B2B
Looking back, looking forward
Six years ago today I wrote here “Spam isn’t going away“, talking about systemic problems at Google, Cloudflare and Amazon and in India.
Read MoreIt’s not marketing, it’s spam
There are times when I hesitate to call what marketers do “spam.” I can use the euphemisms with the best of ’em. “Cold emails” “Targeted Marketing” “B2B marketing.”
Read MoreFilters working as intended
One of the toughest deliverability problems to deal with is when mail is blocked or going to spam because the filters are working as intended. Often the underlying issue is a lack of permission.
Read MoreB2B mail and compliance failures
This morning I got an email to a tagged address. The tag matched the company so it’s very likely I did actually sign up. Digging back through my mailbox, I see one previous email to that account – back in 2008.
Read MoreWho are mimecast?
Mimecast is a filter primarily used by businesses. They’re fairly widely used. In some of the data analysis I’ve done for clients, they’re a top 10 or top 20 filter.
Earlier today someone asked on Facebook if mimecast may be blocking emails based on the TLD. The short answer is it’s unlikely. I’ve not seen huge issues with them blocking based on TLD of the domain. They’re generally more selective than that.
The good news is mimecast is really pretty good about giving you explanations for why they’re blocking. They’ll even tell you if it’s mimecast related or if it’s a specific user / user-company block.
Some example rejection messages from a recent dive into some bounce logs.
What kind of mail do filters target?
All to often we think of filters as a linear scale. There’s blocking on one end, and there’s an inbox on the other. Every email falls somewhere on that line.![]() Makes sense, right? Bad mail is blocked, good mail goes to the inbox. The bulk folder exists for mail that’s not bad enough to block, but isn’t good enough to go to the inbox.
Makes sense, right? Bad mail is blocked, good mail goes to the inbox. The bulk folder exists for mail that’s not bad enough to block, but isn’t good enough to go to the inbox.
Once we get to that model, we can think of filters as just different tolerances for what is bad and good. Using the same model, we can see aggressive filters block more mail and send more mail to bulk, while letting less into the inbox. There are also permissive filters that block very little mail and send most mail to the inbox.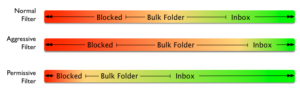 That’s a somewhat useful model, but it doesn’t really capture the full complexity of filters. There isn’t just good mail and bad mail. Mail isn’t simply solicited or unsolicited. Filters take into account any number of factors before deciding what to do with mail.
That’s a somewhat useful model, but it doesn’t really capture the full complexity of filters. There isn’t just good mail and bad mail. Mail isn’t simply solicited or unsolicited. Filters take into account any number of factors before deciding what to do with mail.
Spam isn't going away
I got a piece of B2B spam last week that showed in several different ways why spam isn’t going away any time soon.
Systemic problems dealing with abuse at scale at Google. Ethics problems at Cloudflare. Problems dealing with abuse at scale at Amazon. Cultural problems in India, several times over.
Buckle up.
Social media connections are not opt-ins
It seems silly to have to say this, but connecting on social media is not permission to add an address to your newsletter or mailing list or prospecting list or spam list. Back in 2016, I wrote:
Read MoreNovember 2017: The Month in Email
We’re in the thick of the busiest time of the year for email. It’s been so busy, in fact, that we’ve seen some slowdowns and delivery issues across the email universe. It may be worth thinking about alternate strategies for end of year promotions beyond Black Friday and Cyber Monday.
I was delighted to chat with Julia Angwin for her ProPublica piece on subscription bombing and abuse prevention. Her piece is a good introduction to the topic, and very much worth reading.
ICYMI, I did a rough analysis of the data from our survey on Google Postmaster Tools. Stay tuned for more insights when I have a moment to explore this further.
Not fooling anyone…
A question came up on the Women of Email Facebook page about sending cold B2B emails. This is one of those areas I have strong opinions about, mostly because I am so tired of getting deceptive and unending messages from folks.
Realistically, cold emailing isn’t going to stop just because recipients hate receiving it. We haven’t wiped out spam in 20+ years, we’re not going to manage it for this one tiny piece. But I do think there are things senders can do to minimize the amount of frustration their spam creates.
