ESPs
How to choose an ESP based on deliverability
Despite what a lot of SEO slop will try and tell you there’s no way to measure deliverability performance across multiple ESPs in any way that’s meaningful.
Read MoreESPs need to step up their compliance game
I don’t send a lot of spam complaints generally. Mostly I block and move on. There are some companies, though, that I offer the professional courtesy of sending a complaint or a report to their abuse@ address. Former clients, friends and colleagues generally get that courtesy.
Read MoreRaising the standard
Last week news broke that Mailchimp had disconnected a number of anti-vaccination activists from their platform and banned anti-vax content. I applaud their decision and hope other companies will follow their lead in banning harmful content from their network.
Read MoreESPs are failing recipients
Over the last few years I’ve reduced the complaints I send to ESPs about their customers to almost nothing. The only companies I send complaints to are ones where I actually know folks inside the compliance desk, and I almost never expect action, I just send them as professional courtesy.
ESPs and deliverability
There’s an ongoing discussion, one I normally avoid, regarding how much impact an ESP has on deliverability. Overall, my opinion is that as long as you have a half way decent ESP they have no impact on deliverability. Then I started writing an email and realised that my thoughts are more complex than that.
Share your average bounce rates
The question came up on slack this morning about bounce rate benchmarks. What are the normal / average bounces that different ESPs see? Does region matter? What’s acceptable for bounce rates?
Read MoreSuccessful sends on Black Friday
Last year a number of ISPs mentioned the Black Friday email volume was congesting their systems and causing delays. While anecdotally it seems that volume is up over last year I also haven’t heard any ISPs talking about congestion. Likewise, most of the delivery folks I’ve spoken too today and over the weekend are saying there were no major problems.
Read MoreSaaS systems are spammer targets
There are probably hundreds of thousands of really awesome SaaS products out there. They provide a framework to do all sorts of stuff that used to be really hard to do. Almost all of them include some email component. They dutifully build the email piece into their platform and, because they’re smart, they outsource the actual sending to one of SMTP providers. They’re happy, their customers are happy, and spammers are happy.
Read MoreEvolution of policy
Last week, I talked about policy, using some different blocklist policies as examples. In that post I talked about how important it is that policy evolve. One example of that is how we’ve been evolving policy related to companies that get listed on Purchased Lists and ESPs. Who is listed has evolved over time, and we’re actually looking at some policy changes right now.
Read MoreSocial media connections are not opt-ins
It seems silly to have to say this, but connecting on social media is not permission to add an address to your newsletter or mailing list or prospecting list or spam list. Back in 2016, I wrote:
Read MoreNot a customer you want
Earlier this week one of my ESP clients contacted me. They have a new (potential?) customer dealing with some delivery challenges. Client was looking for advice on how to move the customer over and improve their delivery at the same time.
My advice was actually pretty simple: this isn’t a customer you want. Walk away.
I reached that conclusion about 10 seconds after I loaded the customer’s website. Because I know sometimes initial impressions are wrong, I did spend about 10 more minutes poking around. What I found did nothing to change my mind or convince me my initial impression was wrong. In fact, everything I found reinforced the belief that this was not a good customer for my client.
I sent my client an email explaining what I’d found and they agreed. Future deliverability problem averted!
Some of what I found inspired the conversations with spammers blog post from earlier this week. For instance, the website had two different signup forms, each pointing to a different ESP. Both links were dead.
Then I looked at the company’s whois record and found a bunch of cookie cutter websites, all with different domain names, all with the same broken subscription links.
I do this manually and I can’t fathom how you would automate this kind of checking. For me, it seems there absolutely needs to be a human in the loop. But I suspect that there are ways to automate these types of checks.
In any case, there’s a spammer looking for an email service provider. He’s having problems with IP reputation at his current ESP. He sends content and will even share with you the domain he’s using to collect email addresses. Pro tip: try and sign up for his mail before he signs your contract.
Marketing automation plugins facilitate spam
There’s been an explosion of “Google plugins” that facilitate spam through Gmail and G Suite. They have a similar set of features. Most of these features act to protect the spammer from spam filtering and the poor reputation that comes from purchasing lists and incessantly spamming targets. Some of these plugins have all the features of a full fledged ESP, except a SMTP server and a compliance / deliverability team.
I’ll give the folks creating these programs credit. They identified that the marketers want a way to send mail to purchased lists. But ESPs with good deliverability and reputations don’t allow purchased lists. ESPs that do allow purchased lists often have horrible delivery problems. Enter the spam enabling programs.
From the outside, the folks creating these programs have a design goal to permit spam without the negatives. What do I mean? I mean that the program feature set creates an environment where users can send spam without affect the rest of their mail.
The primary way the software prevents spam blocking is using Google, Amazon or Office 365 as their outbound mail server. Let’s be frank, these systems carry enough real mail, they’re unlikely to be widely blocked. These ISPs are also not geared up to deal with compliance the same way ESPs or consumer providers are.
There seem to be more and more of these companies around. I first learned of them when I started getting a lot of spam from vaguely legitimate companies through google mail servers. Some of them were even kind enough to inform me they were using Gmail as their marketing strategy.
I didn’t realize quite how big this space was, though. And it does seem to be getting even bigger.
Then a vendor in the space reached out looking for delivery help for them and their customers. Seems they were having some challenges getting mail into some ISPs. I told them I couldn’t help. They did mention 3 or 4 names of their competitors, to help me understand their business model.
Last week, one of the companies selling this sort of software asked me if I’d provide quotes for a blog article they were writing. This blog article was about various blocklists and how their software makes it such that their customers don’t really have to worry about blocking. According to the article, even domain based blocking isn’t an issue because they recommend using a domain completely separate from their actual domain. I declined to participate. I did spend a little time on their website just to see what they were doing.
This morning a vendor in the space joined one of the email slack channels I participate in asking for feedback on their software. Again, they provide software so companies can send spam through google outbound IPs. Discussions with the vendor made it clear that they take zero responsibility for how their software is used.
I don’t actually expect that even naming and shaming these companies facilitating spam will do anything to change their minds. They don’t care about the email ecosystem or how annoying their customers are. About the best they could do is accept opt-out requests from those of us who really don’t want to be bothered by their customers. Even that won’t really help, even domain based opt-outs are ineffective.
