Fbl
When opens hurt reputation
Podia has scraped the Word to the Wise blog and I’m currently receiving an ongoing drip campaign from them absolutely begging me to mention them in my blog post on cold emails.
Read MoreAOL FBL petering out
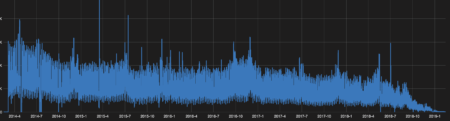
This is pretty clear evidence that AOL accounts are being transferred to the Oath / Verizon Media / Yahoo backend.
Read MoreReturn Path FBL page down
As of 6pm UTC the fbl.returnpath.com website is down. Return Path are aware of the issue and are working to fix it. I haven’t seen any estimated time to fix.
Read MoreMarking mail as spam says what?
I wear a number of hats and have a lot of different email addresses. I like to keep the different email addresses separate from each other, “don’t cross the streams” as it were.
Oh, Microsoft
Things have been a little unsettled at Microsoft webmail properties over the last few months. A number of ESPs reported significantly increased deferrals from Microsoft properties starting sometime late in November. Others saw reduced open rates across their customer base starting in late October. More recently, people are noticing higher complaint rates as well as an increase in mail being dropped on the floor. Additionally, Return Path announced certification changes at the end of November lowering the Microsoft overall complaint rate to 0.2%, half of what is was previously.
Overall, sending mail to Microsoft is a challenge lately. This is all correlated with visible changes which may seem unrelated to deliverability, but actually are. What are the changes we know about?
Looking forward
I had a number of very good talks with folks at the Email Innovations Summit earlier this week. I’m still digesting it all. It’s clear that getting to the inbox isn’t a solved problem. Around a decade ago I figured that the explosion of complaint feedback loops would make my job obsolete. That more data would mean anyone could manage delivery. That’s not the case for a couple reasons. The biggest is that filters don’t look just at complaints and there aren’t FBLs for all the other factors.
For whatever reason, many companies are still struggling with delivery.
Even more interesting is how changes in filters and inboxes are making it harder to measure delivery. In some ways I feel like we’re losing ground on inbox measurement. Filters changes and will keep changing, both to address emerging threats and to meet the needs and wants of subscribers. Gone are the days where Panels have their problems. Seed lists have their problems. There’s a longer blog post here, but it’s nearly the weekend and I’ve had a long week.
Hope you have something great planned.
Poor delivery at Gmail but no where else
I’ve mentioned before that I can often tell what ISP is making filter changes by what my calls are about. The last few weeks it’s been Gmail where folks are struggling to get to the inbox. One of the things most clients and potential clients have mentioned is that they’re not having any problems at the other major ISPs.
Read MoreAbuse, triage and data sharing
The recent subscription bombs have started me thinking about how online organizations handle abuse, or don’t as the case may be. Deciding what to address is all about severity. More severe incidents are handled first. Triage is critical, there’s never really enough time or resources to investigate abuse.
What makes an event severe? The answer is more complicated that one might think. Some of the things that ISP folks look at while triaging incoming complaints include:
Things you need to read
The email solicitation that made me vow to never work with this company again. When sending unsolicited email, you never know how the recipient is going to respond. Writing a public blog post calling you out can happen.
The 2016 Sparkies. Sparkpost is looking for nominations for their email marketing awards. Win a trip to Insight 2016!
5 CAN SPAM myths. Send Grid’s General Counsel speaks about CAN SPAM myths. Personally, asking for an email to unsubscribe is annoying. I never know if the unsubscribe request worked or not. Give me a link any day.
The most misunderstood statistic in email marketing. A good discussion of why raw complaint rates isn’t the metric the ISPs use, and how it can mislead folks about their email program.
Office 365 is expanding it’s DKIM signing. Terry Zink discusses the upcoming changes to how Office365 handles DKIM signatures. This is exactly the kind of changes I was talking about in my 2016 predictions post – background changes that are going to affect how we authenticate email. He even specifically calls out whether or not a particular signature is DMARC aligned or not.
Yahoo FBL confirmation problems
![]() Over the last few months I’ve seen people complaining about losing the Yahoo FBL emails with verification codes. This seems to be intermittent and no one could really explain what was going on.
Over the last few months I’ve seen people complaining about losing the Yahoo FBL emails with verification codes. This seems to be intermittent and no one could really explain what was going on.
Dale Lopez, VP of operations for V12 group, shared that their operations group discovered that one issue with the missing verification emails has to do with the length of the From: address and a port25 default settings.
