Dmarc
Google and Alignment Update
Earlier this month, I published a post about some changes with how Google is displaying information related to authentication in their “View Original” page. There’s one condition I apparently didn’t report and it brought up a question earlier today.
Read MoreGoogle, Alignment and DMARC
Google has been making a number of changes to their systems over the last few weeks. Folks are seeing a lot of changes in Google postmaster tools and they’re seeing changes in how Google is displaying headers in the “show original” tab.
Read MoreDon’t add your domain to the Public Suffix List
(At least, not if you ever intend to use it for email. It might break the domain for email, maybe forever.)
Read MoreDo we care about SPF alignment?
SPF and DKIM are the two main ways we associate a domain name with a stream of email in an authenticated way. We can choose the DKIM signing domain fairly freely – we can choose any domain or subdomain we control and put it in the d= field of the DKIM signature. But our choice for the SPF domain is more constrained.
Read MoreSending domains and hostnames
Lots of times I see someone asking a question and they talk about their sending domain. And it’s sometimes not 100% clear which domain they mean by that – and when we’re talking about alignment and reputation it can make a difference. So here’s a list of (some of?) the different places a mailserver uses a domain.
Read MoreDMARC: The good, the bad and the ugly
DMARC is the newest of the authentication protocols. It compares the domain in the From: address to the domains authenticated by SPF and DKIM. If either SPF or DKIM pass and they are in the same organizational domain as the domain in the From: address then the email is authenticated with DMARC.
Read MoreWildcards and DKIM and DMARC, oh my!
If you’re an ESP with small customers you may have looked at the recent Google / Yahoo requirements around DMARC-style alignment for authentication and panicked a bit.
Read MoreDon’t break the (RFC) rules
It looks like Microsoft are getting pickier about email address syntax, rejecting mail that uses illegal address formats. That might be what’s causing that “550 5.6.0 CAT.InvalidContent.Exception: DataSourceOperationException, proxyAddress: prefix not supported – ; cannot handle content of message” rejection.
Read MoreGmail Program for Election Mail
A few months ago, Google made a splash in the political press and the email marketing space when they asked the FEC the following question:
Read MoreAuthentication at Office365
This is a followup from a post a few weeks ago about authentication changes at Office365. We have some more clarity on what is going on there. This is all best information we have right now.
Read MoreSome Microsoft thoughts
Right at the end of January, Microsoft appears to have made couple of changes to how they’re handling authentication. The interesting piece of this is that, in both cases, Microsoft is taking authentication protocols and using them in ways that are slightly outside the spec, but are logical extensions of the spec.
Read MoreCost of authentication
At the end of last year, Steve wrote a post about the different types of authentication. I thought I’d build on that and write about the costs associated with each type. While I know a lot of my readers are actually on the sending side, I’m also going to talk about the costs associated with the receiving side and a little bit about the costs for intermediaries such as CRM systems or ESPs.
Read MoreAuthentication
Some notes on some of the different protocols used for authentication and authentication-adjacent things in email. Some of this is oral history, and some of it may be contradicted by later or more public historical revision.
Read MoreWhy is DMARC failing?
Multiple times over the last few weeks folks have posted a screenshot of Google Postmaster tools showing some percentage of mail failing DMARC. They then ask why DMARC is failing. Thanks to how DMARC was designed, they don’t need to ask anyone this, they have all the data they need to work this out themselves.
Read MoreShould you publish a DMARC policy statement?
DMARC is a protocol that makes it very, very simple to shoot yourself in the foot. Setup is tricky and if you don’t get it exactly right you risk creating deliverability problems. The vast majority of companies SHOULD NOT publish a DMARC policy with p=reject or p=quarantine for their existing domains.
Read MoreDMARC doesn’t fix phishing
Over the last few weeks I’ve had a lot of discussions with folks about DMARC and the very slow adoption. A big upsurge and multiple Facebook discussions were triggered by the ZDNet article DMARCs abysmal adoption explains why email spoofing is still a thing.
There are a lot of reasons DMARC’s adoption has been slow, and I’m working on a more comprehensive discussion. But one of the absolute biggest reasons is that it doesn’t actually fix phishing.
Gradual DMARC Rollout
Over on twitter Alwin de Bruin corrected me on an aspect of DMARC soft rollout I’d entirely forgotten about. It’s useful, so I thought I’d write a quick post about it.
Read MoreGood morning DMARC
I’m thinking I may need to deploy DMARC report automation sooner rather than later.
Read MoreMinimal DMARC
The intent of DMARC is to cause emails to silently vanish.
Ideally deploying DMARC would cause all malicious email that uses your domain in the From address, but which has absolutely nothing to with you to vanish, while still allowing all email you send, including mail that was sent through third parties or forwarded, to be delivered.
For some organizations you can get really close to that ideal. If you control (and know about) all the points from which email is sent, if your recipients are individuals with normal consumer or business mailboxes, their mailbox providers don’t do internal forwarding in a way that breaks DKIM before DMARC is checked and, most importantly, if your recipients are a demographic that doesn’t do anything unusual with their email – no vanity domain forwarding, no automated forwarding to other recipients, no alumni domain forwarding, no forwarding to their “real” mailbox on another provider – then DMARC may work well. As long as you follow all the best practices during the DMARC deployment process it’ll all be fine.
What, though, if you’re not in that situation? What if your recipients have been happily forwarding the mail you send to them to internal mailing lists and alternate accounts and so on for decades? And that forwarding is the sort that’s likely to break DKIM signatures as well as break SPF? And while everyone would advise you not to deploy DMARC p=reject, or at least to roll it out very slowly and carefully with a long monitoring period where you watch what happens with p-none, you have to deploy p=reject real soon now?
What can you do that’s least likely to break things, while still letting you say “We have deployed DMARC with p=reject” with a straight face?
Brand indicators in email
A number of companies in the email industry have been working on a way to better identify authenticated emails to users. One proposal is Brand Indicators for Message Identification (BIMI). A couple weeks ago, Agari announced a pilot program with some brands and a number of major consumer mail providers. These logos should be available in the Yahoo interface now and will be rolling out at other providers.
Authentication is about Identity, not Virtue
I just got some mail claiming to be from “Bank of America <secure@bofasecure.com>”.
It passes SPF:
Organizational Domain
We often want to know whether two hostnames are controlled by the same person, or not.
Read MoreAbout that DMARC "exploit"
A security researcher has identified a rendering flaw that allows for “perfect” phishing emails. From his website:
Read MoreThe feds are deploying DMARC
The US National Cybersecurity Assessments & Technical Services Team have issued a mandate on web and email security, including TLS+HSTS for web servers, and STARTTLS+SPF+DKIM+DMARC for email.
It’s … pretty decent for a brief, public requirements doc. It’s compatible with a prudent rollout of email authentication.
Email pranks and spoofing
Earlier today a twitter user calling himself Email Prankster released copies of email conversations with various members of the current US administration. Based on his twitter feed, and articles from BBC News and CNN, it appears that the prankster forged “friendly from” names in emails to staffers.
A bunch of folks will jump on this bandwagon and start making all sorts of claims about how this kind of thing would be prevented if the Whitehouse and other government offices would just implement DMARC. Problem is, that’s not true. It wouldn’t have helped at all in this case. Looking at the email screenshots all of the mail seems to come from legitimately registered addresses at free email providers like mail.com, gmail.com, and yandex.com.
One image indicates that some spam filter noticed there may be a problem. But apparently SUSPECTED_SPAM in the subject line wasn’t enough to make recipients think twice about checking the email.
The thing is, this is not “hacking” and this isn’t “spear phishing” and it’s not even really spoofing. It’s social engineering, at best. Maybe.
People are the weakest link
All of the technical security in the world won’t fix the biggest security problem: people. Let’s face it, we are the weakest link. Adding more security doesn’t work, it only causes people to figure out ways to get around the security.
