and Dell’s website helpfully told me that address was not on their mailing lists. Looks like Dell bought a list.
The second address is one that was involved with the purchase of software from Dell last July. This is the first non-transactional mail sent to that address. I can’t necessarily call the email spam as I did give it to Dell during the course of a transaction. However, Dell could have done a lot better in managing our “relationship” than they did.
Dell collected my email address as part of a transaction in July 2010. They did not start sending marketing mail to this address until May 2011. While Dell is a major brand and most people would recognize the name and may be a little less inclined to hit “this is spam” waiting 10 months between a purchase and regular mailings is a bad idea. People who don’t use tagged addresses may forget they gave the sender an email address and automatically send in a spam complaint.
Sitting on an address for 10 months means Dell really should have done a welcome series, or even just a single welcome email, to ease the transition from no mail to regular mail. But, no, they just send me an email advertising their sales.
We’ve been Dell customers for quite a while, and all of our purchases have been enterprise grade hardware or software to run on those servers. We’ve never purchased anything remotely like office computers. But the sales flyer was for desktops, printers and monitors. Dell knows what I purchased from there, so why are they sending me ads for things I’ve never bought?
We have our own Dell sales rep, and my only involvement in the transaction is source of payment. Adding me to a product list really feels like spam.
Then there was the email itself. The “update your subscription” link was broken and told me I wasn’t subscribed to their list. I mentioned it to Steve and he pointed out that particular link had been broken “forever.” How long has it been since anyone inside of Dell has checked that their footer links work?
What is Dell up to? Who knows. But they unarguably are sending mail to addresses that never opted in. And even if you consider an email giving during a purchase process their handling of that particular address was appalling and in violation of almost every good practice out there.
Relevance?
- laura
- May 25, 2011
As a past guest and/or meeting planner of Millennium Hotels and Resorts we are pleased to share these occasional special offers. If you no longer wish to receive email communications from us, please click the unsubscribe link. Please note that this broadcast is sent from an address which is not monitored. If you have questions about the offer, please contact us directly. Our hotel contact details may be found in this email offer above or you may visit www.millenniumhotels.com.
Read More
Don't take my subscribers away!
- laura
- May 13, 2011
Tom Sather has a good summary of the problems with inactive email addresses and why data hygiene is critical to maintain high deliverability. These recommendations are some of the most difficult to convince people to implement.
Some of my clients even show me numbers that show that a recipient that hadn’t opened or read and email in 18 months, suddenly made a multi-hundred dollar purchase. Another client had clear numbers that showed even recipients that didn’t open for an entire year were responsible for 10% of revenue.
They tell me I can’t expect them to let their customers go. These are significant amounts of money and they won’t let any potential revenue go without a fight.
I understand this, I really do. The bottom line numbers do make it tough to argue that inactive subscribers should be removed. Particularly when the best we can offer is vague statements about how delivery may be affected by sending mail to unengaged users.
I don’t think many senders realize that when they talk about unengaged users they are actually talking about two distinct groups of recipients.
The first group is that group of users that actively receive email, but who aren’t opening or reading emails from particular senders. This could be because of their personal filters, or because the mail is going to the bulk folder or even simply because they don’t load images by default. This is the pool that most senders think of when they’re arguing against removing unengaged users.
The second group is that group of users that never logs in ever. They have abandoned the email address and never check it. I wrote a series of posts on Zombie Emails (Part 1, 2, 3) last September, finishing with suggestions on how to fight zombie email addresses.
Unlike senders ISPs can trivially separate the abandoned accounts from the recipients who just don’t load images. Sending to a significant percentage of zombie accounts makes you look like a spammer. Not just because spammers send mail to really old address lists, but a number of spammers pad their lists with zombie accounts in order to hide their complaint rates. The ISPs caught onto this trick pretty quickly and also discovered this was a good metric to use as part of their filtering.
I know it’s difficult to face the end of any relationship. But an email subscription isn’t forever and if you try to make it forever then you may face delivery problems with your new subscribers.
Character encoding
- steve
- May 3, 2011
This morning, someone asked an interesting question.
Last time I worked with the actual HTML design of emails (a long time ago), <head> was not really needed. Is this still true for the most part? Any reason why you still want to include <head> + meta, title tags in emails nowadays?
Read More
Defending against the hackers of 1995
- steve
- Apr 29, 2011
Passwords are convenient for the end user, but it’s too easy to lose control of them. People share them with other people. People write them down, where they can be read. People send them in email, and that email is easily intercepted. People’s web browsers store the passwords, so they can log in automatically. Worst of all, perhaps, people tend to use the same username and password at many different websites. If just one of those websites is compromised (or even run as a password collecting scam) then those passwords can be used to attack accounts at all of the others.
Two factor authentication that uses an uncopyable physical device (such as a cellphone or a security token) as a second factor mitigates most of these threats very effectively. Weaker two factor authentication using digital certificates is a little easier to misuse (as the user can share the certificate with others, or have it copied without them noticing) but still a lot better than a password.
Security problems solved, then?
You can't always get what you want
- laura
- Apr 22, 2011
It’s a problem anyone who has done any delivery work has faced. There’s a client who is having blocklist problems or ISP delivery problems and they won’t pay any attention to what you say. They insist that you talk to the blocklist or the ISP or hand over contacts directly so they can “dialog with” someone internally. They don’t like what they’re hearing, and they hope that the answer will be different if they find a new person to talk to.
The reality is many of the people at ISPs and blocklists don’t want to talk to these types of senders. They may answer a friendly question from someone they know and trust, but sometimes not even then.
Some very large ISPs and major blocklists don’t even take sender questions. They won’t communicate with anyone about any delivery issues.
I’ve had to tell more than a few clients recently that various ISPs and blocklists weren’t interested in helping those clients with their delivery problems. There are two classes of reactions I get from clients. Some clients focus on moving forward. “OK, now what? How can we identify the issue, what data do we have and how can we figure out what the problem is?”
Other clients continue to look for ways to talk to whomever is blocking their mail. They’re convinced if they can just “explain their business model” or be told what they’re doing wrong, that all their delivery problems will magically disappear.
Needless to say those clients who focus on moving forward and looking at the information they do have have much better success resolving their delivery problems. What many senders don’t understand is the wealth of data they have that will help them resolve the issue. And even if they know it’s buried in their files, they don’t always know where to start looking or even what they’re looking for.
But that is, of course, why you hire someone like me who understands spamfiltering and email. I help senders understand how email filters work and identify what parts of their programs are likely to be responsible for delivery issues. I often find the most valuable service I provide to clients is a fresh set of eyes that can see the forest. With my help, they manage to stop obsessing unproductively about one particular symptom and focus on the underlying problems.
Senders who think the holy grail of problem resolution is speaking to the right person at an ISP or blocklist generally are disappointed, even when they hire someone who knows all the right people at the ISPs. They can’t always get what they want. But I can often help them get what they need.
Security, security, security
- laura
- Apr 16, 2011
James Hoddinott posts, over on the Cloudmark blog, about another arrest associated with hackers infecting machines with a trojan that steals personal information.
There are so many security risks out there, and these messages have been hammered home recently. Home users are at risk from trojans, some spread by spam and some spread by advertising networks. Corporate users are at risk from all of those, but also from spear phishers who set out to infiltrate their business.
We all need to think hard about security. Not just keeping our Windows machines patched, but also thinking about what information we’re sharing and what passwords we’re using and all of the many things that create security.
We’re making some improvements to our security here. What are you doing at home and at work to keep your information, and your customer’s information, secure?
Feedback loops
- laura
- Apr 14, 2011
There are a lot of different perspectives on Feedback Loops (FBLs) and “this is spam” buttons across the email industry.
Some people think FBLs are the best thing since sliced bread and can’t figure out why more ISPs don’t offer them. These people use use the data to clean addresses off their lists, lower complaints and send better mail. They use the complaints as a data source to help them send mail their recipients want. Too many recipients opted out on a particular offer? Clearly there is a problem with the offer or the segmentation or something.
Other people, though, think the existence of “this is spam” buttons and FBLs is horrible. They call people who click “this is spam” terrorists or anti-commerce-net-nazis. They want to be able to dispute every click of the button. They think that too many ISPs offer this is spam buttons and too many ESPs and network providers pay way to much attention to complaints. The argue ISPs should remove these buttons and stop paying attention to what recipients think.
Sadly, I’m not actually making up the terminology in the last paragraph. There really are who think that the problem isn’t with the mail that they’re sending but that the recipients can actually express an opinion about it and the ISPs listen to those opinions. “Terrorists” and “Nazis” are the least of the things they have called people who complain about their mail.
One of the senior engineers at Cloudmark recently posted an article talking about FBLs and “this is spam” buttons. I think it’s a useful article to read as it explains what value FBLs play in helping spam filters become more accurate.
Filtering adjustments at Hotmail
- laura
- Apr 12, 2011
I’ve been seeing a lot of discussion on various fora recently about increased delivery issues at Hotmail. Some senders are seeing more deferrals, some senders are seeing more mail in the bulk folder. Some senders aren’t seeing any changes.
This leads me to believe that Hotmail made some adjustments to their filtering recently. Given some senders are unaffected, this appears to be a threshold change or a calculation change, tightening up their standards. The changes have been around for long enough now it does look like the filtering is working as intended and Hotmail is not going to roll these changes back.
So what can you do to fix delivery of mail that was good enough at Hotmail a few weeks ago and now isn’t?
Real. Or. Phish?
- steve
- Apr 6, 2011
After Epsilon lost a bunch of customer lists last week, I’ve been keeping an eye open to see if any of the vendors I work with had any of my email addresses stolen – not least because it’ll be interesting to see where this data ends up.
Yesterday I got mail from Marriott, telling me that “unauthorized third party gained access to a number of Epsilon’s accounts including Marriott’s email list.”. Great! Lets start looking for spam to my Marriott tagged address, or for phishing targeted at Marriott customers.
I hit what looks like paydirt this morning. Plausible looking mail with Marriott branding, nothing specific to me other than name and (tagged) email address.
It’s time to play Real. Or. Phish?
1. Branding and spelling is all good. It’s using decent stock photos, and what looks like a real Marriott logo.
All very easy to fake, but if it’s a phish it’s pretty well done. Then again, phishes often steal real content and just change out the links.
Conclusion? Real. Maybe.
2. The mail wasn’t sent from marriott.com, or any domain related to it. Instead, it came from “Marriott@marriott-email.com”.
This is classic phish behaviour – using a lookalike domain such as “paypal-billing.com” or “aolsecurity.com” so as to look as though you’re associated with a company, yet to be able to use a domain name you have full control of, so as to be able to host websites, receive email, sign with DKIM, all that sort of thing.
Conclusion? Phish.
3. SPF pass
Given that the mail was sent “from” marriott-email.com, and not from marriott.com, this is pretty meaningless. But it did pass an SPF check.
Conclusion? Neutral.
4. DKIM fail
Authentication-Results: m.wordtothewise.com; dkim=fail (verification failed; insecure key) header.i=@marriott-email.com;
As the mail was sent “from” marriott-email.com it should have been possible for the owner of that domain (presumably the phisher) to sign it with DKIM. That they didn’t isn’t a good sign at all.
Conclusion? Phish.
5. Badly obfuscated headers
From: =?iso-8859-1?B?TWFycmlvdHQgUmV3YXJkcw==?= <Marriott@marriott-email.com>
Subject: =?iso-8859-1?B?WW91ciBBY2NvdW50IJYgVXAgdG8gJDEwMCBjb3Vwb24=?=
Base 64 encoding of headers is an old spammer trick used to make them more difficult for naive spam filters to handle. That doesn’t work well with more modern spam filters, but spammers and phishers still tend to do it so as to make it harder for abuse desks to read the content of phishes forwarded to them with complaints. There’s no legitimate reason to encode plain ascii fields in this way. Spamassassin didn’t like the message because of this.
Conclusion? Phish.
6. Well-crafted multipart/alternative mail, with valid, well-encoded (quoted-printable) plain text and html parts
Just like the branding and spelling, this is very well done for a phish. But again, it’s commonly something that’s stolen from legitimate email and modified slightly.
Conclusion? Real, probably.
7. Typical content links in the email
Most of the content links in the email are to things like “http://marriott-email.com/16433acf1layfousiaey2oniaaaaaalfqkc4qmz76deyaaaaa”, which is consistent with the from address, at least. This isn’t the sort of URL a real company website tends to use, but it’s not that unusual for click tracking software to do something like this.
Conclusion? Neutral
8. Atypical content links in the email
We also have other links:
Does your unsubscribe process work? Are you sure?
- steve
- Mar 30, 2011
I stumbled across an interesting problem today.
A company I bought something from a while back added me to their newsletter. They seem to be having trouble making sales this quarter, as they’ve gone from an occasional email every few weeks to bombarding me with increasingly desperate offers in the past week or two. So I do what most recipients do in that situation (well, the ones who don’t just mark the mail as spam, anyway). I click the unsubscribe link.
I get a perfectly normal, standard unsubscription page, with a nice, prominent “Unsubscribe from all” button with good text explaining that that will remove me from all of the companies mailing lists. No requirements to log in, set dozens of checkboxes or provide a password I don’t have. So far this is a textbook example of a good unsubscription process.
I click the button. Nothing happens. That’s not good.
So I grab one of the people I know over at that ESP and we start looking at it. He clicks the button, and it loads a new page saying that I’ve been unsubscribed from all of the companies mailing lists.
A bit more testing shows that the unsubscription works if you use Internet Explorer or Firefox, but not if you use Safari. The cause of the bug was threefold:
Getting it so wrong
- laura
- Mar 22, 2011
One of the things I notice is when vendors send me badly formatted emails. There’s one vendor of ours that gets it so wrong I find it offensive to receive their mails. Not only have they not managed to invoice or process payments correctly for months, but their billing emails come to me with one of the ugliest From: lines I’ve ever seen.
Now, I’ve seen Dave Crocker’s lectures on email address. I believe that technically this is a legal From: address. But, seriously? I’m amazed they ever get mail delivered.
“COMPANY <Firstname.Lastname”@company.com
Yes, I changed the name to protect the stupid.
I tried to reply to the email address and my mail client tells me “this does not appear to be a valid email address.” Well, no. No it doesn’t. But let’s try anyway.
And there’s the bounce. “Invalid address!!!”.
This vendor is sending out invoices with totally broken From: address. I wonder how many of their customers are not getting an actual invoice from them?
But, being the helpful person I am, I actually mailed the person and pointed out that their From: address was horribly broken and may be negatively impacting their delivery. I’m not expecting an answer, but at least I have done my good deed for the day.
As part of the deployment process of any new email system you should check to make sure the address is correct and people can reply to it. That single test “reply to mail” would have identified this problem 5 months ago and not taken one of their recipients to point it out to them.
Multipart MIME cheat sheet
- steve
- Mar 14, 2011
I’ve had a couple of people ask me about MIME structure recently, especially how you create multipart messages, when you should use them and which variant of multipart you use for different things. (And I’m working on a MIME parser / generator for Abacus at the moment, so it’s all fresh in my mind)
So I’ve put together a quick cheat sheet, showing the structure of four common types of email, and how their MIME structure looks.
Guaranteed email delivery
- laura
- Mar 11, 2011
Ben over at Mailchimp has a good post about his response (and his support staff’s more professional and helpful response) to inquires asking if Mailchimp can guarantee an improvement in delivery.
I sympathize with Ben, and commend his staff. I often get potential clients asking me if I can guarantee I can get their mail to the inbox or get them off a public or private blocklist. And, the answer really is no, I can’t guarantee anything. Much of delivery is solely in the hands of the actual sender. Sure, ESPs can enforce a certain standard of behaviour and they can do all the technical things right. And consultants like me can tell you how ISP spam filters work and explain how some of your choices and processes affect delivery. But none of us can guarantee inbox delivery.
Only one company has tried to guarantee inbox delivery, and they shut down earlier this year because they were non-viable and couldn’t get enough of a recipient userbase to attract customers.
For the rest of us, though, the best we can do is give senders the tools and information they need to succeed in getting mail delivered to the inbox.
Permission-ish based marketing
- steve
- Mar 10, 2011
My Mum flew in to visit last week, and over dinner one evening the talk turned to email.
Read MoreWhy is shared hosting like phishing?
- steve
- Jan 26, 2011
A client of a friend was getting rejection messages when they tried to send mail
Read MoreConversational foreplay
- laura
- Jan 13, 2011
How do you approach the first contact with a potential customer or prospect? Do you just jump right in and start making your pitch or do you actually take the time to introduce yourself and your company?
Most good sales reps spend a little time socializing with prospects before they launch into the sales process, particularly when they are cold calling the target. This courtesy doesn’t seem to apply when cold emailing a prospect, though.
I can only imagine how Al might have reacted differently if Douglas Karr had sent a personal contact and introduced himself instead of sending out bulk mail. I know for a fact I would have reacted very differently to the email sent to my LinkedIn account address had it been even vaguely personalized and interested in me.
We even have ESPs getting into the sending cold email game. A reasonably well know ESP added me to their mailing list and sent me an advertisement for a free service they’re providing at Marketing Sherpa this year. I was grumbling about spam to a group of friends, one of whom happens to be their delivery guy. He asked for a copy and spent time chasing down how they got the address.
Evidently I sent mail to the privacy manager who left the company over 2 years ago. That puts me in the “prospect” database. Well, OK, maybe. But there are some many better ways to reactivate a prospect than just adding me to their newsletter. Would it really have taken so much work to send me a personal note from the sales person? It doesn’t have to be very long, just introducing the sales person and telling me they’d seen my inquiry about product and asking if they could talk to me about their offerings.
Had this ESP spent a little time to cultivate me, my response would have been totally different. I could have referred customers to them and given them the name of the sales person that was so helpful and respectful of me and my time. That’s not what they did. In a fit of insouciance they just grabbed a 2+ year old email address and added it to their mailing list. They didn’t bother to tell me why or introduce it to me gently.
Seriously, folks, email is about relationships. Adding someone to a mailing list without their knowledge or permission is a really, really bad way to start a relationship. Show a little respect to your prospects. Send welcome messages, even an automated one, before adding just discovered prospect addresses to mailing lists.
Some thoughts on permission
- laura
- Jan 11, 2011
A lot of email marketing best practices center around getting permission to send email to recipients. A lot of anti-spammers argue that the issue is consent not content. Both groups seem to agree that permission is important, but more often than not they disagree about what constitutes permission.
For some the only acceptable permission is round trip confirmation, also known as confirmed opt-in or double opt-in.
For others making a purchase constitutes permission to send mail.
For still others checking or unchecking a box on a signup page is sufficient permission.
I don’t think there is a global, over arching, single form of permission. I think context and agreement matters. I think permission is really about both sides of the transaction knowing what the transaction is. Double opt-in, single opt-in, check the box to opt-out area all valid ways to collect permission. Dishonest marketers can, and do, use all of these ways to collect email addresses.
But while dishonest marketers may adhere to all of the letters of the best practice recommendations, they purposely make the wording and explanation of check boxes and what happens when confusing. I do believe some people make the choices deliberately confusing to increase the number of addresses that have opted in. Does everyone? Of course not. But there are certainly marketers who deliberately set out to make their opt-ins as confusing as possible.
This is why I think permission is meaningless without the context of the transaction. What did the address collector tell the recipient would happen with their email address? What did the address giver understand would happen with their email address? Do these two things match? If the two perceptions agree then I am satisfied there is permission. If the expectations don’t match, then I’m not sure there is permission involved.
What are your thoughts on permission?
Broken signup processes
- laura
- Dec 22, 2010
DJ Waldow wrote a post on explicit permission over on Mediapost. I think he hit on some interesting bits and wanted to comment on them. In order to comment on a Mediapost blog, you have to register.
I’ve thought about it before, but every time I start the process I get to the page asking for detailed demographic information and decide no. This time, I was inspired enough by DJ to get to the second page of the signup process. This requires me to identify what type of marketing I’m interested in and won’t let me past the page until I click something. I’m not interested in anything, so I close the webpage. I can always write my own blog post responding to DJ.
I return to my inbox to discover a welcome message from Mediapost. It seems I am now a member and will be receiving email and specials and all the stuff I didn’t want from them.
This isn’t unusual. There are tons of websites on the net that don’t require you to complete a signup process in order to be added to their database. One of the worst I experienced was 1-800-Pet-Meds. They added me to their database when I abandoned a cart (what I wanted required a prescription from them, whereas I could just go into my vet’s and pick it up, so I’ll just pay the vet’s prices). They added me to their mailing list and couldn’t unsubscribe me because I was not in their customer database. Everything was done with the magic order number, which I didn’t have because I never ordered with them. That was fun to sort out.
It’s a bad idea to add people who don’t complete the signup or purchase process to your mailing lists. If you’re worried about losing a potential customer, then you can send mail reminding them to complete the process (or purchase). If you’re very into customer service, you can ask them if they are interested in future specials from you: would you like to opt-in to our mailing list anyway? Or you can give them the opportunity to remove their information from your database.
TWSD: lie about the source of address
- laura
- Dec 14, 2010
A few months ago I got email from Staff of Norman Rockwell Museum of Vermont, to an addresses scraped off one of my websites. At the bottom it says:
Read MoreRelevance or Permission
- laura
- Nov 16, 2010
One of the discussions that surrounds email marketing is whether relevance trumps permission or permission trumps relevance. I believe this entire discussion is built on a false dichotomy.
Sending relevant email is important. Not only do recipients expect mail to be relevant, but the ISPs often make delivery decisions on how relevant their users find your mail. Marketers that send too much irrelevant mail find themselves struggling to get inbox placement.
Permission makes sending relevant mail all that much easier. Sure, really good marketers can probably collect, purchase, beg, borrow and steal enough information to know that their unsolicited email is relevant. But how many marketers are actually that good?
My experience suggest that most marketers aren’t that good. They don’t segment their permission based lists to send relevant mail. They’re certainly not going to segment their non-permission based lists to send relevant mail.
Macy’s, for instance, decided that I would find their Bloomingdales mail relevant. I didn’t, and unsubscribed from both publications, after registering a complaint with their ESP. Had Macy’s asked about sending me Bloomies mail I wouldn’t have opted-in, but I probably wouldn’t have unsubbed from Macy’s mail, too.
