CAN SPAM
It’s not marketing… it’s harassment
Many years ago, we bought a VMWare license to manage the various virtual machines running our business infrastructure. As part of our move to Dublin, we decommissioned our cabinet and moved all of services into various bits of the cloud. This meant that when our VMWare support contract came up for renewal we declined the renewal.
Read MoreCAN SPAM says I can!

Saw a new disclaimer on mail sent to an address harvested off our website today:
Read MoreUpdate on Tulsi Gabbard sues Google
Back in July the Tulsi Gabbard campaign sued Google for deactivating their “advertising account” on the night of the first Democratic debate. I’ve been waiting for the Google response, which was due to be filed today.
Read MoreOne subscription should equal one unsubscription
One of the side effects of using tagged addresses to sign up for things is seeing exactly what companies do with your data once they get it.
Read MoreTransactional mail can be spam
Marketers have a thing about transactional mail. In the US, transactional mail is exempt from many of the CAN SPAM regulations. If they label a mail transactional, then they can send it even when the recipient has opted-out! The smart marketer looks for opportunities to send transactional mail so they can bother spam get their brand in front of people who’ve opted out.
Unsubscribe means unsubscribe
But, unfortunately, some senders don’t actually think unsubscribe means stop sending mail.
Today, for instance, the nice folks at The Container Store sent me an email with an “important update to my POP! account”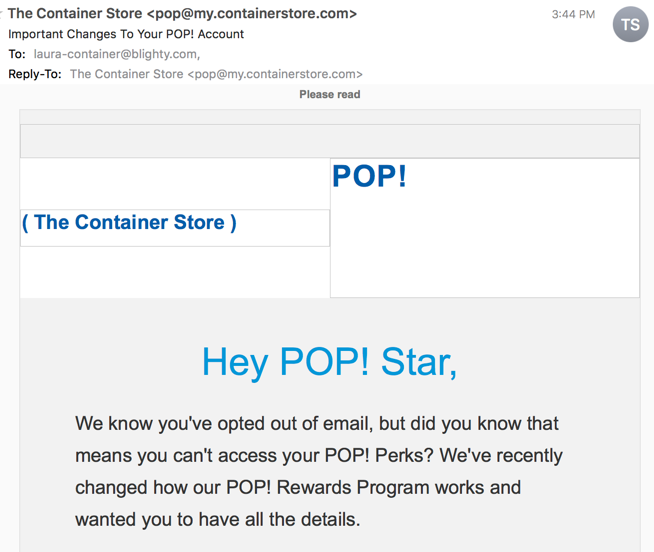
Yes, that’s an address I gave them. But I don’t have any record of setting up an account. I was on their mailing list for all of 4 emails back in November 2016 before unsubscribing. But, they’ve decided they can email me despite my unsubscribe request.
They’ve cloaked this as an “Important Account Update” about some account I don’t have. In fact, when I go to their website and try and see what this oh so important account is about they tell me: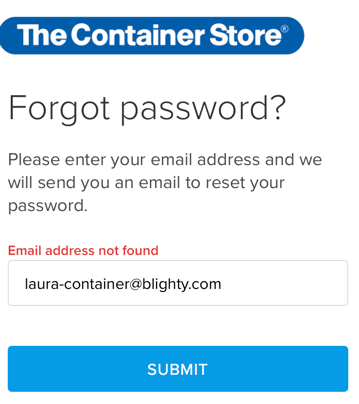
I understand legitimate account notifications might be an acceptable excuse to send mail even after the recipient opted out. This, however, was done extremely poorly. There is no record of the account that they are sending me information about. Neither the company nor I have any record of this account of mine.
At a minimum the emails should have only be sent to the folks that actually had an account. But, they weren’t.
I also have some issues with a company requiring recipients to accept email in order to continue using reward points. As a recipient, if I wanted what they were offering I might go ahead and continue receiving emails. But, I might not. It would all depend on how aggressive their email program is and how good the rewards are. As a deliverability consultant, this strikes me as a great way to create a mailing list full of unengaged users. Unengaged users lead to spam foldering and eventual failure of an email marketing program.
Whatever some executives think, and having been in this industry for a decade and I half I’m sure this is coming from the top down, this is not a good way to build an email program. You really can’t force folks to accept your email. ISPs are too protective of their users to make that a viable strategy.
Want some history?
I was doing some research today for an article I’m working on. The research led me to a San Francisco Law Review article from 2001 written by David E. Sorkin. Technical and Legal Approaches to Unsolicited Electronic Mail (.pdf link). The text itself is a little outdated, although not as much as I expected. There’s quite a good discussion of various ways to control spam, most of which are still true and even relevant.
From a historical perspective, the footnotes are the real meat of the document. Professor Sorkin discusses many different cases that together establish the rights of ISPs to filter mail, some of which I wasn’t aware of. He also includes links to then-current news articles about filtering and spam. He also mentions different websites and articles written by colleagues and friends from ‘back in the day’ discussing spam on a more theoretical level.
CNET articles on spam and filtering was heavily referenced by Professor Sorkin. One describes the first Yahoo spam folder. Some things never change, such as Yahoo representatives refusing to discuss how their system works. There were other articles discussing Hotmail deploying the MAPS RBL (now a part of Trend Micro) and then adding additional filters into the mix a few weeks later.
We were all a little naive back then. We thought the volumes of email and spam were out of control. One article investigated the effectiveness of filters at Yahoo and Hotmail, and quoted a user who said the filters were working well.
Affiliate marketing overview
Most retailers have realized that sending unsolicited email is bad for their overall deliverability. Still, the idea they can send mail to people who never heard of them is seductive.
Enter affiliate email. That magical place where companies hire an agency, or a contractor, or some other third party to send email advertising their new product. Their mail and company reputation is protected because they aren’t sending the messages. Even better, affiliates assure their customers that the mail is opt-in. I’m sure some of them even believe it.
The reality is a little different from what affiliates and their customers want to believe.
Following CAN SPAM isn't enough to reach the inbox
One of the top entries on the list of things deliverability folks hear all the time is, “But my mail is all CAN SPAM compliant!” The thing is… no one handling inbound mail really cares. Seriously. CAN SPAM is a law that is little more than don’t lie, don’t hide, and heed the no. Even more importantly, the law itself states that there is no obligation for ISPs to deliver CAN SPAM compliant mail.
Read MoreThat's not how you do it…
Got an email this morning from a company advertising their newest webinar “The Two Pillars of Effective Large-Scale Email: Security and Deliverability.” The message came to a tagged address, so clearly I’d given them one at some point. But I didn’t recognize the name or company or anything. I did a search to seen when I may have interacted with this company in the past.
Looking through my old emails, it appears I contacted this company through their support form back in 2007. They were blocking a client’s newsletter. This is what I sent:
FTC solicits CAN-SPAM feedback
The FTC (US Federal Trade Commission) is soliciting comments on CAN-SPAM legislation:
A. General Issues
Mailbox tools are a security risk
On Sunday the NYTimes published an article about Uber’s CEO. One of the pieces of information that came out of that article is services like unroll.me sell information they scrape out of emails sent to their users.
Read MoreNews in the email space
Various things happening in the email space recently that are worth mentioning but don’t have enough to justify a whole blog post.
Verizon announced a new umbrella company for the AOL and Yahoo media properties, including things like Engadget, Huffington Post. Based on the various press articles I’ve seen this doesn’t appear to affect the email handling for either set of domains.
Outreach or spam?