Read MoreDMARC doesn't fix Phishing
Not a new thing, but a nice example just popped up in my inbox on my phone.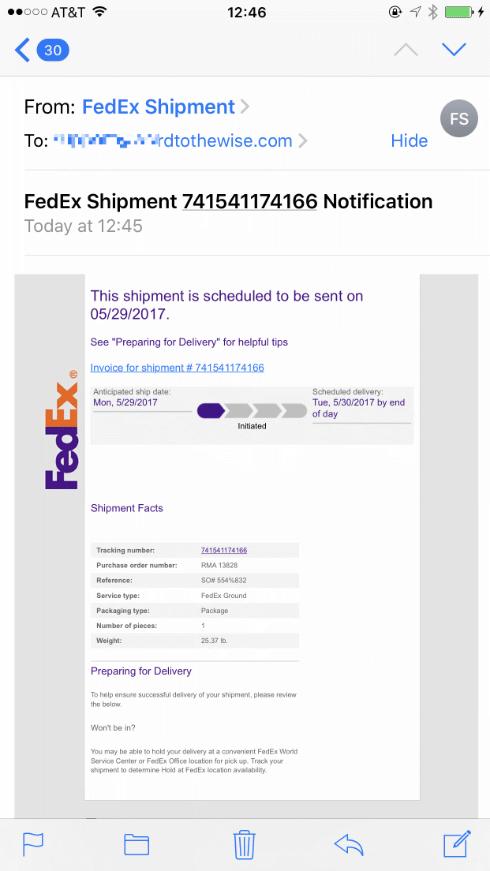
But FedEx solved their entire phishing problem when they published a strict p=reject DMARC record, right?
This didn’t come from fedex.com. It came from another domain that looks vaguely like fedex.com – what that domain is doesn’t matter, as the domain it’s sent from isn’t displayed to the user on my phone mail client. Nor is it displayed to the user by Mail.app on my desktop, unless you turn off Mail → Preferences … → Viewing → Use Smart Addresses.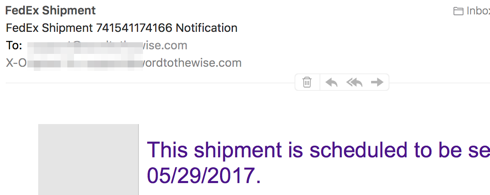
That lookalike domain could pass SPF, it could be used as d= in DKIM signing, it could even be set up with DMARC p=reject. And the mail is pixel identical to real mail from fedex.com.
On my desktop client I can hover over the link and notice it looks suspicious – but it’s no more suspicious looking than a typical ESP link-tracking URL. And on mobile I don’t even get to do that.
SPF and DKIM and DMARC can temporarily inconvenience phishers to the extent that they have to change the domain they’re sending from, but it’ll have no effect on the vulnerability of most of your audience to being phished using your brand.
ARC: Authenticated Received Chain
On Friday I talked a little about DMARC being a negative assertion rather than an authentication method, and also about how and when it could be deployed without causing problems. Today, how DMARC went wrong and a partial fix for it that is coming down the standards pipeline.
What breaks?
DMARC (with p=reject) risks causing problems any time mail with the protected domain in the From: field is either sent from a mailserver that is not under the control of the protected domain, or forwarded by a mailserver not under the control of the protected domain (and modified, however trivially, as it’s forwarded). “Problems” meaning the email is silently discarded.
This table summarizes some of the mail forwarding situations and what they break – but only from the original sender’s perspective. (If forwarding mail from a users mailbox on provider A to their mailbox on provider-Y breaks because of a DMARC policy on provider-A that’s the user’s problem, or maybe provider-A or provider-Y, but not the original sender’s.)
The philosophy of DMARC
We know that legitimate email sent with valid SPF and a DKIM signature often breaks in transit.
SPF will fail any time mail is forwarded – via a mailing list, a forwarding service used by the recipient, or just ad-hoc forwarding.
DKIM will fail any time the message is modified in transit. That can be obviously visible changes, such as a mailing list tagging a subject header or adding a footer to the body. It can also be less obvious changes, such as intermediate MTAs wrapping lines that are too long, reencoding content or repackaging the message altogether – perhaps when delivering from a mailserver that is 8BITMIME compliant to one that isn’t.
(This image has absolutely nothing to do with email authentication, but searching for stock photography about email or authentication or chains or, well, pretty much anything like that leads to horribly depressing corporate imagery. So, no. Have something colourful and optimistic instead.)
As SPF and DKIM are typically used, none of this is much of a problem. A message being authenticated provides a little extra information to the receiving mailserver, and the domain attached to the authentication can be used to look up a senders reputation, giving a potential boost to the chances of the mail being sent to the inbox. If the authentication is broken, though, the mail will still be judged on it’s merits – is it coming from an IP address that’s a source of good mail, does the content look legitimate, and all the other things a spam filter looks at.
That authentication is a (potentially big) positive signal, but lack of authentication isn’t really any signal at all is why SPF and DKIM being fragile wasn’t an issue. SPF and DKIM are positive assertions – “IF this mail IS authenticated THEN IT IS from me”.
That changed when DMARC became popular, though.
DMARC allows the owner of a domain to say “We send no mail that is not authenticated, and we promise that none of that authentication will be broken in transit”. DMARC is a negative assertion – “IF this mail IS NOT authenticated THEN it IS NOT from me”. It converts the absence of a positive assertion into a negative assertion.
This isn’t the first attempt to layer a “we authenticate everything” negative assertion on top of fragile email authentication. SPF did it, with the -all flag (which is universally ignored, leaving SPF purely as a positive assertion). DomainKeys did it, with DomainKeys policy records (which you occasionally still see published, but were never really used to reject mail). DKIM did it with ADSP – which didn’t see much use either.
The reason none of them were used much is because even when senders were telling the truth about “we send no email that is not authenticated” they were always lying, to varying degrees, about “none of the authentication will be broken in transit”.
If your domain that is solely used for bulk email. If it’s never for used mail sent by human beings, not even customer support employees. If it’s a newly created domain with no legacy usage that only sends email from a very tightly controlled infrastructure. If you only send email that’s been created via a well implemented message composition pipeline that ensures the content of the is not just RFC compliant but also “well formed”, with short lines, simple widely implemented encoding, vanilla mime structure and so on. And it’s sent out via conservatively configured smarthosts that deliver directly to the end recipients MX. And if you know that the demographics of your recipients are such that the minority that are forwarding that mail elsewhere (e.g. from their Yahoo account to their Google account or via an alumni mail alias) is a small enough group that you don’t care about them…
If all of those things are true, then your domain is going to be able to deploy DMARC pretty easily and safely. If not, though, how can you tell?
That’s the place where DMARC improves over it’s predecessors. It allows you not only to publish a DMARC policy record in test mode, so it’s not actually used to filter your mail (well, mostly, but that’s a longer story) but also to ask recipients to notify you of mail that seems to be from you but which isn’t authenticated.
You can publish a “p=none” DMARC record with notification addresses in it and wait and see what happens. You’ll get notification of mail that has your domain in the From: field but which isn’t authenticated.
As a first round of action that lets you see where you’re sending email from that you didn’t know about. Sysadmin notification email. That marketing splinter group in Sasketchwan. The outsourced survey company.
Once you’ve cleaned all that up, and made sure everyone is authenticating their mail then you can look at what’s left. The next step is likely to be mistakes you’re making in authentication or message composition that’s causing some of your mail – typically depending on content, and source and recipient domain – to become unauthenticated. Clean that up, make sure all your message composition is squeaky clean, make sure employees aren’t sending mail using that domain in ways you don’t authorize (interacting with mailing list, for example).
By that point you’ll have reduced the torrent of reports you’re getting to two types. One is mail that you send that has it’s authentication broken in transit through some process you have no control over. The other type is mail that has your domain in the “From” field but which you didn’t send. Some of that may be legitimate use of your domain by your employees, such as forward-to-a-friend services, signing up for document delivery via email, third-party notification services. By deploying DMARC you are declaring all that sort of usage to be illegitimate, and you’ll need to get all your employees to stop doing it (or, at least, know that it’s going to stop working). The rest of it is likely a mix of spam and phishing mail. The spam, that’s just using your domain in random from addresses, you probably don’t care about. The phishing you do.
You’ve finally cleaned up your mail infrastructure and policies enough to gather the data you need. How much of my legitimate email will have it’s authentication broken (and hence be silently thrown away by DMARC)? And how much hostile phishing mail is targeting my users (and using the exact domain you are)?