In Dale’s words:
More Yahoo! Challenges
A lot of people are reporting they’re not getting confirmation emails when signing up for the new Y! FBL program. This is causing problems with folks attempting to transfer domains to the new FBL.
Will update when I hear anything.
Best practices … what are they?
“We follow all the best practices!” is a common refrain from many senders. But what does best practices really mean?
To me the bulk of best practices are related to permission, technical setup and identity.
Yahoo FBL Down
We’re seeing multiple reports that the Yahoo feedback loop stopped working some time in the past couple of days. If you’re not seeing reports, it’s not just you.
Read MoreWho pays for spam?
A couple weeks ago, I published a blog post about monetizing the complaint stream. The premise was that ESPs could offer lower base rates for sending if the customer agreed to pay per complaint. The idea came to me while talking with a deliverability expert at a major ESP. One of their potential customer wanted the ESP to allow them to mail purchased lists. The customer even offered to indemnify the ESP and assume all legal risk for mailing purchased lists.
While on the surface this may seem like a generous offer, there aren’t many legal liabilities associated with sending email. Follow a few basic rules that most of us learn in Kindergarten (say your name, stop poking when asked, don’t lie) and there’s no chance you’ll be legally liable for your actions.
Legal liability is not really the concern for most ESPs. The bigger issues for ESPs including overall sending reputation and cost associated with resolving a block. The idea behind monetizing the complaint stream was making the customer bear some of the risk for bad sends. ESP customers do a lot of bad things, up to and including spamming, without having any financial consequences for the behavior. By sharing in the non-legal consequences of spamming, the customer may feel some of the effect of their bad decisions.
Right now, ESPs really protect customers from consequences. The ESP pays for the compliance team. The ESP handles negotiations with ISPs and filtering companies. The cost of this is partially built into the sending pricing, but if there is a big problem, the ESP ends up shouldering the bulk of the resolution costs. In some cases, the ESP even loses revenue as they disconnect the sender.
ESPs hide the cost of bad decisions from customers and do not incentivize customers to make good decisions. Maybe if they started making customers shoulder some of the financial liability for spamming there’d be less spamming.
How useful are feedback loops
Things are extremely busy here and blogging is going to be light for a few weeks. I’ll be reposting some older blog posts that are still relevant for today’s email senders.
Today’s post is a repost from November 2008. I look at the whys and hows of FBLs, address some of the objections people had to them and discuss how senders should deal with FBL mail.
There has been a very long, ongoing discussion on one of my mailing lists about whether or not feedback loops are a net good or a net harm. I believe, overall, they are a net good, but there are people who believe they are not. The biggest objection is that the lawyer mandated redaction of the To: address combined with the fact that some users use the “this is spam” button to delete unwanted email, makes it difficult for some FBL recipients to sort out the real issues from the cruft.
Redaction can be a problem for some senders, particularly for the small mailing list hosted as a hobby or contribution to the community. In order to effectively deal with FBL emails, a sender needs to have tools on the email sending side and on the FBL receiving side. This is often more overhead than the volunteer list maintainer wants to handle. Unfortunately, these senders are a minority and therefore their issues are often not addressed by the ISPs.
Some of the objections and complaints about “broken” or “useless” FBLs come from people who do not really have any history for the FBLs, where they are, what they were designed for and who their target audience is. A bit of history may help explain why things are how they are.
The First FBL
The “this is spam” button evolved from the “notify AOL” button. This button was a way email recipients could notify AOL staff about any number of problems, including threats, viruses and other unwanted emails. As time went on, this was changed to “this is spam” to encourage users to report more spam so the AOL would have the data to make delivery decisions. Eventually, AOL made the decision to share that data with some senders and ISPs. The lawyers made the decision to redact the “To:” address, but not make any other changes to the message because they believe they should not be sharing subscriber email addresses with third parties. As some people correctly point out, the lawyers are not interested in hearing from non lawyers about changing this. It is possible that another lawyer may be able to put together a position paper and convince them this stance is overly cautious. I am pretty sure, though, that no one without a legal degree will be given any audience from them.
Given the success of the AOL FBL and the demand from both ESPs and ISPs for FBLs, other ISPs started offering FBLs as well. Many of them also redacted the To: address, either just following AOL’s lead or under advice of their own counsel.
