Engagement
The Future of Deliverability
There always seems to be appetite from folks to read the tea leaves and follow up with predictions about what the future holds. I mean, how many folks in the US are obsessively refreshing polls for the last few weeks? (American’s: don’t forget to vote on Tuesday!)
Read MoreDeliveries and Opens and Clicks
I always want to say “Emails, and Opens, and Clicks… Oh My!” when I’m talking about them.
Read MoreCleaning old lists
There comes a time in many marketers’ lives where they are faced with and old, stale database and a management chain that wants to mail those addresses. Smart marketers know that delivery problems will arise if they just reactivate all those users. They also know that mailing older addresses can affect current and engaged addresses as well. Still, many executives think there is no downside to mailing old addresses.
Read MoreLet’s Talk: Engagement
I’m working on a more formal schedule for the Let’s Talk events and hope to have that out over the next few days. Meanwhile, we’re moving ahead with the next talk: Engagement!
Read MoreWhen opens hurt reputation
Podia has scraped the Word to the Wise blog and I’m currently receiving an ongoing drip campaign from them absolutely begging me to mention them in my blog post on cold emails.
Read MorePurging to prevent spamtraps
Someone recently asked when they should purge addresses to remove spamtraps. To my mind this is actually the wrong question. Purging addresses that don’t engage is rarely about spamtraps, it’s about your overall communication processes.
Read MoreForget about engagement, think inboxing
While answering a question about how to improve IP reputation at Gmail I realized that I no longer treat Gmail opens as anything about how a user is interacting with email. There are so many cases and ways that a pixel load can be triggered, without the user actually caring about the mail that it’s not a measure of the user at all.
Read MoreRaising the standard
Last week news broke that Mailchimp had disconnected a number of anti-vaccination activists from their platform and banned anti-vax content. I applaud their decision and hope other companies will follow their lead in banning harmful content from their network.
Read MoreWhat’s up with gmail?
Increasingly over the last few months I’ve been seeing questions from folks struggling with reputation at Gmail and inbox delivery. It seems like everything exploded in the beginning for 2019 and everything changed. I’ve been avoiding blaming it all on TensorFlow, but maybe the addition of the new ML engine really did fundamentally change how things were working at gmail.
Delivery is not dependent on authentication
All too often folks come to me with delivery problems and lead off with all of the things they’ve done to send mail right. They assure me they’re using SPF and DKIM and DMARC and they can’t understand why things are bad. There is this pervasive belief that if you do all the technical things right then you will reach the inbox.
Read MoreEconomics of spam
There was a discussion on Slack about the economics of email. It’s probably not a surprise that I have opinions (Who owns the inbox? Ownership of the Inbox). There was a discussion about this that was useful enough I’d share it.
Read MoreRe-adding subscribers after reputation repair
A comment came in on Engagement and Deliverability and I thought it was a good question and deserved a discussion.
Read MoreAutomated link checking getting more sophisticated
As the volume and severity of malicious email increases, filters are increasingly following links in emails. This is really nothing new. Barracuda and other filters have been inspecting links automatically for years. From what I’ve seen there does seem to be some level of risk analysis based on domain reputation. That makes sense, not only is following links computationally expensive, it can also delay mail receipt.
Read MoreNo, I won't rate you!
Brick and mortar stores have tried to use feedback as a means of driving customer engagement for a while. Anyone who’s shopped at a big chain here in the US knows what I mean. You buy a pack of gum and end up with a 2 foot long receipt. At the bottom of the receipt there is a URL and bar code. The cashier circles the bar code and cheerfully tells you to go online and tell corporate about their service.
If you go to the website, they ask you for specific specific purchase information (time, date, store number, amount, cashier) and ask a bunch of questions about the store. Then, they offer you a chance to win something (gift card, something) if you’ll provide them with your personal information. 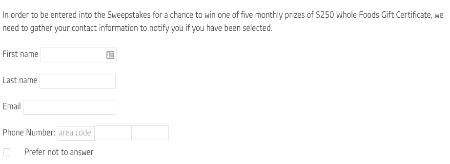
Note: This particular form does not allow you to continue at all unless you’ve filled in the information request. Even if you check “prefer not to answer” the page throws up an error message and tells you to provide a valid phone number.
More recently email marketers have jumped on the asking for feedback bandwagon. Over the last few weeks multiple companies have sent me emails asking how my visit to their website was. It… was a website? I mean I went to your website and checked my credit card bill, it told me how much I owed. Your tech support told me they couldn’t fix my problem over chat, I’d have to take my laptop in for repairs. My package arrived and if it didn’t you can be sure I would have reached out to you.
And it’s not just online services that do this. Hotels send followup surveys, which if you’re a frequent traveler turns into a full time job. Yes, I visited your hotel it’s very nice. If I’m in town and that’s where the conference I’m attending is hosted, I’ll probably be back.
I get it, the more chances you provide for people to interact with your brand the more engaged they are and the more likely they are to purchase from you. But a simple search of my mailbox shows over a dozen messages from companies over the last few weeks, all of them asking me for feedback on their services. I’d like a little less email, please. The bank, the mortgage company, the credit card company, the food delivery service I used, the clothing website, the travel website, the ride share service, the hotel… the list goes on and on.
If only a few companies did this, it wouldn’t be such a big deal. But as more and more companies adopt the triggered email followup (and the followup reminder and the final reminder and the final final reminder), recipients are going to get tired of the messages. Some of the requests don’t even have opt-outs, although the majority of the ones in my mailbox do.
I get that each company is only responsible for the mail they, in particular, are sending. But the user has a different frame of reference, and maybe it’s time to consider that using surveys and triggered emails to drive engagement may not be a long term sustainable business model. The rest of the companies out there using the same strategy are going to ruin it for everyone.
Updating the filtering model
One thing I really like about going to conferences is they’re often one of the few times I get to sit and think about the bigger email picture. Hearing other people talk about their marketing experiences, their email experiences, and their blocking experiences usually triggers big picture style thoughts.
Earlier this week I was at Activate18, hosted by Iterable. The sessions I attended were interesting and insightful. Of course, I went to the deliverability session. While listening to the presentation, I realized my previous model of email filtering needed to be updated.
Metric Monetization
As a digital channel, email provides a lot of different metrics for marketers to use. Not only can marketers measure things like open and click rates, but they can tie these numbers back to a particular recipient. This treasure trove of information leads to obsessing over making the numbers look good. For good deliverability senders want low bounce rates, low spamtrap rates, and high engagement rates.
These metrics are important because they’re some of the things that filters look at when making delivery decisions. We care about this data because the receiver ISPs care about the data. The ISPs care about this data because they are characteristics of wanted and/or opt in email.
Over the past few years a number of companies sell services selling good metrics.
July 2017: The month in email
August is here, and as usual, we’re discussing spam, permissions, bots, filters, delivery challenges, and best practices.
One of the things we see over and over again, both with marketers and with companies that send us email, is that permission is rarely binary — companies want a fair amount of wiggle room, or “implied permission” to send. There are plenty of examples of how companies try to dance around clear permissions, such as this opt form from a company we used to do business with. But there are lots of questions here: can you legitimately mail to addresses you haven’t interacted with in 5 years? 10 years? What’s the best way to re-engage, if at all?
We frequently get questions about how to address deliverability challenges, and I wrote up a post about some of the steps we take as we help our clients with this. These are short-term fixes; for long-term success, the most effective strategy is sending email that people want and expect. Engagement is always at the core of a sustainable email program.
We’ve also discussed the rise of B2B spam, and the ways in which marketing technologies contribute to the problem. B2B marketers struggle to use social and email channels appropriately to reach customers and prospects, but still need to be thoughtful about how they do it. I also wrote about some of the ways that marketing automation plugins facilitate spam and how companies should step up to address the problem. Here’s an example of what happens when the automation plugins go awry.
I wrote a few posts about domain management and the implications for security and fraud. The first was about how cousin domain names can set users up for phishing and fraud, and the second was a useful checklist for looking at your company’s domain management. We also looked at abuse across online communities, which is an increasing problem and one we’re very committed to fighting.
I also highlighted a few best practices this month: guidelines for choosing a new ESP and active buttons in the subject line for Gmail.
And finally, we celebrated the 80th birthday of the original SPAM. If you’re a regular reader of this blog, you probably already know why unwanted email is called SPAM, but just in case, here’s a refresher….