What needs to happen is companies like Google, Amazon and Microsoft need to step up and enforce their anti-spam policies.
Searching for a new ESP?
250OK has compiled advice about what buyers should ask when looking at new ESPs. The advice from various folks is spot on.
Changing ESPs is a big undertaking, bigger than most people expect. It’s not like changing vendors for other services. It is a process and most of the time moving creates a short term dip in deliverability. I have a lot of theories and speculation as to why, but the evidence is pretty clear. I think Mike Hillyer summed it up best: “I think the most commonly missed question is ‘will changing ESPs truly affect the outcomes we are looking to change?’”
I also liked the answers to the question about using multiple ESPs. My view is that unless there are specific requirements for different mail streams the answer is no, don’t do it. And don’t think you can keep a “backup” ESP with “partially warmed IPs” and be able to turn it on as disaster recovery. Email doesn’t work that way.
It’s an article well worth a read.
Arguing against the anti-spam policy
Not long ago I was talking with a colleague who works for an ESP. She was telling me about this new client who is in the process of negotiating a contract. Normally she doesn’t get involved in negotiations, but the sales group brought her. It seems this new client is attempting to remove all mention of the anti-spam policy from the contract. As she is the deliverability and compliance person, the sales people won’t agree unless compliance does.
Her sales team needs props for bringing her in to negotiate a contract where the anti-spam clause is removed.
This isn’t that unusual situation. Many well managed ESPs will include deliverability and compliance personnel in negotiations if the customer indicates they want changes to the language of the anti spam clause.
On the face of thing it seems reasonable for customers to want to negotiate compliance terms. They want to protect themselves from unexpected outages. It seems irresponsible to allow a service provider to have the ability to made such a business affecting decision.
Many folks try to negotiate their way out of anti-spam clauses. Just asking for changes isn’t a big deal. However, some companies push the issue with sales and contract folks to an extreme. They threaten to not sign if the anti-spam clauses are removed completely. 
Threatening a contract over compliance issues can poison an entire working relationship. The fact is that most people who argue about anti-spam clauses and compliance issues are people who have had problems with other ESPs in the past. For better or worse, prospects that try and remove anti-spam clauses from contracts are often problem customers.
On the compliance side, if someone is pushing hard to get the spam clause removed, they think a few different things:
March 2016: The Month In Email
Happy April! I’m just back from the EEC conference in New Orleans, which was terrific. I wrote a quick post about a great session on content marketing, and I’ll have more to add about the rest of the conference over the next week or so. Stay tuned!
Here’s a look at what caught our attention in March:
On the DMARC front, we noted that both Yahoo and mail.ru are moving forward with p=reject, and Steve offered some advice for ESPs and software developers on methods for handling this gracefully. I also answered an Ask Laura question about making the decision to publish DMARC. Look for more on that in this month’s Ask Laura questions…
Our other Ask Laura question this month was about changing ESPs, which senders do for many reasons. It’s useful to know that there will generally be some shifts in deliverability with any move. Different ESPs measure engagement in different ways, and other issues may arise in the transition, so it’s good to be aware of these if you’re contemplating a change.
In industry news, I wrote a sort of meta-post about how the Internet is hard (related: where do you stand on the great Internet vs. internet debate? Comment below!) and we saw several examples of that this month, including a privacy debacle at Florida State University. Marketing is hard, too. I revisited an old post about a fraud case where a woman sued Toyota over an email marketing “prank”. As always, my best practices recommendation for these sorts of things (and everything else!) really boils down to one thing: send wanted email.
Steve wrote extensively about SPF this month in two must-read posts, where he explained the SPF rule of ten and how to optimize your SPF records. He also wrote about Mutt, the much-loved command line email client, and marked the passing of industry pioneer Ray Tomlinson, who, in addition to his many accomplishments, was by all accounts a very thoughtful and generous man.
Finally, I occasionally like to take a moment and follow the twisty paths that lead to my spam folder. Here’s a look at how Ugg spams my email doppelganger, MRS LAURA CORBISHLEY. In other spam news, there’s a lot of very interesting data in the recent 10 Worst list from Spamhaus. Take a look if you haven’t seen it yet.
February 2016: The Month in Email
Happy March! Here’s a look back at our last month of email adventures. It was a busy few weeks for us with the M3AAWG meeting in San Francisco. We saw lots of old friends and met many new people — all in all, a success, despite the M3AAWG plague we both contracted. Hot topics at the conference included DMARC, of course, and I took the opportunity to write up a guide to help you determine if you should publish a DMARC policy.
It was a busy few weeks for us with the M3AAWG meeting in San Francisco. We saw lots of old friends and met many new people — all in all, a success, despite the M3AAWG plague we both contracted. Hot topics at the conference included DMARC, of course, and I took the opportunity to write up a guide to help you determine if you should publish a DMARC policy.
On the subject of advice and guidance, Ask Laura continues to be a popular column — we’ve had lots of interesting questions, and are always looking for more general questions about email delivery. We can’t tackle specifics about your program in this column (get in touch if we can help you with that directly) but we can help with questions like “Will our ESP kick us off for mailing purchasers?” or “Help! I’m confused about authentication.”
Continuing on the authentication front, I noted that Gmail is starting to roll out some UI to indicate authentication status to users. It will be interesting to see if that starts to affect user (or sender) behavior in any way. In other interesting industry news, Microsoft has implemented an Office 365 IP Delisting page. I also wrote a followup post to my 2015 overview of the state of ESPs and purchased lists — it’s worth checking out if this is something your business considers.
I wrote a post about security and backdoors, prompted by both the FBI/Apple controversy and by Kim Zetter’s talk at M3AAWG about Stuxnet. These questions about control and access will only get more complicated as we produce, consume, store, and share more data across more devices.
Speaking of predictions, I also noted my contribution to a great whitepaper from Litmus that explores the state of Email Marketing in 2020.
As always, we looked at some best practices this month. I wrote up some of my thoughts about data hygiene following Mailchimp’s blog post about the value of inactive subscribers. As always, there isn’t one right answer, but there’s a lot of good food for thought. And more food for thought: how best practices are a lot like public health recommendations. As with everything, it comes down to knowing your audience(s) and looking at the relationship(s), which, as you know, is a favorite subject around here.
Mandrill changes
Last week Mandrill announced that they were discontinuing their free services and all customers would be required to have a corresponding paid Mailchimp account.