This showed up in my mailbox earlier today: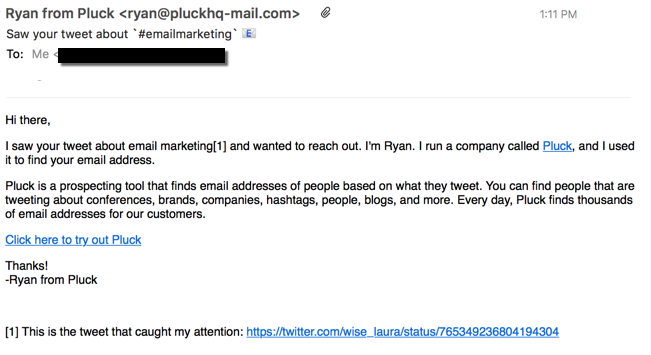
The tweet in question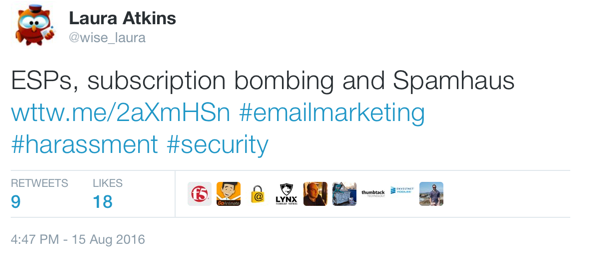
From Crunchbase: “Pluck is an email prospecting tool that gives you the email addresses of the people tweeting about subjects related to your business.”
Prospecting: another name for spamming. Look, I know that you want to sell you’re newest, greatest product to the world. But just because I tweet something with a # that you think is relevant to your product doesn’t mean that I want to get your spam. I also know it’s hard to get attention and find prospects; I’m a small business owner, too and I need to market my own services. But spamming isn’t a good idea. Ever.
There’s been a significant increase in this kind of spam “to help your business” lately. It’s a rare day I don’t get something from some company I’ve never heard of trying to sell me their newest product. It might be something if they tried a contact or two and then went away. But they’ll send mail for weeks or months without getting an answer. Look, silence IS an answer and it means you need to go away and leave your prospects alone.
Unfortunately, there are services out there that sell a product that let you “automatically follow up” with your prospects. Pluck up there uses one of them, as that’s who’s handling all the links in the message. In fact, if you go to the bare domain (qcml.io) they talk a good anti-spam game. “Die, spammers, die.” I reported the message to them. I’m not expecting them to actually do anything, and I’m not expecting a response.
It’s just spam under another name. There’s no pretense that it’s anything else. Even if it’s sent in a way that makes it look like a real person typed the message, like QuickMail offers. “All emails will come straight out of your personal inbox as though you typed them yourself.” As if you typed them yourself.
The worst part is there’s no real way to stop the mail. I can’t unsubscribe. The companies selling the software don’t provide any guidance to their customers about what the law requires. Take the message from Pluck that started the post. It violates CAN SPAM in multiple ways. Moreover, the address they used is not publicly associated with my twitter handle, which means they’re doing some harvesting somewhere. That means treble penalties under CAN SPAM.
I could reply and ask them to stop mailing me. I’ve done that a couple times with a message that says, “Please don’t email me any more.” I’ve got to tell you, some people get really mad when you ask them not to email you. Some just say yes, but others are really offended that you asked them to stop and get abusive. It’s gotten to the point where I don’t ask any more because of that one person who decides to harass, threaten and scream at me. Sure, it’s maybe 1 in 5, but I don’t have the time or energy to figure out who is going to be receptive and who isn’t. I don’t have time for that. No one has time for that.
I’m expecting that filters are going to catch up eventually and these types of mail will be easier to filter out. Until then, though, small business owners like myself are stuck in a place where we have to deal with spam distracting us from our business. At least I get blog content out of it.
April 2016: The Month in Email
We are finishing up another busy month at WttW. April was a little nutty with network glitches, server crashes, cat woes, and other disruptions, but hopefully that’s all behind us as we head into May. I’ll be very busy in May as well, speaking at Salesforce Connections in Atlanta and the Email Innovation Summit in Las Vegas. Please come say hello if you’re attending either of these great events.
Speaking of great events, I participated in two panels at EEC16 last month. We had a lot of great audience participation, and I met many wonderful colleagues. I wrote up some more thoughts about the conference here. I also had a nice conversation with the folks over at Podbox, and they’ve posted my interview on their site.
In the Podbox interview, as always, I talked about sending mail people want to receive. It always makes me roll my eyes a bit when I see articles with titles like “5 Simple Ways to Reach the Inbox”, so I wrote a bit about that here. In addition to sending mail people want to receive, senders need to make sure they are collecting addresses and building lists in thoughtful and sustainable ways. For more on this topic, check out my post on list brokers and purchased lists.
These same not-so-simple tricks came up again in my discussion of Gmail filters. Everyone wants a magic formula to reach the inbox, and — sorry to burst your bubble — there isn’t ever going to be one. And this is for a good reason: a healthy filter ecosystem helps protect all of us from malicious senders and criminal activity. The email channel is particularly vulnerable to fraud and theft. The constant evolution of filters is one way mail providers can help protect both senders and recipients — but it can be challenging for senders and systems administrators to keep up with this constant evolution. For example, companies sometimes even inadvertently filter their own mail!
I also wrote a bit about how B2B spam is different from B2C spam, and how marketers can better comply with CAN SPAM guidelines in order to reach the inbox. We also republished our much-missed friend and colleague J.D. Falk’s DKIM Primer, which is extremely useful information that was at a no-longer-active link.
One of my favorite posts this month was about “dueling data”, and how to interpret seemingly different findings around email engagement. We also got some good questions for my “Ask Laura” column, where we cover general topics on email delivery. This month we looked at “no auth/no entry” and the Microsoft Smartscreen filter, both of which are useful things to understand for optimizing delivery.
Finally, we are pleased to announce that we’ve joined the i2Coalition, an organization of internet infrastructure providers. They posted a nice introduction on their blog, and we look forward to working with them to help advocate and protect these important technical infrastructures.
Let's talk CAN SPAM
 Earlier this week I posted about the increased amount of B2B spam I’m receiving. One message is not a huge deal and I just delete and move on. But many folks are using marketing automation to send a series of emails. These emails often violate CAN SPAM in one way or another.
Earlier this week I posted about the increased amount of B2B spam I’m receiving. One message is not a huge deal and I just delete and move on. But many folks are using marketing automation to send a series of emails. These emails often violate CAN SPAM in one way or another.
This has been the law for 13 years now, I find it difficult to believe marketers are still unaware of what it says. But, for the sake of argument, let’s talk about CAN SPAM.
Things you need to read
The email solicitation that made me vow to never work with this company again. When sending unsolicited email, you never know how the recipient is going to respond. Writing a public blog post calling you out can happen.
The 2016 Sparkies. Sparkpost is looking for nominations for their email marketing awards. Win a trip to Insight 2016!
5 CAN SPAM myths. Send Grid’s General Counsel speaks about CAN SPAM myths. Personally, asking for an email to unsubscribe is annoying. I never know if the unsubscribe request worked or not. Give me a link any day.
The most misunderstood statistic in email marketing. A good discussion of why raw complaint rates isn’t the metric the ISPs use, and how it can mislead folks about their email program.
Office 365 is expanding it’s DKIM signing. Terry Zink discusses the upcoming changes to how Office365 handles DKIM signatures. This is exactly the kind of changes I was talking about in my 2016 predictions post – background changes that are going to affect how we authenticate email. He even specifically calls out whether or not a particular signature is DMARC aligned or not.