That means, as senders, we are in a situation where we really cannot make the ISPs change what they’re doing. We can either adapt our own mailing practices to cope with them or we can forego the data provided by the FBL. One of the challenges in choosing to shun the whitelist at AOL that in order to qualify for whitelisting, you have to accept a FBL. For ISPs, who want to whitelist their outgoing MTAs, but have customers sending mail, maybe running small mailing lists, or who are forwarding mail to their ISP account, this can be a problem. However, any ISP needs some sort of abuse desk automation, and this automation should be able to handle FBLs. This can also be a problem for small ESPs or companies doing in-house email marketing. They buy something off the shelf to handle mail (or install mailman) that does not do VERP or otherwise enter the specific address in the email. When faced with a redacted email they cannot do anything with the complaint.
What does the FBL email tell the FBL recipient?
This really depends on what role the FBL recipient plays in the mail transport system. Bandwidth and network service providers use the FBL as an aggregate tool. They really only deal with FBL complaints if there is a change in complaint volume about an IP, they don’t treat each complaint as a valuable source of information. Typically what happens is that an ISP abuse desk notices a spike in complaints. After investigation, they may discover that a customer machine is compromised. They then notify the customer, the customer patches or disconnects the machine and the problem is fixed.
ESPs tend treat the FBL as an unsubscribe mechanism as well as a way to monitor customers. A few FBL complaints are not necessarily a sign that the sender is spamming, but once a threshold is reached the ESP delivery / abuse team addresses the issue. Spammers can get FBLs and often use them as a way to clean lists of complainants. Some really dirty spammers even suppress those complainants from all their lists.
Is a FBL useful?
This is really something that someone else cannot tell you. Some companies find FBLs to be extremely useful, even after they have had to make investments in software (either off the shelf like our Abacus software, or something custom written internally) to send mail that will survive the FBL redaction process and to handle the actual FBL email. Some companies find the FBLs to be more trouble than they are worth. The question, however, is really one only the sender can answer.
Overall, I think FBLs are more helpful than they are harmful. They do require investment on both sides of the transaction, but does encourage senders and receivers to cooperate with one another.
Clarification on monetizing complaints
There has been quite an interesting discussion in the comment stream of my earlier post about monetizing the complaint stream. I’ve found all the perspectives and comments quite interesting.
There is one thing multiple people have brought up that I don’t necessarily see as a problem. They assert that this idea will only work if all ESPs do it because customers can just say, “Well, Other ESP will let us do this and not charge us.” I don’t quite understand why this is an issue. Customers already do this. In fact, sometimes the assertion is actually true.
There are ESPs that let customers spam. There will always be ESPs that let customers spam. This is not new. Changing a pricing model isn’t going to change this.
As I was envisioning the monetization process, ESPs who wanted to do this could actually offer multiple tier pricing. The customer can choose a lower price point for their overall mail program, while assuming the cost of their recipients complaining. Or the customer can choose a higher price point and let the ESP absorb the cost of handling complaints. In either case, the customer would still have to meet the ESP’s standards for complaints and comply with their TOS.
Clearly I’m seeing the idea and industry differently than a lot of my readers. I’m interested to hear the thought process behind this so I can better understand the objection.
Monetizing the complaint stream
What if ESPs (and ISPs, for that matter) started charging users for every complaint generated? Think of it like peak pricing for electricity. In California, businesses can opt for discounted power, with the agreement that they are the first companies shut off if electrical demand exceeds supply. What if ESPs and ISPs offered discounted hosting rates to bulk senders who agreed to pay per complaint?
I see pricing scheme something like this.
Are FBLs required for a clean mail stream?
A few years ago I would have said that a good mailer could have a good mailing program without necessarily participating in FBL programs. I’m not convinced that’s true any longer. As the mailbox providers and ISPs develop more complex filtering methodologies, it’s important for senders to get any possible feedback from recipients. That press on the this-is-spam button may not actually mean the mail is spam, but it does mean that recipient really didn’t like the message.
Getting the feedback lets a sender fine tune their sending processes and better target what their recipients want to receive.
I do think that senders need to know what users are saying about their email. When users hit the T-i-S button then that is valuable information about how the recipients think about the mail. Senders really on top of things can use positive data (opens and clicks) and negative data (FBLs and unsubscribes) to monitor how wanted their email is and make adjustments to their sending stream.
Yahoo FBL problems
Multiple ESPs are reporting that the volume of Yahoo! FBL reports have slowed to a trickle over the last 24 or so hours. While we don’t know exactly what is going on yet, or if it’s on track for being fixed, there does seem to be a problem.