Read MorePurchased lists and ESPs: 9 months later
It was about 8 months ago I published a list of ESPs that prohibit the use of purchased lists. There have been a number of interesting responses to that post.
ESPs wanted to be added to the list
The first iteration of the list was crowdsourced from different ESP representatives. They shared the info they had with each other. With their permission, I put it together into a post and published it here. Since then, I’ve had a trickle of ESPs asking to be added to the list. I’m happy to add any ESP. The only requirement is a privacy policy (or AUP) that states no purchased lists.
People reference the list regularly
I’ve had a lot of ESP deliverability folks send thanks for writing this post. They tell me they reference it regularly when dealing with clients. It’s also been listed as “one of the best blog posts of 2015” by Pardot.
Some 2016 predictions build on the post
I’ve read multiple future predictions that talk about how the era of purchased lists is over. I don’t think they’re wrong. I think that purchased lists are going to be deliverability nightmares on an internet where users wanting a mail is a prime factor in inbox deliverability. They’re already difficult to deliver, but it’s going to get worse.
Not everyone thinks this is a good post. In fact, I just recently got an comment about how wrong I was, and… well, I’ll just share it because I don’t think my summary of it will do it any justice.
Buying lists costs more than just money
 I’ve been talking to a lot of companies recently who are dealing with some major delivery challenges probably related to their practice of purchasing lists and then sending advertising to every address on the list. They assure me that their businesses would be non-viable if they didn’t purchase lists and it has to be that way.
I’ve been talking to a lot of companies recently who are dealing with some major delivery challenges probably related to their practice of purchasing lists and then sending advertising to every address on the list. They assure me that their businesses would be non-viable if they didn’t purchase lists and it has to be that way.
Maybe that’s true, maybe it is more cost effective to purchase lists and send mail to them. I know, though, that their delivery is pretty bad. And that a lot of the addresses they buy never see their email. And that they risk losing their ESP, or they risk being SBLed, or they risk being blocked at Gmail, or they risk bulk foldering at Hotmail. There are a lot of risks to using purchased lists.
The reality is it’s only getting harder to mail to purchased lists and it’s getting more expensive to mail purchased lists. Paying for the list is a small part of the cost of using them.
Other costs incurred by companies using purchased lists include:
1) Having multiple ESPs. There are certainly legitimate reasons for companies to use different ESPs but there is a cost associated with it. Not only do they have to pay for duplicate services, but they spend a lot of employee time moving lists and recipients around to see who might have the better delivery today.
2) Multiple domains and brand new websites for every send. Landing pages are good marketing and are normal. But some ISPs track the IPs of the landing sites, and those IPs can get their own poor reputation. To get around it, senders using purchased lists often have to create new websites on new IPs for every send.
3) Complicated sending schedules. Sending schedules aren’t dictated by internal needs, they’re dictated by what ISP is blocking their IPs or domains (or even ESP) right now.
All of these costs are hidden, though. The only cost on the actual bottom line is the money they spend for the addresses themselves and that’s peanuts. Because, fundamentally, the folks selling addresses have no incentive to take any care in collecting or verifying the data. In fact, any verification they do only cuts into their profit, as buyers won’t actually pay for the verification and data hygiene and it also reduces the size of the lists they can sell.
And, no, data hygiene companies that look for traps and bounces and “bad addresses” don’t take a bad list and make it good. They just take a bad list and make it a little less bad. If the recipients don’t want the mail, all the hygiene in the world isn’t going to get that message into the inbox.
Outsourcing address collection to list selling companies is more expensive than it looks on paper. That doesn’t stop anyone from building a business around purchased lists, though.
Dealing with blocklists, deliverability and abuse people
There are a lot of things all of us in the deliverability, abuse and blocklist space have heard, over and over and over again. They’re so common they’re running jokes in the industry. These phrases are used by spammers, but a lot of non-spammers seem to use them as well.
The most famous is probably “I’m sure they’ll unblock me if I can just explain my business model.” Trust me, the folks blocking your mail don’t want to hear about your business model. They just want you to stop doing whatever it is you’re doing. In fact, I’m one of the few people in the space who actually wants to hear about your business model – so I can help you reach your goals without doing things that get you blocked.
A few months ago, after getting off yet another phone call where I talked clients down from explaining their business model to Spamhaus, I put together list of phrases that senders really shouldn’t use when talking to their ESP, a blocklist provider or an abuse desk. I posted it to a closed list and one of the participants put it together into a bingo card.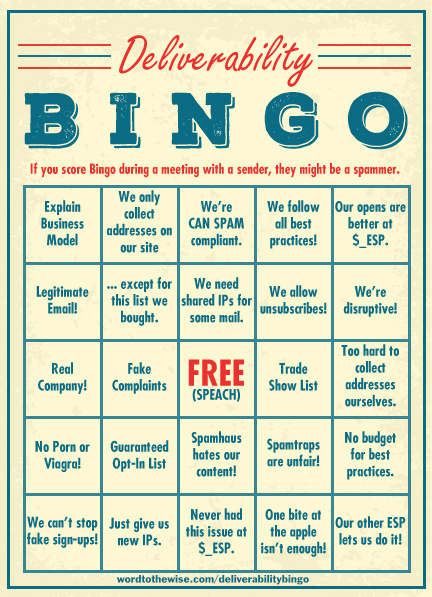
A lot of these statements are valid marketing and business statements. But the folks responsible for blocking mail don’t really care. They just want their users to be happy with the mail they receive.
May 2015: The Month in Email
Greetings from Dublin, where we’re gearing up for M3AAWG adventures.
In the blog this month, we did a post on purchased lists that got a lot of attention. If you’ve been reading the blog for any length of time, you know how I feel about purchased lists — they perform poorly and cause delivery problems, and we always advise clients to steer clear. With your help, we’ve now compiled a list of the ESPs that have a clearly stated policy that they will not tolerate purchased lists. This should be valuable ammunition both for ESPs and for email program managers when they asked to use purchased lists. Let us know if we’re missing any ESPs by commenting directly on that post. We also shared an example of what we saw when we worked with a client using a list that had been collected by a third party.
In other best practices around addresses, we discussed all the problems that arise when people use what they think are fake addresses to fill out web forms, and gave a nod to a marketer trying an alternate contact method to let customers know their email is bouncing.