The FTC answers questions about CAN SPAM
The FTC posted answers to a number of questions about the CAN SPAM act.
Read MoreAre botnets really the spam problem?
Over the last few years I’ve been hearing some people claim that botnets are the real spam problem and that if you can find a sender then they’re not a problem. Much of this is said in the context of hating on Canada for passing a law that requires senders actually get permission before sending email.
Botnets are a problem online. They’re a problem in a lot of ways. They can be used for denial of service attacks. They can be used to mine bitcoins. They can be used to host viruses. They can be used to send spam. They are a problem and a lot of people spend a lot of time and money trying to take down botnets.
For the typical end user, though, botnets are a minor contributor to spam in the inbox. Major ISPs, throughout the world, have worked together to address botnets and minimize the spam traffic from them. Those actions have been effective and many users never see botnet spam in their inbox, either because it’s blocked during send or blocked during receipt.
Most of the spam end users have to deal with is coming from people who nominally follow CAN SPAM. They have a real address at the bottom of the email. They’re using real ISPs or ESPs. They have unsubscribe links. Probably some of the mail is going to opt-in recipients. This mail is tricky, and expensive, to block, so a lot more of it gets through.
Much of this mail is sent by companies using real ISP connections. Brian Krebs, who I’ve mentioned before, wrote an article about one hosting company who previously supported a number of legal spammers. This hosting company was making $150,000 a month by letting customers send CAN SPAM legal mail. But the mail was unwanted enough that AOL blocked all of the network IP space – not just the spammer space, but all the IP space.
It’s an easy decision to block botnet sources. The amount of real mail coming from botnet space is zero. It’s a much bigger and more difficult decision to block legitimate sources of emails because there’s so much garbage coming from nearby IPs. What AOL did is a last resort when it’s clear the ISP isn’t going to stop spam coming out from their space.
Botnets are a problem. But quasi legitimate spammers are a bigger problem for filter admins and end users. Quasi legitimate spammers tend to hide behind ISPs and innocent customers. Some send off shared pools at ESPs and hide their traffic in the midst of wanted mail. They’re a bigger problem because the mail is harder to filter. They are bigger problems because a small portion of their recipients actually do want their mail. They’re bigger problems because some ISPs take their money and look the other way.
Botnets are easy to block, which makes them a solved problem. Spam from fixed IPs is harder to deal with and a bigger problem for endusers and filters.
June 2015: the Month in Email
Happy July! We are back from another wonderful M3AAWG conference and enjoyed seeing many of you in Dublin. It’s always so great for us to connect with our friends, colleagues, and readers in person. I took a few notes on Michel van Eeten’s keynote on botnets, and congratulated our friend Rodney Joffe on winning the prestigious Mary Litynski Award.
In anti-spam news, June brought announcements of three ISP-initiated CAN-SPAM cases, as well as a significant fine leveled by the Canadian Radio-television and Telecommunications Commission (CRTC) against Porter Airlines. In other legal news, a UK case against Spamhaus has been settled, which continues the precedent we’ve observed that documenting a company’s practice of sending unsolicited email does not constitute libel.
In industry news, AOL started using Sender Score Certification, and Yahoo announced (and then implemented) a change to how they handle their Complaint Feedback Loop (CFL). Anyone have anything to report on how that’s working? We also noted that Google has discontinued the Google Apps for ISPs program, so we expect we might see some migration challenges along the way. I wrote a bit about some trends I’m seeing in how email programs are starting to use filtering technologies for email organization as well as fighting spam.
Steve, Josh and I all contributed some “best practices” posts this month on both technical issues and program management issues. Steve reminded us that what might seem like a universal celebration might not be a happy time for everyone, and marketers should consider more thoughtful strategies to respect that. I wrote a bit about privacy protection (and pointed to Al Iverson’s post on the topic), and Josh wrote about when senders should include a physical address, what PTR (or Reverse DNS) records are and how to use them, testing your opt-out process (do it regularly!), and advice on how to use images when many recipients view email with images blocked.
3 new CAN SPAM cases
Xmission, a Utah ISP, has filed suit against 3 companies alleging violations of CAN SPAM. The cases were filed in the Utah District Court in April and June. I’ve downloaded some of the documents and complaints and they are now in RECAP. I’ve also included the complaints here (and the links from here on out are almost all .pdfs of the court documents).
Xmission v. Adknowledge (Case 2:15-cv-00277).
Xmission v. Clickbooth (Case 2:15-cv-00420).
Xmission v. Thompson and Company (Case 2:15-cv-00385).
In all the cases Xmission is alleging similar violations of CAN SPAM.
Falsified header information: part 1
Xmission asserts that the domains in the headers were spoofed, unregistered or belonged to an unrelated 3rd party. One of the complaints listed subject lines of the emails sent, so I dug through my spam folder for similar emails. I found a few examples of what I suspect are the spams mentioned in the suit.
Don't like opt-outs? Target your program better.
I get a LOT of spam here. Most of it is marked and trivial to get rid of. Some of it is what I would call semi-legitimate. It’s a real product, but I never asked to receive any information from this company and am not actually part of their demographic. For one time things I just hit delete and move on. Life is too short to complain or opt out of every spam I get. (Tried that, got more mail)
But sometimes if the same sender keeps bothering me, I will send back an email asking them to cease contact. I recently had an occasion where someone sent an initial email trying to sell me bulk SMS, online video and other services. I ignored it because we’re not in the market for any of these services. A week later I get a followup asking why I hadn’t provided feedback to them and if there was a better person to talk to at the company. I looked for a way to opt-out of this message stream, but there wasn’t one. I send a reply telling them we were not interested in speaking to them and to please cease all communication. (“You didn’t receive feedback because I have no interest in talking to you. Please cease all future contact.” Admittedly that was terse, but it was polite.)
My request to cease communication was not well received, nor was it honored. Mind you, they first contacted me trying to sell me services that are totally off what we offer. When I asked them not to contact me, they turned it around that we’d lost business.
Yahoo.com on FCC wireless "do not mail" list
Update: As of mid-morning pacific time on 10/7 yahoo.com has been removed from the FCC list.
As part of CAN SPAM the FCC maintains a list of wireless domains that require proof of permission to send mail to. Recently, various email folks noticed that yahoo.com was added to this list.
According to the law, senders have 30 days to meet the permission standards for any recipients at domains on the FCC list. In practical terms what this means is that the FCC and Yahoo have 30 days to fix this error and get yahoo.com off the list. Based on conversations with people who’ve talked to Yahoo and the FCC this is in the process of happening.
This isn’t the first time a non-wireless domain has been added to the FCC list.
As a sender what should you do with your yahoo.com subscribers?
Right now, nothing. There is a 30 day grace period between when a domain goes on the FCC list and when senders need to comply. I have every expectation that this will be removed in less than 30 days.
But what if it’s not?
In that case you will need to segregate out yahoo.com subscribers in 30 days and not mail them until the domain is removed from the FCC list. While I can’t actively suggest ignoring the law, it’s unlikely that the FCC is going to start coming after senders for mailing yahoo.com addresses once the 30 days are up.
More information: Al Iverson’s Spam Resource.
Spam disclaimer of the day
Things are extremely busy here so blogging is not getting quite the attention it should. I hope to return to more extensive posts soon. Meanwhile, you’ll have to put up with short posts.
Today is a disclaimer I received in a spam. This is one of my addresses that has, somehow, ended up on UK-specific lists.
Ignoring opt-outs
One of the marketing solutions to the spam problem is just to have recipients opt out.