There has been some ongoing maintenance issues with the Yahoo! FBL, where requests for updates and changes weren’t being handled in a timely fashion. Informed speculation was the resources needed to fix the FBL modification weren’t available. The interesting question is if Y! will commit the resources to fix the FBL. I could make arguments either way. But Yahoo! gets the benefit of the this-is-spam button whether or not they send a complaint back to the sender.
5/21 5pm: Both Yahoo and Return Path (who administer the Y! FBL) are aware of the problem and are working on it.
5/21 6:30pm: Reports are flowing again according to multiple sources.
Sendgrid's open letter to Gmail
Paul Kincaid-Smith wrote an open letter to Gmail about their experiences with the Gmail FBL and how the data from Gmail helped Sendgrid find problem customers.
I know a lot of folks are frustrated with Gmail not returning more than statistics, but there is a place for this type of feedback within a comprehensive compliance desk.
Gmail FBL update
Last week Gmail started contacting ESPs that signed up for their new FBL with more information on how to set up mailings to receive FBL emails.
One of the struggles some ESPs are having is the requirement for DKIM signing. Many of the bigger ESPs have clients that sign with their own domains. Gmail is telling these ESPs to insert a second DKIM signature to join the FBL.
There are a couple reasons this is not as simple or as doable as Gmail seems to think, and the challenges are technical as well as organizational.
The technical challenges are pretty simple. As of now, not all the bulk MTAs support multiple signatures. I’ve heard that multiple signatures are being tested by these MTA vendors, but they’re not in wide use. This makes it challenging for these ESPs to just turn on multiple signatures. For ESPs that are using open source software, there’s often a lot of customization in their signing infrastructure. Even if they have the capability to dual sign, if they’re not currently using that there is testing needed before turning it on.
None of the technical challenges are show stoppers, but they are certainly show delayers.
The organizational challenges are much more difficult to deal with. These are cases where the ESP customer doesn’t want the ESP to sign. The obvious situation is with large banks. They want everything in their infrastructure and headers pointing at the bank, not at their ESP. They don’t want to have that second signature in their email for multiple reasons. I can’t actually see an ESP effectively convincing the various stakeholders, including the marketing, security and legal staff, that allowing the ESP to inset a second signature is good practice. I’m not even sure it is good practice in those cases, except to get stats from Gmail.
Hopefully, Gmail will take feedback from the ESPs and change their FBL parameters to allow ESPs to get information about their customers who sign with their own domain.
Gmail pilots new FBL
Yes, it’s true. Gmail announced last Thursday at M3AAWG that they were piloting a new Feedback loop.
The Gmail FBL is currently for ESPs only. The announcement during MAAWG was that only MAAWG ESP members were eligible. They are requiring a DKIM signature for the FBL, but ESPs using individual customer d= values can get a FBL based on IPs. They are also not providing ANY information that reveals the complainer. Gmail’s intention is only to give ESPs feedback so that ESPs can prevent abuse. They are not giving feedback so complainers can be removed.
The email has a .csv attachment that has 3 columns: date, identifier and complaint rate.
The identifier is an ESP provided customer identifier. One of the ESPs I talked to said they were adding an X-header into their emails.
I’ve heard from beta testers that there is a minimum of 100 complaints before you’ll get any report.
Reports are sent daily if there is sufficient traffic to trigger them.
If you’re a MAAWG member, check the senders list for the signup URL.
Problems with Yahoo FBL
There are a couple problems I’ve been alerted to with the Yahoo FBL today.
The first comes from Michael Ellis and is about broken FBL reporting at Yahoo.
Earthlink opens up FBL
Earlier this week I was at MAAWG and one of the Earthlink postmaster folks stopped me to tell me that Earthlink was now accepting non-ISP applications to their Feedback Loop.
In order to apply for the Earthlink FBL send an email to fblrequest@abuse.earthlink.net with the IP addresses and the FBL email address.
How difficult is it to get on whitelists?
Today’s question comes from Leslie J.
Just how difficult is it for a small business that runs a highly compliant mailing system to find
Read More
their way onto whitelists at the big freemail/spam filter providers?
It seems utterly impossible meaning man hours are completely wasted messing around with subjects and content when if the same business sends the very same message through any number of well know ESPs, the message will hit the inbox like the Mafia are in charge of the shooting match.
It's Thursday: AOL must be having problems
And, in fact, they are.
This time I’m seeing random reports of FBL failures. Some folks are seeing a significant (more than 50%) decrease in FBL emails. Other folks are reporting FBL reports that aren’t really FBL reports, but instead look like failed code output.