Engagement drives deliverability
Return Path released an white paper today offering the Secrets of Successful Senders. I don’t think any of my readers will be surprised that it boils down to identity, reputation, and engagement. Return Path treats these as separate things and I understand why they do. I think however, that the identity and reputation are supporting players to the overarching issue of engagement.
When I’m dealing with clients and troubleshooting deliverability problems and offering solutions, I focus on the root cause. To me the root cause is almost always a data problem. Either there’s a problem with data collection or there’s a problem with data maintenance. These problems result in mail going to people who don’t really want or care about it.
Yes, identity is important. But, realistically, anyone mailing through a decent ESP has SPF and DKIM in place, at least on some level. There may be better ways to authenticate, but the boxes are checked.
Yes, reputation is important. But here’s the thing, reputation just means that the ISP knows how users are going to react to an email. Reputation isn’t some nebulous concept made up by ISPs. It’s an actual measurement. It quantifies the history of an IP or a domain or a mail stream and says we know that this IP sends wanted mail. We know that this domain sends mail our users ignore. It’s a history. Past performance does indicate future results.
Identity says who a sender is. Reputation tells us that sender’s history of sending. Those are the two factors that enable ISPs to make delivery decisions. Mail comes in and the ISP looks at it. They use identity to determine what reputation to assign to a mail. Reputation drives delivery, whether into the inbox or the bulk folder.
5 steps for addressing deliverability issues
Following on from my reading between the lines post I want to talk a little bit about using the channels. From my perspective the right way to deal with 99% of issues is through the front door.
Last week I found myself talking to multiple folks in multiple fora (emailgeeks slack channel, mailop, IRC) about how to resolve blocking issues or questions. All too often, folks come into these spaces and start by asking “does anyone know someone at…” Fundamentally, that’s the wrong first question. Even if the answer is yes. It’s even the wrong question if a representative of the company is on the list where you’re asking for help.
If that’s the wrong question, what is the right question? Where can we start to get help with issues when we’re stuck trying to fix a delivery problem we don’t understand?
Engagement, Engagement, Engagement
I saw a headline today:
New Research from Return Path Shows Strong Correlation Between Subscriber Engagement and Spam Placement
I have to admit, my first reaction was “Uh, Yeah.” But then I realized that there are some email marketers who do not believe engagement is important for email deliverability. This is exactly the report they need to read. It lays out the factors that ISPs look at to determine if email is wanted by the users. Senders have to deal with vague metrics like opens and clicks, but the ISPs have access to user behavior. ISPs can see if mail is replied to, or forwarded or deleted without reading. They monitor if a user hits “this-is-spam” or moves the message to their junk folder. All of these things are signals about what the users want and don’t want.
Still, there are the folks who will continue to deny engagement is a factor in deliverability. Most of the folks in this group profit based on the number of emails sent. Therefore, any message about decreasing sends hurts their bottom line. These engagement deniers have set out to discredit anyone who suggests that targeting, segmentation or engagement provide for better email delivery and getting emails to the inbox.
There’s another group of deniers who may or may not believe engagement is the key to the inbox, but they don’t care. They have said they will happily suffer with lower inbox delivery if it means they can send more mail. They don’t necessarily want to discredit deliverability, but they really don’t like that deliverability can stop them from sending.
Whether or not you want to believe engagement is a critical factor in reaching your subscribers, it is. Saying it’s not doesn’t change the facts.
There are three things important in deliverability: engagement, engagement, engagement.
Are seed lists still relevant?
Those of you who have seen some of my talks have seen this model of email delivery before. The concept is that there are a host of factors that contribute to the reputation of a particular email, but that at many ISPs the email reputation is only one factor in email delivery. Recipient preferences drive whether an email ends up in the bulk folder or the inbox.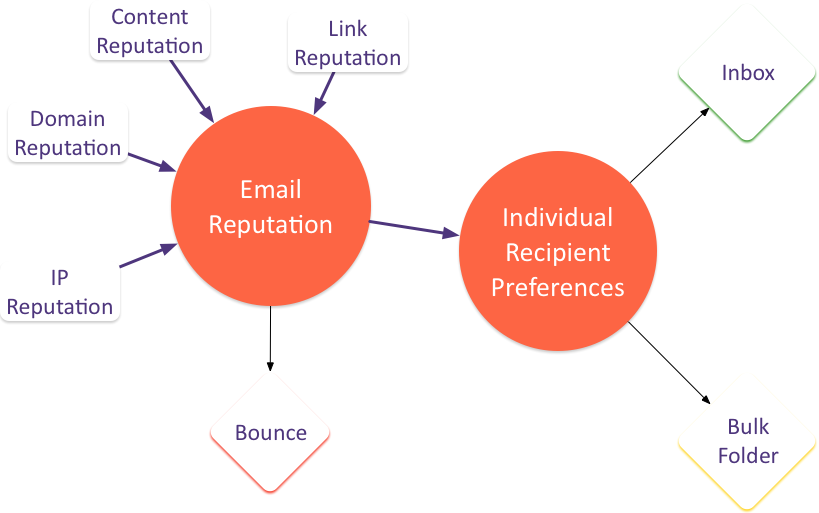
The individual recipient preferences can be explicit or implicit. Users who add a sender to their address book, or block a sender, or create a specific filter for an email are stating an explicit preference. Additionally, ISPs monitor some user behavior to determine how wanted an email is. A recipient who moves an email from the bulk folder to the inbox is stating a preference. A person who hits “this-is-spam” is stating a preference. Other actions are also measured to give a user specific reputation for a mail.
Seed accounts aren’t like normal accounts. They don’t send mail ever. They only download it. They don’t ever dig anything out of the junk folder, they never hit this is spam. They are different than a user account – and ISPs can track this.
This tells us we have to take inbox monitoring tools with a grain of salt. I believe, though, they’re still valuable tools in the deliverability arsenal. The best use of these tools is monitoring for changes. If seed lists show less than 100% inbox, but response rates are good, then it’s unlikely the seed boxes are correctly reporting delivery to actual recipients. But if seed lists show 100% inbox and then change and go down, then that’s the time to start looking harder at the overall program.
The other time seed lists are useful is when troubleshooting delivery. It’s nice to be able to see if changes are making a difference in delivery. Again, the results aren’t 100% accurate but they are the best we have right now.
Use all the channels
One of the hardest deliverability situations to address is when all mail from a certain sender is going to the bulk folder. I’ve had numerous clients come to me to address this situation over the years. Ideally, clients come to me before all their mail is going to bulk. Then we can make some tweaks and changes to their mail program, repair the reputation and then recover other addresses. We have knobs we can twist to fix things if some people are still getting messages in their inbox. We have data to measure.
When all mail is going to bulk, though, we lose access to the knobs and the data. There are zero complaints if mail is going to bulk. There are no opens or clicks, because many ISPs disable images and links in the bulk folder. Our normal “fixing reputation” tools are taken away from us.
Senders with all their mail going to bulk are faced with a profound challenge. How can they engage customers who are unengaged and who are not seeing mail at all? How can we fix deliverability when our normal tools and metrics are unavailable?
If we can get even a small percentage of recipients to go pull mail out of bulk or spam and move it to their inbox, then we’re well on our way to repairing reputation. But how can we get them to go look for the mail in the bulk folder. Recent Litmus research suggests that a significant percentage of folks regularly check their spam folder, but this isn’t always enough to repair reputation,
The question becomes how can the senders encourage recipients to go digging through their spam folder.
This is the point where I start quizzing clients on what other channels they use to communicate with their customers. I’ll run through the whole list: social media, snail mail, push notices through apps, SMS, website popups, Facebook ads. I work with them to identify users who are engaged with their brand and brainstorm ways to get those users to look for mail.
I’m always pleased to see large brands using these strategies. Just recently Blizzard used twitter to communicate with their users about email problems. They tweeted.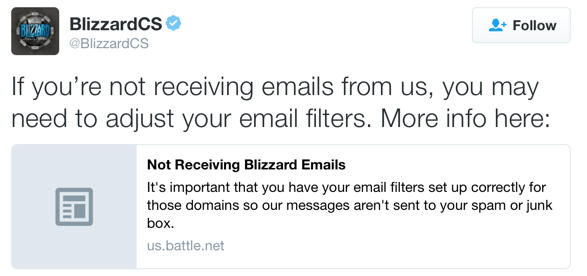
The link takes you to the Blizzard support site. Where they give specific instructions on how to whitelist mail and what mail to whitelist.