Permission and B2B spam
Two of the very first posts I wrote on the blog were about permission (part 1, part 2). Re-reading those posts is interesting. Experience has taught me that recipients are much more forgiving of implicit opt-in than that post implies.
The chance in recipient expectations doesn’t mean, however, that permission isn’t important or required. In fact, The Verge reported on a chatbot that will waste the time of spammers. Users who are fed up with spam can forward their message to Re:Scam and bots will answer the mail.
I cannot tell you how tempted I am to forward all those “Hey, just give me 10 minutes of your time…” emails I get from B2B spammers. I know, those are actually bots, but there is lovely symmetry in bots bothering one another and leaving us humans out of it.
Speaking of those annoying emails, I tweeted about one (with horrible English…) last week. I tagged the company in question and they asked for an example. After I sent it, they did nothing, and I continued to get mail. Because of course I did.
These types of messages are exactly why permission is so critical for controlling spam. Way more companies can buy my email address and add me to their spam automation software than I can opt-out of in any reasonable time frame. My inbox, particularly my business inbox, is where I do business. It’s where I talk with clients, potential clients, customers and, yes, even vendors. But every unsolicited email wastes my time.
It’s not even that the mail is simply unwanted. I get mail I don’t want regularly. Collecting white papers for my library, RSVPing to events, joining webinars all result in me getting added to companies’ mailing lists. That’s fair, I gave them an email address I’ll unsubscribe.
The B2B companies who buy my address are different. They’re spamming and they understand that. The vendors who sell the automation filters tell their customers how to avoid spam filters. Spammers are told to use different domains for the unsolicited mail and their opt-in mail to avoid blocking. The software plugs into Google and G Suite account because very few companies will block Google IPs.
I’ve had many of these companies attempt to pay me to fix their delivery problems. But, in this case there’s nothing to fix. Yes, your mail is being blocked. No, I can’t help. There is nothing I can say to a filtering company or ISP or company to make them list that block. The mail is unwanted and it’s unsolicited.
The way to get mail unblocked is to demonstrate the mail is wanted. If you can’t do that, well, the filters are working as intended.
July 2017: The month in email
August is here, and as usual, we’re discussing spam, permissions, bots, filters, delivery challenges, and best practices.
One of the things we see over and over again, both with marketers and with companies that send us email, is that permission is rarely binary — companies want a fair amount of wiggle room, or “implied permission” to send. There are plenty of examples of how companies try to dance around clear permissions, such as this opt form from a company we used to do business with. But there are lots of questions here: can you legitimately mail to addresses you haven’t interacted with in 5 years? 10 years? What’s the best way to re-engage, if at all?
We frequently get questions about how to address deliverability challenges, and I wrote up a post about some of the steps we take as we help our clients with this. These are short-term fixes; for long-term success, the most effective strategy is sending email that people want and expect. Engagement is always at the core of a sustainable email program.
We’ve also discussed the rise of B2B spam, and the ways in which marketing technologies contribute to the problem. B2B marketers struggle to use social and email channels appropriately to reach customers and prospects, but still need to be thoughtful about how they do it. I also wrote about some of the ways that marketing automation plugins facilitate spam and how companies should step up to address the problem. Here’s an example of what happens when the automation plugins go awry.
I wrote a few posts about domain management and the implications for security and fraud. The first was about how cousin domain names can set users up for phishing and fraud, and the second was a useful checklist for looking at your company’s domain management. We also looked at abuse across online communities, which is an increasing problem and one we’re very committed to fighting.
I also highlighted a few best practices this month: guidelines for choosing a new ESP and active buttons in the subject line for Gmail.
And finally, we celebrated the 80th birthday of the original SPAM. If you’re a regular reader of this blog, you probably already know why unwanted email is called SPAM, but just in case, here’s a refresher….
Marketing automation plugins facilitate spam
There’s been an explosion of “Google plugins” that facilitate spam through Gmail and G Suite. They have a similar set of features. Most of these features act to protect the spammer from spam filtering and the poor reputation that comes from purchasing lists and incessantly spamming targets. Some of these plugins have all the features of a full fledged ESP, except a SMTP server and a compliance / deliverability team.
I’ll give the folks creating these programs credit. They identified that the marketers want a way to send mail to purchased lists. But ESPs with good deliverability and reputations don’t allow purchased lists. ESPs that do allow purchased lists often have horrible delivery problems. Enter the spam enabling programs.