Then you have the information you need to make an informed decision as to how badly deploying DMARC will break your legitimate use of email (after you’ve done everything you can to minimize that) and some idea of whether it will provide you any benefit, at least in the shorter term.
That testing phase, where senders can use other peoples mail infrastructure to investigate their sending practices, gradually fix any problems and finally gather some metrics is what made gave the developers of the DMARC spec confidence that it wouldn’t break things, and made it much more deployable than previous approaches to negative assertion.
On Monday, how all that optimistic reasoning went to hell, what it broke and how we’re trying to fix it.
Tools!
I just added a DMARC validation tool over on tools.wordtothewise.com.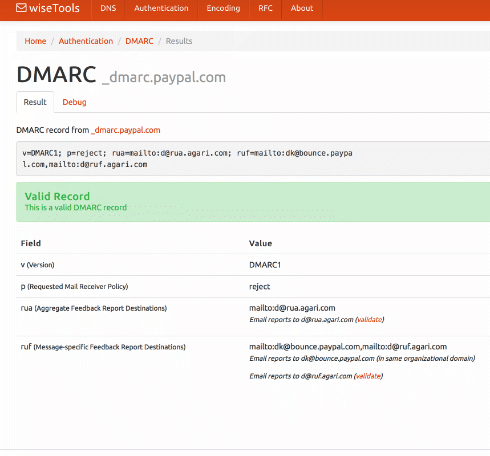
You can give it a domain – such as ebay.com – and it will fetch the DMARC record, then explain and validate it. Or you can paste the DMARC record you’re planning to publish into it, to validate it before you go live.
If you’ve not seen our tools page before, take a look. As well as DMARC we have a DKIM validator, SPF expander and optimizer, general DNS lookup tools, a bunch of RFCs covering all sorts of protocols, and base64 and quoted-printable decoders.
There’s also a widget that lets you add those little unicode pictures to your subject lines, whether you need a snowman ⛄, a forest ????, or a pig getting closer ???.
The results pages all have easily copyable URLs so they’re pretty good for sharing with co-workers or customers if you need that sort of thing.
(And if you need a cidr calculator, whois, or easy access to abuse.net & Microsoft SNDS check out Al’s xnnd.com.)
Fun with opinions
Over the last few weeks I’ve seen a couple people get on mailing lists and make pronouncements about email. It’s great to have opinions and it’s great to share them. But they’re always a little bit right… and a little bit wrong.
Beware the oversimplification

Setting up a DMARC record is the easy bit. Anyone can publish a record in DNS that will trigger reports to them. The challenge is what to do with those reports and now to manage them.
DMARC is a complex protocol. It builds on two other protocols, each with their own nuances and implementation issues. I’ve written in the past about what DMARC is, what you need to know to decide if you’re ready for DMARC and walking through whether or not you should publish DMARC. I’ve done talks where it’s taken me 20 minutes and dozens of slides to set up the context for explaining DMARC. Even experienced email folks can have moments where we get confused by some of the nuances.
DMARC is not a passive protocol. DMARC is an active protocol. Even with a p=none record, there is ongoing monitoring and work. Why consume reports if you’re not going to monitor them? The reports are there so that senders can monitor their authentication. If you’re not monitoring, then why waste cycles and bandwidth to receive them? Do you even know if your mail aligns? Can your mail server handle emails with attachments larger than 10MB? Does your mail server block .zip files? All of these things can cause your mail to be rejected and you won’t receive reports.
Postmark has a great post on DMARC and even has some examples of reports.
I know, I know, there’s a lot of fear mongering about how any company not publishing DMARC isn’t going to get to the inbox. We’re not there, yet. We likely won’t be there in the next few years. We may never get there. In any case, it’s much better to actually think about what you’re going to do with DMARC Plus, ISPs are already checking for DMARC style alignment even in the absence of a DMARC record. You don’t have to publish DMARC for this to happen, it already does.
I’ve said it before: publishing a DMARC record is a good idea. But every company needs to take minimal steps to figure out if publishing DMARC, even just to receive aggregate reports, is the right thing for them. It’s not right for every company or domain at the moment.
More on ARC
ARC – Authenticated Received Chain – is a way for email forwarders to mitigate the problems caused by users sending mail from domains with DMARC p=reject.
It allows a forwarder to record the DKIM authentication as they receive a mail, then “tunnel” that authentication on to the final recipient. If the final recipient trusts the forwarder, then they can also trust the tunneled DKIM authentication, and allow the mail to be delivered despite the DMARC p=reject published by the sending domain.
The specification and interoperability testing are progressing nicely and it’s definitely going to be useful for discussion list operators and vanity forwarders soon. It’s not something that’s as likely to help ESPs targeting small organizations and individuals, so all y’all shouldn’t be holding your breath for that.
There’s a more information about it at arc-spec.org and they’ve just published a great presentation with a technical overview of how it works:
Ask Laura: Can you help me understand no auth / no entry?

Dear Laura,
I’m a little confused by the term “no auth / no entry”. Gmail and other major receivers seem to be moving towards requiring authentication before they’ll even consider delivery.
Does this just mean SPF and DKIM, or does this mean the much more stringent DMARC, as well?
Thanks,
No Shirt, No Shoes, No What Now?
DMARC p=reject
Mail.ru is switching to p=reject.
This means that you should special-case mail.ru wherever …
Actually, no. Time to change that script.
If you operate an ESP or develop mailing list software you should be checking whether the email address that is being used in the From: address of email you’re sending is in a domain that’s publishing p=reject (is a “rejective” email address) automatically. And you should probably do that in real time, whenever you need that piece of information, relying on DNS caching to reduce the network latency.
If you find you’re about to send an email From a rejective email address, you probably shouldn’t send it. Depending on how the recipients’ ISPs handle it, it might be discarded put in the bulk folder or rejected – potentially leading to recipients being unsubscribed.
If you’re writing mailing list software, ideally you should provide your users with several options for handling submissions from rejective email addresses, perhaps some from this list:
More Yahoo domains get DMARC'd
Yahoo is turning on p=reject for 62 of their international domains on March 28, 2016. These domains include:
y7mail.com
yahoo.at
yahoo.be
yahoo.bg
yahoo.cl
yahoo.co.hu
yahoo.co.id
yahoo.co.il
yahoo.co.kr
yahoo.co.th
yahoo.co.za
yahoo.com.co
yahoo.com.hr
yahoo.com.my
yahoo.com.pe
yahoo.com.ph
yahoo.com.sg
yahoo.com.tr
yahoo.com.tw
yahoo.com.ua
yahoo.com.ve
yahoo.com.vn
yahoo.cz
yahoo.dk
yahoo.ee
yahoo.fi
yahoo.hr
yahoo.hu
yahoo.ie
yahoo.lt
yahoo.lv
yahoo.nl
yahoo.no
yahoo.pl
yahoo.pt
yahoo.rs
yahoo.se
yahoo.si
yahoo.sk
yahoogroups.co.kr
yahoogroups.com.cn
yahoogroups.com.sg
yahoogroups.com.tw
yahoogrupper.dk
yahoogruppi.it
yahooxtra.co.nz
yahoo.ca
yahoo.co.in
yahoo.co.nz
yahoo.co.uk
yahoo.com.ar
yahoo.com.au
yahoo.com.br
yahoo.com.hk
yahoo.com.mx
yahoo.de
yahoo.es
yahoo.fr
yahoo.gr
yahoo.in
yahoo.it
yahoo.ro
These may cause some delivery issues with international Yahoo domains during the transition period. Anyone using these domains in mail not sent through the Yahoo interface is likely to experience increased bounces at ISPs who are respecting the p=reject request in the DMARC record.
February 2016: The Month in Email
Happy March! Here’s a look back at our last month of email adventures. It was a busy few weeks for us with the M3AAWG meeting in San Francisco. We saw lots of old friends and met many new people — all in all, a success, despite the M3AAWG plague we both contracted. Hot topics at the conference included DMARC, of course, and I took the opportunity to write up a guide to help you determine if you should publish a DMARC policy.