The perfect email
More and more I’m moving away from consulting on technical setup issues as the solution to delivery problems. Delivery is not about the technical perfection of a message. Spammers get the technical right all the time. No, instead, delivery is about sending messages the user wants. While looking for something on the blog I found an old post from 2011 that’s still relevant today. In fact, I’d say it’s even more relevant today than it was when I wrote it 5 years ago.
Email is a fluid and ever changing landscape of things to do and not do.
Over the years my clients have frequently asked me to look at their technical setup and make sure that how they send mail complies with best practices. Previously, this was a good way to improve delivery. Spamware was pretty sloppy and blocking for somewhat minor technical problems was a great way to block a lot of spam.
More recently filter maintainers have been able to look at more than simple technical issues. They can identify how a recipient interacts with the mail. They can look at broad patterns, including scanning the webpages an email links to.
In short, email filters are very sophisticated and really do measure “wanted” versus “unwanted” down to the individual subscriber levels.
I will happily do technology audits for clients. But getting the technology right isn’t sufficient to get good delivery. What you really need to consider is: am I sending email that the recipient wants? You can absolutely get away with sloppy technology and have great inbox delivery as long as you are actually sending mail your recipients want to receive.
The perfect email is no longer measured in how perfectly correct the technology is. The perfect email is now measured by how perfect it is for the recipient.
Who owns the inbox
One of the questions asked of my panel during Connections 16 last month was who owns the inbox.
Read MorePete and Repeat
Pete and Repeat were on a boat. Pete fell out, who was left?
I was searching the blog for some resources today and these were the first two posts that showed up on the search results. I often feel like I’m repeating myself, but sometimes I am.
Insight into Gmail filtering
Last week I posted a link to an article discussing how Gmail builds defenses to protect their users from malicious mail. One of the things I found very interesting in that article was the discussion about how Gmail deploys many changes at once, to prevent people from figuring out what the change was.
Let’s take a look at what Gmail said.
Ask Laura
An Advice Column on Email Delivery
When we work with brands and senders to improve email delivery, there are many questions that come up again and again. For 2016, we thought it might be interesting to answer some of those questions here on the blog so others can benefit from the information.
Confused about delivery in general? Trying to keep up on changing policies and terminology? Need some Email 101 basics? This is the place to ask. We can’t answer specific questions about your server configuration or look at your message structure for the column (please get in touch if you’d like our help with more technical or forensic investigations!), but we’d love to answer your questions about how email works, trends in the industry, or the joys and challenges of cohabiting with felines.
Your pal,
Laura
Dear Laura,
I’m having a hard time explaining to our marketing team why we shouldn’t send email to addresses on our lists with very low read rates, that are dormant but not bouncing, or that spend less than 2 seconds reading our mail. I’m also struggling to convince them that it’s not a good idea to dramatically increase email volume during the holidays (i.e. going from one send/day to 2-3 sends/day).
We already segment based on recency, engagement, and purchase behavior, and we also have some triggered messaging based on user behavior.
Can you help me find a way to help explain why sometimes less is more?
Thanks,
The Floodgates Are Open
Dear Floodgates,
ISPs ask two fundamental questions about email when it comes in:
- Is it safe?
- Is it wanted?
If the answer to both those questions is yes, the mail is delivered to the inbox.
Read MoreTumblr Confirming Usernames
Today I received an email from Tumblr asking to confirm I still wanted the username I have there. I’ve not really been using Tumblr, I contributed a few things to the now-defunct Box of Meat, but I don’t really post there much.
I think this kind of engagement is great. Confirming user names will do a whole lot to allow Tumblr to release some claimed but unused names back into the pool. It will also actually help their deliverability and their engagement. If people do want to keep their tumblr names, then they have to click on the message. This means more clicks and better engagement and an overall reputation boost for Tumblr mail.
March 2015: The month in email
Happy March! We started the month with some more movement around CASL enforcement from our spam-fighting friends to the north. We noted a $1.1 million fine levied against Compu-Finder for CASL violations, as well as a $48,000 fine to Plentyoffish Media for failing to provide unsubscribe links. We noted a few interesting things: the fines are not being imposed at the maximum limits, violations are not just on B2C marketing, but also on B2B senders, and finally, that it really just makes sense — both from a delivery perspective and a financial perspective — to comply with the very reasonable best practices outlined in CASL.
Read MoreThoughts on Hotmail filtering
One of the new bits of information to come out of the EEC15 deliverability discussions is how Hotmail is looking at engagement differently than other webmail providers.
Many webmail providers really do look at overall engagement with a mail when making delivery decisions. And this really impacts new subscribers the most. If there is a mailing where a lot of subscribers are engaged, then new subscribers will see the mail in their inbox. Based on what was said at the webinar earlier this week engagement has no effect at Hotmail outside of the individual user’s box.
I’ve certainly seen this with clients who’ve tried trimming subscriber lists but that doesn’t really help get mail moved from the Hotmail bulk folder to the inbox.
Instead of subscriber lists, Hotmail is really looking at bounces. They’re watching the number of nonexistent accounts senders are mailing to and they’re counting and a sender hits too many bad addresses and that is a major hit to their reputation.
All of this makes remediation at Hotmail challenging. Right now, we can remediate a bad reputation at a lot of ISPs and the filters catch up and mail starts flowing back to the inbox. Hotmail has set up a system that they say is “hard for spammers to game.” This seems to translate into hard for legitimate senders to fix their reputation.
Hotmail is, IMO, the current tough nut in terms of deliverability. Develop a bad reputation there and it’s difficult to fix it. I’m sure it’s possible, though.
Tweets from engagement and deliverability webinar
Want to see some of the tweets shared during the EEC Deliverability and Engagement webinar on March 17? Check out what was said as it happened.
Read MoreMythbusting deliverability and engagement
Yesterday I published an article talking about an engagement webinar hosted by the EEC and DMA. I made a couple predictions about what would be said.
Read MoreDelivery and engagement
Tomorrow is the webinar Mythbusters: Deliverability vs. Engagement. This webinar brings together the ISP speakers from EEC15, plus Matt from Comcast, to expand on their comments. There’s been some confusion about the impact of engagement on delivery and whether or not senders should care about recipient engagement.
My opinion on the matter is well known: recipient engagement drives delivery to the inbox at some providers. I expect tomorrow we’ll hear a couple things from the ISPs.
February 2015 – The month in email
This was a short and busy month at WttW!
We attended another great M3AAWG conference, and had our usual share of interesting discussions, networking, and cocktails. I recapped our adventures here, and shared a photo of the people who keep your email safe while wearing kilts as well. We also commended Jayne Hitchcock on winning the Mary Litynski award for her work fighting abuse and cyberstalking.
Read MoreEngaging emails for better delivery
MessageSystems is sponsoring a webinar hosted by Direct Marketing discussing engagement as part of delivery.
Read MoreA must read on engagement
I really can’t add anything to what Chad wrote in Opens, Clicks, And Blocks In The Third Age Of Email Deliverability
Read MoreWhat is an open?
I was having a discussion today with a few industry colleagues about engagement and open rates. It was a good discussion and inspired a couple blog posts. Engagement totally matters, Engagement affects deliverability, and ISPs should be the last of your concerns.
I think they’ve covered the engagement issue pretty well, but what I wanted to talk about was metrics, specifically opens. Open is a fairly simple word, and it’s used in email all the time. Recipients open email. Mailbox providers measure that open. Senders measure that open.
It’s critical to remember, though, that open rates as measured by free mailbox provider and open rates tracked by a sender are not really the same thing. They’re measured in very different ways, and there is not a 1:1 mapping between the two measurements.
Facts about engagement
It is reality that ISPs look at the population of recipients that a mail stream is going to.
It is reality that they evaluate the activity of that population.
It is reality that ISPs treat senders that are sending to a significant number of email addresses that have not been logged into or accessed recently negatively.
If you’re having delivery problems, looking at the recipients and their activity is part of troubleshooting the issue and identifying a path back to the inbox.
You can use web and purchase data as a measurement of engagement IF you have, at some point, directly linked the email address and the user.
If you don’t have something that demonstrates a direct link between the person and the address, then it’s a crapshoot as to whether or not that email address belongs to who you think it belongs to.
Happy Friday everyone. It’s been a week.
More from Gmail
Campaign Monitor has an interview with Gmail looking at how to get mail to the Gmail inbox. It’s a great article and I think everyone should go read it.