So what’s your stand? Does relevance trump permission? Or does permission trump relevance? How much relevant, unsolicited mail do you get? How much irrelevant permission based mail do you get? And what drives you to unsubscribe from a permission based list?
Best practices: a meaningless term
- laura
- Nov 10, 2010
Chad White wrote an article for MediaPost about best practices which parallels a lot of thinking I’ve been doing about how the email marketing industry treats best practices.
Read MoreThe myth of the low complaint rate
- laura
- Nov 4, 2010
I have been reading the complaints filed by Holomaxx and will have some analysis and information about them probably Monday or Tuesday next week. I’ve been keeping an eye on the press and something that Ken Magill said caught my eye.
Read MoreEmail appending
- laura
- Nov 2, 2010
Mickey talks about appending and why it’s not a good practice.
Read MoreDon't be Amelia
- laura
- Oct 29, 2010
I have an adorable cat that I ‘taught’ that I would pet her if she tapped me on the arm or shoulder with her paw. It was cute for a while, but then she got more and more demanding. Eventually, she was clawing at my clothes and skin to get attention and petting.
It’s gotten to the point where I have to put a stop to it. She’s just getting too destructive to me and my clothing. So over the last two weeks I’ve been trying to only reward those touches that don’t involve claws and giving her a stern “NO CLAWS” when she does try to claw me.
As I was sitting here this afternoon, going through yet another round of NO CLAWS with her, I realized that my interactions with her were eerily similar to email marketing.
You see, Amelia started using her claws to get my attention because I didn’t always respond to her gentle taps. But claws hurt, and were a problem, so I would respond. This is exactly like marketers who don’t see a response to their email marketing campaigns and thus up the aggressiveness of those campaigns. More mail, more frequency, stronger offers, anything to get a response out of recipients.
Eventually, though, the recipient finally gets annoyed. The aggressive “taps” result in spam complaints. The sender has pushed the recipient from “it’s not so bad” to “make this sender stop bugging me.”
Email marketing is interruption marketing and there is only so much recipients will tolerate. And, trust me, few email marketers are as cute as my Amelia Cat.
Broken Policies
- laura
- Oct 22, 2010
As an email policy wonk, I think a lot about how specific policy implementations can go wrong. Sure, every policy can go wrong, or not fit a common case. A lot of people only write polices that address common cases and don’t worry about the rarer cases. The problem is there are some rare cases that may cause significant harm and those cases should be addressed.
Consumerist has a case up about email policy gone wrong with a clear path to harm but no policy for handling the issue. There are a couple places I see where this policy hole can be fixed.
Chase Bank does no verification when they collect email addresses, which results in them sending email to a person who does not have an account with Chase. This is not an ideal situation for anyone. Chase is revealing private financial information to an outside party, the actual bank customer is not getting their information and someone is getting email about money that’s not theirs.
In terms of policy for institutions handling sensitive personal information, I would always recommend implementing a verification step. This is mail that people want so they should confirm it. It’s also mail that really should be not going to 3rd parties.
Chase does not implement any verification step for email. This isn’t a fatal problem, as long as there is some process in place to get feedback and then correct the issue.
Unfortunately, Chase’s policies failed here, too. Chase requires an account number to speak to a representative about any issues. In this case, the email recipient does not have an account number. All of Chase’s contact channels rely on an account number: no account number, no talking to a human.
In terms of overall policy Chase is hoping here is that, at some point, their actual customer will notice they’re not getting email and call in and attempt to troubleshoot the problem with Chase reps. I’m willing to bet, though, that their tier 1 people don’t have the training or information needed to troubleshoot this problem. I expect they’re going to read the script that says, “We sent you the mail, it must be a problem on your end. Have a nice day.”
Chase, and other bank analogues that require an account number, that do not verify email addresses should not require account numbers to talk to someone about the mail they are receiving. Why? Because although it’s reasonably rare that the mail is going to the wrong party, the potential harm to the bank’s customer is very high. This danger to customers means the bank should invest in a support pathway that allows non-customers to call, or write, to report misdirected email.
If Chase were my customer, I’d recommend adding a button to the email that says “receiving this mail in error, report here.” Make this a simple form that the recipient can fill out, two boxes one for email address and one optional one for “reason”. Once the bank has the report, they can stop the misdirected email and attempt to contact the customer through another channel. I’d also recommend that customers confirm any new address they add to the account in the future.
I know the bank thinks that by requiring an account number they are protecting their customers. Unfortunately, they’re failing to address a rare but potentially harmful case. Sadly, I expect even after this, they will still fail to implement any changes that will stop this from happening in the future.
Clicktracking 2: Electric Boogaloo
- steve
- Oct 21, 2010
A week or so back I talked about clicktracking links, and how to put them together to avoid abuse and blocking issues.
Since then I’ve come across another issue with click tracking links that’s not terribly obvious, and that you’re not that likely to come across, but if you do get hit by it could be very painful – phishing and malware filters in web browsers.
First, some background about how a lot of malware is distributed, what’s known as “drive-by malware”. This is where the hostile code infects the victims machine without them taking any action to download and run it, rather they just visit a hostile website and that website silently infects their computer.
The malware authors get people to visit the hostile website in quite a few different ways – email spam, blog comment spam, web forum spam, banner ads purchased on legitimate websites and compromised legitimate websites, amongst others.
That last one, compromised legitimate websites, is the type we’re interested in. The sites compromised aren’t usually a single, high-profile website. Rather, they tend to be a whole bunch of websites that are running some vulnerable web application – if there’s a security flaw in, for example, WordPress blog software then a malware author can compromise thousands of little blog sites, and embed malware code in each of them. Anyone visiting any of those sites risks being infected, and becoming part of a botnet.
Because the vulnerable websites are all compromised mechanically in the same way, the URLs of the infected pages tend to look much the same, just with different hostnames – http://example.com/foo/bar/baz.html, http://www.somewhereelse.invalid/foo/bar/baz.html and http://a.net/foo/bar/baz.html – and they serve up just the same malware (or, just as often, redirect the user to a site in russia or china that serves up the malware that infects their machine).
A malware filter operator might receive a report about http://example.com/foo/bar/baz.html and decide that it was infected with malware, adding example.com to a blacklist. A smart filter operator might decide that this might be just one example of a widespread compromise, and go looking for the same malware elsewhere. If it goes to http//a.net/foo/bar/baz.html and finds the exact same content, it’ll know that that’s another instance of the infection, and add a.net to the blacklist.
What does this have to do with clickthrough links?
Well, an obvious way to implement clickthrough links is to use a custom hostname for each customer (“click.customer.com“), and have all those pointing at a single clickthrough webserver. It’s tedious to setup the webserver to respond to each hostname as you add a new customer, though, so you decide to have the webserver ignore the hostname. That’ll work fine – if you have customer1 using a clickthrough link like http://click.customer1.com/123/456/789.html you’d have the webserver ignore “click.customer1.com” and just read the information it needs from “123/456/789.html” and send the redirect.
But that means that if you also have customer2, using the hostname click.customer2.com, then the URL http://click.customer2.com/123/456/789.html it will redirect to customer1’s content.
If a malware filter decides that http://click.customer1.com/123/456/789.html redirects to a phishing site or a malware download – either due to a false report, or due to the customers page actually being infected – then they’ll add click.customer1.com to their blacklist, meaning no http://click.customer1.com/ URLs will work. So far, this isn’t a big problem.
But if they then go and check http://click.customer2.com/123/456/789.html and find the same redirect, they’ll blacklist click.customer2.com, and so on for all the clickthrough hostnames of yours they know about. That’ll cause any click on any URL in any email a lot of your customers send out to go to a “This site may harm your computer!” warning – which will end up a nightmare even if you spot the problem and get the filter operators to remove all those hostnames from the blacklist within a few hours or a day.
Don’t let this happen to you. Make sure your clickthrough webserver pays attention to the hostname as well as the path of the URL.
Use different hostnames for different customers clickthrough links. And if you pick a link from mail sent by Customer A, and change the hostname of that link to the clickthrough hostname of Customer B, then that link should fail with an error rather than displaying Customer A’s content.
Would you buy a used car from that guy?
- laura
- Oct 20, 2010
There are dozens of people and companies standing up and offering suggestions on best practices in email marketing. Unfortunately, many of those companies don’t actually practice what they preach in managing their own email accounts.
I got email today to an old work email address of mine from Strongmail. To be fair it was a technically correct email. Everything one would expect from a company handling large volumes of emails. It’s clear that time and energy was put into the technical setup of the send. If only they had put even half that effort into deciding who to send the email to. Sadly, they didn’t.
My first thought, upon receiving the mail, was that some new, eager employee bought a very old and crufty list somewhere. Because Strongmail has a reputation for being responsible mailers, I sent them a copy of the email to abuse@. I figured they’d want to know that they had a new sales / marketing person who was doing some bad stuff.
I know how frustrating handling abuse@ can be, so I try to be short and sweet in my complaints. For this one, I simply said, “Someone at Strongmail has appended, harvested or otherwise acquired an old email address of mine. This has been added to your mailing list and I’m now receiving spam from you. ”
They respond with an email that starts with:
“Thank you for your thoughtful response to our opt-in request. On occasion, we provide members of our database with the opportunity to opt-in to receive email marketing communications from us.”
Wait. What? Members of our database? How did this address get into your database?
“I can’t be sure from our records but it looks like someone from StrongMail reached out to you several years ago. It’s helpful that you let us know to unsubscribe you. Thank you again.”
There you have it. According to the person answering email at abuse@ Strongmail they sent me a message because they had sent mail to me in the past. Is that really what you did? Send mail to very old email addresses because someone, at some point in the past, sent mail to that address? And you don’t know when, don’t know where the address came from, don’t know how it was acquired, but decided to reach out to me?
How many bad practices can you mix into a single send, Strongmail? Sending mail to addresses where you don’t know how you got them? Sending mail to addresses that you got at least 6 years ago? Sending mail to addresses that were never opted-in to any of your mail? And when people point out, gently and subtly, that maybe this is a bad idea, you just add them to your global suppression list?
Oh. Wait. I know what you’re going to tell me. All of your bad practices don’t count because this was an ‘opt-in’ request. People who didn’t want the mail didn’t have to do anything, therefore there is no reason not to spam them! They ignore it and they are dropped from your list. Except it doesn’t work that way. Double opt-in requests to someone has asked to be subscribed or is an active customer or prospect is one thing. Requests sent to addresses of unknown provenance are still spam.
Just for the record, I have a good idea of where they got my address. Many years ago Strongmail approached Word to the Wise to explore a potential partnership. We would work with and through Strongmail to provide delivery consulting and best practices advice for their customers. As part of this process we did exchange business cards with a number of Strongmail employees. I suspect those cards were left in a desk when the employees moved on. Whoever got that desk, or cleaned it out, found those cards and added them to the ‘member database.’
But wait! It gets even better. Strongmail was sending me this mail, so that they could get permission to send me email about Email and Social Media Marketing Best Practices. I’m almost tempted to sign up to provide me unending blog fodder for my new series entitled “Don’t do this!”
Spam is not a marketing strategy
- laura
- Oct 19, 2010
Unfortunately, this fact doesn’t stop anyone from spamming as part of their marketing outreach. And it’s not just email spam. I get quite a bit of blog spam, most of which is caught by Akismet. Occasionally, though, there’s spam which isn’t caught by the filter and ends up coming to me for approval.
Many of these are explanations of why email marketing is so awesome. Some of them are out and out laugh inducing. One of my favorites, and the inspiration for this post.
Clicktracking link abuse
- steve
- Oct 11, 2010
If you use redirection links in the emails you send out, where a click on the link goes to your server – so you can record that someone clicked – before redirecting to the real destination, then you’ve probably already thought about how they can be abused.
Redirection links are simple in concept – you include a link that points to your webserver in email that you send out, then when recipients click on it they end up at your webserver. Instead of displaying a page, though, your webserver sends what’s called a “302 redirect” to send the recipients web browser on to the real destination. How does your webserver know where to redirect to? There are several different ways, with different tradeoffs:
Blasting the message!
- laura
- Sep 28, 2010
Sending frequency is an important part of any email campaign. Too little mail and recipients forget about the mail and don’t open it when it does arrive. Too much mail and folks start complaining, like John Cole over at Balloon Juice.
Read MoreKnow your target audience…
- steve
- Sep 28, 2010
… and the device they’re probably going to read your email on.
@lauter from MailChimp points and laughs at an advertising email from Blackberry-the-company that’s completely unreadable when read on Blackberry-the-device.
That’s really bad marketing on a bunch of different levels.
Beware the TINS Army
- laura
- Sep 24, 2010
When consulting with clients, I spend a lot of time trying to help them better understand the concept of sender reputation. Spam reports, feedback loops, and other data that comes from a collection of positive and negative reputational feedback about a company sending email.
Certainly, the “This is not spam” action – moving an email from the spam folder to the inbox, or clicking the “not spam” button in a web mail’s interface, is a strong positive reputational action. Some webmail providers use this data to decide which bulked senders deserve being let out of the penalty box – which should have their mail once again delivered to the inbox.
A client recently theorized that a great solution to their delivery problems would be to do this “en masse.” Sign up for hundreds or thousands of webmail accounts, send my mail to them, and click on the “not spam” button for each of my own emails. That’ll greatly improve my sending reputation, right?
NO! ISPs have already thought of this. They watch for this. They’re really good at picking up on things like this. I know for a fact that Yahoo and Hotmail and AOL notice stuff like this, and I strongly suspect other webmail providers notice it as well.
What happens when Yahoo or Hotmail pick up on this type of unwanted activity? Well, if it’s at Yahoo, they’re likely to block all mail from you, 100%, forever. I’ve seen it happen more than once. Yahoo might even identify all of your netblocks, ones beyond the ones sending today’s mail or originating today’s activity. And good luck trying to convince them that you’re not a spammer – you have a better chance of winning the lottery two weeks in a row.
As for Hotmail – what would Hotmail do? Ask Boris Mizhen. Microsoft is currently suing him, alleging that he and/or his agents or associates engaged in this very practice.
Spam isn't a best practice
- laura
- Sep 23, 2010
I’m hearing a lot of claims about best practices recently and I’m wondering what people really mean by the term. All too often people tell me that they comply with “all best practices” followed by a list of things they do that are clearly not best practices.
Some of those folks are clients or sales prospects but some of them are actually industry colleagues that have customers sending spam. In either case, I’ve been thinking a lot about best practices and what we all mean when we talk about best practices. In conversing with various people it’s clear that the term doesn’t mean what the speakers think it means.
For me, best practice means sending mail in a way that create happy and engaged recipients. There are a lot of details wrapped up in there, but all implementation choices stem from the answer to the question “what will make our customers happy.” But a lot of marketers, email and otherwise, don’t focus on what makes their recipients or targets happy.
In fact, for many people I talk to when they say “best practice” what they really mean is “send as much mail as recipients will tolerate.” This isn’t that surprising, the advertising and marketing industries survive by pushing things as far as the target will tolerate (emphasis added).
Guide to resolving ISP issues
- laura
- Sep 14, 2010
I often get a chuckle out of watching some people, who are normally on the blocking end of the delivery equation, struggle through their own blocking issues. A recent situation came up on a mailing list where someone who has very vehement opinions about how to approach her particular blocklist for delisting and that the lists policies are immutable. The company she works for is having some delivery issues and she’s looking for a contact to resolve the issues.
While digging through my blog posts to see if there was any help I could provide, I realized I don’t have a guide to resolving blocking issues at ISPs. Much of the troubleshooting can be done without ever contacting the ISPs or the blocklists.
Identify the issue.
There are a number of techniques that ISPs use to protect their users from malicious or problematic mail, from rate-liming incoming mail, putting mail in the bulk folder, or blocking specific IP addresses. Step one to resolving any delivery problem is to identify what is happening to the mail. In order to resolve the issue, you have to know what the issue is.
All too often, the description of a delivery problem is: My mail isn’t getting delivered. But that isn’t very clear as to what the actual problem is. Are you being temp failed? Is mail being blocked? Is mail going to the bulk folder? Is this something affecting just you or is it a widespread problem?
Troubleshoot your side.
Collect as much data about the problem as you can. Dig through logs and get copies of any rejection messages. Follow any URLs that are present in the bounce messages. Try sending a bare bones email to yourself at that ISP with just URLs, is it still blocked? What if you send from a different IP, does the same thing happen?
There is a lot of troubleshooting a sender can do without having to contact an ISP, and the information can lead to resolution that doesn’t involve having to contact the ISP. Also, many current ISP blocks are dynamic, they come up and go down without any human intervention. Those blocks that require contact to get them resolved have clear instructions in the bounce message.
Fix your stuff.
Whether it’s a reputation issue or a minor technical issue, fix the problem on your end. Just moving IP addresses or changing a URL isn’t a sustainable fix. There is a reason mail is being blocked or filtered and if you don’t fix that issue, the blocks are just going to come back. After you do fix your stuff, expect to see changes in a few days or a week. The ISP filters are generally quite responsive to sender improvements so if you’ve fixed the stuff you should see changes pretty quickly. Expect unblocking or filtering to take a little longer than the block was in place.
If you can’t figure out what the problem is, hire a consultant. Here at Word to the Wise we can often quickly identify a problem and provide a path to resolution. Sometimes the problem isn’t even the ISPs, we’ve had multiple cases where our clients were using custom software and their software wasn’t SMTP compliant and we were able to identify the problem and get their mail working again. There are a host of other independent consultants out there that can also help you identify and resolve blocking problems.
Contact the ISPs.
If there is a hard block or after fixing what you think the underlying problem is, you’ll have to contact the ISP. Many ISPs provide self service websites and contact forms to facilitate this process. Generally, though, most issues aren’t going to require contact.
Stop SHOUTING
- steve
- Sep 8, 2010
The nice folks at Box of Meat pointed me at an article about SHOUTING in ALL CAPITALS.
Read MoreContent based filtering
- steve
- Sep 7, 2010
A spam filter looks at many things when it’s deciding whether or not to deliver a message to the recipients inbox, usually divided into two broad categories – the behaviour of the sender and the content of the message.
When we talk about sender behaviour we’ll often dive headfirst into the technical details of how that’s monitored and tracked – history of mail from the same IP address, SPF records, good reverse DNS, send rates and ramping, polite SMTP level behaviour, DKIM and domain-based reputation and so on. If all of those are OK and the mail still doesn’t get delivered then you might throw up your hands, fall back on “it’s content-based filtering” and not leave it at that.
There’s just as much detail and scope for diagnosis in content-based filtering, though, it’s just a bit more complex, so some delivery folks tend to gloss over it. If you’re sending mail that people want to receive, you’re sure you’re sending the mail technically correctly and you have a decent reputation as a sender then it’s time to look at the content.
You want your mail to look just like wanted mail from reputable, competent senders and to look different to unwanted mail, viruses, phishing emails, botnet spoor and so on. And not just to mechanical spam filters – if a postmaster looks at your email, you want it to look clean, honest and competently put together to them too.
Some of the distinctive content differences between wanted and unwanted email are due to the content as written by the sender, some of them are due to senders of unwanted email trying to hide their identity or their content, but many of them are due to the different quality software used to send each sort of mail. Mail clients used by individuals, and content composition software used by high quality ESPs tends to be well written and complies with both the email and MIME RFCs, and the unwritten best common practices for email composition. The software used by spammers, botnets, viruses and low quality ESPs tends not to do so well.
Here’s a (partial) list of some of the things to consider:
Email marketing is hard
- laura
- Aug 30, 2010
I’ve watched a couple discussions around the email and anti-spam community recently with a bit of awe. It seems many email marketers are admitting they are powerless to actually implement all the good advice they give to others.
They are admitting they can’t persuade, cajole, influence or pressure their companies to actually follow best practices. Some of the comments public and private comments I’ve heard from various industry leaders:
How not to build a mailing list
- laura
- Aug 17, 2010
I mentioned yesterday one of the major political blogs launched their mailing list yesterday. I pointed out a number of things they did that may cause problems. Today, I discovered another problem.
This particular blog has been around for a long time, probably close to 10 years. It allows anyone to join and create their own blogs and comment with registered users. As part of their new mailing list, they added everyone who has ever registered to their mailing list. They did not send a “we have a new list, want to join it?” email, they added every registered user to the list and said “you can opt out if you want.”
This is such a bad idea. My own account was used once, to make one comment, back in 2005. Yes, 2005. It’s been almost 5 years since I last logged into the site. Sure, I have email addresses that go back that far, but not everyone does. That list is going to be full of problems: dead addresses, spamtraps, duplicates, unengaged and uninterested.
Seriously, they’re adding people who’ve not logged into their site in 5 years to a mailing list. How can this NOT go horribly wrong?
My initial thought was this was going to blow up in a week. I’m now guessing they’ll start seeing delivery problems a lot sooner than that.
Email and politics
- laura
- Aug 16, 2010
I occasionally consult for activists using email. Their needs and requirements are a little different from email marketers. Sure, the requirements for email delivery are the same: relevant and engaging mail to people who requested it. But there are complicating issues that most marketers don’t necessarily have to deal with.
Activist groups are attractive targets for forged signups. Think about it, when people get deeply involved in arguments on the internet, they often look for ways to harass the person on the other end of the disagreement. They will often signup the people they’re disagreeing with for mailing lists. When the disagreements are political, the logical target is a group on the other side of the political divide.
People also sign up spamtraps and bad addresses as a way to cause problems or harass the political group itself. Often this results in the activist group getting blocked. This never ends well, as instead of fixing the problem, the group goes yelling about how their voice is being silenced and their politics are being censored!!
No, they’re not being silenced, they’re running an open mailing list and a lot of people are on it who never asked to be on it. They’re complaining and the mail is getting blocked.
With that as background, I noticed one of the major political blogs announced their brand new mailing list today. Based on their announcement it seemed they that they may have talked to someone who knew about managing a mailing list.