If you’re seeing this kind of problems it’s not just you.
As always, people at AOL are working to fix things and cooperating with people in the sending community who are having this problem. In other news, I found out last week that the one Really Smart Mail Guys I thought was still there is still at AOL but is no longer in their mail division. That means that the guys who built the AOL version of Skynet have left it to its own devices. Be afraid. Be Very Afraid.
Bounces, complaints and metrics
In the email delivery space there are a lot of numbers we talk about including bounce rates, complaint rates, acceptance rates and inbox delivery rates. These are all good numbers to tell us about a particular campaign or mailing list. Usually these metrics all track together. Low bounce rates and low complaint rates correlate with high delivery rates and high inbox placement.
More about the mail.ru FBL
Len Shneyder has a really interesting post up about the mail.ru feedback loop and the broader message this sends about the intersection of social media and email marketing. Go read it!
Read MoreNew Feedback loop
There’s a new feedback loop at mail.ru. This is a DKIM based FBL (like Yahoo) and is designed primarily for ESPs. I am hearing there is an IP based FBL for ISPs in the works, but there isn’t a firm release date for that yet.
Senders and ESPs can signup for the new FBL at http://postmaster.mail.ru/. One caveat is that you must have a mail.ru account in order to get access to the stats page and there isn’t currently an English webmail page. I tried but couldn’t get online translators to work on the signup page.
Denial
I come up against a lot of denial when talking with people about spam and email. It makes sense, nobody likes spam. Nobody wants to send spam. And I do understand the initial denial when they hear “you’re mail looks like spam” or “you spammed me.”
It often takes overwhelming evidence to convince some senders that their mail is spam. I’ve talked before about some of my clients who insist that I just “forgot” I signed up for their mail. But these aren’t the only excuses I hear.
A sender that denies all feedback about their mailing program isn’t a very good sender, though. The best thing any sender can do when faced with information is to think about why a recipient might not want their mail.
I often describe my role as a translator between marketers and IT folks. I can translate technology to marketing and back again. One of my other major roles, though, is translating uncomfortable or unwelcome recipient feedback. Many marketing programs have been significantly improved because the program maintainers took a minute to look at the feedback and use it.
Abuse Reporting Format
J.D. has a great post digging into ARF, the abuse reporting format used by most feedback loops.
If you’re interested in following along, you might find this annotated example ARF report handy.
Confirming spam reports
Someone floated the idea of having ISPs confirm that a user really wants to report a mail as spam every time they do so. The original poster was asking for comments and what we thought of such an idea.
Read MoreWhy offer a feedback loop?
Someone asked yesterday
What business advantage is there to an ISP in offering a feedback loop? I’ve never really seen one.
Read More
Gmail offering unsubscribe option
This morning Lifehacker reported that Gmail was offering an option to unsubscribe from some legitimate email lists.
Gmail’s help pages say:
Modifying RP managed FBLs
I was recently pointed out the FBL support pages for those feedback loops hosted by ReturnPath. Clicking around, they have the framework and the beginnings of a good source of information for their services. You can also open support tickets for questions and services that are not covered in their knowledge base.
Read MoreVerizon does not have a FBL
When I posted my initial cut of the ISP information page earlier this year, there was a comment asking about a Verizon FBL. At that time, I talked to some of the people-who-would-know over at Verizon and asked if they do have a FBL. The answer was a definite no.
For some reason, though, I continue to receive questions about the Verizon FBL. Based on the questions, the best I can extrapolate is that there is an ESP out there, somewhere, that states they have a Verizon FBL. It is possible, albeit unlikely, that they have a special agreement with Verizon. However, there is no generally available Verizon FBL.
If Verizon does make a FBL widely available, I will mention it here and update the ISP information page with the data. Until then, be very cautious with claims that there is a Verizon FBL.
Cox FBL update
Delivery mailing lists have been a buzz this week trying to figure out what is going on with the Cox FBL. Someone tried to sign up for the FBL and received a message saying Cox was no longer accepting applications. They forwarded the rejection to some of the mailing lists asking if anyone else had seen a similar message. Panic ensued. Rumors and futile suggestions flew wildly. OK, maybe that’s a slight exaggeration, but there did seem to be more than a little consternation and confusion about what was going on.
Everyone can stop panicking now.
Yes, Cox did stop accepting new applications for their FBL. They were swamped and overwhelmed with applications and had quite a significant backlog. One of my clients got caught in this backlog. I applied for them back in mid-October and they were just approved last week.