Read MoreIs harvesting illegal under CAN SPAM
This issue comes up repeatedly, as many people have read the CAN SPAM act and believe that CAN SPAM specifically prohibits sending mail to harvested address. This is not how I read the law.
The FTC publishes a CAN SPAM Compliance Guide for Businesses that only mentions harvesting in the context of criminal penalties for violations. They list the following 7 main requirements of CAN SPAM.
Does CAN SPAM apply to individual prospecting emails
Two different people on two different mailing lists asked very similar questions recently. Are people who send individual prospecting emails required to comply with CAN SPAM.
My opinion (not a lawyer, don’t play one on TV, didn’t stay at a Holiday Inn last night) is that CAN SPAM does not mention anything about volume, and any individual unsolicited email that has a “primary purpose” of advertising is required to include a physical postal address and a way to unsubscribe.
My other take on it is for individual prospecting emails failing to comply with CAN SPAM is like speeding. It’s illegal, and you can get in legal trouble by doing it, but everyone does it and few people get caught.
Are the new Gmail ads email?
I’ve seen lots of opinions over the last few weeks about whether or not the new ads in the Gmail promotions tab are email or not.
Read MoreAds in the Gmail Tabbed Inbox
One of the features of the new Gmail tabbed inbox is email-like ads placed by Gmail.
Bad unsubscribe processes
We recently renewed our support contract with VMWare. It’s a weirdly complicated system, in that we can’t buy directly from VMWare, but have to buy through one of their resellers. In this case, we purchased the original hardware from Dell, so we renewed our contract through Dell.
Dell sends my email address over to VMWare as part of the transaction.
My only role in this is as CFO. I approve the purchase and pay the bill. I don’t do anything technical with the license.
The email failures start when VMWare decides that I need to receive mail about some user group meetings they’re holding all over the US. First off, I’m not the right person to be sending this mail to inside our company. I’m the billing contact, not the user contact. Then, they send me mail about meetings all over the US, when they know exactly where I’m located. Would it be so hard to do a semi-personalized version that highlighted the meetings in my local area then pointing out the other locations? Apparently, yes, it is so hard.
The biggest failures, though are in the unsubscribe process.
The unsubscribe page is no big deal. I get to unsub from all VMWare communications, and submit that request without having to figure out what my VMWare password is or anything.
After I hit submit, I’m taken to this page.
Wait? What?
“Thank you for registering?” I didn’t register! I don’t want you to contact me. Plus, this is a HP co-branded page when I’m not a customer of HP. VMWare knows this, they know they got my address from Dell.
The biggest problem is that I’m not sure that my address was actually unsubscribed. I suspect that someone copied a form from elsewhere on the site to use as an unsubscribe form. This person forgot to change the link after the “submit” button was clicked. But what else did they forget to change? Is the unsubscribe actually registered in the database?
I suppose only time will tell if VMWare actually processed my unsubscribe. If they didn’t they’re technically in violation of CAN SPAM.
The lesson, though, is someone should check unsubscribe forms. Someone in marketing should own the unsubscribe process, and that includes confirming that unsubscribe pages work well enough.
Papa John's settles texting suit
Last year a class action law suit was filed against Papa John’s for violation of the Telephone Consumer Protection Act (TCPA) for texts received by Papa John’s customers. Customers allege they never opted in to receive promotional text from the company. Papa John’s claim that they didn’t send the marketing, but instead was sent by third party contractors.
A blog post on lawyers.com says that Papa John’s settled the case for $16.5 million.
CAN SPAM ruling against whois privacy protection
A number of bloggers (Venkat B., John L. and Rebecca T.) have mentioned ZooBuh, Inc. v. Better Broadcasting, LLC (No.: 2:11cv00516-DN (D. Utah May 31, 2013)) recently.
In summary of the case is that ZooBuh is an ISP that has sued Better Broadcasting for spamming in violation of CAN SPAM. Their case hinged on the receipt of more than 12,000 emails from Better Broadcasting, LLC. ZooBuh said these emails caused the following harm
Logging in to unsubscribe
I have been talking with a company about their unsubscribe process and their placement of all email preferences behind an account login. In the process, I found a number of extremely useful links about the requirements.
The short version is: under the 2008 FTC rulemaking senders cannot require any information other than an email address and an email preference to opt-out of mail. That means senders can’t charge a fee, they can’t ask for personal information and they can’t require a password or a login to unsubscribe.
I’ve talked about requiring a login to unsubscribe in the past here on the Word to the Wise blog.
Let them go
Questions about CAN SPAM
One click, two click, red click, blue click
How not to handle unsubscribes
I’m not the only person, though, that’s written about this.
The FTC has written about it in the FTC CAN SPAM Compliance Guide for business
Social invading everything
I discovered, inadvertently, that there is a business networking site modeled after dating site. If you’re selling something you go on the site and register as a seller. If you’re buying something you go on the site and register as a buyer. Buyers can post RFIs and sellers can respond.
Decent enough business model, they’ve even fleshed it out so the site itself acts as an invoicing and billing mechanism.
That’s how I discovered it, one of our very large international telco customers decided they wanted to use this site for billing. Many large telcos expect vendors to use their proprietary site, so I wasn’t that surprised when they asked. And, given they’re international being able to bill them electronically just means I don’t have to remember to use the international stamps.
At the behest of our customer, I signed up at the website. It’s like most social networking sites, create a profile, categorize yourself, make everything public. The thing is, I don’t want to use this site to find new customers. I am just using it because one of my current customers is expecting it. Don’t get me wrong, Abacus is a great product and our customers are extremely happy with it, but it’s pretty niche. It’s not something that’s going to be searched for on a generic website.
I thought that when I set my profile to private that would be some sort of signal to keep me out of the main directory of the site. This morning I realized that wasn’t true when I got a bunch of emails telling me about all these companies looking for “business software” (the closest category I could find).
Getting a bunch of irrelevant mail was annoying enough. Even worse, there was no unsub link in the email. Eventually, I discovered an entire page of email options that were not made clear to me up front. I also sent mail to support and suggested that they talk to their lawyers to clarify whether their opt-out option was consistent with CAN SPAM. I’m pretty sure it doesn’t, but I am not a lawyer.
To the company’s credit, they did have good support and my questions through support were answered in a timely fashion. One of their support reps even called me on the phone to clarify what it was that I wanted to happen and walk me through their email options. She was very upfront about yes, they opted everyone in to all the mail at the very beginning of the process. “We’re like match.com for businesses!”
I’m sure there are some businesses that will find this service to be great. But it’s not what I want or need. Despite the fact that their support was so helpful, I don’t have a great feeling about this company. It seems a bit dishonest that I thought I was signing up for a billing portal, but was actually joining “match.com for businesses. Why couldn’t they make that clear in the 7 emails in 2 days “inviting” me to sign up?
I know I’m a little more sensitive to bad mailing processes than most people, but this was quite an unpleasant experience from the multiple identical emails and reminders before I signed up to the irrelevant stuff I got afterwards.
Does CAN SPAM require multiple opt-outs on emails?
Today’s Wednesday question comes from M. B.
My company sometimes sends mail to our list on behalf of 3rd parties. A recent 3rd party told us that CAN SPAM requires the email contain their opt-out link as well as ours. Is this correct?”
Read More
Spammers are funny
Dear Spammer,
If you are going to send me an email that claims it complies with the Federal CAN SPAM act of 2003, it would be helpful if the mail actually complies with CAN SPAM.
In this case, however, you are sending to an address you’ve harvested off my website. The mail you are sending does not contain a physical postal email address. You’re also forging headers. Both of those things are violations of CAN SPAM. Given you have also harvested the laura-questions@ email from this website, that is treble damages.