Should you respond to complaints
- laura
- Aug 13, 2010
Should you ever contact someone who made an abuse complaint about your newsletter to find out why
Read More
SPF records: not really all that important
- laura
- Aug 11, 2010
I’ve been working through some Hotmail issues with a client over the last few months. One of the things that has become clear to me is how little Hotmail actually does with SPF records. In fact, Hotmail completely ignored my client’s SPF record and continued to deliver email into the inbox.
This isn’t just a sender that had a “well, we think most of our email will come from these IPs but aren’t telling you to throw away email that doesn’t” record. In fact, this client specifically said “if email doesn’t come from this /28 range of email addresses, then it is unauthorized and should be thrown away.” The email was being sent from an IP outside of the range listed in the SPF record.
As part of the process involved in fixing the delivery problems, I had the client update their SPF record and then I enrolled their domain in the SenderID program at Hotmail. This didn’t have any effect, though. Hotmail is still not checking SPF for this client. When I asked Hotmail what was going on they said, “We do not do lookups on every sender’s mail.”
So, there you have it folks. The last bastion of SPF/SenderID has abandoned the technology. Even a totally invalid SPF record doesn’t matter, mail can still reach the inbox at Hotmail.
Poor delivery can't be fixed with technical perfection
- laura
- Aug 4, 2010
There are a number of different things delivery experts can do help senders improve their own delivery. Yes, I said it: senders are responsible for their delivery. ESPs, delivery consultants and deliverability experts can’t fix delivery for senders, they can only advise.
In my own work with clients, I usually start with making sure all the technical issues are correct. As almost all spam filtering is score based, and the minor scores given to things like broken authentication and header issues and formatting issues can make the difference between an email that lands in the inbox and one that doesn’t get delivered.
I don’t think I’m alone in this approach, as many of my clients come to me for help with their technical settings. In some cases, though, fixing the technical problems doesn’t fix the delivery issues. No matter how much my clients tweak their settings and attempt to avoid spamfilters by avoiding FREE!! in the subject line, or changing the background, they still can’t get mail in the inbox.
Why not? Because they’re sending mail that the recipients don’t really want, for whatever reason. There are so many ways a sender can collect an email address without actually collecting consent to send mail to that recipient. Many of the “list building” strategies mentioned by a number of experts involve getting a fig leaf of permission from recipients without actually having the recipient agree to receive mail.
Is there really any difference in permission between purchasing a list of “qualified leads” and automatically adding anyone who makes a purchase at a website to marketing lists? From the recipient’s perspective they’re still getting mail they don’t want, and all the technical perfection in the world can’t overcome the negative reputation associated with spamming.
The secret to inbox delivery: don’t send mail that looks like spam. That includes not sending mail to people who have not expressly consented to receive mail.
Check your assumptions
- laura
- Jul 27, 2010
One of the things that prompted yesterday’s post was watching a group of marketers discuss how to get subscribers to give them their “real” or “high value” email addresses. Addresses at free email providers are seen as less valuable than addresses at a place of employment or at a cable company or dialup ISP. The discussion centered around how to incentivize recipients to give up their “actual” email addresses.
The underlying belief is that users don’t use free mail accounts for their important mail, and if a recipient gives a marketer a free mail account as a signup that they will not be reading the mail regularly. Better to get an email address that the recipient checks frequently so there is a better chance at a conversion and sale.
Perfectly acceptable marketing goals, but makes a number of assumptions that I am not sure are valid.
Assumption 1: An email address at a freemail provider is less important to the recipient than a different email address.
Wrong! A sender has no idea if a recipient uses a freemail account exclusively or has another real email address. Many people these days use gmail as their primary account and they don’t check the email account associated with their dialup or broadband provider. For instance I have an email account at AT&T associated with our UVerse TV and internet service, but have never logged in to do anything with email.
Assumption 2: A non freemail address gives better response rates.
Really? I haven’t seen data one way or another saying that different classes of email addresses give better responses. It may be true, but it may not. Some users do have separate accounts for friends and family and marketing mail. In that case, are senders better off in the marketing account? Or in the F&F account where the user may hit the “this is spam” button just because that mail is in the wrong place?
Assumption 3: I’ve been invited in, I get free run of the place
Wrong! Just because you’ve been invited onto the front porch for a glass of lemonade, doesn’t mean you’re welcome in the bedroom. Marketing is all about pushing limits and getting more and more from recipients, but in email marketing the recipients get to hit the “this is spam” filter and stop delivery of that email. Limit pushing in email may result in all out blocks and zero inbox delivery, rather than causing a massive increase in sales.
Assumption 4: Incentivized permission is the same as real permission
Wrong! Just because a subscriber hits the “give me a coupon” or “enter me in the drawing” link does not mean they want mail from that sender. What it really means is the recipient wants a chance to win something or get $5 off their next purchase. Just because they closed the loop to get an incentive does not mean the sender gets a free pass through spam filters or is exempt from having their mail marked as spam.
The marketing relationship between sender and recipient is a lot more balanced than any other direct marketing relationship. The sender can’t ignore the recipients’ preferences over the long term without suffering delivery problems. Many email marketers, particularly those that didn’t start in email, forget that the relationship is different and marketers have to respect the recipient.
Thursday mini-audit part 2
- steve
- Jul 22, 2010
A week ago you signed up for your mailing list using a virgin email address. (You didn’t? Maybe you should do that today – there’s no time like Thursday for a quick sanity check!)
Check the mailbox for the account you signed up
Standard Email Metrics
- laura
- Jul 20, 2010
The EEC has been working on standardizing metrics used in email marketing. They have published a set of definitions for different terms many email marketers use. They published their Support the Adoption of Email Metrics (S.A.M.E) guide in June.
Under the new EEC definitions an open is measured when either a tracking pixel is displayed or a user clicks on any link in the email, including the unsubscribe link. Open rate is defined as the number of opens (either unique or total) divided by the number of accepted emails. Accepted emails equals the number of emails sent minus the number of emails rejected by the ISP for any reason.
The authors do caution, however, that even their measurements may under count the number of email subscribers that actually open or read an email. Some readers don’t load images or click on links but happily read and digest the content being sent. Others may not click on a link but actually visit a website or brick and mortar store to purchase something based on the email.
Overall, I think the definitions created by the S.A.M.E. group accurately reflect the things they want to measure within the limits of what is actually measurable. Their definitions won’t affect conversations in the short term, but are likely to drive change to standard terminology over the longer term. I do strongly encourage people to grab a copy of their document and see how their definitions compare with your current measurements.
What you should do Right Now – Thursday Mini-Audit
- steve
- Jul 15, 2010
… if your company runs any sort of email marketing, anyway.
Right now is the best time to do a mini-audit of your mail campaign. It’ll just take ten minutes, and if you put off doing it until tomorrow it’ll probably never get done.
Delivery consulting: it's all about the credibility
- laura
- Jul 14, 2010
A few months ago I found a great blog post written by an ER doctor about how to convince other doctors to come in and deal with a patient in the middle of the night. There are quite few similarities between his advice and the advice I would give delivery experts, ISP relations folks and ESP representatives when dealing with ISPs and spam filtering companies.
Read MoreI'm on a blocklist! HELP!
- laura
- Jul 13, 2010
Recently, an abuse desk rep asked what to do when customers were complaining about being assigned an IP address located on a blocklist. Because not every blocklist actually affects mail delivery it’s helpful to identify if the listing is causing a problem before diving in and trying to resolve the issue.
Read MoreTagged Email Addresses
- steve
- Jul 12, 2010
Sept 17, 2019: Shutting down comments on this post because we cannot help you recover any email account and I am concerned about the number of people who are providing PII (including phone numbers, credit card numbers!!! and email addresses) in the comments.
Read MoreAppendleads is not unusual
- laura
- Jul 9, 2010
I called out David Williams from appendleads.com yesterday for his spam. Sure he’s a spammer, his database is full of garbage information and his email violates CAN SPAM but he’s not that unusual in the realm of list sellers. He is very typical of the people I see offering lists for sale.
List sellers are the internet version of used car salesmen. Everyone knows they are slimy sales guys who will do anything to close the sale. They don’t have a real web presence, just visit appendleads.com and see what I mean.
And yet, people still buy lists from them! I have no doubt that my spammer friend has a nice little business selling email addresses. He sends out spam, he gets a few responses, makes a tidy profit and then sends out another spam, hooks a few more people and makes more money.
OK, so not all list sellers are like appendleads. Some of them go so far to build a website. But at the core they’re the same. They are selling data that isn’t clean, it’s not opt-in, it’s not been verified.
This is why so many of us harp on not buying lists. The sales guys talk a great game, but they aren’t selling what purchasers think they’re getting. They also don’t care. They have no incentive to clean up their data. They have no incentive to accurately represent what they’re selling. All of the risk is on the person that sends the email. Once they have their money, the buyer is on their own.
Can you ever successfully purchase a list? I’m sure some senders have. But that experience is closer to winning more than a thousand dollars in the lottery than an actual good business decision.
ESPs, Non-portable Reputation and Vendor Lock-in
- steve
- Jul 1, 2010
I’ve seen some mentions recently of ESPs suggesting that if you use your own domain in the From: of mail you send through an ESP then that ESP can’t “do email authentication” properly unless they require you to edit your domains DNS settings. That’s not really so, but there is a kernel of truth in there.
The real situation is, unsurprisingly, a bit more complicated.
What authentication features should you look for in an ESP?
Monitoring Email Deliverability
- laura
- Jun 22, 2010
I did an interview with Direct Mag recently about what I recommend mailers do to monitor email deliverability.
Read MoreYou might be a spammer if….
- laura
- Jun 21, 2010
You feel the need to add
PLEASE NOTE THAT THIS IS NOT A SPAM OR AUTOMATED EMAIL, IT’S ONLY A REQUEST FOR A LINK EXCHANGE. YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS HAS NOT BEEN ADDED TO ANY LISTS, AND YOU WILL NOT BE CONTACTED AGAIN.IF YOU’D LIKE TO MAKE SURE WE DON’T CONTACT YOU AGAIN, PLEASE FILL IN THE FOLLOWING FORM: <link>
Read More
PLEASE ACCEPT OUR APOLOGIES FOR CONTACTING YOU.
My ISP might get blacklisted
- steve
- Jun 11, 2010
The last of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreWho can you trust?
- laura
- Jun 2, 2010
I’ve been recently dealing with a client who is looking at implementing authentication on their domains. He’s done a lot of background research into the schemes and has a relatively firm grasp on the issue. At this point we’re working out what policies he wants to set and how to correctly implement those policies.
His questions were well informed for the most part. A few of them were completely out of left field, so I asked him for some of his references. One of those references was the EEC Email Authentication Whitepaper.
My client was doing the best he could to inform himself and relies on industry groups like the EEC to provide him with accurate information. In this case, their information was incomplete and incorrect.
We all have our perspectives and biases (yes, even me!) but there are objective facts that can be independently verified. For instance, the EEC Authentication whitepaper claimed that Yahoo requires DKIM signing for access to their whitelist program. This is incorrect, a sender does not have to sign with DKIM in order to apply for the Yahoo whitelist program. A bulk sender does have to sign with DKIM for a Y! FBL, but ISPs are given access to an IP based FBL by Yahoo. I am shocked that none of the experts that contributed to the document caught that error.
Independent verification is one reason I publish the Delivery Wiki. It’s a resource for everyone and a way to share my knowledge and thought processes. But other experts can “check my work” as it were and provide corrections if my information is outdated or faulty. All too often, senders end up blaming delivery problems on evil spirits, or using “dear” in the subject line or using too much pink in the design.
Delivery isn’t that esoteric or difficult if you have a clear understanding of the policy and technical decisions at a range of ESPs and ISPs, the history and reasoning behind those decisions, and enough experience to predict the implications when they collide.
Many senders do face delivery challenges and there is considerable demand for delivery experts to provide delivery facts. That niche has been filled by a mix of people, of all levels of experience, expertise and technical knowledge, leading to the difficult task of working out which of those “experts” are experts, and which of those “facts” are facts.
How to disable a domain
- steve
- Jun 1, 2010
Sometimes you might want to make it clear that a domain isn’t valid for email.
Perhaps it’s a domain or subdomain that’s just used for infrastructure, perhaps it’s a brand-specific domain you’re only using for a website. Or perhaps you’re a target for phishing and you’ve acquired some lookalike domains, either pre-emptively or after enforcement action against a phisher, and you want to make clear that the domain isn’t legitimate for email.
There are several things to check before disabling email.
1. Are you receiving email at the domain? Is anyone else?
Check the MX records for the domain, using “host -t mx example.com” from a unix commandline, or using an online DNS tool such as xnnd.com.
If they’re pointing at a mailserver you control, check to see where that mail goes. Has anything been sent there recently?
If they’re pointing at a mailserver that isn’t yours, try and find out why.
If there are no MX records, but there is an A record for the domain then mail will be delivered there instead. Check whether that machine receives email for the domain and, if so, what it does with it.
Try sending mail to postmaster@ the domain, for instance postmaster@example.com. If you don’t get a bounce within a few minutes then that mail may be being delivered somewhere.
2. Are you sending email from the domain? Is anyone else?
You’re more likely to know whether you’re sending mail using the domain, but there’s a special case that many people forget. If there’s a server that has as it’s hostname the domain you’re trying to shut down then any system software running no that server – monitoring software, security alerts, output from cron and so on – is probably using that hostname to send mail. If so, fix that before you go any further.
3. Will you need mail sent to that domain for retrieving passwords?
If there are any services that might have been set up using an email address at the domain then you might need a working email address there to retrieve lost passwords. Having to set email back up for the domain in the future to recover a password is time consuming and annoying.
The domain registration for the domain itself is a common case, but if there’s any dns or web hosting being used for the domain, check the contact information being used there.
4. How will people contact you about the domain?
Even if you’re not using the domain for email it’s quite possible that someone may need to contact you about the domain, and odds are good they’ll want to use email. Make sure that the domain registration includes valid contact information that identifies you as the owner and allows people to contact you easily.
If you’re hosting web content using the domain, make sure there’s some way to contact you listed there. If you’re not, consider putting a minimal webpage there explaining the ownership, with a link to your main corporate website.
5. Disabling email
The easiest way to disable email for a domain is to add three DNS records for the domain. In bind format, they look like:
The importance of data hygiene
- laura
- May 26, 2010
Over the weekend, one of the major ISPs purged a lot of abandoned accounts from their system. This has resulted in a massive increase in 550 user unknown bounces at that ISP. This ISP is one of those that uses bounces to feed into their reputation system and the purge may cause otherwise good senders to be blocked temporarily.
Talking to clients and other industry folks, it looks like the addresses that have newly bounced off had zero activity for at least 6 months. Nothing. Nada. No clicks. No opens. No interaction.
This is why data hygiene is so critical. Just because the emails are being accepted at the ISP, and even showing inbox placement at the mailbox monitoring companies does not mean that there is actually someone reading your email. Failure to look at overall data means that when an ISP bulk deletes abandoned accounts then bounces will increase. While I don’t expect this to have any real, long term effect on sender reputation I do expect that some senders with a lot of cruft on their list will see some short term delivery problems.
Companies that run re-engagement campaigns saw a whole lot less bouncing and even less blocking as a result of the purge. They were removing addresses that were non-responsive all along and thus didn’t have major deadwood on their list.
Ongoing data hygiene shows you what your list really is, not your list plus abandoned accounts. The addresses that the ISP purged? They were not valuable anyway. No one was reading that mail for at least 6 months.
If you did see a spike in bounces this weekend at a major ISP, you should really look at engagement. If some percentage of recipients at one ISP are actually non-existent, then it’s likely that about that same number are non-existent at other major ISPs as well. What are you going to do to identify and remove those dead addresses from your lists?
Avoiding spammers in affiliate programs
- laura
- Apr 22, 2010
How can companies avoid paying spammers and having their brand associated with spammers?
One of the easiest ways to avoid spam is to not pay for acquisition email. Simply don’t set up an affiliate email marketing program. There are a lot of folks who don’t like me saying that, and who have argued vociferously with me over the years. But email is not a good medium for acquiring new customers if you don’t intend to spam. Email is a great medium for talking with current customers who are engaged with a brand and a company, but currently it is a poor way to acquire customers without spamming.
There are ways companies have successfully used email to acquire customers. There are actually newsletters that contain content but also sell advertising in the newsletter. Look at the newsletters you are receiving, that are relevant to your business space. One example of a newsletter that did this successfully is Magilla Marketing published by DirectMag. Every week there were 4 new articles from Ken Magill, supported by advertising in the newsletter and on the website. These kind of ads will let you reach your target market without spamming.
Now, I know that there are a lot of marketing departments out there that are going to insist that there aren’t useful newsletters or advertising venues for their field and the only way they can acquire customers is to use affiliate programs. I’ve had clients tell me the exact same things. Often they came to me as clients because their own email marketing was blocked by a blocklist or a spam filtering company due to their hiring of spammers. They wanted to police and clean up their affiliate program without having to give it up.
Policing affiliate programs can be done, if the company invests the time and energy into screening the program.
For every company that wants to send email advertising your company ask them to provide information about their company and their email program.
More on opt-out for B2B marketing
- laura
- Apr 12, 2010
There is still a bit of discussion going on around the HBR article on how B2B mail should be opt-out not opt in on various delivery blogs. Over on the Blue Sky Factory blog new daddy (congratulations!) DJ writes a post about why he thinks opt-out in any context is a poor marketing decision.
One of his commenters follows up with a long comment about how recipients shouldn’t get angry when they get unsolicited email from a company they have interacted with.
I want to avoid network outages
- steve
- Apr 8, 2010
Number six of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreWhen an open is not a sign of interest
- laura
- Mar 29, 2010
A lot of people, including myself, are using opens as one of the measures of engagement. This, as a general rule, is not a bad measure. However, there are people who will open email not because they’re interested in it, but because they know it is spam.
Take, for instance, the email address I acquired in 1993. Yes, I still have this address. I stopped using it to sign up for lists in 1999 and stopped using it for most of the rest of my mail around 2001. This address, though, is on any number of spam mailing lists. The spam that gets through is usually sent by hard-core spammers. The ISP that hosts that mailbox uses Communigate Pro to filter mail, so much of the casual spam is filtered.
Generally, if I open an email (and load images or click through) on that account it is only in order to track down a spammer. For instance, I’m getting a lot of spam there from affiliates offering me the opportunity to purchase printing services for a very low price. I have actually been opening the mail, and clicking through. But I’m not clicking through because I’m interested in purchasing. I’m clicking through to see if my reports to abuse@ printer are resulting in any action against the spammers. (They’re not).
The thing is, though, I know that by clicking through on ads, I’ve now been promoted by the spammer to the “clicks on emails! it’s a live address!” list. Which only means I’m going to get more spam from them. Lucky me.
Using clicks and opens as a measure of engagement isn’t necessarily bad. But when using them you have to understand the limitations of the measurement and that what you may think it’s telling you isn’t actually what it’s telling you.
I need to dodge filters
- steve
- Mar 19, 2010
Number five of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreWhich is better UTF-8 or ISO-?
- steve
- Mar 11, 2010
Someone asked today on a mailing list whether they should be using UTF-8 or “ISO” encoding for sending email. What’s the best choice depends on some of the details of the situation, but here’s the answer I gave:
UTF-8 will work for pretty much anything, as it’s just an 8 bit encoding scheme for Unicode (which is supposed to be the one character encoding to rule them all). It’s well supported in most languages and development environments – Windows has been native UTF-16 under the covers since the mid 90s, for instance – and typical messages that use mainstream glyphs should render well from utf-8 in most western MUAs and browsers.
There are still a very few old or broken clients out there that will not handle UTF-8 well but (outside the asian language market, where there’s still some non-ASCII, non-Unicode legacy usage) they’re typically ones that don’t really handle any character set encoding well and the only thing safe to send to them is either plain ASCII or whichever ASCII superset their OS happens to support natively (which is probably an argument for sending Windows-1252 codepage, but not a terribly strong one).
The various extended ASCIIs (such as ISO-8859-*) will only work for messages that are written solely using characters from that character set. If you have even one character in a message that cannot be expressed in ISO-8859-1, then you can’t use ISO-8859-1 to send that message.
ISO-8859-1 (aka Latin1) is fairly sloppy in some respects – it has no apostrophe, nor single quotes, for instance – but it can handle an awful lot of languages, from Kurdish to Swahili. It can’t handle Dutch, Estonian, Finnish, Hungarian and Welsh particularly well, nor can it show the Euro symbol (ISO-8859-14 or -15 are needed for some characters there).
A common problem is that many people (and the software they write) think that Windows uses Latin1. It doesn’t, it uses Windows-1252. If you accept messages written on Windows, using the Windows-1252 code page, and throw them out on the wire as ISO-8859-1 what you end up with is not quite right. It mostly works, as the two codepages overlap quite a bit, but they have different glyphs in the 0x80-0x9f range. So if you use single or double quotes (“smart quotes”), or the Euro symbol, or ellipses, or bullet, or the trademark symbol in your message they’ll be garbled. This is so common that some mail clients and web browsers will actually treat a document that claims to be ISO-8859-1 as Windows-1252, but that’s a bug workaround and not something it’s really safe to rely on.
If you’re doing personalized messages, and you’re sending one of them to Győző and one of them to Eiður then you may have to use different character sets for the two messages. If you’re talking about Győző and personalizing it for Eiður then you might find things break horribly.
Someone probably has some concrete data on mail client character set support, broken down by region and language, but my understanding is that this is a reasonable approach:
Are you still thinking of purchasing a mailing list?
- laura
- Feb 25, 2010
Last week there was an article published by btobonline promoting the services of a company called Netprospex. Netprospex, as you can probably gather from their company name, is all about the buying and selling of mailing lists. They will sell anyone a list of prospects.
The overall theme of the article is that there is nothing wrong with spam and that if a sender follows a few simple rules spamming will drive business to new heights. Understandably, there are a few people who disagree with the article and the value of the Netprospex lists.
I’ve stayed out of the discussion, mostly because it’s pretty clear to me that article was published solely to promote the Netprospex business, and their point of view is that they make more money when they can convince people to purchase lists from them. Dog bites man isn’t a very compelling news story. Data selling company wants you to buy data from them isn’t either.