One of the most important things it talks about is how complex filters are.
Engagement, it's not what you might think
Most delivery experts will tell you that ISPs measure recipient engagement as a part of their delivery. That’s absolutely true, but I think there’s a language difference that makes it hard for senders to understand what we mean by engagement.
ISPs, and other filtering companies, profile their user base. They know, for instance, who logs in and checks mail every day. They know who checks mail every 20 seconds. They know who gets a lot of spam. They know who hasn’t logged in for months. They know who accurately marks mail as spam and who is sloppy with the this-is-spam button. They know if certain recipients get the same mail, it’s likely to be spam.
Engagement at the ISPs is more about the recipient engaging with their email address and the mail in their mailbox then it is about the recipient engaging with specific emails.
Email against Humanity
“Sending an email is one of the worst things you can do to a person. You are stealing a little part of their life away. 99.99% of all emails are incredibly annoying and a huge imposition. If your job is to write emails, you should always be fighting to send fewer things and make sure each email you send is so incredible that it’s a rare treat to hear from you.”
Cards Against Humanity at MailChimp
One letter off…
I’m working on a blog post about the new Gmail tabbed inbox and the messages Gmail is inserting into the promotions tab. The messages aren’t showing up on most of my accounts, so I logged into an infrequently used account of mine. Ads are there, I got my screenshots and some data about the behaviour of the messages. So far so good.
I also discovered that at least two other women are using my address. One of them apparently ordered a bunch of wedding stuff from David’s Bridal shop using my email address. I hope Kirstie got her special order in time.
The other case is more interesting. I found dozens of emails in my inbox from what appeared to be friends including me in their email forward chain.
The Comic Sans. The FW:FW:FW:FW:FW subject lines. The horribly drawn cartoons. The inspirational messages. The prayer requests. The invites to bridge night. The followup demands that I reply to their invites for bridge night. The sad emails that I didn’t go to bridge night. There were emails from grandchildren. Questions about where I’d been and if I moved. Prayer chains. The messages go on and on.
Looking back through my inbox, this has been going on since sometime late in 2012. (Told you this was an infrequently used account). I looked and looked and I think I figured out what happened. A woman named Helen appears to to have an email address one letter off from mine (string@ vs stringsstring@) and one of her church friends tried to reply to her and dropped the ‘s’ from the email address. Once she did that, everyone else just kept hitting “reply all” and are including me in their forward chain.
It’s not commercial, it’s not spam. It’s just a bunch of people mistyping an email address and sending mail to someone they don’t know. I’m kinda glad it was a bunch of church ladies rather than Carlos Danger sending … well… Carlos Danger type messages.
People get email addresses wrong sometimes. It happens (ask me about the time I almost got my mailserver blocked because I mistyped an address while sending mail to a blocklist maintainer and hit a trap address by mistake…). The problem is that it can overwhelm an uninvolved person’s mailbox, even when it’s not commercial. Sure, if I was logging in to this account more often I’d probably have shut it down, but if they were paying attention they would have realized Helen is never replying to anything they send.
I kinda feel the same about commercial mailers that send me mail over and over and over again. I never open it, I never reply to it, I never respond to it. I wonder if there is actually anyone actually sending the mail, or if there’s just a lonely mailserver bricked up in a wall somewhere continually sending out spam.
Don’t be the bricked up server in the wall. Pay attention to what your recipients are doing.
Barracuda clicking all links in emails
A number of people have asked me recently if I know anything about appliances clicking all the links in emails. Some of those people have asked specifically about Barracuda, some have just asked if I knew of any filters that clicked links.
The answer is, yes, there are cases where spam filters have followed all the links in an email. One of the filters that I know has done this in the past is Barracuda. Based on discussions with the different people who are reporting this behavior, it does seem that this is happening more often. One person did mention that they were primarily seeing this with mail where the click domains were different from the From: domains.
I’m still working on getting more information from folks, and will update if I hear anything more. I’m also working on some advice for folks who get caught in this.
If you have experience with Barracuda (or other spam filters) clicking all the links in an email, drop me an email (contact)
Timely and appropriate mail
I woke up this morning to an exploding twitter and FB feeds with lots of friends cheering the defeat of DOMA and Prop 8. Apparently some companies are getting into the act as well.
(Behind a cut because some of this may be slightly NSFW in some places)
Questions about Spamhaus
I have gotten a lot of questions about Spamhaus since I’ve been talking about them on the blog and on various mailing lists. Those questions can be condensed and summed up into a single thought.
Read MoreMini Cooper and their email oops
I haven’t been able to track down any information about what happened, but it seems MINI USA had a major oops in their email marketing recently. So much so that they’re sending out apologies by snail mail. Pictures of the apology package appeared on Reddit earlier this week, and include a chocolate rose, some duct tape and a SPAM can stress reliever.
It’s a great example of a win-back campaign that really focuses on the recipients rather than the sender.
Increasing engagement for delivery?
I’ve talked a lot about engagement here over the years and how increasing engagement can increase inbox delivery.
But does driving engagement always improve delivery?
Take LinkedIn as an example. LinkedIn has started to pop-up a link when users log in. This popup suggests that the user endorse a connection for a particular skill. When the user clicks on the popup, an email is sent to the connection. The endorsement encourages the recipient to visit the LinkedIn website and review endorsements. Once the user is on the site, they receive a popup asking for endorsement of a connection. Drives engagement both on the website and with email. Win for everyone, right?
I get lots of these endorsements, but I’ve had a few that have made me wonder what’s really going on. Are these people really endorsing my skills? If they are then why am I getting endorsements from people I’ve not seen in 15 years and why are some of the endorsed skills things I can’t do?
This morning I asked one of my connections if he really did endorse me for my abilities in Cloud Computing. His response was enlightening.
Emails that make you smile
This summer’s non-work project for me has been training for a 5K run with Fleet Feet in Menlo Park. As part of the training programs we get weekly emails from the store on Monday. As I was reading through today’s email, I found myself smiling and happy. Lisa, who is one of the store owners and writes the emails, is just so happy and bouncy and thrilled to share her love of running and that comes through in the newsletter.
Our group’s primary coach is the other store owner. During runs we often talk about random stuff, and when I tell people I do email delivery, they always start talking about their experience with email and spam. One night I was running with Jim, and we were talking about Jim’s experiences with sending email. He mentioned their ESP and talked about how convenient it was. But then he mentioned he wasn’t sure that they were sending enough mail (which made me laugh hard enough I almost tripped on a curb).
I realized I am not just a delivery expert when I started thinking about all the ways they could increase the amount of email they send, while still maintaining the quality and the friendly feel of their bulk emails. What could they offer local runners that would increase the value of the store to them? The first very obvious thing was a race calendar. There are dozens of local races every week, telling folks about upcoming races and entry deadlines would be a way to contact folks regularly without it always being a “buy stuff from us!!”
What commercial emails have you gotten recently that have made you smile?
More on Yahoo and Engagement
A friend of the blog contacted me earlier today and pointed out that the news that Dan posted about Yahoo and engagement that I blogged about last week was actually reported by George Bilbrey in a Mediapost article on August 1.
Read MoreYahoo looking harder at engagement
In a post this morning, Dan Deneweth from Responsys says he’s received confirmation from Yahoo that they have increased the value of engagement metrics when making delivery decisions.
The really great thing, for the ISPs, about engagement metrics is that they directly measure how much a particular email is wanted by recipients. There’s no guessing about it, it measures how engaged the recipient is with a mail. Even better is the fact that, unlike proxy metrics, engagement metrics are extremely difficult for the sender to manipulate. As a sender I can artificially lower complaints and bounces without improving the mail I’m sending. But I can’t improve engagement metrics without actually engaging my recipients.
As I wrote back in 2010:
Bounces, complaints and metrics
In the email delivery space there are a lot of numbers we talk about including bounce rates, complaint rates, acceptance rates and inbox delivery rates. These are all good numbers to tell us about a particular campaign or mailing list. Usually these metrics all track together. Low bounce rates and low complaint rates correlate with high delivery rates and high inbox placement.
How to make sure your mail is read
ThinkGeek have a bit of a challenging audience to connect with. Many of their customers are, well, geeks. And many geeks have a reputation for being suspicious of marketing. I’d even go so far as to say that ThinkGeek has a bigger marketing challenge than other popular retailers.