It was a busy few weeks for us with the M3AAWG meeting in San Francisco. We saw lots of old friends and met many new people — all in all, a success, despite the M3AAWG plague we both contracted. Hot topics at the conference included DMARC, of course, and I took the opportunity to write up a guide to help you determine if you should publish a DMARC policy.
On the subject of advice and guidance, Ask Laura continues to be a popular column — we’ve had lots of interesting questions, and are always looking for more general questions about email delivery. We can’t tackle specifics about your program in this column (get in touch if we can help you with that directly) but we can help with questions like “Will our ESP kick us off for mailing purchasers?” or “Help! I’m confused about authentication.”
Continuing on the authentication front, I noted that Gmail is starting to roll out some UI to indicate authentication status to users. It will be interesting to see if that starts to affect user (or sender) behavior in any way. In other interesting industry news, Microsoft has implemented an Office 365 IP Delisting page. I also wrote a followup post to my 2015 overview of the state of ESPs and purchased lists — it’s worth checking out if this is something your business considers.
I wrote a post about security and backdoors, prompted by both the FBI/Apple controversy and by Kim Zetter’s talk at M3AAWG about Stuxnet. These questions about control and access will only get more complicated as we produce, consume, store, and share more data across more devices.
Speaking of predictions, I also noted my contribution to a great whitepaper from Litmus that explores the state of Email Marketing in 2020.
As always, we looked at some best practices this month. I wrote up some of my thoughts about data hygiene following Mailchimp’s blog post about the value of inactive subscribers. As always, there isn’t one right answer, but there’s a lot of good food for thought. And more food for thought: how best practices are a lot like public health recommendations. As with everything, it comes down to knowing your audience(s) and looking at the relationship(s), which, as you know, is a favorite subject around here.
Should you publish DMARC?
 I’ve been hearing a lot lately about DMARC. Being at M3AAWG has increased that. Last night we were at dinner and heard from the next table “And they’re not even publishing DMARC!!!!”
I’ve been hearing a lot lately about DMARC. Being at M3AAWG has increased that. Last night we were at dinner and heard from the next table “And they’re not even publishing DMARC!!!!”
I know DMARC is the future. I know folks are going to have to start publishing DMARC records. I also know that the protocol is the future. I am also not sure that most companies are ready for DMARC.
So lets take a step back and talk about DMARC, what it is and why I’m still a little hesitant to jump on the PUBLISH DMARC NOW!! bandwagon.
Things you need to read
The email solicitation that made me vow to never work with this company again. When sending unsolicited email, you never know how the recipient is going to respond. Writing a public blog post calling you out can happen.
The 2016 Sparkies. Sparkpost is looking for nominations for their email marketing awards. Win a trip to Insight 2016!
5 CAN SPAM myths. Send Grid’s General Counsel speaks about CAN SPAM myths. Personally, asking for an email to unsubscribe is annoying. I never know if the unsubscribe request worked or not. Give me a link any day.
The most misunderstood statistic in email marketing. A good discussion of why raw complaint rates isn’t the metric the ISPs use, and how it can mislead folks about their email program.
Office 365 is expanding it’s DKIM signing. Terry Zink discusses the upcoming changes to how Office365 handles DKIM signatures. This is exactly the kind of changes I was talking about in my 2016 predictions post – background changes that are going to affect how we authenticate email. He even specifically calls out whether or not a particular signature is DMARC aligned or not.
What to expect in 2016
 I don’t always do predictions posts, even though they’re popular. Most years I skip them because I don’t see major changes in the email space. And, I’m not the type to just write a prediction post just to post a prediction.
I don’t always do predictions posts, even though they’re popular. Most years I skip them because I don’t see major changes in the email space. And, I’m not the type to just write a prediction post just to post a prediction.
This year, though, I do see changes for everyone in the email space. Most of them center on finally having to deal with the technical debt that’s been accumulating over the past few years. I see ISPs and ESPs spending a lot of development effort to cope with the ongoing evolution authentication requirements.
When people started seriously looking at how to authenticate email, the first goal was getting organizations to implement the protocols. This was a practical concession; in order for a new protocol to be used it needs to be widely implemented. Phase one of authenticating email was simply about publishing protocols and getting organizations to use them.
During phase one, the organization that authenticated a mail hasn’t been important. In fact, the SPF spec almost guarantees that the ESP domain is the authenticated domain. In DKIM, the spec says any domain could sign as long as they could publish a public key in that domain’s domainkeys record.
ESPs took full advantage of this and lowered their own development overhead by taking most of the authentication responsibility on themselves. Their domains were in the 5321.from and they published the SPF records. Domains they control were in the d= and they generated and published the DKIM keys. Mail was authenticated without ESP customers having to do much.
We’ve hit the end of phase one. Most of the major players in the email space are authenticating outbound email. Many of the major players are checking authentication on the inbound. Phase one was a success.
We’re now entering phase two, and that changes thing. In phase two, SPF and DKIM are used as the foundation for user visible authentication. Neither SPF nor DKIM were designed to be user visible protocols. To understand what they’re authenticating you have to understand SMTP and email. Even now there are days when I begin talking about one of them and have to take a step back and think hard about what is being authenticated. And I use these things every day!
DMARC is the first of these end user visible protocols built on SPF and DKIM. It uses the established and widespread authentication to validate the user visible from address. This authentication requires that the d= value or the 5321.from address belong belong to the same domain in the visible from address. While you can pick whether the alignment between the visible from and the authentication is “strict” or “relaxed” you have no choice about the alignment.
Prior to DMARC no one really paid much attention to the domain doing the authentication. Authentication was a yes or a no question. If the answer was yes, then receivers could use the authenticated domain to build a reputation. But they weren’t really checking much in the way of who was doing the authentication.
In the push to deploy authentication, ESPs assumed the responsibility for authentication deployed ESPs took the responsibility and did most of the work. For many or most customers, authentication was as simple as clicking a checkbox during deployment. Some ESPs do currently let customers authenticate the mail themselves, but there’s enough overhead in getting that deployed that they often charged extra to cover the costs.
DMARC is rapidly becoming an expectation or even a full on requirement for inbox delivery. In order to authenticate with DMARC, the authenticating domain must be in the same domain space as the visible from. If senders want to use their own domain in the visible from, DNS records have to be present in that domain space. Whether it’s a SPF TXT record or a domainkeys record the email sender customer needs to publish the correct information in DNS. Even now, if you try to authenticate with DKIM through google apps, they require you to publish DNS records.
ESPs aren’t in a situation where they can effectively manage authentication alignment for all their customers. Hosting companies are in even worse shape when it comes to letting customers authenticate email. Developers are facing the fact they need to go back and rework their authentication code. Businesses are facing the fact they need to change their processes so customers can authenticate with DMARC.
It’s not just the infrastructure providers that are facing challenges with authentication. Senders are going to discover they can no longer hand authentication off to their ESPs and not worry about it. They’re going to have to get DNS records published by their own staff.
Getting DNS updates through some big companies is sometimes more difficult than it should be. I had one client a few years ago where getting rDNS changed to something non-generic took over a month. From an IT standpoint, changing DNS should require approvals and proper channels. Marketers may find this new process challenging.
And, if organizations want to publish reject policies for their domains, then they will have to publish records for every outside provider they use. Some of those providers can’t support DMARC alignment right now.
In 2016 a lot of companies will discover their current infrastructure can’t cope with modern authentication requirements. A lot of effort, both in terms of product development and software development, will need to be spent to meet current needs. This means a lot of user visible features will be displaced while the technical debt is paid.
These changes will improve the security and safety of email for everyone. It won’t be very user visible, which will give the impression this was a slow year for email development. Don’t let that fool you, this will be a pivotal year in email.
December 2015: The month in email
 Happy 2016! We enjoyed a bit of a break over the holidays and hope you did too. Here’s our December wrap up – look for a year-end post later this week, as well as our predictions for the year ahead. I got a bit of a head start on those predictions in my post at the beginning of December on email security and other important issues that I think will dominate the email landscape in 2016.
Happy 2016! We enjoyed a bit of a break over the holidays and hope you did too. Here’s our December wrap up – look for a year-end post later this week, as well as our predictions for the year ahead. I got a bit of a head start on those predictions in my post at the beginning of December on email security and other important issues that I think will dominate the email landscape in 2016.