We also shared some of the things we advise our clients to do when they are setting up a mailing or optimizing an existing program. You might consider trying them before your own next send. In the “what not to do” category, we highlighted four things that spammers do that set them apart from legitimate senders.
In industry news, we talked about mergers, acquisitions and the resulting business changes: Verizon is buying AOL, Aurea is buying Lyris, Microsoft will converge Office365/EOP and Outlook.com/Hotmail, and Sprint will no longer support clear.net and clearwire.net addresses.
Josh posted about Yahoo’s updated deliverability FAQ, which is interesting reading if you’re keeping up on deliverability and ESP best practices. He also wrote about a new development in the land of DMARC: BestGuessPass. Josh also wrote a really useful post about the differences between the Mail From and the Display From addresses, which is a handy reference if you ever need to explain it to someone.
And finally, I contributed a few “meta” posts this month that you might enjoy:
We're all targets
Last week, another email provider announced their systems had a security incident. Mandrill’s internal security team detected unusual activity and took the servers offline to investigate. While there’s no sign any data was compromised or servers infiltrated, Mandrill sent an email to their customers explaining the incident was due to a firewall rule change.
Email service providers are a high value target for hackers, even if all they have is email addresses. Selling the email addresses is extremely profitable for hackers who can either sell the list outright or sell access to the list. In addition to gaining access to the email addresses, hackers often use the ESP to send these messages essentially stealing the ESP’s reputation to deliver the spam.
It was just over four years ago when a number of major ESPs were targets of a large attack and multiple ESPs were compromised. Earlier this month, three people were arrested for their roles in the attack. While the attacks four years ago were primarily spear phishing attacks, the security incident at Mandrill shows that hackers and botnets are actively probing the ESP’s network looking for access or known vulnerabilities. Spear phishing is an attempt to gain unauthorized access to a system by specifically targeting an individual, group, or organization. The scam attempts to have the user to click a link to infect their computer and network or capture their user id and password via a fake website. The scam email may appear to be sent from the company’s security or human resources department, but the email is either forged or another user’s account has been compromised.
Just because recent arrests have been made does not mean the threat is over. Systems often change, are upgraded, and are integrated with many additional services and systems can become vulnerable. Security will never be a set and forget policy. In the last 12 months there has been two significant vulnerabilities discovered, first Heartbleed and second was POODLE. Security professionals from all industries had to react quickly to secure their systems and hackers immediately began probing for systems that were unpatched. GFI reports there were over 7,000 vulnerabilities discovered in 2014 with 24% of them being rated as high severity. Security must not only cover servers, but the transmission of the data internally and with third-party vendors, and the workstations of employees.
IT and security professionals must be ever vigilant in protecting their network and their customers data. SANS Institute provides a number of security control best practices including a document on Data Protection. The control recommendations range from quick wins to advanced considerations such as monitoring all traffic leaving the organization and being able to detect any unauthorized or unusual transfer of data, blocking access to file transfer protocols and file sharing websites, performing annual reviews of all keys, certifications, and security procedures.
One of the best ways to help the entire industry to be secure is to be transparent and open when incidents happen. Mandrill has published a blog post with the results of their investigation.
ESPs and consolidation
Earlier this week Bloomberg news reported that an anonymous source told them Verizon was looking to acquire or investigate a partnership with AOL. It didn’t take long for the Verizon CEO to quash the acquisition rumors. Acquisitions and partnerships have always been around in technology, this is nothing new. But it made me think a little bit about the acquisitions and mergers in the ESP space.
The last 2 years have seen unexpected purchases of ESPs. Oracle bought Eloqua. Deluxe acquired Vertical Response. IBM has acquired a number of players in the email space, including parts of mail.com, SilverPop and Pivotal Veracity. eBay acquired e-Dialog. Salesforce acquired ExactTarget. Big companies seem to use the acquisition process to acquire the technology needed to send mail to and on behalf of their customers.
I’ve heard some people claim this is the beginning of the end of the stand alone ESP. I disagree. I think there is enough market demand to support stand alone ESPs. But the market is crowded and there are a lot of ESPs out there. There will be some consolidation. Some ESPs will be bought, either for their technology or their staff. Some ESPs will change and add more features. Some big companies will decide to install big appliances to run their own marketing in house.
Things will change but that’s what happen as a market matures. And the ESP market is maturing.
Who do you think will be bought next?
Top Commented Blog Posts on WttW in 2014
Here are the top 6 most commented on blog topics our Industry News & Analysis blog.
Read MoreWho pays for spam?
A couple weeks ago, I published a blog post about monetizing the complaint stream. The premise was that ESPs could offer lower base rates for sending if the customer agreed to pay per complaint. The idea came to me while talking with a deliverability expert at a major ESP. One of their potential customer wanted the ESP to allow them to mail purchased lists. The customer even offered to indemnify the ESP and assume all legal risk for mailing purchased lists.
While on the surface this may seem like a generous offer, there aren’t many legal liabilities associated with sending email. Follow a few basic rules that most of us learn in Kindergarten (say your name, stop poking when asked, don’t lie) and there’s no chance you’ll be legally liable for your actions.
Legal liability is not really the concern for most ESPs. The bigger issues for ESPs including overall sending reputation and cost associated with resolving a block. The idea behind monetizing the complaint stream was making the customer bear some of the risk for bad sends. ESP customers do a lot of bad things, up to and including spamming, without having any financial consequences for the behavior. By sharing in the non-legal consequences of spamming, the customer may feel some of the effect of their bad decisions.
Right now, ESPs really protect customers from consequences. The ESP pays for the compliance team. The ESP handles negotiations with ISPs and filtering companies. The cost of this is partially built into the sending pricing, but if there is a big problem, the ESP ends up shouldering the bulk of the resolution costs. In some cases, the ESP even loses revenue as they disconnect the sender.
ESPs hide the cost of bad decisions from customers and do not incentivize customers to make good decisions. Maybe if they started making customers shoulder some of the financial liability for spamming there’d be less spamming.
Role accounts, ESPs and commercial email
There was a discussion today on a marketing list about role accounts and marketing lists. Some ESPs block mail to role accounts, and the discussion was about why and if this is a good practice. In order to answer that question, we really need to understand role accounts a little more.
Read MoreGmail FBL update
Last week Gmail started contacting ESPs that signed up for their new FBL with more information on how to set up mailings to receive FBL emails.