They are right, there is nothing illegal about spam. Any sender can purchase a list and then send mail to the addresses on that list and as long as that sender meets the rock bottom standards set out in CAN SPAM. As long as your mail has an opt-out link, a physical postal address and unforged headers that mail is legal. The only other obligation on the sender is to honor any unsubscribe requests within ten days. So, yes, it is legal to send spam.
But legal action isn’t the only consequence of spamming. Today I received the following in an email from a colleague.
Watch those role accounts
- laura
- Feb 24, 2010
Ben at Mailchimp has a post up explaining what role accounts are and why mailing to them can be a problem.
Read MoreIntegrating your email channel
- steve
- Feb 22, 2010
I saw a nicely done example of integrating email into other marketing channels over the weekend.
I was helping a friend pick out a receiver and speakers for their home theatre system on Saturday afternoon. As we were chatting over IRC there was a lot of pasting URLs back and forth, as we tried to juggle speaker components to get a nice, balanced setup on a budget that was fairly tight for a separates system.
I like Polk speakers, and NewEgg are offering some nice deals on them right now, so a lot of the URLs were for bottom of the range Polk speakers at NewEgg.
Mid-morning on Sunday, around 16 hours later, this showed up in my inbox:
It’s mail customized for me, triggered by my browsing the site the day before with a web cookie in place that identifies me as someone who has a fairly long history of ordering from them.
I think it’s “just” targetted mail about home audio speakers, triggered by my browsing in that category and not purchasing immediately. But it’s possible that it’s cleverer than that – it’s listing solely Polk speakers, and it’s showing both the ones I was looking at and the higher end ones in the same product line. It’s nicely done, either way.
It’s a great example of an email that’s been prepared for a specific recipients interests, sent at just the right time. Even though I know that it’s a semi-customized boilerplate, sent by a piece of software in response to my browsing a web site it’s good enough that as a recipient I feel like it’s the company I have a relationship with being helpful, rather than it being intrusive upsell advertising.
It might not work so well if I were a brand new customer, or if it wasn’t quite as well tuned to my interests of the day, but it’s done well.
Nice job, NewEgg.
Truths and myths about email
- laura
- Feb 18, 2010
Seven myths and two truths about email
My favorite:
[myth] Engagement is the new reputation. Actually, reputation metrics have always been about engagement, which is what complaint data and sender reputation reflect.Read More
Social network spam
- laura
- Feb 9, 2010
I’ve been seeing more and more social network spam recently, mostly on twitter. In some ways it’s even more annoying than email spam. Here I am, happily having a conversation with a friend and then some spammer sticks their nose in and tweets “myproduct will solve your problem!”
It’s happened twice in the last week.
In most recent example, I was asking my twitter network for some advice on pasta making. I’ve made pasta a few times, but it’s never been exactly right. Not having an Italian grandmother to ask, I was looking for someone with experience in pasta making to answer a few questions. I was having an ongoing conversation with a friend who was helping me troubleshoot my problems. He gave me his recipe to try to see if that would work better. I thanked him profusely and replied that I would give it a try but probably not tomorrow because it was accounting day and those tend to run late. Someone replied to that tweet suggesting I try some random accounting software to make my accounting easier.
Just… No.
Interjecting product ads in a conversation may be the “acceptable” and “best practice” way to market through social networking. But, I can promise that you’re no better the guy who interrupts conversations at parties so he can hand out business cards for his affiliate program selling herbal male enhancement drugs.
Don’t be That Guy.
Update: Today’s twitter spam was from one of the email accreditation services attempting to sell me their email delivery services.
TWSD: Using FOIA requests for email addresses
- laura
- Feb 6, 2010
Mickey has a good summary of what’s going on in Maine where the courts forced the Department of Inland Fisheries and Wildlife to sell the email addresses of license purchasers to a commercial company.
There isn’t permission associated with this and the commercial company has no pretense that the recipients want to receive mail from them. This is a bad idea and a bad way to get email addresses and is no better than spammers scraping addresses from every website mentioning “fishing” or “hunting.”
Spammers aren't who you think they are
- laura
- Jan 25, 2010
Shady direct marketers exploit CAN SPAM to continue spamming but protect themselves from the law. This is something I’ve been talking about for a while (TWSD), and it’s nice to see the mainstream press noticing the same thing.
HT: Box of Meat
Click-wrap licenses again
- laura
- Jan 13, 2010
Earlier this week ARS Technica reported on a ruling from the Missouri Court of Appeals stating that terms and conditions are enforceable even if the users are not forced to visit the T&C pages. Judge Rahmeyer, one of the panel members, did point out that the term in question, under what state laws the agreement would be enforced, was not an unreasonable request. She “do[es] not want [their] opinion to indicate that consumers assent to any buried term that a website may provide simply by using the website or clicking ‘I agree.'”
What does this have to do with email? Well, it means that reasonable terms in the agreements may still be binding even if the user does not read the full terms of the opt in before submitting an email address. In practical terms, though, there’s very little that has changed. Hiding grants of permission deep in a terms document has long been a sneaky trick practiced by spammers and list sellers. Legitimate companies already make terms clear so that users know what type of and how much mail to expect by signing up to a list. They also know that the legal technicalities of permission are not as important as meeting the recipients expectations.
Important notification spammers break the law
- laura
- Jan 11, 2010
I’m currently being inundated at multiple address with spam advertising spamming services. Most of these notices have the subject line: IMPORTANT NOTIFICATION. The text includes:
Read MoreResource hogging
- laura
- Jan 8, 2010
Today on SFGate there was an article talking about how some Bay Area coffee houses were struggling to deal with workers who purchase one cup of coffee and then camp out all day using the free wifi. The final paragraph quoted one of the campers.
Read MoreLessons from the good, the typical and the ugly
- laura
- Jan 8, 2010
What can smart ESPs learn from my recent series The good, The typical and The ugly?
Read MoreTypical ESPs
- laura
- Dec 22, 2009
Yesterday, I gave examples of good ESPs and the benefits that their customers receive from their high standards and standards enforcement. Today I’ll be talking about typical ESPs and the things they say and do.
A few caveats before I get started. Most of these quotes are composite quotes. I am not quoting one particular person or ESP, rather, the statement is representative of a common view point. None of these quotes is a one off, all of these quotes have been said by more than one person. These where chosen as a representation of some of the attitudes and policies that leads ISPs and filtering companies to throw up their hands at the ESPs.
What makes a good ESP?
- laura
- Dec 21, 2009
There are a number of things that make a responsible ESP, including setting and enforcing standards higher than those set by the ISPs.
One of the responsible ESPs is Mailchimp. (Full disclaimer, I do consult for Mailchimp.) This ESP focuses on businesses with small to medium sized lists. They screen new customers for source of permission as well as mail content.
As well as putting a human in the loop and identifying problem customers manually, they have also developed an automated process that predicts the likelihood that a certain customer will violate their standards. This process is very similar to the reputation process in place at many ISPs. Customers that are flagged as potential problems are reviewed by staff members who contact the customer for further clarification.
What’s the benefit of this process? A good reputation, a clean customer base and positive notice by the ISPs. In fact, just recently I was contacted by one of the very large consumer ISPs, confirming that Mailchimp is one of my clients. He informed me that he’d noticed a few of the Mailchimp IPs had a really high reputation but weren’t whitelisted. He asked me to send him all of their IPs so he could make sure all their IPs were whitelisted.
Proactive auditing of customers and predictive modeling of mailing results is working for Mailchimp and their customers.
Some ESPs have aggressive cancellation policies, which helps them police their networks and their customers. I often encounter former customers of these ESPs, either as direct clients or as customers of my ESP clients. In one case, I was asking around about a new client at their old ESP. “They tell me they left you under their own power and there was no spam issue involved, can you comment?” The policy person would not comment specifically about that client, but did comment that “95% of our former customers were disconnected for cause.”
These are two examples of ESPs that are working hard to minimize the amount of unwanted mail going through their network. They have invested time and energy into tools and staff to monitor the network. Staff is empowered to make decisions about customers and management believes no customer is “to big to disconnect.”
Tomorrow we’ll look at typical ESPs and their normal practices.
A series of warnings
- laura
- Dec 15, 2009
Over the last month there have been a number of people sounding warnings about coming changes that ESPs are going to have to deal with. There has been mixed reaction from various people, many people who hear these predictions start arguing with the speaker. Some argue that our predictions are wrong, others argue that if our predictions are right then the senders will just start acting more like spammers.
I have put together a collection of links from recent blog posts looking towards the future and how things may be changing.
I need to deliver my mail fast
- steve
- Dec 14, 2009
Number four of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreHow to fix delivery
- laura
- Dec 14, 2009
For all of you that are asking “What do the ISPs want from us” Annalivia has posted a list of specifics that you can do to improve delivery.
Read MoreTWSD: keep spamming even when they say they'll stop
- laura
- Dec 10, 2009
About a month ago I posted about receiving spam from a psychic attempting to sell me candles and stuff. The spammer was sending mail from a company called “Garden of Sound” using an ESP called OnLetterhead. A brief investigation led me to believe that unsubscribing from the mail was not going to do anything.
The post prompted an email from Scott B. the VP of Marketing of the company that is responsible for OnLetterhead. I replied to his email, pointing out a number of things he was doing that made his business look like an ESP front for spammers.
After he received my mail he called me to talk to me about the content of my post and the email and to assure me they were immediately implementing one of my suggestion (that they not put a generic “here’s how to unsubscribe” link on their 1000+ link domains, instead have those actually point to their AUP and corporate pages). He also assured me they took my complaint seriously and I would no longer be receiving email.
Guess what?
Garden of Sound is still spamming me from OnLetterhead. They’ve not even managed to implement the changes they pledged would be rolled out the same week as my blog post. Sure, the domain I’m getting spam from is different, the physical postal address is different, the product is different, the friendly from is different. But the preheader still says “this mail sent by Garden of Sound.” It’s all the same list, it’s all the same company, it’s all the same group of spammers.
Despite Scott’s attempt to convince me he wasn’t a spammer, it seems my initial impression was right. OnLetterhead is simply are a company attempting to look like they’re legitimate without actually taking any responsibility for the email going out from their network. They can’t even manage the bare minimum.
It’s companies like this that give the rest of ESPs a bad name.
AOL speaks about FBLs
- laura
- Dec 8, 2009
Annalivia posts a guide to FBLs over on the AOL postmaster blog.
Read MoreIs it really permission?
- laura
- Dec 3, 2009
There’s a great post over on the AOL Postmaster blog talking about sending wanted mail versus sending mail to people who have <a href=”https://web.archive.org/web/20100210070640/http://postmaster-blog.aol.com:80/2009/12/03/p/>grudgingly given permission to receive it.
Read MoreWhat she said
- laura
- Dec 2, 2009
Jamie Tomasello on the Cloudmark Blog:
ESPs who require and enforce best permission practices should be applying peer and industry pressure within the ESP community to adopt these policies. Ultimately, ESPs need to take responsibility for their clients’ practices. If you are aware that your clients are engaging in questionable or bad practices, address those issues before contacting an ISP or anti-spam vendor to resolve the issue.
Read More
Legitimate email marketers need to take a stand
- laura
- Nov 27, 2009
I was reading an article on Virus Rants and the opening paragraph really stood out.
Read MoreTroubleshooting the simple stuff
- laura
- Nov 20, 2009
I was talking with one of my Barry pals recently and was treated to a rant regarding deliverability experts that can’t manage simple things. We’ve been having an ongoing conversation recently about the utterly stupid and annoying questions some senders ask. Last week, I was ranting about a delivery person asking what “5.7.1. Too many receipts this session” meant. This morning I got an IM.
Read MoreI don't have a "this is spam" button
- laura
- Nov 18, 2009
Here at Word to the Wise we have some unique requirements for mail. For instance, I need to be able to receive examples of emails that are being blocked elsewhere in order to do my job. This means not only do we not outsource mail to someone else, we also run limited spam filtering on the server side. It does mean I have to wade through a bit more spam than others do, but that’s generally not a problem. My client side filters do a decent job at keeping most of the crud out of my mailboxes.
My work account gets very little spam in the folder I use as my inbox. I’m not even sure exactly why this is, but it’s true. One of the exceptions is a psychic (no, really) who has a copy of one of my work email addresses and she regularly spams me offering her spiritual guidance and the opportunity to buy her stuff in order to make peace within my world. I’ve received these before, usually I just delete them and move on.
Occasionally, though, I long for the ease of a “this is spam” button. Just to be able to hit a single button, no work, no effort and know that I have registered my frustration with a spammer. Today was one of those days. I really don’t want this psychic spam in my mailbox. It seems reasonably professionally done, though, so I check the headers to see if it’s being send from any ESP I know and if it’s worth my time to send in a “hey, didn’t sign up for this, and no, I didn’t forget, either” email.
I visited the website belonging to the domain sending the mail.
Internationalisation (part 2)
- steve
- Nov 16, 2009
In part 1 I talked about internationalised domain names, and how they were mapped onto ASCII strings.
For sending email there are four bits of the message where internationalisation might need to be considered.
Is it ever OK to violate best practices?
- laura
- Nov 13, 2009
Last week @justinpremick tweeted the question “Is it ever OK to break best practices.” My reaction, and reply, was of course it is OK to break best practices, if you know what you’re doing and why.
Best practices are all about things that are safe. If you do these things, in all likelihood you will not encounter any major problems. The things we tell people are best practices are not written in stone and inviolable. Rather, they’re a way to succeed without understanding all the ins and outs of email.
The key to violating best practices is to know why the recommendation is a best practice. Take, for example, practices relating to email design. Best practices say that emails should not be image only and they should be designed in such a way that users don’t have to scroll sideways. However, StyleCampaign recently reported on a campaign from the Canadian Tourist Board that violated both of these best practices.
The email was laid out as a maze, requiring the user to scroll around the message to find the call to action. The designers have reported they are quite pleased with how successful the campaign was received.
So, yes, Justin, you can violate best practices and it is OK. Best practices are not laws, they are guides. If you know what pitfalls the best practices are helping you avoid, then you can violate those guides without problems.
TWSD: Privacy protection for commercial domains
- laura
- Nov 12, 2009
One of my major pet peeves is supposedly legitimate companies hiding behind privacy protection in their whois records. There is absolutely no reason for a legitimate company to do this. There are lots of reasons a non-legitimate company might want to hide behind privacy services, but I have never heard a good reason for legitimate companies to hide.
Look, a company sending any commercial email is required by law to provide a physical postal address in every email they send. What point is there, then, to hiding addresses in whois records? The only thing it does is make a sender look like a spammer. If a sender is a business, then they need to have a real business address anyway, and that address should be available in their domain registration.
It may seem like a trivial point, it may seem minor, but spammers use domain privacy services to hide the various tendrils of their businesses. They don’t want anyone to be able to tell that domain A is related to domain B is related to domain C. Proxy services let them trivially hide their identities. This is the major business use of privacy protection. Real companies don’t need to hide behind privacy services.
Using domain privacy services make senders look like spammers. One trivial thing that ISPs can do is stop providing FBLs or whitelistings to domains behind privacy services. This will weed out spammers without doing harm to real senders. Certification services can refuse to certify companies that hide their identity. My small contribution to the cause is to refuse to represent any company to an ISP if their domain is behind a privacy service.
Just to be clear, I have no problem with personal, non-business domains using privacy services. There are valid reasons individuals may want to hide their physical location. But businesses? Step up and quit hiding.
On the subject of privacy services, Mickey recently reviewed a court ruling that commented on the legality of using privacy services. The court says:
I need IP addresses to avoid throttling
- steve
- Nov 10, 2009
Number three of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MorePrivacy policies in the real world
- laura
- Nov 10, 2009
This weekend we took the car in for service. Instead of dropping it off at the dealership, we found a small, local garage. Prominently positioned on the counter was their Email Privacy Policy.
I need IP addresses to handle the volume
- steve
- Nov 5, 2009
Number two of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreSenders need to take responsibility
- laura
- Nov 4, 2009
Having just returned home from another conference, my head is full of new ideas, new thoughts and new projects. I enjoy seeing old friends, making new contacts and sharing ideas. One thing I don’t enjoy, though, is listening to senders and marketers complaining about how hard it is to be a sender because the ISPs will not tell them what standards they need to meet.
If the ISPs would just tell us what they want us to do, we’ll do it.
The ISPs have told senders what they want them to do. They want senders to stop sending mail that their users don’t want. It is a very simple statement.
Stop sending spam.
For many senders, however, it’s not enough. “Tell us exactly what we need to do to stop sending spam. What complaint rates must we be under? What bounce rates do we have to be under? How do you want us to do this?” By this point in the conversation the ISP person is mentally rolling their eyes and looking for a way to escape the conversation.
The ISPs don’t want to tell senders how to behave, they want senders to start behaving. Stop sending spam should be all they need to tell senders.
Senders who ask for ISPs to tell them how to stop sending mail recipients think is spam are looking for specific thresholds they can stay under. They’re not really interested in actually sending wanted mail, they’re interested in sending good-enough mail, where good-enough mail is simply mail that gets to the inbox.
Want to know why ISPs don’t think much of many senders? Because the senders are not visibly taking any stand against abuse. I know there are a lot of senders out there who stop a lot of spam from ever leaving their systems, but there’s also a lot of unwanted mail that goes out, too. Some of that mail is even spam by any definition of the word. All the ISPs can see is the spam that gets through, and then they hear just tell us what to do and we’ll do it. From an ISP perspective, this means the senders only care about the thresholds and getting in under the ISPs’ radars.
Senders need to take more responsibility for the mail that goes out over their networks.
What do I mean by this? I mean senders need to stop waiting for the ISPs to define good practices. Senders need to implement standards and good practices just because they’re good practices, not because the ISPs are dictating the practices. Senders need to stop customers from doing bad things, and dump them if they won’t stop. Senders need to stop relying on ISPs for specific answers to why mail is being blocked. Senders need to take responsibility for the mail going across their networks.
It’s time for senders to grow up and stop relying on others for guidance. They shouldn’t implement good practices just because the ISPs tell them to, but instead should implement good practices because they are good practices.
The legitimate email marketer
- laura
- Nov 3, 2009
I cannot tell you how many times over the last 10 years I’ve been talking to someone with a problem and had them tell me “but I’m a legitimate email marketer.” Most of them have at least one serious problem, from upstreams that are ready to terminate them for spamming through widespread blocking. In fact, the practices of most companies who proclaim “we’re legitimate email marketers” are so bad that the phrase has entered the lexicon as a sign that the company is attempting to surf the gray area between commercial email and spam as close to the spam side of that territory as possible.
What do I mean by that? I mean that the address collection practices and the mailing processes used by self-proclaimed legitimate email marketers are sloppy. They don’t really care about individual recipients, they just care about the numbers. They buy addresses, they use affiliates, they dip whole limbs in the co-reg pool; all told their subscription practices are very sloppy. Because they didn’t scrape or harvest the email address, they feel justified in claiming the recipient asked for it and that they are legitimate.
They don’t really care that they’re mailing people who don’t want their mail and really never asked to receive it. What kinds of practices am I talking about?
Buying co-reg lists. “But the customer signed up, made a purchase, took an online quiz and the privacy policy says their address can be shared.” The recipient doesn’t care that they agreed to have their email address handed out to all and sundry, they don’t want that mail.
Arguing with subscribers. “But all those people who labeled my mail as spam actually subscribed!!!” Any time a mailer has to argue with a subscriber about the validity of the subscription, there is a problem with the subscription process. If the sender and the receiver disagree on whether there was really an opt-in, the senders are rarely given the benefit of the doubt.
Using affiliates to hide their involvement in spam. A number of companies use advertising agencies that outsource acquisition mailings that end up being sent by spammers. These acquisition mailings are sent by the same spammers sending enlargement spam. The advertiser gets all the benefits of spam without any of the consequences.
Knowing that their signup forms are abused but failing to stop the abuse. A few years back I was talking with a large political mailer. They were insisting they were legitimate email marketers but were finding a lot of mail blocked. I mentioned that they were a large target for people forging addresses in their signup form. I explained that mailing people who never asked for mail was probably the source of their delivery problems. They admitted they were probably mailing people who never signed up, but weren’t going to do anything about it as it was good for their bottom line to have so many subscribers.
Self described legitimate email marketers do the bare minimum possible to meet standards. They talk the talk to convince their customers they’re legitimate:
I need IP addresses for reputation
- steve
- Nov 2, 2009
Number one of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreWhy do you need so many IP addresses (part 2)?
- steve
- Oct 28, 2009
In my last post I discussed the background as to why an ISP will require their users to use their IP address allocation efficiently. I also mentioned in passing that I’d discussed ESP address allocation with both ESPs and ISPs recently.
The ESP was talking about assigning a couple of dozen IP addresses to each customer, because they might be useful for spreading load and it would provide some flexibility for moving from one IP address to another if one should get blocked. And IP addresses are pretty much free. They were wrong.
The ISP was considering an application for 750 IP addresses from a new ESP customer. They assumed that there was no possible reason other than snowshoe spam for an email related customer to need that many IP addresses. While I suspect they may have been right about the specific potential customer, the general assumption was wrong.
I’ve seen a lot of reasons given by ESPs for why they need so many IP addresses:
Who are you and why are you mailing me?
- laura
- Oct 20, 2009
I’ve mentioned here before that I use tagged addresses whenever I sign up for. This does help me mentally sort out what’s real spam and what’s just mail I’ve forgotten I’ve signed up for.
Yesterday, I received and email from e-fense.com thanking me for my interest in their new product. The mail came to a tagged address, but not a tag that I would have given to e-fense.com. Their opening paragraph said:
Permission: it may not be what you think it is
- laura
- Oct 19, 2009
I’ve talked frequently about permission on this blog, and mentioned over and over again that senders should correctly set expectations at the time they collect permission. Permission isn’t permission if the recipient doesn’t know what they’re agreeing to receive.
Read MoreTWSD: My lunch is not spam
- laura
- Oct 16, 2009
My ISP information page occasionally gets trackback pings from various blog posts. This week one of the trackbacks was from a blog post titled “One man’s Spam is another man’s lunch.” The theme of the blog post was that email marketers are poor, put upon business people that have to contend with all sorts of horrible responses from recipients, spam filtering companies and ISPs.