From the outside, the folks creating these programs have a design goal to permit spam without the negatives. What do I mean? I mean that the program feature set creates an environment where users can send spam without affect the rest of their mail.
The primary way the software prevents spam blocking is using Google, Amazon or Office 365 as their outbound mail server. Let’s be frank, these systems carry enough real mail, they’re unlikely to be widely blocked. These ISPs are also not geared up to deal with compliance the same way ESPs or consumer providers are.
There seem to be more and more of these companies around. I first learned of them when I started getting a lot of spam from vaguely legitimate companies through google mail servers. Some of them were even kind enough to inform me they were using Gmail as their marketing strategy.
I didn’t realize quite how big this space was, though. And it does seem to be getting even bigger.
Then a vendor in the space reached out looking for delivery help for them and their customers. Seems they were having some challenges getting mail into some ISPs. I told them I couldn’t help. They did mention 3 or 4 names of their competitors, to help me understand their business model.
Last week, one of the companies selling this sort of software asked me if I’d provide quotes for a blog article they were writing. This blog article was about various blocklists and how their software makes it such that their customers don’t really have to worry about blocking. According to the article, even domain based blocking isn’t an issue because they recommend using a domain completely separate from their actual domain. I declined to participate. I did spend a little time on their website just to see what they were doing.
This morning a vendor in the space joined one of the email slack channels I participate in asking for feedback on their software. Again, they provide software so companies can send spam through google outbound IPs. Discussions with the vendor made it clear that they take zero responsibility for how their software is used.
I don’t actually expect that even naming and shaming these companies facilitating spam will do anything to change their minds. They don’t care about the email ecosystem or how annoying their customers are. About the best they could do is accept opt-out requests from those of us who really don’t want to be bothered by their customers. Even that won’t really help, even domain based opt-outs are ineffective.
What needs to happen is companies like Google, Amazon and Microsoft need to step up and enforce their anti-spam policies.
Social marketing
The following showed up in my mailbox a few moments ago
I commented to Steve that social marketing was about connecting with people, and businesses aren’t people. That’s why social marketing for B2B is hard: there are no people involved. Or, as he pointed out, B2B in the social space is bot to bot marketing.
Of course, there aren’t literal bots behind most brands. In the B2C space, brands have cultivated a social media presence that personifies the business in a way that appeals to their consumers. But that’s the brand projecting onto people and responding to people. When a business tries to connect to a business, it’s just two puppets talking.
Sure, there are small businesses where there isn’t the case. But generally businesses aren’t on social media to consume marketing. They’re on social media to generate marketing. They aren’t targets because you can’t market to a puppet.
The cycle goes on
Monday I published a blog post about the ongoing B2B spam and how annoying it is. I get so many of these they’re becoming an actual problem. 3, 4, 5 a day. And then there’s the ongoing “drip” messages at 4, 6, 8, 12 days. It is getting out of control. It’s spam. It’s annoying. And most of it’s breaking the law.
But, I can also use it as blog (and twitter!) fodder.
Reaching targets, the wrong way
I’ve been increasingly annoyed by these drip automation campaigns. You know the ones I mean. Senders use some software to find some flimsy pretext to send a mail. Then there emails drop every few days. Sometimes this cycle goes on for months. Most of these messages violate CAN SPAM. It’s annoying. It’s illegal. It is spam.
I can even opt out of most of these messages, they don’t offer that ability.
One way to deal with B2B spam
We’ve been talking a lot about B2B spam recently. I’ve posted repeatedly, Steve wrote a post about it yesterday. It’s in the forefront of our minds because we’re dealing with just so much of it. Multiple emails a day asking for “just 10 minutes of your time.” Of course, the 10 minutes isn’t really just 10 minutes. Sure, the call might be 10 minutes, but there’s overhead to that call that will probably eat 20 – 30 minutes of time. That’s at best.
Because they’re using providers who don’t notice or don’t care about the spam, there’s little to be done. No one is going to stop them from mailing me. They are required to comply with the law, but 99% of the mail doesn’t. Which gave me an idea.