One of the struggles some ESPs are having is the requirement for DKIM signing. Many of the bigger ESPs have clients that sign with their own domains. Gmail is telling these ESPs to insert a second DKIM signature to join the FBL.
There are a couple reasons this is not as simple or as doable as Gmail seems to think, and the challenges are technical as well as organizational.
The technical challenges are pretty simple. As of now, not all the bulk MTAs support multiple signatures. I’ve heard that multiple signatures are being tested by these MTA vendors, but they’re not in wide use. This makes it challenging for these ESPs to just turn on multiple signatures. For ESPs that are using open source software, there’s often a lot of customization in their signing infrastructure. Even if they have the capability to dual sign, if they’re not currently using that there is testing needed before turning it on.
None of the technical challenges are show stoppers, but they are certainly show delayers.
The organizational challenges are much more difficult to deal with. These are cases where the ESP customer doesn’t want the ESP to sign. The obvious situation is with large banks. They want everything in their infrastructure and headers pointing at the bank, not at their ESP. They don’t want to have that second signature in their email for multiple reasons. I can’t actually see an ESP effectively convincing the various stakeholders, including the marketing, security and legal staff, that allowing the ESP to inset a second signature is good practice. I’m not even sure it is good practice in those cases, except to get stats from Gmail.
Hopefully, Gmail will take feedback from the ESPs and change their FBL parameters to allow ESPs to get information about their customers who sign with their own domain.
Spamhaus on ESPs
Promoted from yesterday’s comments, Spamhaus comments on my discussion of filtering companies getting tired of ESPs.
You hit the nail square on, Laura.
As Laura knows but many here might not, I am with the Spamhaus project. At one time I was leading efforts to clean up ESP spam. I am not deeply involved with ESP listings any longer. I can however testify that ESPs ask Spamhaus volunteers for a great deal of information about their SBL listings, considerably more than most ISPs or web hosting companies. Certain team members avoid ESP listings except in extreme cases because they don’t want to spend that much time on one SBL.
Whilst I was doing many ESP listings, I attempted to provide requested information, often at great length, with mixed results. In one notable case, an ESP that I provided with a report on hits from that ESP’s IPs on our spamtraps took that report and turned around their entire business. They had been an average ESP: not worse than most ESPs, but not better either. It’s been about three years now. This ESP is now in any list of the least spam-friendly two or three ESPs in the business. I’m honored to have been able to contribute to that change, am delighted at the results, and have learned a great deal from that ESP’s abuse team, which is superb.
That hasn’t happened often, though. I’ve provided similar reports to a number of other ESPs; I try not to play favorites. It is Spamhaus policy not to treat ISPs, ESPs, web hosts, and others whose IPs are listed for spamming differently except based upon our observations of which responds to spam issues effectively and which do not. I would also rather see a spam problem fixed than a spammer terminated just to move somewhere else and continue to spam.
The spam flow from many ESP customers that I reported to the ESP dropped, then slowly rose to previous and often higher levels. There are strings of SBL listings as a spam problem is mitigated, then inexplicably (according to the ESP) comes back. I do not find most of those recurrences inexplicable. I conclude, in many cases, that the ESP is unwilling to do the proactive work necessary to catch most spam before it leaves their IPs, even when they know what needs to be done.
To make matters clear, the ESP representatives that I communicate with are not usually to blame for this problem. Their managers and the policymakers at the ESP are to blame. The decisionmakers at the ESP are not willing to require paying customers to adhere to proper bulk email practices and standards and enforce permanent sanctions against most who fail to do so.
Granted, some customers resist not because they are deliberately spamming non-opt-in email addresses, but because they think that quantity (of email) is more important than quality. Such customers don’t want to see lists shrink even when those lists are comprised largely of non-responsive deadwood email addresses. Such customers send a great deal of spam and annoy a great many of our users, who really do not care whether the spam problem is due to carelessness or deliberate action.
In other cases, of course, ESP customers resist following best practices because they cannot. They are mailing email appended and purchased lists. If they don’t maintain some sort of plausible deniability about the sources of those lists, they know that we will list their IPs (at the ESP and elsewhere) and refuse to remove those listings til they do.
In either case, an ESP that is unwilling to impose sanctions on customers whose lists persist in hitting large numbers of spamtraps after repeated mitigation attempts needs to fire those customers. Otherwise it is failing to act as a legitimate bulk emailer. Such ESPs must expect to see their IPs blocked or filtered heavily because they deliver such large quantities of spam compared to solicited email.
Abuse it and lose it
Last week I blogged about the changes at ISPs that make “ISP Relations” harder for many senders. But it’s not just ISPs that are making it a little more difficult to get answers to questions, some spam filtering companies are pulling back on offering support to senders.
For instance, Cloudmark sent out an email to some ESPs late last week informing them that Cloudmark was changing their sender support policies. It’s not that they’re overwhelmed with delisting requests, but rather that many ESPs are asking for specific data about why the mail was blocked. In December, Spamcop informed some ESPs that they would stop providing data to those ESPs about specific blocks and spam trap hits.
These decisions make it harder for ESPs to identify specific customers and lists causing them to get blocked. But I understand why the filtering companies have had to take such a radical step.
Support for senders by filtering companies is a side issue. Their customers are the users of the filtering service and support teams are there to help paying customers. Many of the folks at the filtering companies are good people, though, and they’re willing to help blocked senders and ESPs to figure out the problem.
For them, providing information that helps a company clean up is a win. If an ESP has a spamming customer and the information from the filtering company is helping the ESP force the customer to stop spamming that’s a win and that’s why the filtering companies started providing that data to ESPs.
Unfortunately, there are people who take advantage of the filtering companies. I have dozens of stories about how people are taking advantage of the filtering companies. I won’t share specifics, but the summary is that some people and ESPs ask for the same data over and over and over again. The filtering company rep, in an effort to be helpful and improve the overall email ecosystem, answers their questions and sends the data. In some cases, the ESP acts on the data, the mail stream improves and everyone is happy (except maybe the spammer). In other cases, though, the filtering company sees no change in the mail stream. All the filtering company person gets is yet another request for the same data they sent yesterday.
Repetition is tedious. Repetition is frustrating. Repetition is disheartening. Repetition is annoying.