DMARC will continue to be a big story in 2016, and we’re starting to see more emphasis on DMARC alignment as a significant component of delivery decisions. I wrote a bit more on delivery decisions and delivery improvement here.
December in the world of email is all about the holidays, and this year was no exception. We saw the usual mix of retailers creating thoughtful experiences (a nice unsubscribe workflow) and demonstrating not-so-great practices (purchased list fails). We took a deeper look at the impacts and hidden costs of list purchasing – as much as companies want to expand their reach, purchased lists rarely offer real ROI. And on the unsubscribe front, if you missed our discussion and update on unroll.me unsubs, you may want to take a look.
Steve wrote a detailed post looking at what happens when you click on a link, and how you can investigate the path of a clickthrough in a message, which is useful when you’re trying to prevent phishing, fraud, and other spam. In other malicious email news, the CRTC served its first ever warrant as part of an international botnet takedown.
In other industry news, some new information for both ESPs and recipients interested in feedback loops and a somewhat humorous look at the hot-button issues that divide our ranks in the world of email marketing. Please share any we may have missed, or any other topics you’d like us to address.
Are you ready for DMARC?
 The next step in email authentication is DMARC. I wrote a Brief DMARC primer a few years ago to help clear up some of the questions about DMARC and alignment. But I didn’t talk much about where DMARC was going. Part of the reason was I didn’t know where things were going and too much was unclear to even speculate.
The next step in email authentication is DMARC. I wrote a Brief DMARC primer a few years ago to help clear up some of the questions about DMARC and alignment. But I didn’t talk much about where DMARC was going. Part of the reason was I didn’t know where things were going and too much was unclear to even speculate.
We’re almost 2 years down the line from the security issues that prompted Yahoo to turn on p=reject in their DMARC record. This broke a lot of common uses of email. A lot of the damage created by this has been mitigated and efforts to fix it continue. There’s even an IETF draft looking at ways to transfer authentication through mailing lists and third parties.
For 2016, DMARC alignment is going to be a major factor in deliverability for bulk email, even in the absence of a published DMARC record.
A brief history of TXT Records

When the Domain Name System was designed thirty years ago the concept behind it was pretty simple. It’s mostly just a distributed database that lets you map hostname / query-type pairs to values.
If you want to know the IP address of cnn.com, you look up {cnn.com, A} and get back a couple of IP addresses. If you want to know where to send mail for aol.com users, you look up {aol.com, MX} and you get a set of four hostname / preference pairs back. If you want to know the hostname for the IP address 206.190.36.45 you look up {45.36.190.206.in-addr.arpa, PTR} and get a hostname back.
There’s a well-defined meaning to each of those query types – A is for IP addresses, MX is for mailservers, PTR is for hostnames – and that was always the intent for how DNS should work.
When DNS was first standardized, though, there was one query type that didn’t really have any semantic meaning:
DMARC=BestGuessPass
Looking at the headers within the mail received with my Office365 domain I see dmarc=bestguesspass. BestGuessPass? That’s a new.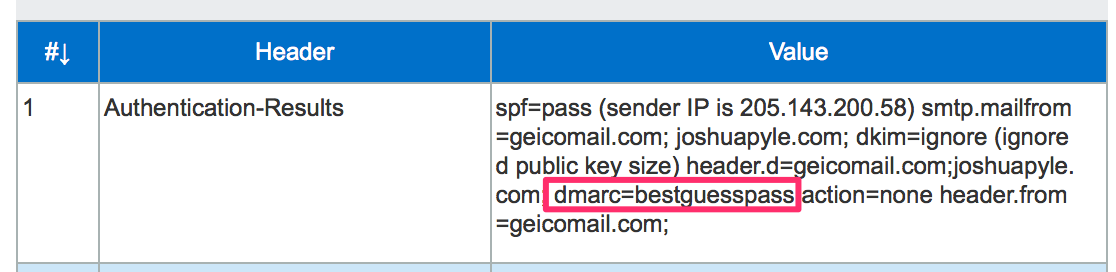
A few days after seeing dmarc=bestguesspass, Terry Zink at Microsoft posted an explanation. Exchange Online Protection, the filtering system for Office365, is analyzing the authentication of incoming emails and if the domain is not publishing a DMARC record, EOP attempts to determine what the results would be if they did. If an email is received that is not authenticated with either SPF or DKIM, the dmarc= results show none just as it always had. DMARC=BestGuessPass will appear if the message is authenticated and the matching authenticated domain does not have a DMARC record.
Having this information is helpful to see what the results would be before setting up a DMARC record. If you are seeing dmarc=bestguesspass when your mail is sent to an Office365 address and you are considering DMARC, the next step would be to publish a p=none DMARC policy and begin to document where your mail is being sent from. P=none will not have an impact on your delivery and asks the receiving mail server to take no action if a DMARC check fails. Once you have setup SPF and DKIM for your mail, p=none policy gives you the ability to begin receiving failure reports from receiving mail servers when unauthenticated mail is sent from your domain.
Authentication and Repudiation
Email Authentication lets you demonstrate that you sent a particular email.
Email Repudiation is a claim that you didn’t send a particular email.
SPF is only for email authentication1
DKIM is only for email authentication
DMARC is only for email repudiation
1 SPF was originally intended to provide repudiation, but it didn’t work reliably enough to be useful. Nobody uses it for that now.
Ransomware email protected by DMARC
Virus bulletin has an interesting post about DMARC and how some criminals are protecting their emails with DMARC.
Read MoreSalesforce SPF and now DKIM support
Salesforce has published a SPF record for sending emails from Salesforce for years and with the Spring ’15 release, they will provide the option to sign with DKIM.
The SPF record is straight forward, include:_spf.salesforce.com which includes _spf.google.com, _spfblock.salesforce.com, several IP address blocks, mx, and ends with a SoftFail ~all.
Salesforce Knowledge Article Number: 000006347 goes in-depth with information regarding their SPF Record.
Email Authentication in a nutshell
 There are 3 types of authentication currently in use for email.
There are 3 types of authentication currently in use for email.
January 2015 – The Month in Email
It’s February already! January went fast, right? At WttW, we are gearing up for MAAWG SF later this month — will we see you there?
We started the year with a set of predictions about email. Mostly we think email will continue to be great at some things and not-so-great at other things, and we’ll keep fighting the good fight to make it better.
As always, I’m interested in filters and how spammers continue to work around them to reach the inbox. I also wrote about how the language of an email impacts delivery, and wrote an expanded response to a comment suggesting email filters should be illegal. You can guess where I stand on that (and if you can’t, perhaps you might read more about how email is an inherently malicious traffic stream…)
I also took a moment to point out a trend I’m really enjoying, which is the rise of content marketing (a.k.a. giving customers useful and interesting information they can’t find elsewhere). As I said in the post, I’ll be curious to see how ROI plays out with this strategy.
We also talked about some of the less exciting content we see in email, notably the infamous Murkowski Statement, by which a spammer declares “Nope! Nothing to see over here!”
Steve also pointed out some content shenanigans in the form of hidden preview text, with some additional clarification from the original marketer in the comments.
In industry news, the big story was that Microsoft has partially implemented DMARC for Office365, and was the first to make a public statement about the specific ways they’ve chosen to implement. In my post, I did a walkthrough of a message to illustrate a bit about how this works, which might be useful if you’re trying to wrap your head around DMARC implementations.
We also talked about consolidation in the ESP space, and got a number of comments from readers about who they think might be next. Shortly thereafter, Listcast was acquired by MailerMailer.
Josh noted a few major shutdowns: Yahoo China email services and the AHBL list. The latter explores the challenges inherent in decommissioning a blacklist, and there’s a good discussion in the comments, so you might check it out if you missed that earlier this month.
Josh also pointed to the Salesforce State of Marketing report, which is always a useful set of metrics about how marketers are using email and other channels. It’s definitely worth a read.
Office365 checking DMARC on the inbound
According to a recent blog post, Office365 is starting to evaluate incoming messages for DMARC. I talked a little bit about DMARC in April when Yahoo started publishing a p=reject message.