I’ve started replying to every incident of “just 10 minutes of your time” with a pleasant email thanking them for their interest in our CAN SPAM verification program. I point out that I have noticed at least one violation and we’re happy to consult with them on how to fix it for a fee.
Wait? You mean they’re not interrupting my time simply to receive a sales pitch? Well. Gee. I’m just replying to them.
It seems petty, but we’re less than 2 weeks into 2017 and I already have over a dozen of these “one time” emails. If history tells me anything, these same people will follow up in a week, and then 2 weeks, and then a month. Meanwhile, new people are going to be sending me a request for 10 minutes of my time, and their followups and in a month I’ll be getting a dozen emails a week. In two months I’ll be getting 2 dozen. In 3 months it will be 4 dozen.
And, yeah, most of these messages do violate CAN SPAM. Most of them by not including an unsubscribe links, which makes getting the mail to stop a challenge. There’s no way to unsubscribe, so it’s either answer it or just keep getting contacted. I wrote last year about the woman who continued to email me for months. She even announced she was going to call 911 because clearly I was injured and unable to answer her mail. Multiple times she promised to stop mailing me, but never did.
I do feel bad for many of these senders. They’ve been sold on a prospecting tool by vendors who fail to provide them with a minimal level of guidance. Even just mentioning that there are laws regulating email, and they should comply with them would be better than nothing.
In many ways I find this kind of spam more annoying than the viagra or the malware that ends up in my mailbox. Those can be selected and deleted pretty easily. These, however, have subject lines that look just like my legitimate business mail. I have to read them and figure stuff out. It’s a total PITA.
EDIT: And it’s not even effective according to some experts.
Google and Amazon and B2B spam
Many of the operational goals of a commercial spammer aren’t related to email delivery at all, rather they revolve around optimizing ROI and minimizing costs. That’s even more true when the spammer isn’t trying to sell their own product, rather they’re making money by sending spam for other companies.
Most legitimate network providers pay at least lip service to not allowing abusive behaviour such as spam from their networks, so a spammer has to make a few choices about what infrastructure to use to optimize their costs.
They can be open about who they are and what they do, and host with a reputable network provider, and build out mailservers much as any legitimate ESP would do. But eventually they’ll get blacklisted by one of the more reputable reputation providers – leading to little of their mail being delivered, and increasing the pressure on their provider to terminate them. They social engineer their provider’s abuse desk, and drag their feet, and make small changes, but eventually they’ll need to move to another provider. Both the delaying tactics and the finally moving are expensive.
Or they can host with a network provider who doesn’t care about abuse from their network, and do the same thing. But they’ll still get blacklisted and, unlike on a more reputable network, they’re much less likely to get any benefit of the doubt from any reputation providers.
Every time they get blacklisted they can move to a new network provider. That’s easy to do if your infrastructure is virtual machine based and moving providers just involves buying a new hosting account. But as anyone who’s heard the phrase “ramping-up” knows mail from new network space is treated with suspicion, and as they’re continually moving their mail won’t reach the inbox much.
Preemptively spreading the sources of your spam across many different IP addresses on different providers, and sending spam out at low enough levels from each address that you’re less likely to be noticed is another approach. This is snowshoe spam and spam filters are getting better at detecting it.
What to do? In order to get mail delivered to the inbox the spammer needs to be sending from somewhere with a good reputation, ideally intermingled with lots of legitimate email, so that the false-positive induced pain of blocking the mailstream would be worse than their spam. That’s one reason a lot of spammers send through legitimate ESPs. They’re still having to jump from provider to provider as they’re terminated, but now they’re relying on the delivery reputation of the shared IP pools at each new ESP they jump to. But that still takes work to move between ESPs. And ESP policy enforcement people talk to each other…
As a spammer you want your mail to be sent from somewhere with good reputation, somewhere you can use many different accounts, so your spam is spread across many of them, flying below the radar. Ideally you wouldn’t have any documented connection to those accounts, so your activity won’t show up on any aggregated monitoring or reporting.
If nothing in the mail sent out identifies you there is nowhere for recipients to focus their ire. And if recipients can’t tell that the hundreds of pieces of spam in their inbox came from a single spammer, they’re much less likely to focus efforts on blocking that mail stream.