What we’re seeing from both Spamcop and Cloudmark is the logical result from their reps being tired of dealing with ESPs that aren’t visibly fixing their customer spam problems. Both companies are sending some ESPs to the back of the line when it comes to handling information requests, whether or not those ESPs have actually been part of the problem previously.
The Cloudmark letter makes it clear what they’re frustrated about.
VerticalResponse acquired
The acquisition of email service providers continues. Last week Deluxe (yes, the check printing people) acquired Vertical Response. This appears to be positioning themselves to improve their collection of business services to include email marketing.
Read MoreJust… make it stop
It used to be when I’d send in a complaint to an ESP, I’d want them to take it seriously. To actually fix their customer problems. To stop their customers from spamming. To fix the broken process that resulted in their customer thinking I asked for email.
These days? These days I just want the ESP to suppress my address and make the mail stop. Even better would be suppressing the address from their entire customer base – the only addresses I send in complaints for these days are traps.
Sadly, there are ESPs out there that can’t manage to stop customers from spamming people who have reported the spam. But, I am forever the optimist and keep sending the complaints when I think someone will care.
Salesforce buying Exacttarget
Reports today say that Salesforce is buying Exacttarget for around 2.5 billion dollars.
Read MoreEvaluating usability at an ESP
Clients and random people often ask me to recommend an ESP based on “the best delivery.” I usually point out that most of the reputable ESPs are similar in terms of their delivery. There aren’t many widely used reputation services that block based on ESPs unless there is long term and ongoing problem from the ESP.
This is even more true when the ESP uses dedicated IPs for customers. ESPs that use shared IPs can have poor delivery if they don’t effectively police customers and lower the reputation of all their IP addresses.
My normal comment about ESPs is to find a price point and feature set that meets the client’s needs. Clickmail has a good post about how to evaluate an ESP for usability.
How difficult is it to get on whitelists?
Today’s question comes from Leslie J.
Just how difficult is it for a small business that runs a highly compliant mailing system to find
Read More
their way onto whitelists at the big freemail/spam filter providers?
It seems utterly impossible meaning man hours are completely wasted messing around with subjects and content when if the same business sends the very same message through any number of well know ESPs, the message will hit the inbox like the Mafia are in charge of the shooting match.
Spamming ESPs: the followup
Campaign Monitor contacted me about yesterday’s post. The phrasing I picked out of the spammers AUP matched their AUP quite closely. In fact, if you plug the AUP into Google, Campaign Monitor comes up as one of the first hits.
It was not Campaign Monitor I was talking about. In fact, the ESP I received the mail from is not on the first 8 pages of Google hits for the phrases I posted.
A similar thing happened when I posted about Dell spamming me. Dell has multiple ESPs, and one of their ESPs contacted me directly in case they were the ones Dell was spamming through. It was no surprise to me that they weren’t the ESP involved.
This is what good ESPs do. Good ESPs monitor their reputation and monitor what people are saying about them. Good ESPs notice when people claim they’re being spammed and effectively reach out to the complainers so they can investigate the claim.
Good ESPs don’t just rely on the complaint numbers to take action. They keep an eye out on social networks to see who might be receiving mail they never asked for.
Spamming ESPs
In my mailbox there is a definite uptick in spam from ESPs advertising their services.
Today’s email was from a company that has the following in their anti-spam policy:
Where do you accept reports?
One of the things that is most frustrating to me about sending in spam reports is that many ESPs and senders don’t actively monitor their abuse address. A few months ago I talked about getting spam from Dell to multiple email addresses of mine.
What I didn’t talk about was how badly broken the ESP was in handling my complaint. The ESP was, like many ESPs, an organization that grew organically and also purchased several smaller ESPs over the course of a few years. This means they have at least 5 or 6 different domains.
The problem is, they don’t effectively monitor abuse@ for those different domains. In fact, it took me blogging about it to get any response from the ESP. Unfortunately, that initial response was “why didn’t you tell us about it?”
I pointed out I’d tried abuse@domain1, abuse@domain2, abuse@domain3, and abuse@domain4. Some of the addresses were in the mail headers, others were in the ESP record at abuse.net. Three of those addresses bounced with “no such user.” In other words, I’d tried to tell them, but they weren’t accepting reports in a way I could access.
Every ESP should have active abuse addresses at domains that show up in their mail. This means the bounce address domain should have an abuse address. The reverse DNS domain should have an abuse address. The d= domain should have an abuse address.
And those addresses should be monitored. In the Dell case, the ESP did have an active abuse@ address but it was handled by corporate. Corporate dropped the ball and never forwarded the complaint to the ESP reps who could act on the spam issue.
ESPs and all senders should have abuse@ addresses that are monitored. They should also be tested on a regular basis. In the above case, addresses that used to work were disabled during some upgrade or another. No one thought to test to see if they were working after the change.
You should also test your process. If you send in a complaint, how does it get handled? What happens? Do you even have a complaint handling process outside of “count and forward”?
All large scale senders should have appropriate abuse@ addresses that are monitored. If you don’t, well, you look like a spammer.
Spear phishing
It’s been about a year since people started publicly talking about spear phishing attacks against ESPs and major emailers. There was a lot of energy put into talking about how to protect against future attacks. I have to wonder, though, how much of that talk translated into action?
What processes do you have in place to protect your company against attacks?
If you’re at an ESP, do you have the ability to scan your outgoing stream for keywords or domains?
If you’re a brand, have you implemented restrictions on which employees have access to your databases?
What have you done since the last set of attacks? Are you vulnerable if new attacks start?
More information on ESP attacks:
Be on the lookout
Time for a real security response
Email attacks
ESPs, complaints and spam
Steve wrote a while back about how Mailchimp handled his complaint.
Sadly, I have a counter example from recently.
Just go read here…
I wrote earlier this week about bad ways to evaluate and choose an ESP. It was all going to end today in an insightful and profound post telling all of you exactly how to find the best ESP.
Then Smartinsights published an insightful and useful article on choosing an ESP yesterday.
So, yeah, just go read what Jordie has to say. I have a couple other things to add, but I’ll drop those in another post.
Gmail reports spear phishing attack
No one, it seems, is immune from account compromise attempts. Today Google reported they had identified a systemic campaign to compromise Gmail accounts belonging to “senior U.S. government officials, Chinese political activists, officials in several Asian countries (predominantly South Korea), military personnel and journalists.”