Since the poster took the time to link to my blog, I thought I’d take the time to look in detail at his post and talk about how likely it is to work.
Suppressing email addresses: it's good for everyone
- laura
- Oct 15, 2009
Every sender, big or small, should have the ability to suppress sending to any particular email address. They must, absolutely, be able to stop sending mail to anyone for any reason. Not only is this a legal requirement in every jursidiction that has laws about email marketing, it’s just good business sense.
What happens when marketers fail to be able to suppress email addresses? At some point they’re going to mail someone who gets annoyed enough with them to make it public that they are too incompetent to run an email program.
This happened to the folks over at spamfighter.com recently. They have been spamming Neil Schwartzman (spamfighter, Executive director of CAUCE North America, Director of Standards and Certification at ReturnPath) since somewhere in 2007. Yes, really, 2007. Neil has asked them politely to stop spamming him. He’s explained he’s not actually using their software. They appear to be incapable of running a suppression list, despite telling him 3 times that they have removed his address.
Showing much more restraint than I would have with a sender who couldn’t stop sending me email, Neil gave them years to fix their process before blogging about his experiences. Instead of fixing their broken process they instead responded to his blog post insisting their mail wasn’t spam because they weren’t sending Viagra mail or 3rd party offers.
We can argue about the definition of opt-in, we can argue about whether registration is permission, we can argue about a lot of things, but when the recipients says “stop sending me email” and a sender says “we’ll stop sending you email” and then fails to actually stop sending email I think the recipient is fully justified in calling the email spam. Sorry spamfighter.com, your process is broken and your inability to fix it 2 years after the brokenness was brought to your attention does not give anyone a good impression.
Every email sender should have the ability to stop sending mail to recipients. If that’s not currently possible with your technology, it should be a very high development priority.
Demanding everything might mean you get nothing
- steve
- Oct 14, 2009
What do you do when you have a potential customers name and address, but know nothing else about them? You’d really like to be able to send them some targeted marketing, ideally via email. You send them a good old-fashioned letter asking them to volunteer more contact information and answers to a bunch of business classification questions – “What industry are you in?”, “How many employees do you have?”, “What might you want to buy from us?”, that sort of thing.
Verisign – the people who’ll sell you certificates for SSL websites – sent me exactly that letter yesterday. And over and above their costs for sending the mail, developing the online survey and capturing the data they’re also offering a $10 gift card to everyone who fills in their survey. They must really want that data and those subscribers.
And a fair bit of the work I do is security-related and I use SSL fairly heavily, so I’d be interested in the occasional email from Verisign. If they pitch me a decent offer for an interesting product I’d even be likely to buy it. This is just how email marketing can work well and make both sender and recipient happy – much better, from my perspective, than intrusive cold calls from sales reps desperate to sell me something interrupting my work day.
I fill in their online survey. I give them an email address. I don’t give them a ‘phone number.
And they refuse to accept the form, because there’s no ‘phone number. I’m mildly annoyed that I’ve wasted five minutes filling in a useless form; they’ve lost a potential subscriber. Neither of us is happy with the result.
Being sensitive to recipients preferences is likely to make them happier and more receptive to your message, and improve the effectiveness of your overall campaign.
Refusing to let someone sign up for email marketing because they don’t want your telemarketing is a fairly extreme example, but recipients preferences is something to bear in mind elsewhere in your campaigns. If you’re mailing daily maybe you’re losing subscribers simply because the volume is too high. Possibly offering an alternative “weekend edition” with the best bits of the weeks daily editions would work better for them. Offering them the option to sign up for that instead on the unsubscription page for your daily list might help you keep them as a subscriber.
Transparency in sending
- laura
- Oct 12, 2009
Al has a post listing some of the bad things some sender representatives do when approaching ISPs for delisting.
One of the things I would add to the list is hiding behind a privacy protected domain registration. No matter how you dice it, having a business domain behind privacy protection makes a company look illegitimate. For any company sending commercial mail, it’s not even an issue as senders are required by law to include an address in every email. With this sort of requirement, it’s not like customers aren’t going to be able to find them.
This is an issue I feel so strongly about, I will not represent senders to ISPs unless they have a valid, unprotected whois registration. I do offer consulting and other services to them, but will not contact the ISPs on their behalf. This is not the reputation I want to create with the ISPs for myself or my other clients.
I challenge anyone who is running a business and using a whois privacy protection service to put the same address in their whois record as is on every email you send out.
I challenge ISPs to stop offering whitelisting, FBL or other services to senders who insist on using whois privacy services.
Rescuing reputation
- laura
- Oct 9, 2009
One of the more challenging things I do is work with companies who have poor reputations that they’re trying to repair. These companies have been getting by with poor practices for a while, but finally the daily delivery falls below their pain threshold and they decide they need to fix things.
That’s when they call me in, usually asking me if I can go to the ISPs and tell the ISPs that they’re not spammers, they’re doing everything right and will the ISP please stop unfairly blocking them. Usually I will agree to talk to the ISPs, if fixing the underlying problems doesn’t improve their delivery on its own. But before we can talk to the ISPs, we have to try to fix things and at least have some visible changes in behavior to take to them. Once they have externally visible changes, then we can ask the ISPs for a little slack.
With these clients there isn’t just one thing they’ve done to create their bad reputation. Often nothing they’re doing is really evil, it’s just a combination of sorta-bad practices that makes their overall reputation really bad. The struggle is fixing the reputation requires more than one change and no single change is going to necessarily make an immediate improvement on their reputation.
This is a struggle for the customer, because they have to start thinking about email differently. Things have to be done differently from how they’ve always been done. This is a struggle for me because I can’t guarantee if they do this one thing that it will have improved delivery. I can’t guarantee that any one thing will fix their delivery, because ISPs measure and weight dozens of things as part of their delivery making decisions. But what I can guarantee is that if they make the small improvements I recommend then their overall reputation and delivery will improve.
What small improvement have you made today?
Overusing ISP contacts
- laura
- Oct 7, 2009
I’ve written frequently about personal contacts at ISPs and how the vast majority of delivery problems can be solved without picking up the “Bat Phone” and having someone at the ISP do something. Al touches on the same subject today, blogging about his recent experiences having to contact “Barry” multiple times for many different issues.
Al resolves
Registration is not permission
- laura
- Oct 6, 2009
“But we only mail people who registered at our website! How can they say we’re spamming?”
In those cases where website registration includes notice that the recipient will be added to a list, and / or the recipient receives an email informing them of the type of email they have agreed to receive there is some permission involved. Without any notice, however, there is no permission. Senders must tell the recipient they should expect to receive mail at the time of registration (or shortly thereafter) otherwise there is not even any pretense of opt-in associated with that registration.
Take, for example, a photographers website. The photographer took photos at a friend’s wedding and put them up on a website for the friend and guests to see. Guests were able to purchase photos directly from the site, if they so desired. In order to control access, the photographer required users to register on the site, including an email address.
None of this is bad. It’s all standard and reasonably good practice.
Unfortunately, the photographer seems to have fallen into the fallacy that everyone who registers at a website wants to receive mail from the website as this morning I received mail from “Kate and Al’s Photos <pictage@pictage.example.com>.” It includes this disclaimer on the bottom:
Sharing content, sharing reputation
- laura
- Oct 1, 2009
Over at SpamResource Al talks about how sharing content is like sharing needles.
Read MoreEmail address validation
- laura
- Sep 30, 2009
One thing anyone collecting email addresses anywhere has to think about is address validation. How do you prevent users from typing bad addresses into your forms?
I ran into this yesterday attempting to take an online quiz. Before I was allowed to take the quiz, I had to provide my name, phone number and email address. Initially I attempted to use a tagged email address. This is one that delivers to my wordtothewise.com mailbox, but lets me identify who I initially gave the address to. The form wouldn’t let me give a tagged address “contains invalid characters.” Well, no, it doesn’t, but there are a lot of websites that think + and – and other characters are invalid.
So what did I do? I ended up using a yahoo address associated with my yahoo IM account. An account that may actually not be accepting mail any longer as I rarely log into it.
What did address validation get them in this case? Well, it got them an address I don’t read and may not even be active rather than the address I wanted to give them which would have delivered directly to my primary mail box. Somehow I don’t think this solution is really ideal for them. (It’s great for me, I’ll never know if they ever attempt to contact me.)
Coincidentally, UserGlue posted about email address validation and alternatives to “make them type their address twice.” (Do people do this? I typically cut and paste my address instead of retyping.)
How are other people validating email addresses?
DKIM: what it's not
- laura
- Sep 25, 2009
An ESP twittered this past week about their new DKIM implementation going live. They were quite happy with themselves. Unfortunately, in their blog post, they mentioned 3 things that DKIM would provide for their customers, and got it wrong on all 3 points. Their confusion is something that a lot of people seem to get wrong about DKIM so I thought I would explain what was wrong.
Read MoreDelivery emergencies
- laura
- Sep 23, 2009
There is no such thing as a delivery emergency. They just do not happen.
Delivery is fluid, delivery is changing, delivery is complex.
But when delivery goes bad it is not an emergency. There is no need to call up an ISP person at home on a Saturday afternoon and ask them to remove the filters. (And, BTW, experience indicates if you do this that you may have future delivery issues at that ISP.)
I’m sure that people will provide me with examples of delivery emergencies. And, in some cases I might even concede that the receivers will be happy to receive email immediately when it was sent. However, email as a protocol was designed for store and forward. It was not designed to transmit messages instantaneously from sender to receiver. Sure, it works that way much of the time these days. On the whole the Internet is fairly reliable and major servers are connected 24/7 (which wasn’t always the case).
Among many people, particularly recipients and ISP employees, there isn’t the expectation that bulk email is instantaneous. This leads to the belief that delivery problems are not an emergency. Everyone faces them, they get dealt with, life goes on. Demanding an escalation to deal with a “delivery emergency” may backfire and slow down how long it takes to get a response from an ISP.
Permission is not a legal concept
- laura
- Sep 8, 2009
One trap I see companies fall into when looking at opt-in and permission is they seem to think that permission is a blanket thing. They believe permission can be bought and sold by the companies that collected email addresses.
Read MoreSubscription practices in the wild
- laura
- Aug 28, 2009
It’s always interesting to look at what other email marketers are doing and how closely their practices align with what I am recommending to clients.
Today’s example is a welcome message I received from Marriott. During my recent trip to visit a client, I gave Marriott my email address. They sent me a welcome message, primarily text that looked good even with images turned off. The text of the email told me why I was receiving the email and what I could expect.
Blocking specific domains
- laura
- Aug 26, 2009
Multiple times in the last few days people have asked me the question “What do you think about blocking domains owned by anti-spam companies as a way to prevent blocklisting?” The question is not necessarily a bad one, and there are cases where blocking mail to specific domains is a good decision. Often, though, if a spam prevention program consists solely of avoiding sending email to people that may be able to cause delivery pain, there are deeper problems that should be addressed.
When I am asked about doing so, my first question is always “Why do you want to do this? What are you trying to accomplish?” Typically, the person asking the question will tell me they are attempting to prevent employees of anti-spam companies from getting mail that they will then report to the operations team as spam.
First, employees don’t always have the ability to get a specific sender blocked just because the sender spammed them. It’s not necessarily something senders should rely on, but often there are policies in place to prevent an employee from using the company to punish a “personal” spammer. And even when someone who can add a sender to their global blocking list receives spam, the listing still must comply with the corporate policies. In other words, just mailing someone “powerful” isn’t enough to result in a block. It may bring the sender to the attention of the company, but unless over all stats and show that the sender is a problem, a listing won’t happen.
Second, employees at companies do sometimes opt in to mail from commercial senders. In fact, I had one discussion with a anti-spam company about a client who was seeing intermittent delivery problems. I sent in the information about the client and the employee handling the case said “Oh, them! I signed up for mail from them. Yeah, they’re a good bunch and their stats are reasonable, they shouldn’t have any more problems.” And they didn’t.
Third, many of us who work in email, particularly those of us who have been around for a long time on the anti-spam side, have our own domains and use multiple email addresses. Just removing clearly identifiable anti-spam domains does not mean that a sender will never spam someone powerful or important. It is impossible to clean off all those email addresses from lists. We have many, many addresses, including ones at ISPs.
One extreme example is AOL.com. Every AOL employee has an AOL.com address and they are indistinguishable from the addresses used by AOL.com customers. But, if a sender spams an employee with access to the anti-spam system, and the stats are bad enough to justify a block, then that sender may see poor AOL delivery. But senders aren’t really going to block mail to all AOL.com addresses, just to avoid that scenario.
When is blocking emails to domains or a set of email addresses a good idea?
Another list purchase horror story
- laura
- Jul 21, 2009
Last week Ken wrote about a marketer who is claiming he was ripped off by Target Point in a purchased list deal. To the purchaser’s credit he actually looked at the email addresses provided by Target Point, something many list purchasers don’t seem to do. This gave him some idea that the list was not opt-in.
Read MoreBlocked for phishing
- laura
- Jul 17, 2009
A couple clients recently have had bounces from different places indicating that their mails were caught by the recipients’ anti-virus filter. These are some of my better clients sending out daily newsletters. They’ve been mailing for years and I know that they are not phishing. They asked me to investigate the bounce messages.
The information I had to work with was minimal. One bounce said:
Troubleshooting Yahoo delivery
- laura
- Jul 14, 2009
Last week Jon left a comment on my post Following the Script. He gives a familiar story about how he’s having problems contacting Yahoo.
Read MoreUnsubscribe rates as a measure of engagement.
- laura
- Jul 11, 2009
Over at Spamtacular Mickey talks about the email marketers’ syllogism.
- Anyone who doesn’t want our mail will opt-out.
- Most people don’t opt-out.
- Therefore, most people want our mail.
This clearly fallacious reasoning is something I deal with frequently with my clients, particularly those who come to me for reputation repair. They can’t understand why people are calling them spammers, because their unsubscribe rates and complaint rates are very low. The low complaints and unsubscribes must mean their mail is wanted. Unfortunately, the email marketers’ syllogism leads them to faulty conclusions.
There are many reasons people don’t opt-out of mail they don’t want. Some of it may be practical, the mail never hits their inbox, either due to ISP level filters or their own personal filters. Some people take a stance that they do not opt out of mail they did not opt-in to and if they don’t recognize the company, they won’t opt-out.
In any case, low levels of opt-outs or even this-is-spam hits does not mean that recipients want that mail. The sooner marketers figure this out, the better for them and their delivery.
CAN SPAM compliance information in images
- laura
- Jul 10, 2009
A fellow delivery specialist sent me a question this morning.
Read MoreBad subject lines
- laura
- Jul 2, 2009
I tend not to blog too much on subject lines as they are really a marketing issue and a subscriber relationship issue. The subject lines a particular mailer uses should be directed and developed with an eye towards making the mail relevant and useful to the recipient.
What subject lines shouldn’t be is deceptive, either intentionally or inadvertantly. How can a subject line be inadvertantly deceptive? Take this: “Today only! One day sale!” The email in question was a printable coupon to get a discount at a bookstore. Unfortunately, the sales was not “Today” – the day the email was received.
On the one hand, I can sympathize with the sender. Sometimes email takes a while to get delivered, particularly for large mail drops. So you want to send before the mail needs to be in the inbox and in front of the recipient. But, that means that some of your recipients may get the email before “Today.” A much better subject line would have been “Friday only! One day sale!”
Tragic mistakes in appending
- laura
- Jun 3, 2009
Last week, Chief Marketer ran an article listing the Top 10 E-mail Appending Mistakes to Avoid. While the article has some good information, I think it missed the mark. In most cases the first mistake companies make when deciding to do an appending run on a customer list is: to append the list.
There is no permission with an appended list. None. Theoretically, senders can kinda get around the lack of permission by sending one email asking users to opt-in. However, every company I’ve ever suggested that to has recoiled in shock and horror. Their protests are all eerily similar.
Another perspective on the Politico article
- laura
- May 27, 2009
Yesterday, I talked about the delivery advice that could be gleaned from the Politico article The best e-mail lists in politics. While there are some good practices and attitudes expressed in the article, there are problems with how some of the political lists are being handled.
For instance, Ken Magill signed up for any number of political lists during the last election cycle and has been chronicling the email he has received from the various campaigns. Yesterday he posted about the mail he has received at the address he gave Secretary Clinton’s campaign and how far and wide the list is being shared. He points out a couple truths missed by the Politico article.
Winning friends and removing blocks
- laura
- May 14, 2009
I do a lot of negotiating with blocklists and ISPs on behalf of my clients and recently was dealing with two incidents. What made this so interesting to me was how differently the clients approached the negotiations.
In one case, a client had a spammer slip onto their system. As a result the client was added to the SBL. The client disconnected the customer, got their IP delisted from the SBL and all was good until the spammer managed to sweet talk the new abuse rep into turning his account back on. Predictably, he started spamming again and the SBL relisted the IP.
My client contacted me and asked me to intercede with Spamhaus. I received a detailed analysis of what happened, how it happened and how they were addressing the issue to prevent it happening in the future. I relayed the info to Spamhaus, the block was lifted and things are all back to normal.
Contrast that with another client dealing with widespread blocking due to a reputation problem. Their approach was to ask the blocking entity which clients they needed to disconnect in order to fix the problem. When the blocking entity responded, the customer disconnected the clients and considered the issue closed. They didn’t look at the underlying issues that caused the reputation problems, nor did they look at how they could prevent this in the future. They didn’t evaluate the customers they disconnected to identify where their processes failed.
The first client took responsibility for their problems, looked at the issues and resolved things without relying on Spamhaus to tell them how to fix things. Even though they had a problem, and is statistically going to have the occasional problem in the future, this interaction was very positive for them. Their reputation with the Spamhaus volunteers is improved because of their actions.
The second client didn’t do any of that. And the people they were dealing with at the blocking entity know it. Their reputation with the people behind the blocking entity was not improved by their actions.
These two clients are quite representative of what I’ve seen over the years. Some senders see blocking as a sign that somehow, somewhere there is a flaw in their process and a sign they need to figure out how to fix it. Others see blocking as an inconvenience. Their only involvement is finding out the minimum they need to do to get unblocked, doing it and then returning to business as usual. Unsurprisingly, the first type of client has a much better delivery rate than the second.
Sending mail from unread email addresses
- laura
- May 8, 2009
Some marketers, even large marketing companies, send mail from email addresses that are unread. Justin Premick posted a list of reasons this is a very, very bad idea. Be sure to read the comments, too.
Read MoreWalking the Walk
- laura
- May 7, 2009
Last week I mentioned a Smith-Harmon report about how to handle email when going out of business. I mentioned at the end of the post that I was pleasantly surprised at how well done their email program was. Let’s walk through the process.
1) The download process. Clicking on the “download report” page popped up a signup window. They ask for first name, last name, company and and email address, but only require an email address. There is a link to their privacy policy and two unchecked boxes. The first is “I would like to subscribe to Smith-Harmon’s monthly newsletter, which is full of email marketing tips, news and research.” The second is “Please have a representative contact me to discuss how Smith-Harmon can help my company with its email program.”
How does their process incorporate best practices?
TWSD: Run, hide and obfuscate
- laura
- May 5, 2009
Spammers and spamming companies have elevated obfuscating their corporate identities to an artform. Some of the more dedicated, but just this side of legal, spammers set up 3 or 4 different front companies: one to sell advertising, one or more to actually send mail, one to get connectivity and one as a backup for when the first three fail. Because they use rotating domain names and IP addresses all hidden behind fake names or “privacy protection services”, the actual spammer can be impossible to track without court documents.
One example of this is Ken Magill’s ongoing series of reports about EmailAppenders.
Aug 5, 2008 Ouch: A List-Purchase Nighmare
Sept 9, 2008 Umm… About EmailAppenders’ NYC Office
Sept 15, 2008 E-mail Appending Plot Thickens
Nov 11, 2008 EmailAppenders Hawking Bogus List, Claims Publisher
Dec 23, 2008 Internet Retailer Sues EmailAppenders
Feb 1, 2009 EmailAppenders Update
Mar 10, 2009 Another Bogus E-mail List Claimed
April 14, 2009 EmailAppenders a Court No-Show, Says Internet Retailer
April 21, 2009 EmailAppenders Gone? New Firm Surfaces
May 5, 2009 EmailAppenders Back with New Web Site, New Name
Their actions, chronicled in his posts, are exactly what I see list providers, list brokers and “affiliate marketers” do every day. They hide, they lie, they cheat and they obfuscate. When someone finally decides to sue, they dissolve one company and start another. Every new article demonstrates what spammers do in order to stay one step ahead of their victims.
While Ken has chronicled one example of this, there are dozens of similar scammers. Many of them don’t have a persistent reporter documenting all the company changes, so normal due diligence searches fail to turn up any of the truth. Companies looking for affiliates or list sources often fall victim to scammers and spammers, and suffer delivery and reputation problems as a result.
Companies that insist on using list sellers, lead generation companies and affilates must protect themselves from these sorts of scammers. Due diligence can be a challenge, because of the many names, domains and businesses these companies hide behind. Those tasked with investigating affiliates, address sources or or mailing partners can use some of the same investigative techniques Ken did to identify potential problems.
Going out of business email strategies
- laura
- May 1, 2009
Chad White of Smith-Harmon posted a report today on shutting down email marketing programs when going out of business. He looks in detail at how a number of companies handled their email marketing during the going-out-of-business process. There is a very solid mix of examples of how companies handle things. Some companies do things very badly, like never mention over email that they’re going out of business or neglect to follow CAN SPAM regulations. Others used their list as a communications tool that survived the dissolution of the parent company.
The full report is well worth a read, but the take home messages are clear.
Buying lists and other stupid marketing tricks
- laura
- Apr 21, 2009
Back in November, I commented on Zoominfo and that they were selling senders very bad lists. At that time, Zoominfo did not have my current information. They have since rectified that problem and are now selling my information to people.
This morning, I received an email that said:
I have an email delivery problem. Can you help?
- steve
- Apr 3, 2009
I see a lot of requests for help with some sort of delivery problem, sent to me as an individual, sent to Laura as part of a consulting relationship, sent to ISPs, sent to organizations running blacklists or sent to industry mailing lists, both public and private.