One of the challenges all marketers face, though, is getting people to actually open and read an email carefully. ThinkGeek have addressed this challenge by turning reading email into a competitive game.
In June they sent out an email with a hidden coupon code in it. The first person to redeem the code received $100 off their order. What a creative way to get people to actually look through an email and make a purchase.
This, of course, is not a new marketing technique. I have at least 2 different Sigma t-shirts using the same style of marketing. This was in the dark ages and we didn’t have online forms, but the new catalog came with a postcard of questions to answer and return and the first 100 post cards got t-shirts. It was actually kinda nifty. As head tech, I got catalogs all the time. But answering the questions got me to look through the Sigma catalog and see their new products. Plus! T-shirt!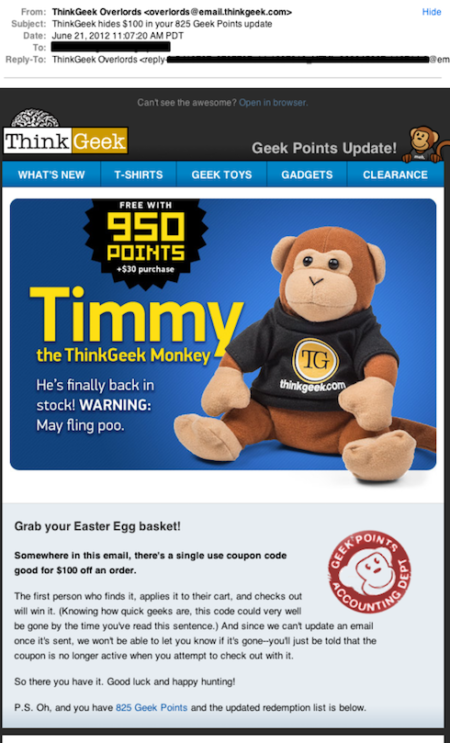
What new an interesting ways have you seen marketers use to engage recipients?
Engagement in email
From Tim Roe at eConsultancy.com: Is engagement email marketing finally here?
Tim lays out a number of factors for why engagement is important in email marketing and how to use engagement to improve ROI.
Delivery reflects recipient desires
Ken has an article today about how Pro Flowers managed to get their mail out of the bulk folder at Gmail by asking their recipients for help.
Read MoreSpamhaus rising?
Ken has a good article talking about how many ESPs have tightened their standards recently and are really hounding their customers to stop sending mail recipients don’t want and don’t like. Ken credits much of this change to Spamhaus and their new tools.
Read MoreDelivery versus marketing
I’ve been thinking lately that sometimes that what works for marketing doesn’t always work for delivery.
For instance in many areas of marketing repetition is key. Repeat a slogan and forge an association between the slogan and the product in the mind of the consumer. More repetition is better. Marketers can even go so far as using the same ad to drive consumer action. Television advertising is a prime example of this. Companies don’t create new content for every advertising slot, they create one or a few ads and then replay them over and over. The advertiser doesn’t even really care if the consumer consciously ignores the ads. The unconscious connection is still being made.
In the world of email delivery, though, having many or most recipients ignore advertising is the kiss of death. Too many unengaged users and filters decide that mail shouldn’t go into the inbox. These don’t even have to be ISP level filters, but Bayesian filters built into desktop mail clients.
Sending repetitive ads over email may be an effective marketing strategy, but may not be an effective delivery strategy.
Am I off base here and missing something? Tell me I’m wrong in the comments.
About that Junk Folder
I use a pretty standard mail filtering setup – a fairly vanilla SpamAssassin setup on the front end, combined with naive bayesian content filters in my mail client. So I don’t reject any mail, it just ends up in one of my inboxes or a junk folder. And I have a mix of normal consumer mail – facebook, twitter, lots of commercial newsletters, mail from friends and colleagues and spam. (As well as that I have a lot of high traffic industry mailing lists, but overall it’s a fairly normal mix.)
My bayesian filter gets trained mostly by me hitting “this is spam” when spam makes it to my inbox. If I’m expecting an email “immediately” – something like a mailing list COI confirmation or email as part of buying something online – I’ll check my spam filter and move the mail to my inbox in the rare case it ended up there. Other than that I let it and spamassassin chug along with no tweaking.
I’m starting a data analysis project, based on my own inboxes, and as part of that I’m using some tools to look for false positives in my junk folders, and manually fixing anything that’s misclassified. I’ve been doing this for a couple of hours now, and I’ve found some interesting things.
Social media to improve email delivery
Mail delivered to the bulk folder is likely to continue landing in the bulk folder without intervention. Sometimes a sender can talk to the ISP involved and get mail moved back to the inbox. Sometimes a sender can make hygiene changes and get mail moved back to the inbox.
The most effective way to get mail delivered to the inbox, however, is for recipients to go into the bulk folder and mark the mail as “not spam.” Nothing is more effective at getting mail delivered to the inbox.
But there is a bit of a catch 22 there. If mail ends up in the bulk folder consistently, recipients tend to forget about it. Many people trawl through their bulk folder sporadically, if at all. If recipients aren’t engaged with mail and don’t know when they should see it, then they won’t miss it and won’t look for it.
So if mail is ending up in the bulk folder and recipients aren’t expecting it what can a sender do? One of the obvious answers is find another channel. Let recipients know through some channel besides email that they need to look in their bulk folder for a particular email.
In the past it was difficult to find non-email ways to connect recipients. I worked with customers who really had no other way to interact with recipients than email. They weren’t running a website, they didn’t have any other contact methods, they were really stuck. But a recent tweet from AppSumo shows how social media can be used to improve email delivery.
Engagement based delivery makes testing tricky
Yesterday I wrote about how important recipients are to achieving good delivery. The short version of yesterday’s post is that delivery is all about engagement, and how the ISPs were really focusing on engagement and proving custom user experiences.
This is great, for the user. Take the common example where a commercial list has some highly engaged recipients and a bunch of recipients that can take or leave the mail. The ISP delivers the newsletter into the inbox of the highly engaged recipients and leaves it in the bulk folder of less engaged recipients.
With user focused delivery people get the mail they are interested in where they can read it and interact it. People who have demonstrated a lack of interest for a topic or a sender don’t see that mail.
This can get complicated for those of us trying to troubleshoot deliver problems, though. I have a couple mail accounts I use for testing at various ISPs. Even though I do very little to try and personalize the account I am seeing behaviour that leads me to wonder if ISP personalizing the inbox experience is going to make it that much more difficult to troubleshoot delivery issues.
I have to wonder, too, where this leaves delivery monitoring services in the future. If delivery is personalized, how can you know that the delivery monitoring addresses are representative any longer? Is there even a “representative” mailbox any longer?
Recipients are the secret to good delivery
Many, many people hire me to educate them on delivery and fix their email problems. This is good, it’s what I do. And I’m quite good at helping clients see where their email program isn’t meeting expectations. I can translate tech speak into marketing. I can explain things in a way that shifts a client’s perception of what the underlying issues are. I can help them find their own way into the inbox.
But…
Most of what I do is simply think about email delivery from the point of view of a recipient and help clients better meet their recipient’s expectations. This works. This works really well. If you send mail that your recipients want your mail gets to the inbox.
Here’s the secret: ISPs and most spam filters have a design goal to deliver mail their users want. They only want to block mail their users don’t want.
Filters are not designed to block wanted mail.
Sure there are complicated situations where senders have gotten behind the 8 ball and need some help cleaning up. There are situations where filters screw up and block mail they shouldn’t (and aren’t quite designed to). Spam filters are complicated bits of code and sometimes they do things unexpectedly. All of these things do happen.
But these situations happen a lot less than most senders think. Most of the time when mail is hitting the bulk folder, or is throttled at the MTA the issue is that recipients don’t care about the mail.
Recipients aren’t engaged with a particular sender or particular brand. So ISPs react accordingly and that mail ends up slowly delivered or bulked. This upsets the senders to no end, but the recipients? The recipients often don’t care that some mail shows up in bulk or arrives Wednesday afternoon instead of Tuesday evening.
When recipients are engaged with a particular sender or brand, though? Delivery is fast and reliable. Mail is rarely delayed or bulked. When recipients want mail, they interact with it. They look in the bulk folder. They miss it when it’s not there. They complain to the ISPs when they don’t get it. The ISPs react accordingly and prioritize or “red carpet” that email.
The secret to really good delivery is to get your recipients to handle your ISP relations for you. Send mail they miss when they don’t get it, and you’ll discover most of your delivery problems go away.