Google offers a number of solutions for users, including the ability to add 2 factor authentication to your Gmail account. I strongly recommend anyone who uses Gmail to do this.
This isn’t a security blog, but email is one of the major vectors used to infect machines. We’ve seen numerous break ins targeting email senders and ESPs, resulting in customer and recipient data being stolen and then used for spam. Everyone who uses email needs to be aware of the risks and maintain their email account integrity. Be careful clicking links in emails. Be careful opening webpages. Keep your antivirus software up to date.
Everyone is a target.
Email marketing firm smacked by the SEC
Yes, the SEC. Really.
Apparently the email marketing firm mUrgent, which provides services to the restaurant and hospitality industry also had a side business. According to the complaint filed by the SEC last month, they had an entire boiler room set up to sell shares for their non-existent IPO.
I’d never heard of this firm before, so I did a little digging. First step, check out their website.
Be on the lookout
I’m hearing more rumors of ESPs seeing customer accounts being compromised, similar to what happened with The Children’s Place.
Read MoreGoodmail shutting down
Yesterday Goodmail sent out mail to all their customers announcing they are ceasing operations and taking all their token generators offline as of 5pm pacific on February 8th.
While this is a bit of a surprise on one level, I’m not that shocked. Ken Magill mentioned in August that Goodmail was on the sales block and rumors have been circulating for weeks about significant changes coming to Goodmail.
Goodmail has struggled to find a market since they first started. At one point they were even giving services away to customers at partner ESPs. Despite the free service, people at some of those ESPs told me they were having difficulty getting customers to adopt Goodmail.
Likewise, on the ISP side, Goodmail didn’t seem to have much penetration into the market. They had AOL, Yahoo and some cable companies, but not much else. And as of early last year, Yahoo removed the Goodmail machines.
I think the real underlying problem was that most companies who are doing things well don’t need certification services. Sure, there are a couple exceptions but in general anyone who is sending good mail is getting to the inbox. Even for companies where delivery was not quite as good as they might want, the marginal improvement at those ISPs that do use Goodmail was not sufficient to justify the cost of Goodmail services.
While I have the utmost respect for the Goodmail management team I think this result was almost inevitable. I never got the impression they valued the end recipient quite as much as the ISPs do. That was just one thing that lead me to believe they just didn’t seem to understand the email ecosystem quite the way that a certification service should.
I echo Dennis’ thoughts and well wishes towards the Goodmail folks. The experiment in sender financed delivery was well worth doing and I think they did it as well as anyone could have.
ESPs being targeted
There has been an ongoing, concerted attack against ESPs recently. Today ReturnPath published some of what is known about the attack.
Read MoreStandard Email Metrics
The EEC has been working on standardizing metrics used in email marketing. They have published a set of definitions for different terms many email marketers use. They published their Support the Adoption of Email Metrics (S.A.M.E) guide in June.
Under the new EEC definitions an open is measured when either a tracking pixel is displayed or a user clicks on any link in the email, including the unsubscribe link. Open rate is defined as the number of opens (either unique or total) divided by the number of accepted emails. Accepted emails equals the number of emails sent minus the number of emails rejected by the ISP for any reason.
The authors do caution, however, that even their measurements may under count the number of email subscribers that actually open or read an email. Some readers don’t load images or click on links but happily read and digest the content being sent. Others may not click on a link but actually visit a website or brick and mortar store to purchase something based on the email.
Overall, I think the definitions created by the S.A.M.E. group accurately reflect the things they want to measure within the limits of what is actually measurable. Their definitions won’t affect conversations in the short term, but are likely to drive change to standard terminology over the longer term. I do strongly encourage people to grab a copy of their document and see how their definitions compare with your current measurements.
My ISP might get blacklisted
The last of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreI want to avoid network outages
Number six of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreThis is why the ISPs throw up their hands at senders
I recently saw a question from an ESP rep asking if anyone had a personal contact at a particular ISP. The problem was that they had a rejection from the ISP saying: 571 5.7.1 too many recipients this session. The ESP was looking for someone at the ISP in order to ask what the problem was.
This is exactly the kind of behaviour that drives ISPs bonkers about senders. The ISP has sent a perfectly understandable rejection: “5.7.1: too many recipients this session.” And instead of spending some time and energy on the sender side troubleshooting, instead of spending some of their own money to work out what’s going on, they fall back on asking the ISPs to explain what they should do differently.
What, exactly, should you do differently? Stop sending so many recipients in a single session. This is not rocket science. The ISP tells you exactly what you need to do differently, and your first reaction is to attempt to mail postmaster@ the ISP and then, when that bounces, your next step is to look for a personal contact?
No. No. No.
Look, connections and addresses per connections is one of the absolute easiest things to troubleshoot. Fire up a shell, telnet to port 25 on the recipient server, and do a hand SMTP session, count the number of receipts. Sure, in some corporate situations it can be a PITA to do, sometimes you’re going to need to get it done from a particular IP which may be an interface on an appliance and doesn’t have telnet or whatever. But, y’know what? That Is Your Job. If your company isn’t able to do it, well, please tell me so I can stop recommending that as an ESP. Companies have to be able to test and troubleshoot their own networks.
Senders have been begging ISPs for years “just tell us what you want and we’ll bother you less.” In this case the ISP was extremely clear about what they want: they want fewer recipients per connection. But the ESP delivery person is still looking for a contact so they can talk to the ISP to understand it better.
This is why the ISPs get so annoyed with senders. They’re tired of having to do the sender’s job.
Return Path Changes certification standards
Return Path recently announced changes to their certification program. They will no longer be certifying 3rd party mailers.
Read MoreESPs leaking email addresses
Two of my tagged email addresses started getting identical pharma spam over the weekend. It is annoying me because I am now getting spam in a mailbox that was previously spam free. The spam is overwhelming the real traffic and I am having to make some decisions about what to do with the email addresses and their associated accounts with the companies I gave them to.
One thing I did notice, though, is that both companies use iContact as their ESP. A cursory check of my other mailboxes shows that none of my other tagged addresses are mailed through iContact. I don’t think it’s very likely that these two individual, unrelated companies made deals with the same spammers to sell address lists at the same time. It’s much more likely that there was a compromise somewhere and address lists were stolen.