Over the past couple of years I’ve seen a new approach from dedicated B2B spammers, the sort who sell “buy and upload a list, blast out something advertising your company, track responses, send multiple mails over a series of weeks” services to salespeople. They’re the ones who tend to have glossy, legitimate websites, talking about “lead nurturing”, “automated drip campaigns” or “outreach automation”.
They have each of their customers sign up for gmail or google apps accounts, or use their existing google apps accounts, and then the spammer funnels the spam sent on behalf of that customer through that google account. There’s no obvious connection between the spammer and the google account so there’s no risk to the spammer. Google is fairly unresponsive to spam complaints, so as long as the volume sent by each customer isn’t spectacularly high it’s going to be well below Google automation’s threshold of notice.
Google do record where mail that’s injected into their infrastructure in this way comes from, in the Received headers. But the spammers run their sending infrastructure – list management, message composition, tracking and so on – on anonymous, throwaway virtual machines hosted on Amazon’s EC2 cloud, so there’s nothing in the email that leads back to the spammer.
And, for recipients, that’s a problem. Spam filters aren’t going to block this sort of mail, as they can’t easily tell it is this sort of mail. It’s coming from Google MTAs, just like a lot of legitimate mail does. In terms of sheer volume it’s dwarfed by botnet sourced mail or dubious B2B manufacturing spam out of Shenzhen. But, unlike most of that, it’s in your inbox, in front of your eyeballs and costing you time and focus. And that’s much more expensive than network infrastructure or mailbox storage space.
I’m not sure what, if anything, Google or Amazon can do about it at scale, but it’s something that’s going to need to be dealt with eventually.
Meanwhile, if you receive some marginally personalized mail from a sales rep, one attempting to look like 1:1 mail, look at the headers. If you see something like this …
If I can't tell, it's spam
Judging by the amount of B2B spams I’ve gotten this past week, a number of businesses got bright, shiny new email programs for Christmas. “Like to set up a call with you…” “Just need 10 minutes of your time to explore…” “Love to jump on a call and tell you about our product…”
That’s just the mail that comes into my personal address. There’s also a raft of mail coming into our contact address. The majority of those are trying to sell me FB or Twitter followers, although Instagram is rising in the ranks. Some of those messages are kinda funny, though. They try so hard to pretend there’s a real person who really did look at our website and who really has a comment.
Most of the time it’s pretty obvious that it’s not from a human. But every once in a while a message comes in that might be from a real person. I’ve finally decided that if I have any question if a message was written by a human or a bot, it will be treated as written by a bot.
Unfair? Maybe. But I’m a small business owner and a consultant; I don’t have tons of spare time to sit around letting folks pitch me on their business. I don’t think I’m actually that unusual when it comes to entrepreneurs. We’re busy, we don’t like distractions and we go out and search for the things we actually do need.
Targeted marketing done badly
There was quite a bit of content I cut out on my rant about parasites in the email ecosystem earlier this week. I had whole section on people who ask to connect on LinkedIn and then immediately send a pitch or scrape your address and add it to their marketing automation software and start spamming. Generally, the only reason I will drop someone off LinkedIn is because they do this.
Today, one of the deliverability mailing lists has been hopping over spam many folks in the industry received. The discussion started off simple enough, someone said “Is <companyname> spamming the industry?” People immediately chimed in that yeah, it did appear so.
A few people said they’d gotten the message and thought it was personal and were disappointed it wasn’t. Others weren’t sure why they were chosen to receive this message, or why some of their co-workers were chosen. A few of us didn’t get them. I didn’t.
This is a great example of marketing that was reasonably well planned, but a total fail for not knowing their audience. The product in question is an anti-abuse product. The company wants to reach people in the anti-abuse industry. They go off and find people in the anti-abuse industry and send them an email. Mail that seems personalized. It was a perfectly reasonable email. It asked questions and did get some people to engage with it by replying. They even appear to have done A/B testing on subject lines.
All solid marketing decisions. All great things to do.
But, the anti-abuse community is small, particularly the ESP anti-abuse community. We talk on mailing lists, IRC, LinkedIn, Facebook and Slack – and those are just the places I’m connected to. I’m sure there are other meeting places. The fact is, we’re a community and we do interact. If you’re going to try and do something like this, you have to expect that we’re going to realize you’re spamming. And many of us have very low tolerance for this kind of stuff.