Hotmail fights greymail
I’ve heard a lot of marketers complaining about people like me who advocate actually purging addresses from marketing lists if those addresses are non-responsive over a long period of time. They have any number of reasons this advice is poor. Some of them can even demonstrate that they get significant revenue from mailing folks who haven’t opened an email in years.
They also point out that there isn’t a clear delivery hit to leaving those abandoned addresses on their list. It’s not like bounces or complaints. There isn’t a clear way to measure the dead addresses and even if you could there aren’t clear threshold guidelines published by the ISPs.
Nevertheless, I am seeing more and more data that convinces me the ISPs do care about companies sending mail that users never open or never read or never do anything with.
The most recent confirmation was the announcement that Hotmail was deploying more tools to help users manage “greymail.” I briefly mentioned the announcement last week. Hotmail has their own blog post up about the changes.
It seems my initial claim that these changes this won’t affect delivery may have been premature. In fact, these changes are all about making it easier for Hotmail users to deal with the onslaught of legitimate but unwanted mail.
Mailing old addresses: 5 questions to ask first
James asked the question on twitter:
If you haven’t mailed an address in 5-10 yrs, would you include it in a re-engagement mail?
Read More
Relevance?
As a past guest and/or meeting planner of Millennium Hotels and Resorts we are pleased to share these occasional special offers. If you no longer wish to receive email communications from us, please click the unsubscribe link. Please note that this broadcast is sent from an address which is not monitored. If you have questions about the offer, please contact us directly. Our hotel contact details may be found in this email offer above or you may visit www.millenniumhotels.com.
Read More
It would be nice…
It’d be nice to have a tool to uncover the zombie email addys, but until then, read this from @wise_laura: http://bit.ly/jxjZ9M Kelly Lorenz
Read More
Don't take my subscribers away!
Tom Sather has a good summary of the problems with inactive email addresses and why data hygiene is critical to maintain high deliverability. These recommendations are some of the most difficult to convince people to implement.
Some of my clients even show me numbers that show that a recipient that hadn’t opened or read and email in 18 months, suddenly made a multi-hundred dollar purchase. Another client had clear numbers that showed even recipients that didn’t open for an entire year were responsible for 10% of revenue.
They tell me I can’t expect them to let their customers go. These are significant amounts of money and they won’t let any potential revenue go without a fight.
I understand this, I really do. The bottom line numbers do make it tough to argue that inactive subscribers should be removed. Particularly when the best we can offer is vague statements about how delivery may be affected by sending mail to unengaged users.
I don’t think many senders realize that when they talk about unengaged users they are actually talking about two distinct groups of recipients.
The first group is that group of users that actively receive email, but who aren’t opening or reading emails from particular senders. This could be because of their personal filters, or because the mail is going to the bulk folder or even simply because they don’t load images by default. This is the pool that most senders think of when they’re arguing against removing unengaged users.
The second group is that group of users that never logs in ever. They have abandoned the email address and never check it. I wrote a series of posts on Zombie Emails (Part 1, 2, 3) last September, finishing with suggestions on how to fight zombie email addresses.
Unlike senders ISPs can trivially separate the abandoned accounts from the recipients who just don’t load images. Sending to a significant percentage of zombie accounts makes you look like a spammer. Not just because spammers send mail to really old address lists, but a number of spammers pad their lists with zombie accounts in order to hide their complaint rates. The ISPs caught onto this trick pretty quickly and also discovered this was a good metric to use as part of their filtering.
I know it’s difficult to face the end of any relationship. But an email subscription isn’t forever and if you try to make it forever then you may face delivery problems with your new subscribers.
Food for thought
Companies that can’t be bothered to implement good subscription practices will rarely be bothered to send relevant or engaging email.
True or False?
Setting expectations at the point of sale
In my consulting, I emphasize that senders must set recipient expectations correctly. Receiver sites spend a lot of time listening to their users and design filters to let wanted and expected mail through. Senders that treat recipients as partners in their success usually have much better email delivery than those senders that treat recipients as targets or marks.
Over the years I’ve heard just about every excuse as to why a particular client can’t set expectations well. One of the most common is that no one does it. My experience this weekend at a PetSmart indicates otherwise.
As I was checking out I showed my loyalty card to the cashier. He ran it through the machine and then started talking about the program.
Cashier: Did you give us your email address when you signed up for the program?
Me: I’m not sure, probably not. I get a lot of email already.
Cashier: Well, if you do give us an email address associated with the card every purchase will trigger coupons sent to your email address. These aren’t random, they’re based on your purchase. So if you purchase cat stuff we won’t send you coupons for horse supplies.
I have to admit, I was impressed. PetSmart has email address processes that I recommend to clients on a regular basis. No, they’re not a client so I can’t directly take credit. But whoever runs their email program knows recipients are an important part of email delivery. They’re investing time and training into making sure their floor staff communicate what the email address will be used for, what the emails will offer and how often they’ll arrive.
It’s certainly possible PetSmart has the occasional email delivery problem despite this, but I expect they’re as close to 100% inbox delivery as anyone else out there.
Brand engagement in social media
Adobe has a good post up about consumer reaction and interaction with brands in social media like Twitter and Facebook.
Read MoreEmail marketing ulcers for the holiday
I’ve mentioned here before that I can usually tell when the big ISPs are making changes to their spam filtering as that ISP dominates my discussions with current and potential clients and many discussions on delivery mailing lists.
The last two weeks the culprit has been Yahoo. They seem to be making a lot of changes to their filtering schemes right at the busiest email marketing time of the year. Senders are increasing their volume trying to extract that last little bit of cash out of holiday shoppers, but they’re seeing unpredictable delivery results. What worked to get mail into the inbox a month ago isn’t working, or isn’t working as well, now.
Some of this could be holiday volume related. Many marketers have drastically increased their mail volume over the last few weeks. But I don’t think the whole issue is simply that there is more email marketing flowing into our mailboxes.
As I’ve been talking with folks, I have started to see a pattern and have some ideas of what may be happening. It seems a lot of the issue revolves around bulk foldering. Getting mail accepted by the MXs seems to be no different than it has been. The change seems to be based on the reputation of the URLs and domains in the email.
Have a domain with a poor reputation? Bulk. Have a URL seen in mail people aren’t interested in? Bulk. Have a URL pointing to a website with problematic content? Bulk.
In the past IPs that were whitelisted or had very good reputations could improve delivery of email with neutral or even borderline poor reputations. It seems that is no longer an effect senders can rely on. It may even be that Yahoo, and other ISPs, are going to start splitting IP reputation from content reputation. IP reputation is critical for getting mail in the door, and without a good IP reputation you’ll see slow delivery. But once the mail has been accepted, there’s a whole other level of filtering, most of it on the content and generally unaffected by the IP reputation.
I don’t think the changes are going to go away any time soon. I think they may be refined, but I do think that reputation on email content (particularly domains and URLs and target IP addresses) is going to play a bigger and bigger role in email delivery.
What, specifically, is going to happen at Yahoo? Only they can tell you and I’m not sure I have enough of a feel for the pattern to speculate about the future. I do think that it’s going to take a few weeks for things to settle down and be consistent enough that we can start to poke the black box and map how it works.
Now you know…
The key to email marketing, at least if you read blogs and talk to experts who blog about such things, is to segment your lists. But what does segmenting your lists really mean? Ken touches on it in a recent article about engagement and segmenting.
Segmenting your list means, quite simply, knowing your audience. It means tailoring your message to them, in order to extract as much money from them as possible. It means knowing which subscribers you can push with volume and which you will lose if you increase things too far.
In short, it means not treating all your subscribers the same, instead treating them slightly differently based on how they interact with your message.
To some people, this is too difficult. Ken even quoted someone in the industry as saying
Preferences pages
As often as I talk about how badly companies send mail, I think it’s always a good idea to highlight when I find companies doing good things.
Today’s example of a company making me happy is Sur la Table. I’ve been on their mailing list for quite a while and do enjoy the offers and information they send. With the advent of the holiday cooking season, though, they’ve massively increased their volume. 21 emails in September, 25 emails in October and 37 emails in the month of November.
Size isn't the only metric
MarketingSherpa has a case study up today about a company that took an aggressive stance on re-engagement that reduced their house list size by over 95%. While the size of the list went down, online sales doubled.