Oh, and while we’re at it, you might want to consider your current disclaimer.
Yahoo changes
Thanks to tips by a couple blog readers and some clients, I have been looking into Yahoo disabling links in the bulk folder. It does appear Yahoo is no longer allowing users to click on links in emails that Yahoo places in the bulk folder.
In fact, some of the spam in my Yahoo mailbox even has a notice about this.
Harvesting is alive and well
I’m finding out that email address harvesting off websites is alive and well on the Internet. We have a rotating address on the contact page, which does get harvested but usually the spam is attempting to sell me blog related services. I didn’t expect to get a very different collection of emails to the address I posted here. I’m quite surprised that address is getting a completely different type of spam from the contact address.
The one thing that harvesters appear to have in common is sending CAN SPAM violating email. Both the contact address and the questions address get lots of mail that is in violation of US (and California) law. One of these days I might get bored enough to file a suit against one of them and blog about it.
Let them go!
Unsubscribing should be so simple. Even if someone signed up for mail, senders should let them go when they unsubscribe. Unfortunately, there are a lot of senders that make it difficult to unsubscribe. In fact, many companies are still hiding unsubscribe links behind login pages.
Read MoreQuestions about CAN SPAM.
In the US, the law governing the sending of commercial email is CAN SPAM. I’ve seen a number of questions about CAN SPAM recently.
One came from twitter, where someone was asking if just having an email address meant permission to send to it. Clearly, just being able to dig up an email address doesn’t imply permission to send marketing or commercial email to it. I can promise you April23@contact.wordtothewise.com did not sign up to receive information on increasing Facebook followers.
CAN SPAM doesn’t prohibit unsolicited email. All it says is that if you send unsolicited email you must do a few things.
Letting people stop transactional mail
The question of putting unsub links on transactional messages came up on multiple lists recently. As with any question that has to do with email and controlling it, there were a lot of different opinions.
A number of people believed that transactional mail should never, ever have an unsubscribe. Their argument was that transactional mail is too valuable to allow recipients to unsubscribe from it.
Other people argued that the recipient should always be able to stop mail and that an unsub link was important, even in transactional mail.
A third group pointed out that under CASL transactional mail to Canadian residents may have to have an unsub link, even if the sender doesn’t want to add one in.
As with most questions, I don’t think there is necessarily a single answer for every mailer or sender.
There are absolutely cases where transactional messages should have an unsubscribe. Twitter notifications and Facebook notifications are just some of the examples of mail a lot of people just want to stop.
But should companies allow recipients to unsubscribe from receipts? Some people feel very, very strongly that recipients should never be allowed to unsubscribe from receipts.
The problem with that stance is it ignores the fact that people don’t always correctly type their email addresses and end up giving the address of another person as part of a purchase. Al found a report at the Consumerist where someone is getting flooded with receipts for Nook books she’s never purchased.
This isn’t the first time this has happened, not by a long shot. In fact, in the past year I negotiated a Spamhaus delisting for a very large company that wasn’t confirming email addresses of their customers. This company sells a service that sends email alerts triggered when certain actions happen. Because they were not confirming their customer’s email addresses, they ended up sending alerts to spamtraps. The alerts triggered a SBL listing.
I don’t think that the Nook owner or the alert purchaser are actually malicious or that they purposely gave the wrong email address to their vendors. But it happens, and it happens not infrequently.
What do I recommend?
Transactional mail that is only ever a single event and where that address is not associated with an account don’t need to have an unsubscribe link. If it’s a one-time email, then it’s OK to not have an opt-out link. It’s OK to have an opt-out link, but not necessary.
Transactional mail that’s associated with some sort of account should have a process in place to make sure that mail is going to the right person and if it’s not, that the wrong person can make the mis-directed mail stop. There are multiple ways to do this. One is to confirm the email address associated with the account during the account creation process. Or you can allow anyone receiving the mail to click on a link and opt-out of receiving mail.
Whatever it is, it needs to be effective and protect everyone involved. Requiring the victim recipient to hand over a bunch of personal information, like Virgin Mobile does, helps no one. Continuing to send purchase receipts to an unrelated third party is poor business practice, particularly when you’ve been informed that this is the wrong person.
One Click, Two Click, Red Click, Blue Click
I’ve seen a lot of discussion and arguments over the CAN SPAM rule about whether or not an unsubscribe needs to be a One-Click unsubscribe. It’s gotten so common, I have a stock email I use as a template when wading into such discussions. It’s probably useful for a lot of other people, too, so I thought I’d share.
The regs say:
Proxy registrations and commercial email
Yesterday the law firm Venable, LLP published a document discussing the recent California appellate court decision in Balsam v. Trancos. Their take is that commercial email that contains a generic from line and is sent from a proxied domain is a violation of the California Business and Professions Code § 17529.5(a)(2).
Read MoreCA court requires sender identification on emails
Venkat analyzes the appeals court decision in Balsam v. Trancos, Inc.. In this case the appeals court decided that emails have to identify some actual person or entity they are sent by or from. Emails that do not identify the sender are in violation of the California anti-spam statute.
Venkat talks about all the reasons he thinks this is a problematic ruling, and the CA courts and anti-spam activists certainly have their share of bad rulings. I’m less convinced. The crux of the case seems to be that the advertiser used a number of random domains to hide the responsible party for an email. Rotating domains is a very, very common spammer tactic that is specifically a way to avoid domain based filters.
I understand Venkat’s concern but as someone who gets a lot of these spams I think the court is certainly ruling within the spirit of the CA statute. These mailers are using random domains to avoid filters and mislead recipients as to the source of the mail. Even if the domains are legitimately owned by the advertiser, they are usually hidden behind privacy protection and give the recipient no real information about who is sending the mail.
Another interesting point is the court speaking out against privacy registration. Personally, I don’t think any business should ever hide their domain registration behind privacy protection. If you’re a business, then you should stand up and give real contact information. I know it can be scary, particularly for people working out of their home, but if you’re a real business, you need to have an address registered with your state. Furthermore, if you’re a business sending email, all that email must contain a physical postal address. Your address already needs to be public, and including that in whois records isn’t actually going to change anything.
Spamhaus rising?
Ken has a good article talking about how many ESPs have tightened their standards recently and are really hounding their customers to stop sending mail recipients don’t want and don’t like. Ken credits much of this change to Spamhaus and their new tools.
Read MoreYahoo awarded $610 million
The Federal district court in New York awarded Yahoo $610 million dollars in a suit they filed in 2008.
Read MoreSpam is not illegal
I was recently taken to task for claiming that unsolicited bulk email was spam.
Read MoreSpot the CAN SPAM violations
I received this piece of unsolicited email today, to an address harvested off a website. How many CAN SPAM violations can you count?
Read MoreCAN SPAM and the first amendement
From Venkat at Eric Goldman’s blog we find the federal court has rejected an attempt to claim spam was “protected anonymous speech.”
Holomaxx v. Yahoo and MS: The hearing
I visited Judge Fogel’s courtroom this morning to listen to the oral motions in the Holomaxx cases. This is a general impression, based on my notes. Nothing here is to be taken as direct quotes from any participant. Any errors are solely my own. With that disclaimer in mind, let’s go.
The judge is treating these two cases as basically a single case. When it came time for arguments, the cases were called together and both Yahoo and Microsoft’s lawyers were at the defendant’s table.
Oral arguments centered on the question of CDA immunity and to a lesser extent if there is an objective industry standard for blocking and dealing with blocks. Nothing at all was mentioned about the wiretapping arguments.