Some of them could be done better. OK, most of them could be done better, some of them could be done a lot better. Here’s some things to do to get the best response from your delivery consultant, your fellow mailing list members or your ISP contact.
Be specific about what delivery problem you’re seeing
Are you seeing SMTP hard rejections? Are you seeing slow delivery (due to soft rejections, or connection level timeouts)? Or is the mail being delivered, but ending up in the bulk folder?
Bad question and answer: “Is anyone seeing delivery problems with Yahoo?” leads to “There’s a ‘y’ in the month, of course we’re seeing delivery problems at Yahoo.”
Better question for a useful answer: “I started to see a lot more soft bounces from Yahoo last Thursday, and our probe accounts there are seeing mail ending up in the bulk folder – is anyone else seeing this?”
Describe the symptoms
One of the most important things is to describe the symptoms you’re seeing, rather than just your guess at what the underlying problem is.
Bad question: “Our client, the Breast Cancer Foundation, is seeing delivery problems because of the word ‘breast’ – how do we get them whitelisted?”
Better question: “Our client, the Breast Cancer Foundation, is getting filed in the junk folder at AOL – what should we look at to work out why?”
Mention where you’re getting your information
Are you seeing detailed rejections in your mail logs, or just seeing your outbound mail queues growing? Are you seeing bulk folder delivery on your own email accounts at the receiver, or are you relying on data from a commercial mailbox monitoring company?
Provide the basic information about delivery that’s usually going to be needed
What IP address are you sending email from? What domain are you sending to? Or, if you’re contacting the ISP, what email address? What sort of mail are you sending? (If you’re contacting a blacklist or ISP, include the IP address in the subject line).
Are you the only person sending email from that IP address, or is it shared by other users?
If you’re getting rejections, bounces or deferrals, include the rejection message or bounce message.
How much mail are you sending to the domain where you’re seeing a problem? How much is being rejected or delayed?
What, if anything, have you changed recently? If you’re mailing for yourself, did you just start mailing a new bunch of contacts you’ve acquired (or discovered, in an old database)? If you’re an ESP, is this a new customer, or have they been mailing successfully for a while?
What are your typical complaint / feedback loop rates? What are your typical user unknown or rejection rates? If you’re monitoring inbox delivery, what are your inbox rates at this receiving domain?
Do you have a feedback loop or whitelist set up with this receiving domain? Are you using any sort of authentication (SPF, DKIM)?
Bad question: “I’m seeing a lot of bounces from AOL. Any idea why?”
Better question: “I’ve been sending mail without any problems for a while, but most of my AOL recipients have been rejected today, with the message 554 HVU:B1 http://postmaster.info.aol.com/errors/554hvub1.html. We don’t have a feedback loop or whitelist with AOL. What happened?”
Say what you’ve already done
If there’s a URL in the rejection message, did you click on it? Did the page it led to help?
Did you contact the receiving ISP already? What did they say?
Timeliness – there’s no such thing as a delivery emergency
Email delivery problems are never a life-or-death issue. Don’t demand immediate responses to email. Don’t follow up with a phone call five minutes after sending the email.
Conversely, if you saw a delivery problem three weeks ago which has since fixed itself then not only does nobody care, it’s likely that some of the information that would have helped diagnose the problem may no longer exist.
Appropriate communication channel
It’s very difficult to resolve a delivery issue by ‘phone. Partly that’s because you need to communicate some detailed information (like IP addresses) where even a single typo can make any analysis worthless, so cutting and pasting is the only way to avoid problems. But it’s also partly because it’s often something that can require significant work to analyse (checking databases, delivery logs, reputation sources, email structure, checking with other people working in the field), all of which is difficult to do while also dealing with someone on the ‘phone.
Avoid using IM for this too, unless you’ve been asked to do so. And if you’re using IM, offer to send the bulkier data (logs, IP addresses, sample messages) by email.
If you’re communicating with someone where answering your questions is part of their job description it’s even more important to use email, so that all the information is stored in their ticketing system – both for future reference by them or their colleagues, and also to make sure that their work is visible to their employer.
Respond appropriately to questions
It’s likely that whoever you’re asking may need additional information, such as a sample message. If they ask you for more information, respond with it as soon as possible, while they still have the issue in their mind.
Don’t argue that the information is irrelevant, or they don’t need to know it. Really, they wouldn’t ask if they didn’t think it might be relevant. If you can’t provide it (because you don’t have it, or for privacy or contract reasons) explain that, and see if there’s something else that might provide the same useful information.
Respond appropriately to answers
You asked the question because you didn’t know the answer, and you thought the person or group you asked might. So rejecting an answer you get just because it seems wrong to you or you don’t fully understand it is probably a bad idea.
I regularly see clients who are paying good money for extremely competent deliverabilty advice refuse to accept the answer they’re given – insisting that the problems can’t possibly be due to the content of the email, or the reputation of the sending IP address, or the types of links included in the email. Then, after wasting several (billable) hours arguing with their consultant they actually try the change suggested, and it helps with the problem.
If you’re asking a mailing list, rather than an individual, then it’s possible you will get some completely useless suggestions. It’s still better to politely explain why you think they don’t apply (and listen to any replies you get to that) than to reject or ignore them out of hand.
Courtesy
You’re asking for help. Even if you’re paying the person you’re asking for advice you’re still more likely to get service above and beyond if you’re pleasant to deal with. Wrap a little social lubricant around your question – a “Hi!”, “When you get a moment, could you take a look at…”, “Thanks!” goes a long way.
Be respectful of their time. If it’s not an urgent issue, let them know that. Try not to ramble.
When the problem is resolved, write and thank them for their effort. If you identified the problem and it wasn’t what they thought, explain briefly what the issue was. You never stop learning, and it’s possible that knowing that will help them elsewhere.
Be nice. Be brief. If you’re easy to deal with, you’ll get more helpful responses.
What is an email address? (part three)
- steve
- Mar 24, 2009
As promised last week, here are some actual recommendations for handling email addresses.
First some things to check when capturing an email address from a user, or when importing a list. These will exclude some legitimate email addresses, but not any that anyone is likely to actually be using. And they’ll allow in some email addresses that are technically not legal, by erring on the side of simple checks. But they’re an awful lot better than many of the existing email address filters.
What is an email address? (part two)
- steve
- Mar 20, 2009
Yesterday I talked about the technical definitions of an email address. Eventually on Monday I’m going to talk about some useful day-to-day rules about email address acquisition and analysis, but first I’m going to take a detour into tagging or mailboxing email addresses.
Tagging an email address is something the owner of an email address can do to make it easier to handle incoming email. It works by adding an extra word to the local part of the email address separated by a special character, such as “+”, “=” or “-“. So, if my email address is steve@example.com, and I’m signing up for the MAAWG mailing lists I can sign up with the email address steve+maawg@example.com. When mail is sent to steve+maawg@example.com it will be delivered to my steve@example.com mailbox, but I’ll know that it’s mail from MAAWG. I can use that tag to whitelist that mail, to filter it to it’s own mailbox and a bunch of other useful things.
In some ways this is similar to recent disposable email address services, but rather than being a third party service it’s something that’s been built in to many mailservers for well over a decade. It doesn’t require me to create each new address at a web page, instead I can make tags up on the fly. And it works at my regular mail domain.
If you’re an ESP it can be interesting to look for tagged addresses in uploaded lists. If it’s a list owned by Kraft and you see the email address steve+gevalia@example.com in the list, that’s a strong sign that that email address at least was really volunteered to the list owner. If you see the email address steve+microsoft@example.com then it’s a strong sign that it wasn’t, and you might want to look harder at where the list came from.
One reason that this is relevant to email address capture is that tagged addresses are something that you should expect people, especially more sophisticated users of email, to use to sign up to mailing lists and that they’re something you don’t want to discourage. Yet many web signup forms forbid entering email addresses with a “+” or, worse, have bugs in them that map a “+” sign in the email address to a space – leading to the signup failing at best, or the wrong email address being added to the list at worst. This really annoys people who use tagged addresses to help manage their email, and they’re often exactly the sort of tech-savvy people who make a lot of online purchases you want to have on your lists.
More on Monday.
What is an email address? (part one)
- steve
- Mar 20, 2009
Given we deal with email addresses every day, dozens or thousands or millions of them, it seems a bit strange to ask what an email address is – but given some of the problems people have with the grubbier corners of address syntax it’s actually an interesting question.
There are two real standards that define what is a valid email address and what isn’t. The most complex is RFC 5322 – Internet Message Format, which describes all sorts of things about the structure of an email, including what’s valid to put in From: and To: headers. It’s really too liberal in what it allows an email address to look like to be terribly useful, but it does provide for one very commonly used feature – the friendly from where the name that’s displayed to the recipient is not just the email address.
How to devalue your mailing lists
- steve
- Mar 17, 2009
This morning I got spam about college basketball – Subject: Inside: your ESPN Tourney Guide. That’s anything but unusual, but this spam got through my spam filters and into my inbox. That’s a rare enough event that I’m already annoyed before I click on the mail in order to mark it as spam.
Wait a second, the spam claims to be from Adobe. And it’s sent to a tagged address that I only gave to Adobe. Sure enough, it’s Adobe and ESPN co-branded spam about college basketball sent to an Adobe list.
Down at the bottom of the email there’s a blob of tiny illegible text, in very pale grey on white. Buried in there is an opt-out link: “If you’d prefer not to receive e-mail like this from Adobe in the future, please click here to unsusbscribe“.
I’d prefer not to receive college sports spam from anyone, including Adobe, so I click on it and find a big empty white webpage with this in the middle of it:
Asking the right question
- laura
- Mar 12, 2009
My job as a consultant does involve answering questions and solving problems. Often the most important, and most overlooked, thing that I do is change the question that clients are asking. It is not that this changes the problem or even, really, changes the solution. It does change how people think of the problem, and changing how they think of the problem drives better solutions.
This can be applied to the current Email Experience Council (EEC) discussion on metrics and defining what a render rate was. Loren has a post up today detailing a number of common email situations and explaining in which cases an email is counted as open and in which cases an email is counted as unopened.
Right now an open in email terms is actually quite simple: a tagged image on a remote webserver was loaded. That’s all an open is. It used to be that no one was blocking images by default, so this was actually quite an accurate way to measure how many people were opening and presumably reading an email (at least for people using mail clients that display HTML and images).
But, as spammers started including more and more explicit images in email, recipients started asking for images to be blocked. In response to recipient requests, ISPs started blocking images by default. No longer was open rate a measure of which recipients opened and read an email, it became a measure of something completely different.
The EEC has recognized this is a problem and have decided that standardization would be a solution. As the first step to standardization they have identified two problems: open rate isn’t calculated in any standard way and the resulting ratio doesn’t describe what most people think it describes. Their recent publication The Email Render Rate defines standard calculations for render rates. This way render rates as reported by different ESPs can be directly compared. Changing the name from open rate to render rate changes what most people expect that the term means. No longer is this a measure of how many recipients opened the mail, but rather it is a measure of how many email clients rendered the images in the mail.
Maybe a better solution could be arrived at by changing the question? Instead of “how can we standardize render rate?” perhaps they should ask the question: “What do people think they’re measuring when they talk about open rates?”
Once the “what?” question is answered, perhaps a good solution to the “how?” question will become more obvious.
Email frequency vs. Response
- laura
- Mar 5, 2009
Mark Brownlow has a great post today detailing how response to a marketing campaign changes with the frequency of a campaign and the value of the campaign.
Read MoreWho is Julia and why won't she leave me alone?
- laura
- Feb 5, 2009
There seems to be some new spam software in use. Julia <random last name> keeps telling me about her new webcam, how much she wants to date me and wants to know when I want to visit. These spams started February 1. I’ve had 179 caught by my MUA filters, and 152 caught by spamassassin (SA score >7 are filtered to a special account).
This is exactly the type of pattern that causes people to write filters that years later people look at and ask why someone thought this was a reasonable marker for spam.
The good folks over at MailChimp have examined some of the scoring rules that their clients trigger. They found some “Julia” type markers. Some oddities they reported on:
Negative brand building with email
- laura
- Feb 2, 2009
Seth Godin compares and contrasts two different email campaigns he’s received. One is a opt-in campaign that is highly relevant to him. The other is spam, sent to two “discovered” email addresses. The whole post is very good, but there are a couple things he said that bear repeating.
Read MorePersonal Contacts at ISPs: Part 2
- laura
- Jan 29, 2009
I’ve talked quite a bit recently about working with ISPs and personal contacts. Today I have an example of what not to do.
One of my ISP friends informed me that another blogger published correspondence from an individual at that ISP, including the individual’s full contact information. The correspondence wasn’t a big deal, the blogger was assigned an IP address by their ISP that was previously used by a spammer. The ISP had a block on the address and he was contacting them to get the block removed. It was totally a misunderstanding on the blogger’s part and the blogger removed the info when the ISP contacted him. Still, once something is out on the net, it’s out there forever.
Don’t do that. Really. When someone at an ISP helps you, don’t go publishing their information on a blog somewhere. They will find out, even if it’s just because their mailbox explodes or their phone starts ringing off the hook with multiple calls about an “emergency” situation. It hurts the person who helped you, who now has to deal with a major increase in volume and work load, and they’re never going to help you again.
This also hurts the rest of us, as ISP employees retreat farther and farther away from contact with senders. Even those of us who are careful with contact information may find it hard to get responses when others in the field are spreading info around.
I know some ISPs can be difficult to get any information from. That’s part of my reason for publishing the ISP information page was to help people find the right contact information. I think it’s extremely important for delivery professionals to understand that you don’t need a personal contact at an ISP to resolve most issues. What you do need is a deep understanding of SMTP, a smattering of knowledge about DNS and HTTP, a firm grasp of privacy issues and an understanding of the dynamics of email.
Landing pages
- laura
- Jan 27, 2009
One thing I don’t talk about very much is what to do after mail has successfully been delivered to the inbox and the recipient has clicked on a link. Bronto Blog has a post from Friday with tips for successful landing pages.
Read MoreWhen the script doesn't work
- laura
- Jan 20, 2009
DJ asks in the comments of Friday’s post:
As Seth said, great reminder. For those that have great processes/channels in place, I’ve found incredible success. However, sometimes I’ve found my answer on Twitter (i.e., @godaddyguy). Also, there have been times where I’ve gone through the script (i.e., shaw.ca) and have never heard back. What then?
Read More
But that's what spammers do!
- laura
- Dec 4, 2008
A few weeks ago I was asked my opinion about a delivery situation. It seems that a sender wanted to mail to a purchased email list. They asked what I thought about getting fresh IP addresses and domains to use to send mail to the purchased list. “We know we’re going to get complaints, probably hit spamtraps and generally have problems with the first few sends of the list. We want to do this without harming our reputation. We figure if we move over to different domains and different IP addresses than we can send this mail and not suffer a reputation hit.”
Uh. Yeah. That’s what spammers do. They split off their mail into discrete sets so that they can spam with impunity and still have one or two ranges that have a good reputation and decent delivery. Some spammers have taken the discrete companies to extremes, and have a series of companies. They purchase a new list and send it through their companies one by one. At each step, they aggressively purge off bounces and complainers. Gradually, they move the list through their steps, resulting in a list that generates few complaints that they can send through their high reputation companies with few delivery problems.
Sure, legitimate mailers can do the same type of thing. But how legitimate can a sender be if they are using spammer tactics? And these are not mailers unwittingly doing something that spammers also do, these are mailers who are using spammer tactics for exactly the same reason spammers do it. They are trying to send mail people do not want, but send it in a way that does not negatively affect their bottom line.
Spammers hide and try to avoid their bad reputation. Legitimate mailers do not.
Confirmed unsubscribe
- laura
- Dec 1, 2008
Whatever one might think about confirming opt-ins I think we can all agree that requiring someone to jump through hoops and confirm an unsubscription request will just annoy that person.
Today I attempt to opt-out from a discussion list. It’s one I *thought* I had opted out of previously, but I could find no record of the request anywhere. OK. So I imagined unsubscribing, I’ll just unsub again and keep better records.
After digging through the headers, I find the unsub link and dutifully mail off my unsubscribe request. I then receive an email that requires I click on a link to confirm my unsub request. This causes me to grumble a bit. I have heard all the arguments about forged unsub requests and the various reasons this is good practice. I believe none of them. Requiring people to confirm an unsubscription request is bad practice.
In this case, the mailing list is a discussion list so there is no CAN SPAM violation. However, I know that some commercial mailing lists have also implemented confirm your opt-out request. For commercial mailing lists, this is a CAN SPAM violation. It’s also just plain rude. If someone says, “Stop!” then you should stop, no questions asked
TWSD: breaking the law
- laura
- Nov 25, 2008
I tell my clients that they should comply with CAN SPAM (physical postal address and unsubscribe option) even if the mail they are sending is technically exempt. The bar for legality is so low, there is no reason not to.
Sure, there is a lot of spam out there that does not comply with CAN SPAM. Everything you see from botnets and proxies is in violation, although many of those mails do actually meet the postal address and unsubscribe requirements.
One of my spams recently caught my eye today with their disclaimer on the bottom: “This email message is CAN SPAM ACT of 2003 Compliant.” The really funny bit is that it does not actually comply with the law. Even better, the address it was sent to is not published anywhere, so the company could also be nailed for a dictionary attack and face enhanced penalties.
It reminds me of the old spams that claimed they complied with S.1618.
McCain Campaign Spamming
- laura
- Oct 22, 2008
As I mentioned in my post on spam from the Obama campaign, there have been reports of spam coming from the McCain campaign. However, the McCain campaign does not seem to be sending the volume of mail that the Obama campaign is, and so they are not as visible.
A recent post over at Denialism Blog shows that the McCain campaign has some of the same problems as the Obama campaign. Chris talks about the unsubscribe options he is presented when trying to stop the spam he is receiving. He suggests the campaign adds another option:
Same old stuff
- laura
- Oct 22, 2008
Al talks about the “new” email preference service run by the DMA. Except it is not actually new nor is it really used.
Read MoreEmail and the Obama Campaign
- laura
- Oct 21, 2008
Late in the summer there were people talking about the spam coming from Senator Obama’s presidential campaign. At that time, most of the discussion was focused on the open subscription form on their website and that there were some individuals who had been fraudulently signed up and were now receiving email from the campaign.
Last week, the Senator’s campaign again became a topic of discussion among some anti-spam groups. The maintainer of one of the more respected public blocklists and members of his family received mail from Senator Obama’s presidential campaign at their personal addresses. Because the mail was unsolicited and met the qualifications for listing, the sending IP addresses were listed on the blocklist. In response, the campaign’s ESP started moving the Senator’s mail to other IP addresses, resulting in those IPs also being listed on the blocklist as well.
I talked with the blocklist maintainer and I believe that his address, and those of his family members, were added to the Senator’s mailing list as the result of an email append. All of them are registered Democrats and they all live in a battleground state.
This may have made for good campaign strategy, not being an expert I cannot comment on that. It is, however, very poor email marketing strategy.
First, the campaign decided to appropriate permission to send email. There is not ever permission associated with an email append. Just because you have a name and a street address does not mean that you have permission to send email. In very, very limited circumstances, an opt-in append (click here to continue receiving email) may be acceptable. However, that is not how appending is normally done.
There is no pretense of permission to send email. Just because someone is registered to a particular party does not mean they want to receive email from that party.
Second, when the campaign started seeing delivery problems they started sending off different IP addresses. Moving IPs around is out and out spammer behavior, no questions asked.
Now, I know this is a very hotly contested election and I know that some people believe that any method of getting the word out is good. I also expect that there may have been some positive reaction from recipients. The overall reaction, based on the IPs changing, may not have been so positive.
Do I really believe that Senator Obama is a evil and willful spammer? No, not really. But that does not change the fact that the Obama campaign seems to be sending email without the permission of the recipient and seem to be attempting to evade blocks by moving IP addresses.
From a marketing perspective, the campaign may be using email effectively and doing everything right. But from an email delivery perspective, they are getting many, many of the basics wrong and are looking like spammers in the process.
Other news and blogs that talk about spam from the Obama campaign:
Vetting customers: an intro
- laura
- Oct 14, 2008
I promised a couple weeks ago, pre-MAAWG, to write about screening new customers. Things have been a bit busy and I have not had a lot of time for the blog. However, today there has been a long conversation on one of the spam related mailing lists relating to ESPs and customer screening. This conversation inspired me to write this introduction to customer vetting.
I have designed customer screening programs for a number of clients as well as actually had an active role in some of those processes. I also screen my own customers and have taught other people how to vet customers.
When designing a vetting process a company must target the process to the size and revenue potential of their customers. If an ESP has a small number of customers, each having a very large recipient base, one single bad customer has the potential to affect the overall reputation of all the ESP customers. With large number of customers sending to very small recipient bases, then one single bad customer is not going to affect overall reputation as dramatically as larger senders will
Because the larger customers have an actual impact on reputation, it is really important to vet the customer. It’s going to cost money and some time, but responsible ESPs have to do it. Really good customers are going to be vetting the ESP at the same time. They don’t want to go with an ESP that has a poor reputation. It is much like dating, each party is assessing the other party and the suitability of a longer term relationship.
For the tiny mailers, though, there is a very small chance that one, single bad customer sending a single bad mailing will destroy the overall delivery of an ESP and ruin their reputation at large receivers. In this case, it makes a lot more sense, both financially and in terms of resource allocation, to screen the email address list rather than the individual customer. This can be mostly automated, with clearly bad lists being prohibited from being mailed and suspicious lists being kicked to humans for decisions.
Let’s be honest, anyone who comes to an ESP with a list of under 20K names is not a big time spammer trying to steal their reputation. Those are the easy ones to deal with, screen the list, limit the number of addresses that can be uploaded upload and limit, even if just by price, the number of mails that can be sent out during any period. Some ESPs really do cater to the small, community group market and they do tend to screen lists not customers.
For larger customers ESPs have a greater challenge. They must identify the real, legitimate mailers that have permission to send mail and identify the ones that are spammers attempting to steal an ESPs reputation. Spammers attempting to steal an ESPs reputation go out of their way to subvert the screening process. One of the hardest things about screening customers is getting the subversive ones to give an ESP enough information to make an informed decision about that customer. I will not lie, a subversive potential customer is expensive to screen, but that investment protects a sender’s reputation and the reputation of their other customers.