Read MoreEmail predictions for 2015
Welcome to a whole new year. It seems the changing of the year brings out people predicting what they think will happen in the coming year. It’s something I’ve indulged in a couple times over my years of blogging, but email is a generally stable technology and it’s kind of boring to predict a new interface or a minor tweak to filters. Of course, many bloggers will go way out on a limb and predict the death of email, but I think that’s been way over done.
Even major technical advancements, like authentication protocols and the rise of IPv6, are not usually sudden. They’re discussed and refined through the IETF process. While some of these changes may seem “all of a sudden” to some end users, they’re usually the result of years of work from dedicated volunteers. The internet really doesn’t do flag days.
One major change in 2014, that had significant implications for email as a whole, was a free mail provider abruptly publishing a DMARC p=reject policy. This caused a lot of issues for some small business senders and for many individual users. Mailing list maintainers are still dealing with some of the fallout, and there are ongoing discussions about how best to mitigate the problems DMARC causes non-commercial email.
Still, DMARC as a protocol has been in development for a few years. A number of large brands and commercial organizations were publishing p=reject policies. The big mail providers were implementing DMARC checking, and rejection, on their inbound mail. In fact, this rollout is one of the reasons that the publishing of p=reject was a problem. With the flip of a switch, mail that was once deliverable became undeliverable.
Looking back through any of the 2014 predictions, I don’t think anyone predicted that two major mailbox providers would implement p=reject policies, causing widespread delivery failures across the Internet. I certainly wouldn’t have predicted it, all of my discussions with people about DMARC centered around business using DMARC to protect their brand. No one mentioned ISPs using it to force their customers away from 3rd party services and discussion lists.
I think the only constant in the world of email is change, and most of the time that change isn’t that massive or sudden, 2014 and the DMARC upheaval notwithstanding.
But, still, I have some thoughts on what might happen in the coming year. Mostly more of the same as we’ve seen over the last few years. But there are a couple areas I think we’ll see some progress made.
Spam, Phish or Malware?
Some mornings I check mail from my phone. This showed up this morning.
My first thought was “oh, no, Pizza Hut is spamming, wonder who sold them my address.”
Then I remembered that iOS is horrible and won’t show you anything other than the Friendly From and maybe it was some weird phishing scheme.
When I got to my real mail client I checked headers, and sure enough, it wasn’t really from Pizza Hut. I’m guessing actually malware, but I don’t have a forensics machine to click the link and I’m not doing it on anything I can’t wipe (and have isolated from the rest of my network).
The frustrating thing for me is that this is an authenticated email. It not from Pizza Hut, the address belongs to some company in France. Apparently, that company has had their systems cracked and malware sent through them. Fully authenticated malware, pretending to be Pizza Hut, and passing authentication on various devices.
Pizza Hut isn’t currently publishing a DMARC record, but in this case, a DMARC record for Pizza Hut wouldn’t matter. None of the email addresses in the headers point to Pizza Hut.
I spent last week listening to a lot of people discussing DMARC and authentication and protecting people from scams and headers. But those all the protocols in the world won’t protect against this kind of thing. Phishing and malware can’t be fixed by technology alone. Even if every domain on the planet published a p=reject policy, mail like this would still get through.
September 2014: The Month in Email
September was another busy month for us, but Steve stepped up and wrote a number of really interesting posts on email history, cryptography, and current technical issues in the email landscape.
We started the month with a look at the various RFCs that served as the technical specifications for developing message transfer protocols in the 1970s. It’s really fascinating to look at the evolution of these tools we use every day 40 years later. We followed up with a second post on the origins of network email, which is a great primer (or refresher) on the early days of email.
Steve’s four-part series on cryptography and email started with an in-depth look at how the industry is evolving with respect to encryption and privacy issues. He then introduced us to Alice and Bob (or reintroduced those of us who have been following the adventures of the first couple of cryptography), and described symmetric-key and public-key encryption. His next post described message signing, and how DKIM is used to manage this. He finished up the series with a post on PGP keys.
In industry news: Spamcop is shutting down its email service. There shouldn’t be any major impact on senders, but the post has some specific notes on DMARC implications. We also noted an interesting mail routing suggestion on Twitter, and wrote a post on using Mail.app for this.
In other DMARC news, we wrote about DMARC and report size limits, which might be useful information, depending on your configuration. We also launched a new DMARC tool to help senders understand who is publishing DMARC. Let us know what you think and if you’re finding it useful.
We couldn’t let a month go by without mentioning filters. We looked at a sector we don’t usually discuss, corporate filtering, and went in-depth on a much-misunderstood topic, content filtering.
Finally, Laura offered a webinar on a favorite topic, deliverability, in conjunction with the AMA and Message Systems. If you missed it, you can watch the recorded version here, or just take a peek at some of the reaction via Twitter.
Spamcop mail changes
Spamcop is shutting down it’s email service. While anyone could report spam using Spamcop, the system also provided users email addresses behind the Spamcop filters. This shut down should have no major impact on senders. Email addresses in use will still be accepting email, but that mail will simply be forwarded to another address, instead of users being able to access it through POP or IMAP.
The one problem some senders may have is IF they are solely authenticating through SPF and they are publishing a p=reject DMARC statement. This may result in some of the mail being rejected at the forwarding mail server, like AOL, Yahoo and other services respecting DMARC policy statements.
User forwarded mail will be coming from 68.232.142.20 (esa1.spamcop.iphmx.com) and 68.232.142.151 (esa2.spamcop.iphmx.com). If you don’t want to apply DMARC policy to known forwarded mail, those are the IPs to special case.
DMARC and report size limits
I just saw an interesting observation on the dmarc-discuss mailing list. Apparently some of the larger providers who are implementing DMARC for inbound email may not be handling some of the grubbier corners of the spec perfectly. That’s not surprising at all – early adopters tend to deploy code that implements early versions of the draft specification – but I can see this particular issue tripping up people who are beginning to deploy DMARC for their outbound mail.
DMARC includes the feature of requesting feedback reports about authentication failures – you just include the email address you want them sent to as a mailto: URI in the rua= and ruf= fields:
Who's publishing DMARC?
DMARC is a way for a domain owner to say “If you see this domain in a From: header and it’s not been sent straight from us, please don’t deliver the mail”. If a domain is only used for bulk and transactional mail, it can mitigate a subset of phishing attacks without causing too many problems for legitimate email.
In other cases, it can cause significant problems. Some of those problems impact discussion lists, but others cause problems for ESPs servicing small companies and individuals. ESP customers use their email addresses in the From: field; if they’re a small customer using the email address provided by their ISP, and that ISP publishes a DMARC record with p=reject, a large chunk of the mail they’re sending will bounce. When that happens recipients will stop getting their email, they’ll be removed from the mailing list due to bounces, and there’s some risk of blocks being raised against the sending IP address.
Because of that, it’s good to be able to see what consumer ISPs are doing with DMARC.
I’ve created a tool at dmarc.wordtothewise.com that regularly checks a list of large consumer ISPs and webmail providers and sees what DMARC records they’re publishing.
There are two main variants of DMARC records.
One is policy “reject” – meaning that mail that isn’t authenticated (or for which authentication has been broken in transit) will likely be rejected.
The other is policy “none” – meaning that the ISP publishing the record doesn’t want recipients to change their delivery decisions, but are asking for feedback about their mailstream, and how much of it fails authentication. That can mean that the ISP is evaluating whether or not to publish p=REJECT, or is in the process of deploying p=REJECT. Or it can just mean that they’re using DMARC to monitor where mail using their domain in the From: address is being sent from. There’s no way to tell which is the case unless they’ve made an announcement about their plans.
Hopefully this will be a useful tool to monitor DMARC deployment by consumer ISPs, and to help diagnose delivery problems that may be caused by DMARC.
June 2014: The month in email
Each month, we like to focus on a core email feature or function and present an overview for people looking to learn more. This month, we addressed authentication with SPF.
We also talked about feedback mechanisms, and the importance for senders to participate in FBL processes.
In our ongoing discussions about spam filters, we took a look at the state of our own inboxes and lamented the challenge spam we get from Spamarrest. We also pointed out a post from Cloudmark where they reiterate much of what we’ve been saying about filters: there’s no secret sauce, just a continuing series of efforts to make sure recipients get only the mail they want and expect to receive. We also looked at a grey area in the realm of wanted and expected mail: role accounts (such as “marketing@companyname.com”) and how ESPs handle them.
As always, getting into the Gmail inbox is a big priority for our clients and other senders. We talked a bit about this here, and a bit more about the ever-changing world of filters here.
On the subject of list management, we wrote about the state of affiliate mailers and the heightened delivery challenges they face getting in the inbox. We got our usual quota of spam, and a call from a marketer who had purchased our names on a list. You can imagine how effective that was for them.
And in a not-at-all-surprising development, spammers have started to employ DMARC workarounds. We highlighted some of the Yahoo-specific issues in a post that raises more questions.
We also saw some things we quite liked in June. In the Best Practices Hall of Fame, we gave props to this privacy policy change notification and to our bank’s ATM receipts.
We also reviewed some interesting new and updated technology in the commercial MTA space, and were happy to share those findings.
Spammers react to Y! DMARC policy
It’s probably only a surprise to people who think DMARC is the silver bullet to fixing email problems, but the spammers who were so abusing yahoo.com have moved on… to ymail.com.
In the rush to deploy their DMARC policy, apparently Yahoo forgot they have hundreds of other domains. Domains that are currently not publishing a DMARC policy. Spammers are now using those domains as the 5322.from address in their emails. The mail isn’t coming through any yahoo.com domain, but came through an IP belonging to Sprint PCS.
This is just one example of how spammers have reacted to the brave new world of p=reject policies by mailbox providers. If only the rest of us could react as quickly and as transparently to the problems imposed by these policy declarations. But changing software to cope with the changes in a way that keeps email useful for end users is a challenge. What is the right way to change mailing lists to compensate for these policy declarations? How can we keep bulk email useful for small groups that aren’t necessarily associated with a “brand”?
The conversation surrounding how we minimize the damage to the ecosystem that p=reject policy imposed hasn’t really happened. I think it is a shame and a failure that people can’t even discuss the implications of this policy. Even now that people have done the firefighting to deal with the immediate problems there still doesn’t seem to be the desire to discuss the longer effect of these changes. Just saying “these are challenges” in certain spaces gets the response “just deal with it.” Well, yes, we are trying to deal with it.
I contend that in order to “just deal with it”, we have to define “IT.” We can’t solve a problem if we can’t define the problem we’re trying to solve. Sadly, it seems legitimate mailers are stuck coping with the fallout, while spammers have moved on and are totally unaffected.
How is this really a win?
April: The month in email
April was a big month of changes in the email world, and here at Word to the Wise as we launched our new site, blog and logo.
DMARC
The big story this month has been DMARC, which started with a policy change Yahoo made on April 4 updating their DMARC policy from “report” to “reject”. We began our coverage with a brief DMARC primer to explain the basics around these policy statements and why senders are moving in this direction. We shared some example bounces due to Yahoo’s p=reject, and talked about how to fix discussion lists to work with the new Yahoo policy. We gathered some pointers to other articles worth reading on the Yahoo DMARC situation, and suggested some options for dealing with DMARC for mail intermediaries. Yahoo issued a statement about this on April 11th, explaining that it had been highly effective in reducing spoofed email. We also noted a great writeup on the situation from Christine at ReturnPath. On April 22nd, AOL also announced a DMARC p=reject record. We talked a bit about who might be next (Gmail?) and discussed how Comcast chose to implement DMARC policies, using p=reject not for user email, but only for the domains they use to communicate directly with customers. We expect to see more discussion and policy changes over the next few weeks, so stay tuned.
Spamtraps
We wrote three posts in our continuing discussion about spamtraps. The first was in response to a webinar from the DMA and EEC, where we talked about how different kinds of traps are used in different ways, and, again, how spamtraps are just a symptom of a larger problem. Following that, we wrote more about some ongoing debate on traps as we continued to point out that each trap represents a lost opportunity for marketers to connect with customers, which is really where we hope email program managers will focus. And finally, we tried to put some myths about typo traps to rest. As I mentioned in that last post, I feel like I’m repeating myself over and over again, but I want to make sure that people get good information about how these tools are used and misused.
Security
We started the month by saying “Security has to become a bigger priority for companies” and indeed, the internet continued to see security breaches in April, including the very serious Heartbleed vulnerability in SSL. In the email world, AOL experienced a compromise, which contributed to some of the DMARC policy changes we discussed above. In a followup post, we talked about how these breaches appear to be escalating. Again, we expect to hear more about this in the next weeks and months.
Best Practices
Ending on a positive note, we had a few posts about best practices and some email basics. We started with a pointer to Al Iverson’s post on masking whois info and why not to do it. Steve wrote up a comprehensive post with everything you ever wanted to know about the From header and RFC5322. I talked about how companies ignore opt-outs, and why they shouldn’t. I shared a really good example of a third-party email message, and also talked about message volume. And finally, we talked about how and why we warm up IP addresses.
Let us know if there’s anything you’d like to hear more about in May!
DMARC and organizations
Comcast recently published a statement on DMARC over on their postmaster page. The short version is that Comcast is publishing a DMARC record, but has no current intentions to publish a p=reject policy for Comcast user email. Comcast will be publishing a p=reject for some of their domains that they use exclusively to communicate with customers, like billing notices and security notices.
Comcast does point out that Yahoo! and AOL’s usage of p=reject is “not common usage.”
This is something a lot of people have been arguing loudly about on various mail operations lists and network lists. DMARC is about organizational identity. In fact, I was contacted about my DMARC primer and told that I didn’t mention that it’s not about domains, it’s about organizations.
The way I read the DMARC spec, it is all about organizational identity. The underlying theme being that the domain name is linked to a particular organization and everyone using email at that domain has some official relationship with that organization. I’ve always read the spec mentally replacing organization with corporate brand. This was for brands and organizations that strictly control how their domains are used, who can use those domains and how the mail is sent with those domains.
I never expected any mailbox provider or commercial ISP to publish a p=reject message as it would just break way too much of the way customers use email. And it did break a lot of legitimate and end user uses of email. Many organizations have had to scramble to update mailing list software to avoid bouncing users off the lists. Some of these upgrades have broken mailbox filters, forcing endusers to change how they manage their mailboxes.
Even organizations see challenges with a p=reject message and can have legitimate mail blocked. At M3AAWG 30 in San Francisco I was talking with some folks who have been actively deploying DMARC for organizations. From my point of view anyone who wants to publish a DMARC p=reject should spend at least 6 months monitoring DMARC failures to identify legitimate sources of email. The person I was talking to said he recommends a minimum of 12 months.
This is just an example of how difficult it is to capture all the legitimate sources of emails from a domain and effectively authenticate that mail. For a mailbox provider, I think it’s nearly impossible to capture all the legitimate uses of email and authenticate them.
It remains to be seen if the other mailbox providers imitate Yahoo! and AOL or if they push back against the use of DMARC reject policies at mailbox providers. Whatever the outcome, this is a significant shift in how email is used. And we’re all going to have to deal with the fallout of that.
AOL admits to security breach
According to Reuters AOL has admitted there was a breach of their network security that compromised 2% of their accounts. Users are being told to reset their passwords, and security questions.
AOL started investigating the attack after users started reporting an uptick in spam from aol.com addresses. This spam was using @aol.com addresses to send mail to addresses in that user’s address book.
According to the AOL mail team, they are still investigating the attack, but they do not believe financial information was compromised. Their statement reads in part:
Is gmail next?
I’m hearing hints that there are some malware or phishing links being sent out to gmail address books, “from” those gmail addresses. If that is what’s happening then it’s much the same thing as has been happening at Yahoo for a while, and AOL more recently, and that triggered their deployment of DMARC p=reject records.
It’s going to be interesting to see what happens over the next few days.
I’ve not seen any analysis of how the compromises happened at Yahoo and AOL – do they share a server-side (XSS?) security flaw, or is this a client-side compromise that affects many end users, and is just being targeted at freemail providers one at a time?
Does anyone have any technical details that go any deeper than #AOLHacked and #gmailhacked?