The judge opened the hearing with a quick summary of the case so far and what he wanted to hear from the lawyers.
Judge Fogel pointed out that current case law suggests that the CDA provides a robust immunity to ISPs to block mail. The plaintiff can’t just say that the blocks were done in bad faith, there has to be actual evidence to show bad faith. The law does permit subjective decisions by the ISPs. Also, that it is currently hard to see any proof of bad faith by the defendants.
The judge asked the plaintiff’s attorney for his “absolute best argument” as to the bad faith exhibited by the defendants.
The plaintiff responded that they are a competitor who is being stonewalled by the defendants. That their email is not spam (as it is CAN SPAM compliant) and it is wanted email. The defendants are not following the “objective industry standard” as defined by MAAWG.
The judge responded clarifying that the plaintiff really claimed he didn’t need to present any evidence. “Yes.” Judge Fogel mentioned the Towmbly standard which says that a plaintiff must have enough facts to make their allegations plausible, not just possible.
Yahoo!’s lawyer pointed out that both case law and the statutes require a robust showing to invalidate claims under the CDA. And that the purpose of the CDA is to protect ISPs from second guessing. She started to bring up the absolute numbers of emails, but was interrupted and told the numbers weren’t relevant. My notes don’t say if that was the judge or Holomaxx’s lawyer that interrupted, and the numbers discussion did come up again.
Yahoo continued that the CAN SPAM compliance is not a litmus test for what is spam. The decision for what is and is not spam is left to the subjective judgement of the ISP. She also pointed out that the numbers are important. She defined the amount of spam as a tax on the network and a tax on users.
She also addressed the anti-competitive claim. Even if Holomaxx is right, and neither defendant was conceding the point, and it is doubtful that the anti-competitive point can be proven, competition alone cannot establish bad faith. What evidence is there that either defendant exhibited bad faith? In Yahoo’s case there is zero advertiser overlap and in the Microsoft case Holomaxx showed one shared customer.
She then pointed out that the MAAWG document was a stitched collection of experiences from desks. That the document itself says it is not a set of best practices. She also pointed out that there was nothing in the document about how to make spam blocking decisions. That it was solely a recommendation on how to handle people who complain.
According to Yahoo!’s lawyer the plaintiffs brought this suit because they disagreed with the ISPs’ standards for blocking and they were upset about how they were treated. That the worst Holomaxx can say is the MS and Y! had bad customer service.
At this point there was some discussion between the judge and lawyers about how they were currently in a “grey area” between Rule 9(b) and Rule 12(b)6. I am not totally sure what this was about (one of my lawyer readers can help me out?) but there was also mention of using these rules in the context of the ISPs’ robust immunity under the CDA.
Finally, the judge asked Microsoft’s lawyer if he had anything more to add. He reiterated that the MAAWG document was not a standard, it was a collection of options. He also brought up the volume issue again, asserting that even if it is a true standard that the volume of unwanted mail sent by Holomaxx does not mean ISPs need to follow it.
Judge Fogle asked him if he meant there was no legal obligation for the ISPs to be warm and fuzzy.
The judge and defendant lawyers talked around a few general ideas about the MAAWG document. First that there was no obligation to tell senders enough information so that senders could reverse engineer spam filters. Microsoft also brought up the volume issue again, saying that the volume of unwanted 3rd party mail that the plaintiff was sending was, in itself, proof that the mail was bad.
Holomaxx interrupted claiming that the volume is a red herring. Judge Fogel countered with “but the gross number of unwanted emails is a huge number of emails.” Holomaxx’s lawyer argued that both Yahoo and Microsoft had large, robust networks, and the volume is irrelevant. I thought this was funny, given how often both of them have outages due to volume. However, the Holomaxx lawyer did have a point. Facebook sends billions of emails a day and both Yahoo and Hotmail can cope with that volume of mail and that volume dwarfs what Holomaxx sends.
The judge asked if he should look at the percentage of complaints about the mail rather than the gross number. Holomaxx replied that both were just a drop in the bucket and neither number was relevant.
Holomaxx then claimed again that MAAWG was a standard. The judge pointed out it was a standard for customer service, not a standard for blocking. Holomaxx disagreed and said that the MAAWG document was a standard for both how to block and how to deal with blocks afterwards.
The judge asked Holomaxx if there was any actual evidence of their claims. He talked about a case he heard a few years ago. Some company was suing Google because their search results were not on the front page of Google results. That company didn’t prevail because they never offered any actual evidence that Google was deliberately singling them out. He asked Holomaxx how they were being singled out.
Holomaxx replied there was no industry standard to measure against.
The judge wrapped up the hearing by pointing out that he was being asked to show where the exceptions to the CDA were and that he had to consider the implications of his ruling. He agreed that bad faith was clearly an exception to CDA protection, but what was the burden of proof required to identify actual bad faith. He seemed to think this was the most important point and one that would take some deliberation.
Overall, the hearing took about 15 minutes, which seemed in line with the case immediately before this one.
My impression was that the judge was looking for Holomaxx to argue something, anything with facts rather than assertion. But, I am scientist enough to see that may be my own biases at work. But the judge gave Holomaxx the opportunity to show their absolute best evidence, and Holomaxx provided exactly zero, instead falling back to it’s true because we said it’s true.
The judge will issue a written ruling, I’ll keep an eye out for it and post it when it’s out.
Legal analysis of Hypertouch v. Valueclick
Venkat has an analysis of the Hypertouch v. Valueclick case and recent appeals court ruling.
Read MoreCAN SPAM preemption of CA law
The California court of appeals returned a ruling yesterday in the Hypertouch v. ValueClick case. This is a case I haven’t talked about at all previously, but I think this ruling deserves a mention.
The short version is that Hypertouch sued Valueclick in 2008 under both CAN SPAM and the California anti-spam law. Eventually the judge in the case ruled that there was no clear evidence of fraud, therefore CAN SPAM preempted the California law.
Hypertouch appealed the case.
Yesterday the appeals court published their opinion and kicked the case back down to the lower court.
Canada passes anti-spam bill
Call it C-28, call it FISA, call it COPL, just don’t call it a pipe dream any longer.
Today the Canadian anti spam law received royal assent and is now law. ReturnPath is saying it will take effect September 2011, but that’s the only date I’ve seen published. The full text of the bill as passed by the House of Commons can be found at http://www2.parl.gc.ca/content/hoc/Bills/403/Government/C-28/C-28_3/C-28_3.PDF
It’s fairly dense and I’m still reading through the final version. Of critical importance for anyone marketing in Canada is that it sets requirements that commercial email be sent with the permission of the recipient. This is different from CAN SPAM here in the US which doesn’t require consent of the recipient, but allows anyone to send unsolicited email as long as it meets the standards set by the law.
CBC Story
Return Path blog post
CAUCE posts
Thin Data implementation guide
One beeelion dollars
 Facebook won another round in their court case against a Canadian spammer last week. Their $873,000,000 judgment was upheld by the Quebec Superior court. At today’s exchange rates, the judgment translates to over CDN$1,000,000,000.
Facebook won another round in their court case against a Canadian spammer last week. Their $873,000,000 judgment was upheld by the Quebec Superior court. At today’s exchange rates, the judgment translates to over CDN$1,000,000,000.
In fine spammer style the defendant, Adam Guerbuez, is flouting the judgment and claiming he won’t pay a dime. In fact, he’s already filed bankruptcy and is reported to have transferred a number of assets to family members. From what I’m hearing from some of my Canadian colleagues the courts up there take a very dim view of his behaviour. Like many things that go through the court system, though, it is unlikely that the process will be rapid.