A few years ago I worked with some senders who acquired most of their email addresses from technical conferences. They had a lot of delivery problems because a lot of their audience were the people who wrote and maintained filters. Spam the person who writes a spam filter and you may find yourself locked out from all of those filter users. I finally realized I couldn’t help those clients. No amount of technical perfection, personalization, looking like one-to-one mail or magic address cleaning is going to make this audience want your mail.
Marketing starts at understanding your audience. Permission is one of the better ways to understand your audience. Marketing to the anti-abuse crowd is a challenge. I can’t see any place where unsolicited email successfully fits into that plan.
Parasites hurt email marketing
As a small business owner I am a ripe target for many companies. They buy my address from some lead generation firm, or they scrape it off LinkedIn, and they send me a message that pretends to be personalized but isn’t really.
“I looked at your website… we have a list of email addresses to sell you.”
“We offer cold calling services… can I set up a call with you?”
“I have scheduled a meeting tomorrow so I can tell you about our product that will solve all your technical issues and is also a floor wax.”
None of these emails are anything more than spam. They’re fake personalized. There’s no permission. On a good day they’ll have an opt out link. On a normal day they might include an actual name.
These are messages coming to an email address I’ve spent years trying to protect from getting onto mailing lists. I don’t do fishbowls, I’m careful about who I give my card to, I never use it to sign up for anything. And, still, that has all been for naught.
I don’t really blame the senders, I mean I do, they’re the ones that bought my address and then invested in business automation software that sends me regular emails trying to get me to give them a phone number. Or a contact for “the right person at your business to talk to about this great offer that will change your business.”
The real blame lies with the people who pretend that B2B spam is somehow not spam. Who have pivoted their businesses from selling consumer lists to business lists because permission doesn’t matter when it comes to businesses. The real blame lies with companies who sell “marketing automation software” that plugs into their Google Apps account and hijacks their reputation to get to the inbox. The real blame lies with list cleansing companies who sell list buyers a cleansing service that only hides the evidence of spamming.
There are so many parasites in the email space. They take time, energy and resources from large and small businesses, offering them services that seem good, but really are worthless.
The biologically interesting thing about parasites, though, is that they do better if they don’t overwhelm the host system. They have to stay small. They have to stay hidden. They have to not cause too much harm, otherwise the host system will fight back.
Email fights back too. Parasites will find it harder and harder to get mail delivered in any volume as the host system adapts to them. Already if I look in my junk folder, my filters are correctly flagging these messages as spam. And my filters see a very small portion of mail. Filtering companies and the business email hosting systems have a much broader view and much better defenses.
These emails annoy me, but I know that they are a short term problem. As more and more businesses move to hosted services, like Google Apps and Office365 the permission rules are going to apply to business addresses as well as consumer addresses. The parasites selling products and services to small business owners can’t overwhelm email. The defenses will step in first.
About that permission thing
I wrote a few days ago about permission and how it was the key to getting into the inbox. It’s another one of those “necessary but not sufficient” parts of delivery. There are, however, a lot of companies who are using email without the recipient permission. These companies often contact me to help them solve their delivery problems. Often these are new companies who are trying to jumpstart their business on the cheap by using email.
The calls have a consistent pattern.
Your purchased list … is spam.
This morning I got spam from someone selling email addresses. The mail starts:
Read MoreApril 2016: The Month in Email
We are finishing up another busy month at WttW. April was a little nutty with network glitches, server crashes, cat woes, and other disruptions, but hopefully that’s all behind us as we head into May. I’ll be very busy in May as well, speaking at Salesforce Connections in Atlanta and the Email Innovation Summit in Las Vegas. Please come say hello if you’re attending either of these great events.
Speaking of great events, I participated in two panels at EEC16 last month. We had a lot of great audience participation, and I met many wonderful colleagues. I wrote up some more thoughts about the conference here. I also had a nice conversation with the folks over at Podbox, and they’ve posted my interview on their site.
In the Podbox interview, as always, I talked about sending mail people want to receive. It always makes me roll my eyes a bit when I see articles with titles like “5 Simple Ways to Reach the Inbox”, so I wrote a bit about that here. In addition to sending mail people want to receive, senders need to make sure they are collecting addresses and building lists in thoughtful and sustainable ways. For more on this topic, check out my post on list brokers and purchased lists.
These same not-so-simple tricks came up again in my discussion of Gmail filters. Everyone wants a magic formula to reach the inbox, and — sorry to burst your bubble — there isn’t ever going to be one. And this is for a good reason: a healthy filter ecosystem helps protect all of us from malicious senders and criminal activity. The email channel is particularly vulnerable to fraud and theft. The constant evolution of filters is one way mail providers can help protect both senders and recipients — but it can be challenging for senders and systems administrators to keep up with this constant evolution. For example, companies sometimes even inadvertently filter their own mail!
I also wrote a bit about how B2B spam is different from B2C spam, and how marketers can better comply with CAN SPAM guidelines in order to reach the inbox. We also republished our much-missed friend and colleague J.D. Falk’s DKIM Primer, which is extremely useful information that was at a no-longer-active link.
One of my favorite posts this month was about “dueling data”, and how to interpret seemingly different findings around email engagement. We also got some good questions for my “Ask Laura” column, where we cover general topics on email delivery. This month we looked at “no auth/no entry” and the Microsoft Smartscreen filter, both of which are useful things to understand for optimizing delivery.
Finally, we are pleased to announce that we’ve joined the i2Coalition, an organization of internet infrastructure providers. They posted a nice introduction on their blog, and we look forward to working with them to help advocate and protect these important technical infrastructures.
It's still spam
Companies are always trying to find new ways to use and abuse email. My mailbox has been rife with mail from companies trying to sell me stuff for my business. It’s been interesting to watch the new ways they’re trying to get attention, while not honoring the most important rule of email marketing.
Are you blocking yourself?
One thing that catches me up with clients sometimes is their own spam filters block their own content. It happens. In some cases the client is using an appliance. The client’s reputation is bad enough that the appliance actually blocks mail. Often these clients have no idea they are blocking their own mail, until we try and send them something and the mail is rejected.
Typically, the issue is their domains are the problem. We mention the domains in email, and the filters do what filters do. We work around this by abbreviating the domains or calling, it’s not a big deal.
It’s a great demonstration of content filters, though. The content (the client’s domain) is blocked even when it comes from an IP with a good reputation. In fact, with Gmail I can often tell “how bad” a domain reputation is. Most mail I send from WttW to my gmail address goes to the inbox, even when the client is reporting bulk foldering at Gmail. But every once in a while a domain has such a bad reputation that any mail mentioning that domain goes to bulk.
Most folks in the deliverability space know the big players in the filtering market: Barracuda, Cloudmark, ProofPoint, etc. Those same people have no idea what filters their company uses and have never even really thought about it.
Do you know what filter your company is using to protect employees from spam?
B2B email filtering
I’ve written about B2B filtering in the past, but I don’t blog too much about corporate filtering overall. The reason for this is that the corporate landscape is a lot broader and less consistent than the consumer space. That makes it much more difficult to tell senders how to handle corporate filtering, because each corporation is different.
But as I think I about it, I realize that’s not necessarily true. In the corporate space there are a few big filtering providers, a couple major hosting systems and a major open source package. While the overall goals of business filtering are slightly different, many businesses have similar goals for their inbound filtering.
Can I assume consumer and business filtering is the same?
Today’s question comes from Steve B.
I wondered if you know much about hosted email providers such as google apps, Microsoft and yahoo.
Read More
I have seen a rise in number of people using them to provide their corporate email service. I am using the same logic that the rules governing delivery to gmail will effect those using google hosted email for example. For Microsoft i have been using Hotmail due to the SmartScreen filters. Would you agree with that logic?
Confusing opt-in and opt-out
Harvard Business Review posted a blog earlier this week suggesting that all businesses should treat email marketing as an opt-out process. Unfortunately, the post seemed to me to conflate and confuse a number of things.
She mixes in potential customers providing business cards to an exhibitor at a trade show with current customers that are using a product. She promotes businesses using opt-out as a default communication practice, but then talks about giving customers preference centers to manage the contact.
Overall, it was a very confusing article.
For instance the author says:
Happy Friday
Mark Brownlow released a video earlier this week titled “If B2B marketing emails could talk.” Enjoy.
HT: Mickey