The whole article is a lesson in how to do email right. They are sending relevant and engaging mail to their subscribers. They kept the addresses of people who wanted the mail, but designed a new program from the ground up. All of the key points I, and others, keep talking about is present in their new program.
Mail that looks like spam
One thing I repeat over and over again is to not send mail that looks like spam. Over at the Mailchimp Blog they report some hard data on what looks like spam. The design is simple, they took examples of mail sent by their customers and forwarded them over to Amazon’s Mechanical Turk project to be reviewed by humans.
In a number of cases they discovered that certain kinds of templates kept getting flagged as spam, even when Mailchimp was sure that the sender had permission and the recipients wanted the mail. They analyzed some of these false positives and identified some of the reasons that naive users may identify those particular emails as spam.
Ben concludes:
How not to build a mailing list
I mentioned yesterday one of the major political blogs launched their mailing list yesterday. I pointed out a number of things they did that may cause problems. Today, I discovered another problem.
This particular blog has been around for a long time, probably close to 10 years. It allows anyone to join and create their own blogs and comment with registered users. As part of their new mailing list, they added everyone who has ever registered to their mailing list. They did not send a “we have a new list, want to join it?” email, they added every registered user to the list and said “you can opt out if you want.”
This is such a bad idea. My own account was used once, to make one comment, back in 2005. Yes, 2005. It’s been almost 5 years since I last logged into the site. Sure, I have email addresses that go back that far, but not everyone does. That list is going to be full of problems: dead addresses, spamtraps, duplicates, unengaged and uninterested.
Seriously, they’re adding people who’ve not logged into their site in 5 years to a mailing list. How can this NOT go horribly wrong?
My initial thought was this was going to blow up in a week. I’m now guessing they’ll start seeing delivery problems a lot sooner than that.
Email and politics
I occasionally consult for activists using email. Their needs and requirements are a little different from email marketers. Sure, the requirements for email delivery are the same: relevant and engaging mail to people who requested it. But there are complicating issues that most marketers don’t necessarily have to deal with.
Activist groups are attractive targets for forged signups. Think about it, when people get deeply involved in arguments on the internet, they often look for ways to harass the person on the other end of the disagreement. They will often signup the people they’re disagreeing with for mailing lists. When the disagreements are political, the logical target is a group on the other side of the political divide.
People also sign up spamtraps and bad addresses as a way to cause problems or harass the political group itself. Often this results in the activist group getting blocked. This never ends well, as instead of fixing the problem, the group goes yelling about how their voice is being silenced and their politics are being censored!!
No, they’re not being silenced, they’re running an open mailing list and a lot of people are on it who never asked to be on it. They’re complaining and the mail is getting blocked.
With that as background, I noticed one of the major political blogs announced their brand new mailing list today. Based on their announcement it seemed they that they may have talked to someone who knew about managing a mailing list.
Ownership of the inbox
Marketers often treat recipient inboxes with a certain level of ownership. They talk about getting mail to the inbox with the underlying implication that inboxes are for use by marketers and they tend to forget that recipients use email for a lot of things, not just being marketing targets.
This was crystallized for me a few years ago when I was running a conference session. The session had a very diverse group of attendees and as part of the session they broke up into smaller groups to talk about various email related topics. One of the questions was how do people use email. Those groups with more ISP representatives produced a list with dozens of ways people use email. The groups dominated with email marketers, though, came up with a much more limited set of uses, all of them related to marketing or commerce. They didn’t mention mailing lists or one on one discussions or connecting with friends as part of the things people use email for.
Marketers seem to forget that email was not adopted by users so they could be marketed to. In fact, email is primarily used by people to interact with friends, colleagues, allies and family members. Most recipients really don’t really care about marketing in their inbox. They’re much more interested in the mail from mom with pictures of the new puppy. They’re looking for that mail from a friend linking to a silly video. They’re deeply involved in an online discussion with friends or colleagues about anything at all.
This doesn’t mean they don’t want marketing in their inbox. Every subscription is an invitation to visit the recipient’s mailbox. They are inviting a sales person to visit them at home or at work; spaces where marketers are not traditionally invited.
The problem is that a lot of email marketers do not respect the space they’ve been invited into. They assume, usually incorrectly, they are being given ownership of that space. The marketer sees the inbox as their marketing space, not as space that the recipient feels ownership over.
When someone buys a magazine or watches TV, there are a lot of ads, but that’s OK because they don’t feel any ownership of those spaces. But when they subscribe to something in email, they don’t cede ownership of their inbox to the senders. It is still their inbox and marketers are there only because the recipient invited them. The recipient will kick marketers out if they start writing on the walls or otherwise disrespecting their space.
Many delivery consultants talk about engagement and sending timely, relevant email. All of those are really coded phrases meaning “when you’re invited into somebody’s house don’t scrawl on the walls or poop on the carpets.”
The rules of delivery success
Senders with delivery problems ask about “the rules.” “Just tell us what the rules are!” “If the ISPs would just tell us what to do we’d do it!” There is only one rule anyone needs to pay attention to for good mail delivery: Respect the recipient.
Not good enough for you? Want more specific rules? OK.
The two rules everyone must follow for good mail delivery.
Public reputation data
IP based reputation is a measure of the quality of the mail coming from a particular IP address. Because of how reputation data is collected and evaluated it is difficult for third parties to provide a reputation score for a particular IP address. The data has to be collected in real time, or as close to real time as possible. Reputation is also very specific to the source of the data. I have seen cases where a client has a high reputation at one ISP and a low reputation at another.
All this means is that there are a limited number of public sources of reputation data. Some ISPs provide ways that senders can check reputation at that ISP. But if a sender wants to check a broader reputation across multiple ISPs where can they go?
There are multiple public sources of data that I use to check reputation of client IP addresses.
Blocklists provide negative reputation data for IP addresses and domain names. There are a wide range of blocklists with differing listing criteria and different levels of trust in the industry. Generally the more widely used a list the more accurate and relevant it is. Generally I check the Spamhaus lists and URIBL/SURBL when investigating a client. I find these lists are good sources for discovering real issues or problems.
For an overall view into the reputation of an IP address, both positive and negative, I check with senderbase.org provided by Ironport and senderscore.org provided by ReturnPath.
All reputation sources have limitations. The primary limitation is they are only as good as their source data, and their source data is kept confidential. Another major limitation is reputation sources are only as good as the reputation of the maintainer. If the maintainer doesn’t behave with integrity then there is no reason for me to trust their data.
I use a number of criteria to evaluate reputation providers.
The secret to fixing delivery problems
There is a persistent belief among some senders that the technical part of sending email is the most important part of delivery. They think that by tweaking things around the edges, like changing their rate limiting and refining bounce handling, their email will magically end up in the inbox.
This is a gross misunderstanding of the reasons for bulk foldering and blocking by the ISPs. Yes, technical behaviour does count and senders will find it harder to deliver mail if they are doing something grossly wrong. In my experience, though, most technical issues are not sufficient to cause major delivery problems.
On the other hand, senders can do everything technically perfect, from rate limiting to bounce handling to handling feedback loops through authentication and offer wording and still have delivery problems. Why? Sending unwanted mail trumps technical perfection. If no one wants the email mail then there will be delivery problems.
Now, I’ve certainly dealt with clients who had some minor engagement issues and the bulk of their delivery problems were technical in nature. Fix the technical problems and make some adjustments to the email and mail gets to the inbox. But with senders who are sending unwanted email the only way to fix delivery problems is to figure out what recipients want and then send mail meeting those needs.
Persistent delivery problems cannot be fixed by tweaking technical settings.
Return Path Changes certification standards
Return Path recently announced changes to their certification program. They will no longer be certifying 3rd party mailers.
Read MoreTruths and myths about email
Seven myths and two truths about email
My favorite:
[myth] Engagement is the new reputation. Actually, reputation metrics have always been about engagement, which is what complaint data and sender reputation reflect.Read More
Permission versus forgiveness
Stephanie at Return Path has a great blog post on permission and how permission is an ongoing process not a one time thing. There were a couple statements that really grabbed my attention.
Read MoreTWSD: Using FOIA requests for email addresses
Mickey has a good summary of what’s going on in Maine where the courts forced the Department of Inland Fisheries and Wildlife to sell the email addresses of license purchasers to a commercial company.
There isn’t permission associated with this and the commercial company has no pretense that the recipients want to receive mail from them. This is a bad idea and a bad way to get email addresses and is no better than spammers scraping addresses from every website mentioning “fishing” or “hunting.”