This is one of the largest, if not the largest, fines levied for violations of the CAN SPAM act. I don’t think Facebook will see much, if anything, of the money. But, hey, maybe the Canadian courts will throw this spammer in jail for flouting their ruling.
Suing spammers
I’m off to MAAWG next week and seem to have had barely enough time to breathe lately, much less blog. I have a half written post, but it’s taking a little more research to put together. That can wait until I get the chance to do the research.
Instead I thought I’d talk about the North Coast Journal article “The Rise and Fall of a Spam Crusader.” It’s quite an interesting article and looks into the personal and business sacrifices that people make in order to chase down spammers.
In my experience a lot of the serial litigators have very poor practices around data collection and analysis. They don’t collect evidence, they just collect email and then make assertions and assumptions. This not every effective when having to convince a judge that you are right.
The article actually does nothing to change this impression. The cases ASIS won are the cases where the defendants didn’t respond. That also means that ASIS couldn’t collect.
I do disagree with Mr. Singleton, the lawyer, where he says CAN SPAM is dead. In many cases I’ve seen there aren’t clear CAN SPAM violations. So if he’s trying to sue these spammers under CAN SPAM his cause of action is wrong. Secondly, the article goes on to talk about the broader implications.
Buying Lists
One of my email addresses at a client got spammed today offering to sell me appending services. I was going to post the email here and point out all of the problems in how he was advertising it, including violating CAN SPAM.
As I often do, I plugged his phone number into google, only to discover that my blog post from March about this spammer was the 2nd hit for that number. Well, go me.
I can report nothing has changed. He’s still violating CAN SPAM. He’s still claiming I have no right to post, share, spindle, mutilate or fold his spam. Well, in the interest in something, I thought I’d share the whole post this time. Just to warn folks from attempting to purchase services from appendleads.com (nice website, by the way).
CAN SPAM Plaintiff ordered to pay 800K in lawyer fees
Asis Internet service has been ordered to pay over $800,000 in lawyer fees to Optin Global. Venkat has details. This is the same company that was recently awarded $2.5M judgment in a different case.
Read MoreWhat Happens Next…
or Why All Of This Is Meaningless:
Guest post by Huey Callison
The analysis of the AARP spam was nice, but looking at the Mainsleaze Spammer Playbook, I can make a few educated guesses at what happens next: absolutely nothing of consequence.
AARP, if they acknowledge this publicly (I bet not) has plausible deniability and can say “It wasn’t us, it was an unscrupulous lead-gen contractor”. They probably send a strongly-worded letter to SureClick that says “Don’t do that again”.
SureClick, if they acknowledge this publicly (I bet not) has plausible deniability and can say ‘It wasn’t us, it was an unscrupulous affiliate”. They probably send a strongly-worded letter to OfferWeb that says “Don’t do that again”.
OfferWeb, if they acknowledge this publicly (I bet not) has plausible deniability and can say ‘It wasn’t us, it was an unscrupulous affiliate”. And maybe they DO fire ‘Andrew Talbot’, but that’s not any kind of victory, because he probably already has accounts with OTHER lead-gen outfits, which might even include those who also have AARP as
a client, or a client-of-a-client.
So the best-case result of this analysis being made public is that two strongly-worded letters get sent, the URLs in the spam and the trail of redirects change slightly, but the spam continues at the same volume and with the same results, and AARP continues to benefit from the millions of spams sent on their behalf.
I’m not a lawyer, but I was under the impression that CAN-SPAM imposed liability on the organization that was ultimately responsible for the spam being sent, but until the FTC pursues action against someone like this, or Gevalia, corporations and organizations will continue to get away with supporting, and benefiting from, millions and millions of spams.
As JD pointed out in a comment to a previous post: sorry, AARP, but none of us are going to be able to retire any time soon.
Spammers aren't who you think they are
Shady direct marketers exploit CAN SPAM to continue spamming but protect themselves from the law. This is something I’ve been talking about for a while (TWSD), and it’s nice to see the mainstream press noticing the same thing.
HT: Box of Meat
Click-wrap licenses again
Earlier this week ARS Technica reported on a ruling from the Missouri Court of Appeals stating that terms and conditions are enforceable even if the users are not forced to visit the T&C pages. Judge Rahmeyer, one of the panel members, did point out that the term in question, under what state laws the agreement would be enforced, was not an unreasonable request. She “do[es] not want [their] opinion to indicate that consumers assent to any buried term that a website may provide simply by using the website or clicking ‘I agree.'”
What does this have to do with email? Well, it means that reasonable terms in the agreements may still be binding even if the user does not read the full terms of the opt in before submitting an email address. In practical terms, though, there’s very little that has changed. Hiding grants of permission deep in a terms document has long been a sneaky trick practiced by spammers and list sellers. Legitimate companies already make terms clear so that users know what type of and how much mail to expect by signing up to a list. They also know that the legal technicalities of permission are not as important as meeting the recipients expectations.
Defining spam
This is a post I’ve put off for a while as the definition of spam is a sticky subject. There are online fora where the definition of spam has been debated for more than 10 years, and if there isn’t a working definition after all that time, it’s unlikely there will ever be a definition the participants can agree on.
This came up again recently because one of the comments on my “Reputation is not permission” post took me to task for daring to call the mail “spam.” I’m going to assert here that the mail was unsolicited bulk email. I did not ask for it and I know at least 4 other people that received it.
The commenter, and a few marketers, argue that if the mail is sent without any forgery and the mail contains an opt-out link then it is not spam. It is a definition I have only seen folks who want to send unsolicited bulk email use, however. What they are really arguing is their mail isn’t spam because they provide a valid return address and a way to opt-out. Few people actually agree with this definition.
Here are 10 of the many definitions of spam that I’ve seen.
You might be a spammer if…
… the best thing you have to say about your email practices is “They’re CAN SPAM compliant.”
… text to .gif is a vital part of your email generation process
… you have to mail from multiple ESPs in order to get good delivery
Please contribute your own in the comments.
I’d also like to thank Al for guest posting 2 days this week. Thanks, Al!
More Gordon v. Virtumundo news
Eric Goldman reviews the appeals court decision in Gordon vs. Virtumundo.
Read MoreCAN SPAM compliance information in images
A fellow delivery specialist sent me a question this morning.
Read MoreAiding and abetting violations of CAN SPAM
The US DOJ announced today the guilty plea of David Patton. Patton was charged with “aiding and abetting violations of the CAN SPAM act. Software written by Patton’s company provided the ability to modify email headers and use open proxies to disguise the source of the email.
The Ralsky convictions are, to the best of my knowledge, the first criminal prosecution for CAN SPAM violations and so far 9 of the 12 defendents charged have pled guilty.
Guilty of violating CAN SPAM
Al Ralsky has long been known as “the king of spam.” He has a long history of spamming, suing ISPs who block his mail and refusing to provide him with connectivity. He was profiled in the Detroit Free Press based on his spamming activity more than 5 years ago. He also has a history of convictions for fraud and other related crimes.
Yesterday, he and some of his family and business partners pled guilty to another raft of charges including fraud, money laundering and CAN SPAM violations. This may be the first time someone has pled guilty to violating CAN SPAM. Press reports indicate there is jail time in his future.
Detroit Free Press article
Washinton Post article
DirectMag article
This is the type of mailer that all mailers compete with. Everyone had to deal with spam from Al Ralsky: recipients, senders and ISPs. Thanks to the justice department, FBI and everyone involved for their hard work.
CAN SPAM pre-emption in the courts
Ethan Ackerman has a summary of recent cases where judges are splitting over rulings on CAN SPAM pre-emption.