Edit: Checked my other account and, likewise, I’m getting the same spam to a 3rd address serviced by iContact. I’ve sent mail to all 3 companies involved and we’ll see how they react.
And, as I was thinking about this, iContact just laid off a bunch of staff about the same time they announced their partnership with Goodmail. Based on past history with companies in this situation, it seems possible this is a disgruntled former employee. I’ve also seen reports from other people noticing spam to addresses given to iContact customers.
Resource hogging
Today on SFGate there was an article talking about how some Bay Area coffee houses were struggling to deal with workers who purchase one cup of coffee and then camp out all day using the free wifi. The final paragraph quoted one of the campers.
Read MoreLessons from the good, the typical and the ugly
What can smart ESPs learn from my recent series The good, The typical and The ugly?
Read MoreTypical ESPs
Yesterday, I gave examples of good ESPs and the benefits that their customers receive from their high standards and standards enforcement. Today I’ll be talking about typical ESPs and the things they say and do.
A few caveats before I get started. Most of these quotes are composite quotes. I am not quoting one particular person or ESP, rather, the statement is representative of a common view point. None of these quotes is a one off, all of these quotes have been said by more than one person. These where chosen as a representation of some of the attitudes and policies that leads ISPs and filtering companies to throw up their hands at the ESPs.
What makes a good ESP?
There are a number of things that make a responsible ESP, including setting and enforcing standards higher than those set by the ISPs.
One of the responsible ESPs is Mailchimp. (Full disclaimer, I do consult for Mailchimp.) This ESP focuses on businesses with small to medium sized lists. They screen new customers for source of permission as well as mail content.
As well as putting a human in the loop and identifying problem customers manually, they have also developed an automated process that predicts the likelihood that a certain customer will violate their standards. This process is very similar to the reputation process in place at many ISPs. Customers that are flagged as potential problems are reviewed by staff members who contact the customer for further clarification.
What’s the benefit of this process? A good reputation, a clean customer base and positive notice by the ISPs. In fact, just recently I was contacted by one of the very large consumer ISPs, confirming that Mailchimp is one of my clients. He informed me that he’d noticed a few of the Mailchimp IPs had a really high reputation but weren’t whitelisted. He asked me to send him all of their IPs so he could make sure all their IPs were whitelisted.
Proactive auditing of customers and predictive modeling of mailing results is working for Mailchimp and their customers.
Some ESPs have aggressive cancellation policies, which helps them police their networks and their customers. I often encounter former customers of these ESPs, either as direct clients or as customers of my ESP clients. In one case, I was asking around about a new client at their old ESP. “They tell me they left you under their own power and there was no spam issue involved, can you comment?” The policy person would not comment specifically about that client, but did comment that “95% of our former customers were disconnected for cause.”
These are two examples of ESPs that are working hard to minimize the amount of unwanted mail going through their network. They have invested time and energy into tools and staff to monitor the network. Staff is empowered to make decisions about customers and management believes no customer is “to big to disconnect.”
Tomorrow we’ll look at typical ESPs and their normal practices.
The good, the typical and the ugly
In the theme of the ongoing discussions about ESPs and their role in the email ecosystem, I thought I’d present some examples of how different ESPs work.
The good ESPs are those that set and enforce higher standards than the ISPs. They invest money and time in both proactive and reactive policy enforcement. On Monday I’ll talk about these standards, and the benefits of implementing these policies.
The typical ESPs are those that have standards equivalent to those of the ISPs. They suspend or disconnect customers when the customers generate problems at the ISPs. They have some proactive policy enforcement, but most of their enforcement is reactive. On Tuesday I’ll talk about these standards and how they’re perceived by the ISPs and spam filtering companies.
The ugly ESPs are those that have low standards and few enforcement policies. They let customers send mail without permission. Some of the ugly ESPs even abuse other ESPs to send some of their mail, thus sharing their bad reputations across the industry. On Wednesday I’ll look at some of their practices and discuss how they affect other players in the industry.
A series of warnings
Over the last month there have been a number of people sounding warnings about coming changes that ESPs are going to have to deal with. There has been mixed reaction from various people, many people who hear these predictions start arguing with the speaker. Some argue that our predictions are wrong, others argue that if our predictions are right then the senders will just start acting more like spammers.
I have put together a collection of links from recent blog posts looking towards the future and how things may be changing.
Blocking of ESPs
There’s been quite a bit of discussion on my post about upcoming changes that ESPs will be facing in the future. One thing some people read into the post is the idea that ISPs will be blocking ESPs wholesale without any regard for the quality of the mail from that company.
The idea that ESPs are at risk for blocking simply because they are ESPs has been floating around the industry based on comments by an employee at a spam filter vendor at a recent industry conference.
I talked to the company to get some clarification on what that spam filtering company is doing and hopefully to calm some of the concerns that people have.
First off, and probably most important, is that the spam filtering company in question primarily targets their service to enterprises. Filtering is an important part of this service, but it also handles email archiving, URL filtering and employee monitoring. The target market for the company is very different than the ISP market.
The ISPs are not talking about blocking indiscriminately, they are talking about blocking based on bad behavior.
Secondly, this option was driven by customer request. The customers of the spam filtering appliance were complaining about “legitimate” mail from various ESPs. Despite being reasonable targeted the mail was unrequested by the recipient. While ESPs use FBLs and other sources of complaints to clean complainers off rented or epended lists at ISPs, the option is not available for mail sent to corporations. Enterprises don’t, nor should they have to, create and support FBLs. Nor should employees be expected to unsubscribe from mail they never requested.
This option is the direct result of ESPs allowing customers to send spam.
Thirdly, this option is offered to those customers who ask for it. It is not done automatically for everyone. The option is also configurable down to the end user.
While I haven’t seen the options, nor which ESPs are affected, I expect that the ones on the list are the ones that the filtering vendor receives complaints about. If you are not allowing your customers to send spam, and are stopping them from buying lists or epending, then you probably have not come to the attention of the filtering company and are not on the list of ESPs to block.
What she said
Jamie Tomasello on the Cloudmark Blog:
ESPs who require and enforce best permission practices should be applying peer and industry pressure within the ESP community to adopt these policies. Ultimately, ESPs need to take responsibility for their clients’ practices. If you are aware that your clients are engaging in questionable or bad practices, address those issues before contacting an ISP or anti-spam vendor to resolve the issue.
Read More