Project Omnivore
Ben at Mailchimp has posted some information about Project Omnivore. This is a predictive system that not only predicts potential abuse, but can also be used to predict poor campaigns. Steve and I had a chance to see Omnivore in action when we were in Atlanta last fall, and were impressed by the accuracy for bad stuff. It seems, however, that Omnivore is useful to predict good behaviour as well.
Read MoreIt doesn't matter what you say
“What should we tell the ISP?” is a frequent question from my customers. The answer is pretty simple. It doesn’t usually matter what you tell the ISP. What matters are your actions.
If a sender is having delivery problems then the solution is not to call the ISP and talk to them about why the sender’s mail should not be delivered to the bulk folder. Instead, the solution is to evaluate the email and the address acquisition process and the list hygiene process. Identify where potential problems are and then resolve those problems.
Typically, the ISPs won’t need to be contacted. The changes to the email will register and delivery will improve. In some cases, particularly when there’s been some major mistake, contacting the ISP and explaining the mistake and what steps have been taken to stop the mistake from happening in the future may help resolve the issue faster. But if nothing has changed, then there’s no reason for the ISP to expect anything to change.
It doesn’t matter what you say. It matters what you do.
Bad year coming for sloppy marketers
MediaPost had an article written by George Bilbrey talking about how 2010 could be a difficult year for marketers with marginal practices. George starts off the article by noticing that his contact at ISPs are talking up how legitimate companies with bad practices are causing them problems and are showing up on the radar.
This is something I talked about a few weeks ago, in a series of blog posts looking at the changes in 2010. The signs are out there, and companies with marginal practices are going to see delivery get a lot more difficult. George lists some practices that he sees as problems.
How do unengaged recipients hurt delivery?
In the comments Ulrik asks: “How can unengaged recipients hurt delivery if they aren’t complaining? What feedback mechanism is there to hurt the the delivery rate besides that?”
There are a number of things that ISPs are monitoring besides complaint rates, although they are being cautious about revealing what and how they are measuring things. I expect that ISPs are measuring things like:
Keep subscribers happy
Mark Brownlow writes about engagement. “…the people we really need to keep happy are the subscribers.” Go read the whole thing.
Read MoreThe coming changes
Yesterday I talked about how I’m hearing warnings of a coming paradigm shift in the email industry. While these changes will affect all sender, ESPs in particular are going to need to change how they interact with both ISPs and their customers.
Currently, ESPs are able to act as “routine conveyers.” The traffic going across their network is generated by their customers and the ESP only handles technical issues. Responsible ESPs do enforce standards on their customers and expect mailings to meet certain targets. They monitor complaints and unknown users, they monitor blocks and reputation. If customers get out of line, then the ESP steps in and forces their customer to improve their practices. If the customer refuses, then the ESP disconnects them.
Currently standards for email are mostly dictated by the ISPs. Many ESPs take the stance that if any mail that is not blocked by the ISPs then it is acceptable. But just because a certain customer isn’t blocked doesn’t mean they’re sending mail that is wanted by the recipients.
It seems this reactive approach to customer policing may no longer be enough. In fact, one of the large spam filter providers has recently offered their customers the ability to block mail from all ESPs with a single click. This may become a more common response if the ESPs don’t start proactively policing their networks.
Why is this happening? ISPs and filtering companies are seeing increasing percentages of spam coming out of ESP netspace. Current processes for policing customers are extremely reactive and there are many ESPs that are allowing their customers to send measurable percentages of spam. This situation is untenable for the filtering companies or the ISPs and they’re sending out warnings that the ESPs need to stop letting so much spam leave their networks.
Unsurprisingly, there are many members of the ESP community that don’t like this and think the ISPs are overreacting and being overly mean. They do not think the ISPs or filtering companies should be blocking all an ESPs customers just because some of the customers are sending unwanted mail. Paraphrased, some of the things I’ve heard include:
Is it really permission?
There’s a great post over on the AOL Postmaster blog talking about sending wanted mail versus sending mail to people who have <a href=”https://web.archive.org/web/20100210070640/http://postmaster-blog.aol.com:80/2009/12/03/p/>grudgingly given permission to receive it.
Read MoreCyber Monday inundation
The cyber monday inundation of mail has hit my mailbox. There’s been a clear increase in marketing mail over the last week. Unfortunately for those marketers, it’s too much and I am just scanning subject lines and marking as read. I don’t have the time to read all this mail.
Read MoreAOL EWL: low complaints no longer enough
This morning AOL announced some changes to their Enhanced White List. Given I’ve not talked very much about the AOL EWL in the past, this is as good a time as any to talk about it.
The AOL Enhanced Whitelist is for those senders that have very good practices. Senders on the EWL not only get their mail delivered to the inbox, but also have links and images enabled by default. Placement on the EWL is done solely on the basis of mail performance and only the best senders get on the list.
The new announcement this morning says that AOL will take more into account than just complaints. Previously, senders with the lowest complaint rates qualified for the EWL. Now, senders must also have a good reputation in addition to the low complaint rates. Good reputation is a measure of user engagement with a particular sender.
This change only reinforces what I and many other delivery experts have been saying: The secret to good delivery is to send mail recipients want. ISPs are making delivery decisions based on those measurements. Send mail that recipients want, and there are few delivery problems.
For a long time good delivery was tied closely to complaint rates, so senders focused on complaints. Spammers focused on complaints too, thus managing to actually get some of their spam delivered. ISPs noticed and started looking at other ways to distinguish wanted mail from spam. One of the better ways to separate spam from wanted mail is to look at user engagement. And the ISPs are measuring engagement and using that measurement as part of their decision making process. Send so much mail users don’t read it, and your reputation goes down followed by your delivery rates.
Sending too much mail
Not having policies restricting the amount of mail any customer or recipient receives may lead to higher spam complaint rates and blocking warns the DMA Email Marketing Council.
HT: Box of Meat
Controlling delivery
How much control over delivery do senders have? I have repeatedly said that senders control their delivery. This is mostly true. Senders control their side of the delivery chain, but there is a point where the recipient takes over and controls things.
As a recipient I can
The legitimate email marketer
I cannot tell you how many times over the last 10 years I’ve been talking to someone with a problem and had them tell me “but I’m a legitimate email marketer.” Most of them have at least one serious problem, from upstreams that are ready to terminate them for spamming through widespread blocking. In fact, the practices of most companies who proclaim “we’re legitimate email marketers” are so bad that the phrase has entered the lexicon as a sign that the company is attempting to surf the gray area between commercial email and spam as close to the spam side of that territory as possible.
What do I mean by that? I mean that the address collection practices and the mailing processes used by self-proclaimed legitimate email marketers are sloppy. They don’t really care about individual recipients, they just care about the numbers. They buy addresses, they use affiliates, they dip whole limbs in the co-reg pool; all told their subscription practices are very sloppy. Because they didn’t scrape or harvest the email address, they feel justified in claiming the recipient asked for it and that they are legitimate.
They don’t really care that they’re mailing people who don’t want their mail and really never asked to receive it. What kinds of practices am I talking about?
Buying co-reg lists. “But the customer signed up, made a purchase, took an online quiz and the privacy policy says their address can be shared.” The recipient doesn’t care that they agreed to have their email address handed out to all and sundry, they don’t want that mail.
Arguing with subscribers. “But all those people who labeled my mail as spam actually subscribed!!!” Any time a mailer has to argue with a subscriber about the validity of the subscription, there is a problem with the subscription process. If the sender and the receiver disagree on whether there was really an opt-in, the senders are rarely given the benefit of the doubt.
Using affiliates to hide their involvement in spam. A number of companies use advertising agencies that outsource acquisition mailings that end up being sent by spammers. These acquisition mailings are sent by the same spammers sending enlargement spam. The advertiser gets all the benefits of spam without any of the consequences.
Knowing that their signup forms are abused but failing to stop the abuse. A few years back I was talking with a large political mailer. They were insisting they were legitimate email marketers but were finding a lot of mail blocked. I mentioned that they were a large target for people forging addresses in their signup form. I explained that mailing people who never asked for mail was probably the source of their delivery problems. They admitted they were probably mailing people who never signed up, but weren’t going to do anything about it as it was good for their bottom line to have so many subscribers.
Self described legitimate email marketers do the bare minimum possible to meet standards. They talk the talk to convince their customers they’re legitimate:


