Domain Reputation
Let’s Talk: Reputation
The next 3 or 4 Let’s Talk sessions are going to be all about reputation. We’ll start with a general overview of reputation and identity, then move on to specific kinds of reputation (IP, domain, URL, content), then we’ll talk about how to create, maintain and repair reputation. Still working on the outline, but I’m pretty convinced this will be at least 3 sessions.
Read MoreWhat’s a suspicious domain?
The question came up on slack and I started bullet pointing what would make a domain suspicious. Seemed like a reasonable blog post. In no particular order, some features that make a domain suspicious to spam filters.
Read MoreGoogle makes connections
One of the client projects I’m working on includes doing a lot of research on MXs, including some classification work. Part of the work involves identifying the company running the MX. Many of the times this is obvious; mail.protection.outlook.com is office365, for instance.
There are other cases where the connection between the MX and the host company is not as obvious. That’s where google comes into play. Take the domain canit.ca, it’s a MX for quite a few domains in this data set. Step one is to visit the website, but there’s no website there. Step 2 is drop the domain into google, who tells me it’s Roaring Penguin software.
In some cases, though, the domain wasn’t as obvious as the Roaring Penguin link. In those cases, Google would present me with seemingly irrelevant hosting pages. It didn’t make sense until I started digging through hosting documentation. Inevitably, whenever Google gave me results that didn’t make sense, they were right. The links were often buried in knowledge base pages telling users how to configure their setup and mentioning the domain I was searching for.
The interesting piece was that often it was the top level domain, not the support pages, that Google presented to me. I had to go find the actual pages. Based on that bit of research, it appears that Google has a comprehensive map of what domains are related to each other.
This is something we see in their handling of email as well. Gmail regularly makes connections between domains that senders don’t expect. I’ve been speaking for a while about how Gmail does this, based on observation of filtering behavior. Working through multiple searches looking at domain names was the first time I saw evidence of the connections I suspected. Gmail is able to connect seemingly disparate hostnames and relate them to one another.
For senders, it means that using different domains in an attempt to isolate different mainstreams doesn’t work. Gmail understands that domainA in acquisition mail is also the same as domainB in opt-in mail is the same as domainC in transactional mail. Companies can develop a reputation at Google which affects all email, not just a particular mail stream. This makes it harder for senders to compartmentalize their sends and requires compliance throughout the organization.
Acquisition programs do hurt all mail programs, at least at Gmail.
Back from MAAWG
Had an all too short trip to M3AAWG. It was great to see old friends and meet new folks. I have lots to talk about and a poll to get into the field once I get caught up on client work.
While I’m deep in the depths of my inbox, I thought I’d share a bit of insight into the question of new domain vs. subdomain that often comes up.
Filtering by gestalt
One of those $5.00 words I learned in the lab was gestalt. We were studying fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) and, at the time, there were no consistent measurements or numbers that would drive a diagnosis of FAS. Diagnosis was by gestalt – that is by the patient looking like someone who had FAS.
It’s a funny word to say, it’s a funny word to hear. But it’s a useful term to describe the future of spam filtering. And I think we need to get used to thinking about filtering acting on more than just the individual parts of an email.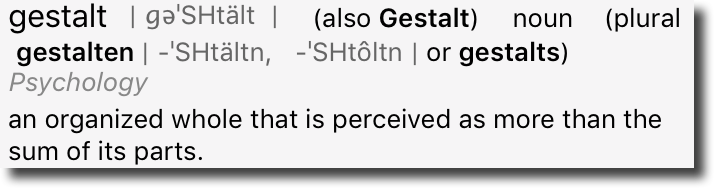
Filtering is not just IP reputation or domain reputation. It’s about the whole message. It’s mail from this IP with this authentication containing these URLs. Earlier this year, I wrote an article about Gmail filtering. The quote demonstrates the sum of the parts, but I didn’t really call it out at the time.
Domain transparency
An email I received this morning got me thinking about how your domain name is one of the main ways you identify yourself if you’re sending email.
We talk about domain reputation quite a lot – DKIM and SPF let a sender volunteer a domain name as a unique identifier for recipients to use to track reputation, DMARC allows them to tie that domain to the domain visible to the user in the From: field. And most ISPs use the domains in links in the body of the message to track reputation, either internally or through third-party reputation providers.
But there’s also a human side. We expect people and companies to be honest in how they identify themselves – and we’re suspicious when they aren’t. We’ve been trained to be wary of messages that claim to be from a company we know but which, for whatever reason, don’t look quite right. Rightly so – a lot of phishing and credential theft is based on bad people using branding and domains that look like legitimate ones.
Here are some header snippets from this morning’s (legitimate) email:
Reputation is about behavior

Reputation is calculated based on actions. Send mail people want and like and interact with and get a good reputation. Send mail people don’t want and don’t like and don’t interact with and get a bad reputation.
Reputation is not
… about who the sender is.
… about legitimacy.
… about speech.
… about message.
Reputation is
… about sender behavior.
… about recipient behavior.
… about how wanted a particular mail is forecast to be.
… based on facts.
Reputation isn’t really that complicated, but there are a lot of different beliefs about reputation that seem to make it complicated.
The reputation of a sender can be different at different receivers.
Senders sometimes target domains differently. That means one receiver may see acceptable behavior but another receiver may see a completely different behavior.
Receivers sometimes have different standards. These include standards for what bad behavior is and how it is measured. They may also have different thresholds for things like complaints and bounces.
What this means is that delivery at one receiver has no impact on delivery at another. Just because ISP A delivers a particular mail to the inbox doesn’t mean that ISP B will accept the same mail. Each receiver has their own standards and sometimes senders need to tune mail for a specific receiver. One of my clients, for instance, tunes engagement filters based on the webmail domain in the email address. Webmail domain A needs a different level of engagement than webmail domain B.
Public reputation measures are based on data feeds.
There are multiple public sources where senders can check their reputation. Most of these sources depend on data feeds from receiver partners. Sometimes they curate and maintain their own data sources, often in the form of spamtrap feeds. But these public sources are only as good as their data analysis. Sometimes, they can show a good reputation where there isn’t one, or a bad reputation where there isn’t one.
Email reputation is composed of lots of different reputations.
Email reputation determines delivery. Getting to the inbox doesn’t mean sending from an IP with a good reputation. IP reputation is combined with domain reputation and content reputation to get the email reputation. IP reputation is often treated as the only valuable reputation because of the prevalence of IP based blocking. But there are SMTP level blocks against domains as well, often for phishing or virus links. Good IP reputation is necessary but not sufficient for good email delivery.
Reputation is about what a sender does, not about who a sender is.
Just because a company is a household name doesn’t mean their practices are good enough to make it to the inbox. Email is a meritocracy. Send mail that merits the inbox and it will get to recipients. Send email that doesn’t, and suffer the repercussions.
Changes at Yahoo
Deliverability.com has a blog post from Naeem Kayani at Adknowledge about the recent Yahoo changes. They point to the reputation of the From: address as a factor. I’m not sure anyone knows what exactly Yahoo is doing, but the suggestions from Naeem are good ones.
Read More