Another thing to remember about vetting is that no vetting process is going to be 100% accurate. ESPs with a good process can screen out 80 – 90% of the bad guys before a single email is sent. Most responsible ESPs do that and then stomp wildly on that remaining percentage that are evil or malicious.
Email marketing tips from The Onion
- laura
- Oct 13, 2008
Bonnie talks about insightful email marketing tips taken from an article in The Onion.
1/7 – closed comments on this post as it seems to be a magnet for comment spam.
Another opt-in in the wild
- laura
- Oct 10, 2008
The EEC has an article today about a poorly done opt-in email that DJ Waldo received. How close is that to what you send?
Read MoreTransactional emails
- laura
- Oct 8, 2008
Tamara has an excellent collection of musts related to transactional email. I would add a few more, specific to traveling (hotel and plane reservations) that occurred to me recently as I was bombing through airports trying to read hotel and airline confirmations on my iPhone.
Read MoreBuying Data
- laura
- Oct 3, 2008
Over on Spam Resource Al posted about data sellers and the ESP that supports them. As part of the post, he lists the pricing for email address lists.
Read MoreAppropriating reputation
- laura
- Sep 22, 2008
One of the thing savvy spammers are doing these days is appropriating the reputation of someone else. Reputation appropriate takes many forms. Some spammers hijack windows machines, turn them into bots and send spam through major ISP smarthosts. “Legitimate email marketers” buy service from mainstream ESPs to send their permission-challenged email that they cannot get delivered through their own IP space.
There are different strategies for companies to prevent bad groups from appropriating their reputation. For the ESP, the prime defense against reputation appropriation is screening new customers and new lists.
When screening potential customers, there are three broad categories that customers fall into. One is the legit prospect that is exactly whom they represent to you, these are the easy guys. Another is the naive mailer, who really does not have any clue about email but wants to move into the digital age. This mailer is often extremely small, but knows nothing about email. The final category is the subversive prospect. This is the company who knows exactly what they are doing, and who is actively working to hide their practices from the ESP. They are attempting to subvert the process.
Over the coming weeks I will be talking more about screening new customers and how to distinguish the naive customer from the subversive one.
Yet more data verification
- laura
- Sep 1, 2008
Friday Al posted about data verification, building on discussions last week about Mr. Poopyhead’s article on open signup forms. He has a very insightful analogy, that I like and I am going to steal (emphasis from the original).
Read MoreData Integrity, part 2
- laura
- Aug 28, 2008
Yesterday I blogged about eROIs contention that consumers should not be wasting the time of lead gen companies by filling in fake data. There were lots of good comments on the post, and I strongly encourage you to go read them if you are interested in different perspectives on the data issue.
One of the arguments I was making is that people are only going to give accurate information if they trust the website that is collecting information. I do, strongly, believe this. I also believe very strongly that websites collecting information need to do so defensively. It is the only way you can get good information.
This ties in with an earlier post about a website that collects email addresses from any visitor, then turns around and submits those addresses to webforms. Hundreds of mailing lists have already been corrupted by this group. They are a prime reason companies must design address collection process defensively. There are people who do bad things, who will take an opportunity to harass senders and recipients. This company is not the first, nor will they be the last to commit such abuses.
Taking a stand against abusive companies and people may be useful, but that will not stop the abuse. It is much easier to design process that limits the amount of abuse. For lead gen, in particular, confirmed opt-in is one way to limit the amount of bad data collected. As a side effect, it also results in less blocked mail, fewer complaints and better delivery.
Collecting information from subscribers
- laura
- Aug 27, 2008
VerticalResponse Blog has a post up about collecting information from subscribers to mailing lists. Go check it out.
Read MoreSpamZa: corrupting opt-in lists, one list at a time
- laura
- Aug 20, 2008
A number of ESPs have been tracking problematic signups over the last few days. These signups appear to be coming from an abusive service called SpamZa.
SpamZa allows anyone to sign up any address on their website, or they did before they were unceremoniously shut down by their webhost earlier this week, and then submits that address to hundreds of opt-in lists. This is a website designed to harass innocent recipients using open mailing lists as the harassment vehicle.
Geektech tested the signup and received almost a hundred emails 10 minutes after signing up.
SpamZa was hosted on GoDaddy, but were shut down early this week. SpamZa appears to be looking for new webhosting, based on the information they have posted on their website.
What does this mean for senders?
It means that senders are at greater risk for bad signups than ever before. If you are targeted by SpamZa, you will have addresses on your list that do not want your mail. Some of those addresses could be turned into spam traps.
RoadRunner FBL changes
- laura
- Aug 15, 2008
RoadRunner announced changes to their FBL this morning. Everyone who is currently getting a FBL should have received an email. Important dates to remember include the following.
August 28: Existing RR FBL will be frozen. No changes to existing loops will be accepted and no new FBL applications will be processed. All current FBLs will continue to work.
November 17 (tentative): The new FBL will go live. Existing FBLs will not be converted from the old FBL to the new one. Everyone wishing to be a part of the new FBL will be required to re-enroll in the program beginning on this date.
December 31 (tentative): The old FBL ceases to exist.
More information about the migration is available at http://postmaster.rr.com/FBL.html
Paypal fixes unsubscribes
- laura
- Jul 11, 2008
Through the grapevine, I have heard that PayPal is actually complying with the new CAN SPAM rulemaking and offering one-click unsubscribes.
Read MoreAnother benefit of email marketing
- laura
- Jul 5, 2008
Kevin Hillstrom over at MineThatData blog talks about using email metrics and other customer information to not market to people who cost a company money.
Read MorePayPal Followup
- laura
- Jul 2, 2008
I thought I would give everyone a brief update on my continuing saga with trying to unsubscribe from PayPal’s marketing list. Because of what I do, I have some options not available to the average recipient. One of the things I did is ask people I know if they had any contacts at PayPal who may be able to address this issue.
I was given an internal contact at PayPal by a colleague who works at one of the certification companies. I sent the PayPal contact a brief summary of my experience. She explained she was not in a department that handled email any more, but that she forwarded my mail on to the responsible people. A little later I received another message saying that I had been unsubscribed and they were examining the tapes of my call. She also mentioned that their unsubscribe process would be changed “sometime in mid-July.” I was not given any details.
A colleague who attended the recent AOTA meeting in Seattle offered this comment.
Customer support surveys
- laura
- Jul 1, 2008
I have seen a lot of companies attempt to send out customer support surveys by email, only to fail dismally. Generally, the intentions of the companies who do this are good, but the executions are appalling. Companies have found any number of ways to invite epic fail to call, including mailing to non-customers, mailing to the wrong person at a customer company and mailing to former customers.
Mailing to non-customers generally happens when companies sort abuse and support mail through the same ticketing system. Good customer support (tell us how we did) turns out to be rotten complaint support. The failure here is multifactorial, but revolves around not understanding the difference between customer support mail and abuse complaints. Abuse is not, usually, mail from your customers. More often mail to abuse is from non-customers. While it may seem like a good thing to follow up with abuse complaints to find out if the person is satisfied, generally someone who complains about spam does not want more mail from a company. The fix it to change the selection process for surveys. Survey customers not complainers.
The second failure is more common with enterprise vendors. Generally the vendor will have multiple contacts at company but send a single survey out to all contacts at the customer. Take an average website that provides statistics about web or email performance. A company establishes an account there, and then provides a logins for customer support people, a manager or two and maybe an outside consultant. These people are all using the same site, but are possibly using different parts of it. The consultant can give some feedback on the API and data access, but is not the right person to ask about pricing, packages or overall usefulness and value for money. Management can provide feedback on pricing and value for money but probably has never logged into the website, despite having a working account. Customer support can provide feedback on the user interface and overall usefulness of the site. Knowing who is who at the customer and who is the right contact for different surveys can be tricky, but it is always better a company to appear to be acting purposely.
Finally, some companies send out surveys to anyone who has ever registered for a website, or game or product no matter how long ago that registration was. They send mail to the person who registered for a website but has not logged in for 6 months, or 12 months or even longer. The recipient may have even taken positive action to close an account, such as discontinuing payments. And, yet, the company still mails them a customer satisfaction survey. If the recipient is not paying for the product, if the recipient is not logging into the website then they are no longer a customer. Sure, there are times to reconnect with old customers, and it can be done well. However, what I am talking about is the survey that is clearly designed to be answered by current users and customers.
The sad thing is, I have received customer satisfaction surveys in all of the above categories in the last 6 months.
If you as a sender, are going to use customer satisfaction surveys, do it in a thoughtful and purposeful manner. Do it in a way that brings value to your company and to the people you are surveying. If you do not, you risk higher complaint rates. Remember, people who are not your customer or who are a former customer are probably more likely to hit “this is spam” then to answer your survey. Like any mail you send, make sure you know who your audience is and have a mental model for how they will treat your mail. Do not just grab all available addresses and mail them. Do some analysis of your customer base before you mail and mail them surveys that apply to them. You will get fewer spam complaints and probably more and more accurate survey responses.
How not to handle unsubscribes
- laura
- Jun 24, 2008
On the heels of my unsubscribe experience last week where an ESP overreacted and unsubscribed addresses that did not belong to me, I encountered another deeply broken unsubscribe process. This one is the opposite, there is no way to unsubscribe from marketing mail at all. Representatives of PayPal have only been able to suggest that if I do not want their mail, that I block PayPal in my email client.
I had a PayPal account years and years ago. They made some extensive privacy policy changes back in 2003 and when I did not actively agree to the new policies, they closed the account. That account closure seemed to take, I heard nothing from PayPal. In early 2008, I made a purchase at a vendor that only accepted credit cards through PayPal. Normally, I do not do business with vendors who only accept payment through PayPal, but there appeared to be a way to make the payment without establishing a PayPal account, so I went ahead and made the purchase.
The receipt from that purchase came from PayPal, and mentioned that I had an existing PayPal account. I figured that because the address was the same as the 2003 account that the boilerplate did not understand ‘closed accounts’. I brushed off the notice and did not worry about it.
On June 23, I received marketing email from PayPal. The mail offered 10% off my first eBay purchase, if I set up an eBay account using the same address on my PayPal account. Yay. Spam. Oh, well, no big deal, there was an unsub link at the bottom of the email. It is PayPal, they are a legitimate company, they will honor an unsubscribe. It will all be fine.
Or. Not.
Clicking on the unsubscribe link in the email takes me to a webpage that tells me I had to login to my account to unsubscribe. But I do not have an account!
They clearly think I have an account linked to the email address they mailed. I decide to see if I can recover the account and then unsubscribe. I put in the email address they sent the marketing email to, the password I probably would have used had I actually set up this account and hit “submit.” PayPal now asks me to set up 3 questions to use to recover my account in case I forget the login in the future. Uh. What? No. I do not want to set up an account, I want them to stop sending me email. I abandon that webpage.
I then attempt to recover the password to the account. Put in the email address that PayPal is sending email to and hit “forgot password”. PayPal, as expected, sends me an email. Click this magic link to recover your account. PayPal then asks me to input the full number of the credit card associated with the account – the credit card number I do not have. What account? What credit card number? Is this from my 2003 subscription that was closed? Is this from the purchase I made in February? I abandon that webpage.
The recover password email helpfully lists a phone number I can call for assistance so I call. In order to be able to talk to someone I have to enter my phone number. And the credit card number associated with my account. I resorted to randomly pounding on “0” and telling the voice recognition software I wanted help. Eventually, it got so confused it transfered me to a real human.
Tragically, the voicemail system was actually more helpful than the real human on the other end. Distilling down hours of sitting on the phone with them, I am told the following:
Unsubscribe policies
- laura
- Jun 19, 2008
Our local brewpub has an email list. For various reasons I have multiple addresses on the list and finally decided that getting 4 copies of each mailing was silly. About a week ago, I sent in unsubscribe requests for 3 of the addresses. Today I get another 4 copies of their mailing. That’s not good. Luckily, I know one of the delivery folks at their ESP so I send her an email.
I know unusubscribes can take a few days to process, but it has been seven and CAN SPAM is pretty clear about the 10 day requirement. My first email to their delivery expert is just asking how long unsbs normally take. She responds they take 3 – 4 days. Uh Oh.
I tell her I unsubscribed these 3 addresses (with the unsub links) on 6/10 and received more email this morning. I did tell her that there were multiple subscriptions and they were all legit, but the reasons were really not important. Just that I didn’t want quite so many emails and their unsubscribe process seemed broken.
Now we get to the part where it all goes a wee bit pear shaped. The next email I get back from her explains why I am on so many lists. Fair enough. The more concerning bit is that they have not only gone through their database and unsubscribed all my addresses, but they have also found Steve’s addresses and unsubscribed those too. What the email does not contain is an explanation of why their unsubscribe process broke.
At this point I am a bit annoyed. I did not want all my addresses unsubscribed, just some of them. And the bit about unsubscribing Steve? That’s just silly and unnecessary. Another round of email ensued, pointing out this is bad and please put everything back how it was except please unsubscribe these three addresses I sent originally.
Things are back how they were, although the technical staff is still looking into how their unsubscribe process broke. The initial thought is that during a technology transition they lost some unsubscribe requests.
This whole process has bothered me for a number of reasons. One is the utterly cavalier attitude of the delivery people at the ESP. Their unsubscribe process broke. This is, to my mind, an emergency. ESPs have been fined for broken unsubscribe processes. Two is the process of unsubscribing addresses that belonged to a completely different person. The ESP did explain the policy behind that, sorta.
Email to mobile devices
- laura
- Jun 13, 2008
There have been numerous blog posts about email to mobile devices, and making sure that your email displays well on the tiny screens with often lobotomized software. What few people have mentioned is the CAN SPAM laws related to sending mail to mobile devices.
While the FTC handles the bulk of the regulation related to CAN SPAM the FCC is responsible for regulating email sent to wireless devices. The act requires the FCC protect consumers from “unwanted mobile service commercial messages.” To that end there are specific regulations that apply to email sent to domains used exclusively for mobile devices that do not apply to messages that go out to non-mobile domains.
A summary of the FCC rules can be found at http://www.fcc.gov/cgb/policy/canspam.html. The FCC describes the ban to consumers thusly:
Mind filters
- laura
- Jun 9, 2008
Stefan has a good article up at ClickZ about getting mail past the “mind filter”.
Read MoreUnsubscribes made difficult
- laura
- Jun 7, 2008
Dennis blogs about his experience trying to unsubscribe from classmates.com list over on deliverability.com. His experience touches on a number of points I have discussed recently.
Dennis initially signed up for a free account at classmates.com around 10 years ago, but has asked to be unsubscribed multiple times. Recently classmates reactivated his subscription again, sending him marketing mail he did not want. Reactivating subscriptions is an extremely bad idea. Not only is it a CAN-SPAM violation to send mail after an unsubscribe has been received, but senders really end up annoying recipients by doing this. Think about it, these are people who have actively told the sender that they do not want mail, and the sender goes out and decides to override the recipients wishes.
I can only imagine how horrible the delivery for this mailing was. ISPs measure how many non-existent addresses senders attempt and mailing a list that has addresses accreted over 10 years is going to have a massive number of dead addresses. Not that many people have the same address now that they did 10 years ago. Some of those dead addresses are probably now being used as spamtraps by the ISPs, another hit to delivery rates. Finally, there are the complaint rates to consider.
For those people who received the mail and want to unsubscribe, Classmates.com does everything possible to discourage that. Dennis describes the process he went through.
Marketers missing out
- laura
- Jun 6, 2008
Many delivery blogs have posted about the recent ReturnPath study showing that marketers are missing prime opportunities to use email to develop a strong relationship with recipients. I finally manged to get a few moments to read through the study and comment on it. Over a few days in February ReturnPath researchers signed up at more than 60 major retailer brands. They then monitored the subscriptions to see how often and what kind of mail the retailers sent.
Overall, it seems the researchers were disappointed in how the retailers were using mail. Even the title of the whitepaper captures this feeling: “Creating Great Subscriber Experiences: Are Marketers Relationship Worthy?” The answer seems to be more no than yes.
From my perspective the data is not all that surprising. In many cases it seems bigger companies rely on the recognition of their brand to get them through minor delivery problems (like complaints) rather than good practices. Whereas a smaller company will have to work harder to develop a relationship, larger companies with wide brand recognition can fall back on their brand.
There were a few areas ReturnPath measured.
Before you send email
- laura
- Jun 5, 2008
Seth Godin lists the 38 things you should do before you send an email.
Read MoreSuppression lists
- laura
- Jun 4, 2008
Mickey has a post up about how long senders must hold on to that suppression list.
Read MoreThose addresses are costing you
- laura
- May 29, 2008
Mark Brownlow has a post up about the hidden costs of bad email marketing. These center around brand damage, but there are other costs to poor email marketing strategies.
Previously, having old and non-responsive email addresses on a mailing list did not hurt and may have helped a reputation at an ISP. In some cases, these addresses may have even helped a reputation by increasing the number of emails delivered thus lowering the overall percentage of complaints.
More recently, some ISPs have started looking at the characteristics of recipients as part of the reputation score of a sender. If a sender is mailing a lot of abandoned email addresses, these ISPs can detect that fact. This counts against a senders reputation and may result in email ending up in the bulk folder or being blocked at the transaction.
Many senders are extremely resistant to removing old addresses from their lists. Some of the more numbers driven ones have even followed the statistics and can tell me exactly how many people ignore their email for 12 months or 18 months, and then come back and make a large purchase. This is true, sometimes people will ignore email for a long time and then come back. Keeping these people on a list may be beneficial.
However, in those recipients who ignore email (no opens, no clicks) for a long time are some addresses that have been abandoned. While these addresses are not spamtraps, repeatedly sending email to large numbers of abandoned addresses will lower the sender’s reputation over time.
All senders should have a process for dealing with non-active addresses. Allowing cruft to accumulate on a list does negatively affect reputation.
Disposable or Temporary Addresses
- laura
- May 20, 2008
Mark Brownlow has a really good post up today about disposable and temporary addresses and how they affect marketers trying to build an opt-in list.
I use tagged addresses for all my signups, and have for more than 10 years now. It lets me track who I gave an address to and if this mail is contrary to what I signed up for or the address has leaked, I can shut down mail to that address entirely.
Tagged addresses also have another function. One of our local brew pubs has a rewards program, spend money there, get points. As part of the signup process, they requested an email address. All the email I have received from them has been clearly branded, well designed, they are an example of how to use email right. That is until last week. Last week I received an email to the tagged address from some survey company. The survey company provided no branding, nothing.
Verifying email addresses
- laura
- May 19, 2008
Over at CircleID Aviram Jenik posts about using email addresses as identification and how that can go horribly wrong if the website does no verification. In his case, the problem is a user who has made a purchase using Aviram’s gmail address and Aviram now has access to the other users personal information. As he explains it:
Read MoreEmail non-viable for acquisition
- laura
- May 13, 2008
Chris Marriott over at iMediaConnection talks about all the reasons email is a non-starter as a replacement for direct mail. This is something I have been telling clients for a while now. Chris mentions a number of reasons for why email is not an acquisition tool.
Read MoreAOL publishes sender recommendations
- laura
- Apr 30, 2008
In a blog post on April 28, AOL pointed to their new Sender Best Practices document. These are not things a sender must do in order to get mail delivered to AOL, but rather things that will help improve your reputation at AOL.
The recommendations are what I have been recommending for a while and there is nothing overly surprising in the recommendations.
Forgery and spamware
- laura
- Apr 23, 2008
Recently there has been a massive uptick in forgeries. I have been seeing hundreds of bounce back messages, peaking at more than 1000 in an hour. I have been talking about this with people who monitor large spamtrap feeds, large MTAs and spamfilters and it seems this is not an isolated experience. The consensus seems to be that there is new spamware out there which is using email addresses on the spam list as a From: address
The volume itself is annoying. Thousands of messages a day from “mailer-daemon” telling me that the mail I sent with the subject line “Get a longer tool” cannot be delivered to some random address some where. These are coming to at least 3 separate email addresses. One of them was given to Intuit back in 2001/2002 when I registered a copy of Quicken, and ended up leaked to loan spammers and is all over spam lists. The other two are addresses scraped from websites. Same spammer has them, same spammer is using them as part of his spam run.
Even more annoying than the volume, though, is the challenge/response emails. “Your email to jobobjimbo@example.com cannot be delivered until you click this link.” I have been adding every domain I can find that is using c/r to my filters, and just discarding the c/r emails so I do not have to deal with them. That is not my ideal solution, it does mean that if someone using c/r ever tries to contact me I will not see the challenge and our communications cannot happen.
Some people have recommended that the right way to deal with challenges from forged spam are actually to answer the challenges. As the reasoning goes, if someone using c/r is going to outsource their spam filtering to a victim of spam forgery, then they should expect that the “spam filter” may have a different opinion than they do. While I always sympathized with this viewpoint, I was not sure I would ever confirm spam forgeries. The sheer volume of c/r stuff I have received in the last few weeks has almost convinced me that people who use c/r deserve every bit of spam they get. If a c/r filter lets in spam, then perhaps they will reconsider their choice to spew challenges out to forged email addresses.
The amount of c/r spam I am getting as part of the forgery runs is decreasing, I think I have finally managed to block the primary sources. It does mean I will not be able to communicate with people who use c/r in the future, but I find this a small price to pay for not having to be an outsourced spam filter. I get enough of my own spam, I really do not want to have to deal with yours.
That's spammer speak
- laura
- Apr 22, 2008
I’ve been hearing stories from other deliverability consultants and some ISP reps about what people are telling them. Some of them are jaw dropping examples of senders who are indistinguishable from spammers. Some of them are just examples of sender ignorance.
“We’re blocked at ISP-A, so we’re just going to stop mailing all our recipients at ISP-A.” Pure spammer speak. The speaker sees no value in any individual recipient, so instead of actually figuring out what about their mail is causing problems, they are going to drop 30% of their list. We talk a lot on this blog about relevancy and user experience. If a sender does not care about their email enough to invest a small amount of time into fixing a problem, then why should recipients care about the mail they are sending?