Read MoreDelivery news April 2009
Penton Media’s Marketing Practices
Ken Magill responds to critics of Penton’s email marketing practices in an article out today. His article is quite open and points out that some of the things Penton does are not good.
TWSD: Lying and Hiding
Another installment in my ongoing series: That’s What Spammers Do. In today’s installment we take a look at a company deceiving recipients and hiding their real identity.
One of my disposable addresses has been getting heavily spammed from mylife.com. The subject lines are not just deceptive, they are provably lies. The mail is coming from random domains like urlprotect.com or choosefrequency.com or winnernotice.com advertising links at safetyurl.com or childsafeblogging.com or usakidprotect.com.
The spam all claims someone is “searching for…” at their website. The only thing is, the email address is associated with a fake name I gave while testing a website on behalf of a client. I know what website received the data and I know what other data was provided during the signup process. I also know that the privacy policy at the time said that my data would not be shared and that only the company I gave the information to would be sending me email.
Just more proof that privacy policies aren’t worth the paper they’re written on. But that’s not my real issue here.
The real issue is that I am receiving mail that is clearly deceptive. The subject lines of the emails up until yesterday were “(1) New Message – Someone Searching for You, Find Out…” Yesterday, I actually clicked through one of the messages to confirm that the emails were ending up at mylife.com. After that, the subject lines of the emails changed to “(1) New Person is Searching for You.” I don’t know for sure that my click has caused the change in subject lines, but the timing seems a bit coincidental.
It’s not that someone, somewhere gave mylife.com bad data, or that someone typed a name into the mylife.com search engine and the mylife.com database showed that name and my email address were the same. Neither this name or this email address show up in a google search and I can say with certainty that this is a unique address and name combination given to a specific website. Therefore, the subject lines are clearly and demonstrably lies.
The spams are also coming from different domains and advertising links in different domains. The content is identical, the CAN SPAM addresses are identical. While the court may not rule this is deceptive under the rules of CAN SPAM, it certainly is an attempt to avoid domain level spam filters.
Who are mylife.com? Well, their website and the CAN SPAM address on their spam claims they are the company formerly known as reunion.com. I’ve talked about reunion.com here before. They have a history of harvesting addresses from users address books. They were sued for deceptive email practices under California law, but won the case just recently. They seem to think that the court case was permission to send deceptive email and have thus ramped up their deceptive practices.
If you are a legitimate email marketer, there are a couple take home messages here.
1) Spammers send mail with different domains, from different IP addresses, that contain identical content, landing pages and CAN SPAM addresses. Legitimate marketers should not rotate content and sends through different domains or different IP addresses. Pick your domain, pick your IP and stick with it.
1a) Spammers use randomly chosen domain names and cycle through domains frequently. Legitimate marketers must not use unrelated domains in marketing. Use a domain name that relates to your product, your industry or you.
2) Spammers send mail with deceptive subject lines. Legitimate marketers should make sure their subject lines are clear and truthful.
3) Spammers send mail in violation of the privacy policy under which information was collected. Legitimate marketers should be very careful to handle data in accordance with their privacy policies.
That’s what spammers do. Is that what you do?
Buying lists and other stupid marketing tricks
Back in November, I commented on Zoominfo and that they were selling senders very bad lists. At that time, Zoominfo did not have my current information. They have since rectified that problem and are now selling my information to people.
This morning, I received an email that said:
Supreme Court declines to hear anti-spam case
Yesterday the Supreme Court declined to hear an appeal for Virginia v. Jaynes. This means that the Virginia state supreme court ruling overturning the Virginia anti-spam law currently stands.
Jeremy Jaynes was a well known spammer who went under the name Gavin Stubberfield. He was pretty famous in anti-spammer circles for sending horse porn spam. In 2003 he was arrested under the Virginia state anti-spam statute. He was initially convicted but the conviction was overturned on appeal.
Ethan Ackerman has blogged about this case, including a recap today.
Venkat Balasubramani has also blogged about this case.
Mickey Chandler has the docs.
John Levine weighed in.
News Articles: CNN, Washington Post, CNET
Negative branding, part 2
Last week I commented on negative branding in email. One of the comments on that post was an advertisement for a company called WrapMail. In the course of attempting to determine if this was spam or a real comment, I checked out their website. While the comment itself may not be spam, and it may not be providing services to spammers, the entire business model strikes me as a delivery nightmare.
Briefly, once you sign up with this company, you set your mail client to use their SMTP server. As all of your mail goes through their server is it “wrapped” with a HTML template of your choosing. All of your email is now branded with that template, allowing you to formally advertise your business even during the course of standard business communications.
There are multiple ways this can negatively impact a specific brand.
Confirmed unsubscribe
Whatever one might think about confirming opt-ins I think we can all agree that requiring someone to jump through hoops and confirm an unsubscription request will just annoy that person.
Today I attempt to opt-out from a discussion list. It’s one I *thought* I had opted out of previously, but I could find no record of the request anywhere. OK. So I imagined unsubscribing, I’ll just unsub again and keep better records.
After digging through the headers, I find the unsub link and dutifully mail off my unsubscribe request. I then receive an email that requires I click on a link to confirm my unsub request. This causes me to grumble a bit. I have heard all the arguments about forged unsub requests and the various reasons this is good practice. I believe none of them. Requiring people to confirm an unsubscription request is bad practice.
In this case, the mailing list is a discussion list so there is no CAN SPAM violation. However, I know that some commercial mailing lists have also implemented confirm your opt-out request. For commercial mailing lists, this is a CAN SPAM violation. It’s also just plain rude. If someone says, “Stop!” then you should stop, no questions asked
TWSD: breaking the law
I tell my clients that they should comply with CAN SPAM (physical postal address and unsubscribe option) even if the mail they are sending is technically exempt. The bar for legality is so low, there is no reason not to.
Sure, there is a lot of spam out there that does not comply with CAN SPAM. Everything you see from botnets and proxies is in violation, although many of those mails do actually meet the postal address and unsubscribe requirements.
One of my spams recently caught my eye today with their disclaimer on the bottom: “This email message is CAN SPAM ACT of 2003 Compliant.” The really funny bit is that it does not actually comply with the law. Even better, the address it was sent to is not published anywhere, so the company could also be nailed for a dictionary attack and face enhanced penalties.
It reminds me of the old spams that claimed they complied with S.1618.
Reunion.com sued under CA anti-spam law
Ethan Ackerman posted a rather long analysis of the class action lawsuit filed against Reunion.com over at Eric Goldman’s Technology and Law Blog. Part of the case is related to Reunion.com’s scraping of address books, something I have discussed here before.
The analysis goes through the case step by step and is well worth a read. There are a lot of issues being explored, including the applicability of CAN SPAM to “forward to a friend” email. This case also touches on CAN SPAM and preemption of state laws.
Definitely a post worth reading and a case worth keeping an eye on.
FTC Opt out clarification
In early July, the Magilla Marketing newsletter has an article about how email preference centers may now be illegal due to the clarifications published by the FTC. Trevor Hughes of the ESPC is quoted extensively, lamenting about how marketers cannot legally interfere in the unsubscribe process.
Read MoreNew email related blog
Mickey Chandler, of SpamSuite.com has launched a new email delivery specific blog: Spamtacular.com. He moved a number of posts from his other blog, but today has a new post up about how a prior business relationship impacts compliance with CAN SPAM. He concludes with:
Read MoreDeclan weighs in on the VA law
Declan McCullagh writes today about the VA anti-spam law being overturned by the state supreme court.
Read More