AOL publishes a p=reject DMARC record
Yesterday I mentioned that there were reports of a compromise at AOL. While the details are hazy, what has been reported is that people’s address books were stolen. The reports suggest lots of people are getting mail from AOL addresses that they have received mail from in the past, but that mail is coming from non AOL servers. In an apparent effort to address this, AOL announced today they have published a p=reject DMARC record.
I expect this also means that AOL is now checking and listening to DMARC records on the inbound. During the discussions of who was checking DMARC during the Yahoo discussion, AOL was not one of the ISPs respecting DMARC policy statements. I’m not surprised. As more information started coming out about this compromise, I figured that the folks attacking Yahoo had moved on to AOL and that AOL’s response would be similar to Yahoo’s.
My prediction is that the attackers will be trying to get into Outlook.com and Gmail, and when they do, those ISPs will follow suit in publishing p=reject messages. For those of you wondering what DMARC is about, you can check out my DMARC primer.
ReturnPath on DMARC+Yahoo
Over at ReturnPath Christine has an excellent non-technical summary of the DMARC+Yahoo situation, along with some solid recommendations for what actions you might take to avoid the operational problems it can cause.
Read MoreYahoo Statement on DMARC policy
Yesterday Yahoo posted a statement about their new p=reject policy. Based on this statement I don’t expect Yahoo to be rolling back the policy any time soon. It seems it was incredibly effective at stopping spoofed Yahoo mail.
Read MoreDealing with DMARC for Mail intermediaries
I’ve been getting some mail and calls from folks looking for help on resolving the issue of DMARC bouncing. Some of these calls are from ESPs, but others are from SAAS providers who have users that have signed up with yahoo.com addresses and are now dealing with mail from those users bouncing, even when mail is going back too those users.
None of the solutions are really great, but here are a couple options.
1) Prohibit users users from sending with @yahoo.com header-from addresses. This will be challenging for some companies for all sorts of reasons. I have seen a number of people suggest switching to @hotmail.com or @gmail.com addresses. This only works as long as Gmail and Hotmail/Outlook don’t start publishing p=reject policies. It’s unclear if they’re even considering this at all, but it may happen.
2) Rewrite the header-from address from @yahoo.com to something you control. One thing I’ve been suggesting to customers is set up a specific domain for rewriting, like @yahoo.ESP.com. This domain would need to forward mail back to the @yahoo.com users, which does add another layer of complexity as these addresses will become spam magnets. Thus the forwarding IP should be on a distinct and separate IP, to prevent interference with other systems. Note, too, that any users sending to these reply addresses from a domain protected by DMARC p=reject will bounce.
If you have questions or want to ask specifically about what to do in your setup, I’ve blocked out some time in my schedule next week for companies. If you want more information about this please contact me to for available times, information requirements and pricing.
Yahoo DMARC articles worth reading
There are a bunch of them and they’re all worth reading.
I have more to say about DMARC, both in terms of advice for senders and list managers affected by this, and in terms of the broader implications of this policy decision. But those articles are going to take me a little longer to write.
How widespread is the problem? Andrew Barrett publishes numbers, pulled from his employer, related to the number of senders using @yahoo.com addresses in their commercial emails. Short version: a low percentage but a lot of users and emails in raw numbers.
What can mailing list managers do? Right now the two answers seem to be stop Yahoo.com addresses from posting or fix your mailing list software. Al has posted how he patched his software to cope, and linked to a post by OnlineGroups.net about how they patched their software.
A number of people are recommending adding an Original Authentication Results header as recommended in the DMARC.org FAQ. I’m looking for more information about how that would work.
For commercial mailers, there doesn’t seem to be that much to do except to not use @yahoo.com address as your header-From address. Yes, this may affect delivery while you’re switching to the new From address, but right now your mail isn’t going to any mailbox provider that implements DMARC checking.
One other thing that commercial mailers and ESPs should be aware of. Depending on your bounce handling processes, this may cause other addresses to bounce off the list. Once the issue of the header-From address is settled, you can reactivate addresses that bounced off the list due to authentication failures since April 4.
Fixing discussion lists to work with new Yahoo policy
Al has some really good advice on how to fix discussion lists to work with the new Yahoo policy.
One thing I would add is the suggestion to actually check dmarc records before assuming policy. This will not only mean you’re not having to rewrite things that don’t need to be rewritten, but it will also mean you won’t be caught flat footed if (when?) other free mail providers start publishing p=reject.
Example bounces due to Yahoo p=reject
There are a number of different bounces that people are reporting due to Yahoo publishing a DMARC record of p=reject. I decided to put some of those bounces here so confused users could find out what they needed to do.
Comcast
A brief DMARC primer
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting and Conformance. What DMARC does is allow domain owners to publish policy statements in DNS telling receiver domains what to do with messages that do not authenticate. In addition, DMARC introduces the concept of “domain alignment.” What this means is that the authentication has to be from the same domain (or a sub-domain) as the address in the header-from: line. The idea behind DMARC is that organizational owners can use SPF and DKIM authentication to authenticate their actual domain in the header-from line. This moves authentication from a important but behind the scenes technology out to an end user visible technology.
Read MoreCNN warns about Target copy-cat phishes
Target did indeed do a blast to customers to offer one year of free credit monitoring. The problem is scammers are also on the prowl and are sending out similar emails.
Read More
Target even says it has identified and stopped at least 12 scams preying on consumers via email, Facebook and other outlets.CNN: Did you get an email from Target?
DMARC: Please Be Careful!
(Cross posted from Spam Resource.)
Every couple of days, somebody new pops up on the DMARC-Discuss mailing list to ask some question or share an observation. It’s great to see people interested and joining the conversation. Clearly, DMARC interest and adoption are growing. What’s really frustrating, though, is that for about a quarter of the new subscribers, their first mailing list message goes to the spam folder in my Gmail account. It has become sort of an intelligence test I apply to new subscribers — I’ve stopped digging those messages out of the spam folder. I’m figuring that if they can’t figure out how to implement a DMARC record, or they don’t understand that it’s not really compatible with mailing lists nor is it meant for hobbyist domains, then I think perhaps they’ve got some things they’ve got to figure out before they’re ready to join the discussion.
To that end, let me take a moment to jot down some recommendations for folks who are considering implementing DMARC.
DMARC makes it a year
Yesterday DMARC.org announced that in a year DMARC protects over 60 million mailboxes worldwide.
Read MoreNew player in the DMARC space
Over on the DMARC-Discuss list, Comcast announced they had turned on DMARC validation and companies that publish DMARC records should start receiving reports from Comcast.
Read MoreHow long is your DKIM key?
While we were at M3AAWG, Wired published an article talking about how simple it was to crack DKIM keys. I didn’t post about it at the time because it didn’t really seem like news. DKIM keys smaller than 1024 are vulnerable and not secure and the DKIM spec does not recommend using keys smaller than 1024. When I asked the DKIM-people-who-would-know they did tell me that the news was that the keys had been cracked and used in the wild to spoof email.
Fair enough.
If you are signing with DKIM, use a key 1024 or longer. Anything shorter and your risk having the key cracked and your mail fraudulently signed.
This morning M3AAWG published recommendations on keeping DKIM keys secure.
Setting up DNS for sending email
Email – and email filtering – makes a lot of use of DNS, and it’s fairly easy to miss something. Here are a few checklists to help:
Read MoreDMARC Interoperability
Facebook hosted a DMARC interoperability event earlier this week. In terms of protocol development, interoperability events are a sign that the protocol is ready for more widespread use.
Read MoreDMARC: an authentication framework
A new email industry group was announced this morning. DMARC is a group of industry participants, including large senders, large receivers and relevant intermediaries working on a framework to reduce the harm from phishing.
DMARC is working on a standard to allow senders to publish sending policies and receivers to act on those policies. Currently, senders who want receivers to not deliver unauthenticated email have to negotiate private agreements with the ISPs to make that happen. This is a way to expand the existing programs. Without a published standard, the overhead in managing individual agreements would quickly become prohibitive.
It is an anti-phishing technique built on top of current authentication processes. This is the “next step” in the process and one that most people involved in the authentication process were anticipating and planning for. I’m glad to see so many big players participating.