A better solution then just throwing away 30% of a list is to determine the underlying reasons for delivery issues, and actually make adjustments to address collection processes and user experience. Build a sustainable, long term email marketing program that builds a loyal customer base.
“We have a new system to unsubscribe people immediately, but are concerned about implementing it due to database shrink.” First off, the law says that senders must stop mailing people that ask. Secondly, if people do not want email, they are not going to be an overall asset. They are likely to never purchase from the email, and they are very likely to hit the ‘this is spam’ button and lower the overall delivery rate of a list.
Let people unsubscribe. Users who do not want email from a sender are cruft. They lower the ROI for a list, they lower aggregate performance. Senders should not want unwilling or unhappy recipients on their list.
“We found out a lot of our addresses are at non-existent domains, so we want to correct the typos.” “Correcting” email addresses is an exercise in trying to read recipients minds. I seems intuitive that someone who typed yahooooo.com meant yahoo.com, or that hotmial.com meant hotmail.com, but there is no way to know for sure. There is also the possibility that the user is deliberately mistyping addresses to avoid getting mail from the sender. It could be that the user who mistyped their domain also mistyped their username. In any case, “fixing” the domain could result in a sender sending spam.
Data hygiene is critical, and any sender should be monitoring and checking the information input into their subscription forms. There are even services which offer real time monitoring of the data that is being entered into webforms. Once the data is in the database, though, senders should not arbitrarily change it.
Signup forms and bad data
- laura
- Apr 16, 2008
One thing I frequently mention, both here on the blog and with my clients, is the importance of setting recipient expectations during the signup process. Mark Brownlow posted yesterday about signup forms, and linked to a number of resources and blog posts discussing how to create user friendly and usable signup forms.
As a consumer, a signup process for an online-only experience that requires a postal address annoys and frustrates me to no end. Just recently I purchased a Nike + iPod sport kit. Part of the benefit to this, is free access to the Nike website, where I can see pretty graphs showing my pace, distance and time. When I went to go register, however, Nike asked me to give them a postal address. I know there are a lot of reasons they might want to do this, but, to my mind, they have no need to know my address and I am reluctant go give that info out. An attempt to register leaving those blanks empty was rejected. A blatantly fake street address (nowhere, nowhere, valid zipcode) did not inhibit my ability to sign up at the site.
Still, I find more and more sites are asking for more and more information about their site users. From a marketing perspective it is a no-brainer to ask for the information, at least in the short term. Over the longer term, asking for more and more information may result in more and more users avoiding websites or providing false data.
In the context of email addresses, many users already fill in random addresses into forms when they are required to give up addresses. This results in higher complaint rates, spamtrap hits and high bounce rates for the sender. Eventually, the sender ends up blocked or blacklisted, and they cannot figure out why because all of their addresses belong to their users. They have done everything right, so they think.
What they have not done is compensate for their users. Information collection is a critical part of the senders process, but some senders seem give little thought to data integrity or user reluctance to share data. This lack of thought can, and often does, result in poor email delivery.
Social network sends spam
- laura
- Apr 15, 2008
Yesterday we talked about social networks that harvest the address books of registered users and send mail to all those addresses on behalf of their registered user. In the specific case, the registered user did not know that the network was going to send that mail and subsequently apologized to everyone.
That is not the only way social networks collect addresses. After I posted that, Steve mentioned to me that he had been receiving invitations from a different social network. In that case, the sender was unknown to Steve. It was random mail from a random person claiming that they knew each other and should network on this new website site. After some investigation, Steve discovered that the person making the invitation was the founder of the website in question and there was no previous connection between them.
The founder of the social networking site was harvesting email addresses and sending out spam inviting people he did not know to join his site.
Social networking is making huge use of email. Many of my new clients are social networking sites having problems delivering mail. Like with most things, there are some good guys who really do respect their users and their privacy and personal information. There are also bad guys who will do anything they can to grow a site, including appropriating their users information and the information of all their users correspondents.
It is relatively early in the social networking product cycle. It remains to be seen how much of an impact the spammers and sloppier end will have. If too much spam gets through, the spam filters and ISPs will adapt and social networks will have to focus more on respecting users and potential users in order for their mail to get delivered.
Address harvesting through social networks
- laura
- Apr 15, 2008
The next killer ap on the Internet seems to be social networking. Everyone has a great idea for the next facebook or or myspace. All of these sites, though, have to find users. The site will fail if there are no users. One way to get new users is to ask all your current users to invite all their friends to join. This tends to lead to the marketing / product decision to insert functionality into the social networking site which allows current users to upload their address book and the site itself will send out invitations to all your friends and contacts.
This is not actually as great as an idea as it sounds, however. First, you end up with situations like what happened to me this past week. On Wednesday I received the following email:
Dealing with ISPs when you are blocked
- laura
- Apr 10, 2008
Here is some advice on dealing with ISPs over a blocking issue.
Read MoreHow to be a spammer
- laura
- Feb 20, 2008
JD had a comment on my Valentines day semi-fluff post, that really summed up the reality for senders. He said
Read MoreValentine's day semi-fluff
- laura
- Feb 14, 2008
There comes an inevitable point in some of my longer term consulting gigs where my client asks me some version of the following question:
Read MoreCAN SPAM compliance.
- laura
- Feb 7, 2008
Over on the ET blog, Al posted about how CAN SPAM compliance is not sufficient for you to not be spamming.
It’s a bit different perspective, but very complimentary to my post yesterday about what is and is not spam. He and I have both heard from ISP people about how many requests for whitelisting or unblocking are prefaced with, “We comply with CAN SPAM” and how meaningless that statement really is. Al has a longer discussion of why.
What really is "spam" anyway?
- laura
- Feb 7, 2008
A few days ago I was reading the attempt by e360 and Dave Linhardt to force Comcast to accept his mail and to stop people posting in the newsgroup news.admin.net-abuse.email from claiming he is a spammer. The bit that pops out at me in this complaint of his, is the fact that he believes that by complying with the minimal standards of the CAN-SPAM act, he is not spamming.
The problem with this claim is that CAN SPAM lists the minimal standards an email must meet in order to avoid prosecution. CAN SPAM does not define what is spam, it only defines the things senders must do in order to not be violating the act. There is no legal definition of spam or of what is not spam.
To add to the confusion there are a number of confusing and contradictory definitions of spam. Definitions people have used over the years include:
Comcast rate limiting
- laura
- Jan 25, 2008
Russell from Port25 posted a comment on my earlier post about changes at Comcast.
Read MoreAOL checking DKIM
- laura
- Jan 23, 2008
Sources tell me that AOL announced on yesterday’s ESPC call that they are now, and have been for about a week, checking DKIM inbound. This fits with a conversation I had with one of the AOL delivery team a month or so back where they were asking me about what senders would be most concerned about when / if AOL started using DKIM.
The other announcement is that AOL, like Yahoo, would like to know how you categorize your outgoing mail stream as part of the whitelisting process.
Both of these changes indicate to me that AOL will be improving the granularity of their filtering scheme. DKIM signing will let them separate out different domains and different reputations across a single sending IP address. The categorization will allow AOL to evaluate sender statistics within the context of the specific type of email. Transactional mail can have different statistics from newsletters from marketing mail. Better granularity means that poor senders will be less able to hide behind good senders. I expect to hear some wailing and gnashing of teeth about this change, but as time goes on senders will clean up their stats and their policies and, as a consequence will see their delivery improve everywhere, not just AOL.
Why do ISPs limit emails per connection?
- steve
- Jan 17, 2008
A few years ago it was “common knowledge” that if you were sending large amounts of email to an ISP the most polite way to do that, the way that would put the least load on the receiving mailserver, was to open a single SMTP session to the mailserver and then to send all the mail for that ISP down that single connection.
That’s because the receiving mailserver is concerned about two main resources when handling inbound email – the pool of “slots” assigned one per inbound SMTP session, and the bandwidth (network and disk, and related resouces such as memory and CPU) consumed by the inbound mail – and this approach means the sender only uses one slot, and it allows the receiving mailserver to control the bandwidth used simply by accepting data on that one connection at a given rate. It also amortizes all the connection setup costs over multiple emails. It’s a beautiful thing – it just doesn’t get any more efficient than that.
That seems perfect for the receiving ISP – but ISPs don’t encourage bulk senders to do this. Instead many of them have been moving from “one connection, lots of mail through it” to “multiple connections, a few messages through each”. They’re even limiting the number of deliveries permitted over a single connection. Why would that be?
The reason for this is driven by three things. One is that the number of simultaneous inbound SMTP sessions that a mailserver can handle is quite tightly limited by the architecture of most mailservers. Another is that the amount of mail that’s being sent to large ISP mailservers keeps going up and up – so there are sometimes more inbound SMTP sessions asking for access than the mailserver can handle. The third is that ISPs know that there are different categories of email being sent to their users – 1:1 mail from their friends that they want to see as soon as possible, wanted bulk mail that their users want to see when it arrives and spam; lots and lots of spam.
So ISPs want to be able to do things like accept 1:1 mail all the time, while deferring bulk mail and spam to allow them to shed traffic at times of peak load. But they can only make decisions about whether to accept or defer delivery in an efficient way at SMTP connection time – they pick and choose amongst the horde of inbound connection attempts to prioritize some and defer others, letting them keep within the number of inbound sessions that they can handle simultaneously.
But once the ISP lets a bulk mailer connect to deliver their mail, they lose most of the ability to further control that delivery as the sender might send thousands of emails down that connection. (Even if the ISP has the ability to throttle bandwidth – as some do to control obvious spam – that just means that the sender would tie up an expensive inbound delivery slot for longer).
So, in order to allow them to prioritize inbound connections effectively the ISP needs to terminate the session after a few deliveries, and then make that sender start competing with other senders for a connection again.
So ISPs aren’t limiting the number of deliveries per SMTP connection to make things difficult for senders, or because they don’t understand how mail works. They’re doing it because that lets them prioritize wanted email to their users. The same is true when they defer your mail with a 4xx response.
It might be annoying to have to deal with these limits on delivery, but for legitimate bulk mail senders all this throttling and prioritization is a good thing. Your mail may be given less priority than 1:1 mail – but, if you maintain a good reputation, you’re given higher priority than all the spam, higher priority than all the email borne viruses, higher priority than all the junk email, higher priority than the 419 spams. And higher priority than mail from those of your competitors who have a worse reputation than yours.
Why does everyone tell you to avoid .biz in your emails?
- steve
- Nov 28, 2007
… or Why do spam filters sometimes have some very strange ideas?
It’s been dogma for a long time that if you’re doing email marketing you should avoid using a .biz domain in your mails. Even if your main website was in .biz, you should use something different in your messages, perhaps a website you buy solely for use in email that redirects to your real .biz website. Last year I looked at why that was, and what could be done about it.
One main reason for avoiding it has been resolved (so if you’ve been avoiding using .biz URLs in your mail now might be a good time to re-test that decision). And enough time has gone by that I can share the ugly reasons as to why .biz was considered a sure sign of spam without good reason for so long without upsetting everyone.
The simple reason was SpamAssassin. SpamAssassin is very widely used to filter mail, both in it’s open source version and buried anonymously deep inside countless commercial spam filters and filtering appliances. Not only that, but SpamAssassin is readily available, so most people looking to do pre-mailing content checks or looking at why content-based filters are objecting to a particular email will use SpamAssassin as their model. It’s very widely deployed, and influential far beyond the size of it’s deployed base.
SpamAssassin is a score-based spam filter – it checks an email against hundreds of rules, adds up the scores of each rule that matches and, in typical setups, decides the mail is spam if the total score is five or more. Pretty reasonable, but here are a few of the rules and scores (from the 2006 version of SpamAssassin)
Wired editor has enough spam!
- laura
- Oct 31, 2007
Seth Godin links to a post up over on The Long Tail about spammers who send PR mail to Chris Anderson, an editor at wired. Apparently lots of people send automated email to the editor of Wired hawking their latest and greatest product, service or photos.
In response to this overwhelming amount of mail, Chris has instituted a new email acceptance policy. He says
Do open rates matter?
- laura
- Oct 31, 2007
Ken Magill over at DirectMag has an article deriding the reliance on ‘open rates’ as a metric for the success (or failure!) of marketing campaigns.
Read MoreDKIM "i=" vs "d=" and Reputation
- steve
- Oct 29, 2007
This really should be part seven of a twelve part series or some such as it deals with an aspect of DKIM that’s really important, but is way down in the details of implementation. (dkim.org is a reasonable place to start for a general overview of DKIM).
There’s an apparently endless thread on the DKIM-SSP spec development mailing list at the moment about the differences between two fields in a DKIM signature that could be used to tie a senders reputation to. Several ESP delivery folks asked me to explain what everyone was talking about, and this post is a first cut at that.
“i=” vs “d=”
There are two possible fields in a DKIM signature that could be used to identify the sender of a message, and so to tie a sender history and reputation record to. They are the so-called “i=” and “d=” field, from the syntax used to include them in the signature.
Experience as a recipient
- laura
- Oct 26, 2007
One of the challenges of my job is to separate my personal feelings and experiences related to email marketing and spam from my advice to clients. I am here to make your delivery better, not to make everyone use email marketing the way that makes me the most comfortable.
That being said, I get a lot of spam across my various email addresses. If I have an extra few minutes I’ll sometimes send complaints, but more and more it is too hard, too complicated and / or the ISPs do not care anyway. In the last 2 weeks I’ve had 3 experiences with unexpected / unwanted email (aka: spam) where I did take action.
Consent does not mean confusing your recipients
- laura
- Oct 22, 2007
Cam Beck on Marketing Prefs has a post today about presenting users with confusing choices in an opt-in process.
Read MoreWhat metrics are you measuring?
- laura
- Oct 19, 2007
Marketers measure a lot of metrics about the email they send. But are they measuring the right metrics?
Mark Brownlow talks about how marketers may not always know what their measuring. He also links to Email Insider where the Email Diva talks about what metrics can be measured. More importantly, she points out that asking questions and determining what you want out of your email marketing program is critical to determining what metrics you should measure. She says:
Viral Marketing by email
- laura
- Oct 11, 2007
Matt talks about a new marketing report from the ThinData Newsletter.
The Newsletter offers the following recommendations on using viral marketing as part of your next email campaign.
MAAWG: Sender Best Practices
- laura
- Oct 8, 2007
The MAAWG Sender Subcommittee has published a Sender Best Current Practices document.
This document details what the current best practices in the sending industry are. Summarized the document says:
Blocklists and standards
- laura
- Oct 4, 2007
I received a comment this morning on my post about e360 v. Spamhaus, which I think brings up a point that deserves a post of it’s own. Skinny says:
Read MoreMailing to corporate domains
- laura
- Sep 28, 2007
One of the struggles of delivery consulting is doing ISP relations and problem resolution for clients attempting to mail to corporate domains. The rules for getting mail into ISPs are generally pretty clear, and if they’re not I can typically find someone there who will give me the time of day. At corporate domains, though, all bets are off.
While ISPs strive to deliver wanted mail to their customers while protecting them from spam, businesses have different goals for email. For most businesses email is a tool. Mail boxes belong to the business, not the employee. In many cases, businesses do allow personal use of email so some marketing mail to employees is acceptable. However, if a corporation blocks personal marketing email, they are less likely than commercial ISPs to let even legitimate email through.
Large corporations typically run their own mail systems. Once a sender is blocked, however, the corporation will not unblock their email unless the sender can demonstrate that the mail is business related.
Smaller businesses typically use commercial appliances or filtering services. In these cases there is less need to justify the business related nature of email. Unfortunately, some commercial filters do not listen to senders or provide block resolution. At least one filter claims that the only way you can deliver mail to their users is for the users themselves to whitelist the sender.
Businesses of all types are much more security conscious than home users. Some “spam” blocking may be more related to security than actual spam. Finally, there are workplace and environment issues. Companies may be liable under the hostile workplace laws if they allow porn or other offensive emails into their employee mailboxes. One company I know of blocks any email with the word “viagra” in it. The email administrator of said company says that in the years this block has been in place there has only been one false positive… and that employee was told his wife should not use that word when emailing him shopping lists in the future.
All of these issues make it difficult to troubleshoot delivery problems at corporations.
Think about that subject line
- laura
- Sep 28, 2007
Ken Magill talks about a study done by People magazine on the importance of subject lines and from lines in getting recipients to open and act on an email.
MailChimp has specific open information about mail sent through their application. They describe the collection of the information used in this blog post.
Recipients really do make open / not-open decisions based just on the visible subject line. MailChimp’s data shows that “boring” subject lines often perform better than pushier more sales like subject lines. One possible explanation is that recipients are used to ignoring spam subject lines, and the more informative a subject line, the more likely it is to be mail they actually open.
Permission, Part 2
- laura
- Sep 25, 2007
Permission Part 1 I talked about the definition of permission as I use it. Before we can talk about how to get permission we need to clarify the type of email that we’re talking about in this post. Specifically, I’m talking about marketing and newsletter email, not transactional email or other kinds of email a company may send to recipients. Also, when I talk about lists I include segments of a database that fit marketing criteria as well as specific list of email addresses.
There are two ways that recipients give permission to receive newsletters or marketing email, explicit permission and implicit permission. Recipients give explicit permission to receive marketing email when they sign up for such email. Implicit permission covers situations where a user provides an email address, either during the course of a purchase, a download or other interaction with a company. There may be some language in the company’s privacy policy explaining that recipients may receive marketing email, but the recipient may not be aware they will receive email.
The easier situation is explicit permission. There are two basic ways a company can gather explicit permission to send marketing email: single opt-in and double (confirmed) opt-in.
Single opt-in: Recipient provides an email address to the sender for the express purpose of receiving marketing email.
Double (or confirmed) opt-in: Recipient provides an email address to the sender for the express purpose of receiving marketing email. The sender then sends an initial email to the recipient that requires a positive action on the part of the recipient (click a link, log into a web page or reply to the email) before the address is added to the sender’s list.
There can be problems with both types of opt-in, but barring fake or typoed email addresses being given to the sender, there is an social contract that the sender will send email to the recipient. I’ll talk about single and double opt-in in later posts.
Implicit permission covers a lot of situations where email is commonly sent in response to a recipient giving the sender and email address. In these cases, though, the recipient may not be aware they are consenting to receive email. This behavior may annoy recipients as well as causing delivery problems for the sender. Common cases of implicit permission include website registration, product purchase and free downloads.
More responsible companies often change implicit opt-in to explicit opt-in. They do this by making it clear to users that they are agreeing to receive email at the point where the user gives the company an email address. Not only is the information about how email addresses will be used in the company’s privacy policy, but there is a clear and conspicuous notice at the point where the user must provide their email address. The recipient knows what the sender will do with the email address and is given the opportunity to express their preferences. If users do agree to receive email, the company will send a message to that recipient with relevant information about how their email address will be used, how often they will receive email and how they can opt-out.
Explicit opt-in is the best practice for building a list, however, there are still companies that successfully use implicit opt-in to build marketing lists. Companies successfully using implicit opt in usually are collecting emails as part of a sales transaction. There is very little incentive for their customers to give them an email address not belonging to the customer.
Outside of purchasers, however, implicit opt-in leaves a company open to getting email addresses that do not actually belong to the person providing the company with the email address. This most often occurs when the sender is providing some service, be it software downloads, music or access to content, in return for a “payment” of a valid email address. In order to protect against users inputting other, valid addresses into the form, the sender must verify that the address actually belongs to their user before sending any sort of marketing email. The easiest way for senders to do this is to send a link to the recipient email. This link can be the download link, or the password to get to restricted content. Because the recipient must be able to receive and act on email, the only addresses the sender has belong to actual users of the site.
In some rare cases, implicit opt-in can be used to build a list that performs well. However, senders must be aware of the risks of annoying their customer base and the recipient ISPs. Mitigating these risks can be done, but it often takes more effort than just using explicit opt-in in the first place.
IP Reputation Portability
- laura
- Sep 25, 2007
Matt posted a discussion of the portability of IP reputation over at his EmailKarma blog.
I have heard about Hotmail/MSN’s claim that if you add your new IPs to your SPF/SenderID record and send from your old IPs that your old IP reputation will transfer to your new IPs. I’ve not heard it working in practice, but it really can’t hurt to add your new IPs to your records as soon as you know what they are.
Permission, Part 1
- laura
- Sep 11, 2007
Before I can talk about permission and how a mailer can collect permission from a recipient to send them email I really need to define what I mean by permission as there are multiple definitions used by various players in the market. Permission marketing was a term coined by Seth Godin in his book entitled Permission Marketing.
The underlying concept beneath permission marketing is that all marketing should be “anticipated, personal and relevant.” Others have defined permission marketing as consumers volunteering or requesting to be marketed to.
When I talk about permission in the email marketing context I mean that the recipient understood *at the time they provided the sender with an email address* that they would receive email from that sender as a result.
Let’s look at some of the relevant parts of that definition.
Solving delivery problems
- laura
- Sep 6, 2007
“The only solution to our delivery problems isn’t double opt-in, is it?” A question I get quite frequently from clients and potential clients. In the vast majority of cases the answer is no, confirmed (double) opt-in [1] is not the only solution to delivery problems. In fact, there are delivery issues that confirmed opt-in will do nothing to solve.
Many other delivery sites and deliverability experts will tell clients that the solution to their deliverability problems is to switch to confirmed opt-in as a method to collect email addresses. This overly simplistic solution only treats one possible source of delivery problems, the collection of addresses. It does not address data hygiene issues, technical delivery issues or complaints.
While address collection is important, the best address collection processes on the planet cannot fix sloppy data handling, failure to unsubscribe recipients, or non-existent bounce handling. All of these factors play a role in delivery. It is critical to identify the underlying source of delivery problems before advising anyone on how to fix it.
Over the course of the next few blog posts, I am going to take a look at the various issues that affect delivery: permission, data hygiene, bounce handling, complaints and authentication. I’ll talk about what is important and what senders need to look for and be aware of when they’re trying to troubleshoot delivery issues.
[1] There is some disagreement between senders and anti-spammers about the correct terminology to use. Senders use double opt-in to describe the process, anti-spammers use confirmed opt-in. I am using both terms here to mean the same process.





 Read More
Read More