In order to solve the backlog problem, they shut down new applications. They will be working through the current applications and when they’ve approved all the current ones, they will start accepting new ones. I expect that it may be a couple months before they’re accepting applications again.
No need to panic. No need to email lots of people at Cox. No need to contact their FBL provider. Remain calm.
If you were lucky enough to get an application in, they will be getting to it as soon as possible. You will receive an email when you are approved.
If you have already been approved, there will be no interruption in your FBL. You will continue to receive reports during the signup hiatus.
Google Apps – where's my abuse@
Most ISP feedback loops require you to demonstrate that you’re really responsible for your domain before they’ll start forwarding reports to you. The usual way that works is pretty similar to a closed-loop opt-in signup for a mailing list – the ISP sends an email with a link in it to the abuse@ and postmaster@ aliases for your domain, and you need to click the link in one or both of the emails to continue with the feedback loop signup process.
That’s mostly there to protect you, by making sure that someone else can’t get feedback loop messages for your domain. And it’s not too difficult to do, as you should already have an abuse@ and postmaster@ alias set up, and have someone reading the abuse@ alias.
But maybe you’re using Google Apps to host your corporate email, and that’s the domain you need to use for your feedback loops. So you go to create abuse and postmaster users, but it won’t let you – you just get the error Username is reserved for email list only. Uhm, what?
Google want to police use of domains hosted on their service, so they automatically set up abuse and postmaster aliases for your domain, and any mail sent to them is handled by Google support staff. You may well be happy with Google snooping on your abuse role account, but you really need to be able to read the mail sent to it yourself too.
So what to do? Well, the way Google set things up they actually create invisible mailing lists for the two role accounts, and subscribe Google Support to the lists. In older versions of Google Apps you could make those mailing lists visible through the user interface by trying to create a new mailing list with the same name, then simply add yourself to the mailing list and be able to read your abuse@ email.
But Google broke that functionality in the latest version of the Google Apps control panel, when they renamed email lists to “groups”. If you try and create a new group with the email address abuse@ your domain you’ll get the error Email already exists in this domain, and no way to make that list visible.
So, what to do?
Well, there’s a workaround for now. If you go to Domain Settings you can select the “Current Version” of the control panel, rather than the “Next Generation” version. That gives you the old version of the control panel, where all this worked. Then you can go to User Accounts, create a new email list delivering to abuse@ and add one of your users to the mailing list. You can then set the control panel back to “Next Generation” and have access to the mailing lists via Service Settings → Email → Email Addresses.
Hopefully Google will fix this bug, but until they do here’s the step-by-step workaround:
RoadRunner FBL information
RoadRunner has decided to delay the launch of their new FBL until after the holidays. Sounds like a good idea to me, the launch is never quite as smooth as the ISP wants it to be. People are checking out and trying to troubleshoot the problems while also dealing with all the extra stress and demands of the holiday season is asking for trouble. The good news is that they are now planning on running the two FBLs in parallel for a few weeks, instead of ending one then starting the other.
Read MoreExcite (BlueTie) FBL live
ReturnPath announced today that the BlueTie FBL is live. You can signup for the new FBL at http://feedback.bluetie.com/.
Read MoreFeedback loops: net benefit or net harm?
There has been a very long, ongoing discussion on one of my mailing lists about whether or not feedback loops are a net good or a net harm. I believe, overall, they are a net good, but there are people who believe they are not. The biggest objection is that the lawyer mandated redaction of the To: address combined with the fact that some users use the “this is spam” button to delete unwanted email, makes it difficult for some FBL recipients to sort out the real issues from the cruft.
Redaction can be a problem for some senders, particularly for the small mailing list hosted as a hobby or contribution to the community. In order to effectively deal with FBL emails, a sender needs to have tools on the email sending side and on the FBL receiving side. This is often more overhead than the volunteer list maintainer wants to handle. Unfortunately, these senders are a minority and therefore their issues are often not addressed by the ISPs.
Some of the objections and complaints about “broken” or “useless” FBLs come from people who do not really have any history for the FBLs, where they are, what they were designed for and who their target audience is. A bit of history may help explain why things are how they are.
The First FBL
The “this is spam” button evolved from the “notify AOL” button. This button was a way email recipients could notify AOL staff about any number of problems, including threats, viruses and other unwanted emails. As time went on, this was changed to “this is spam” to encourage users to report more spam so the AOL would have the data to make delivery decisions. Eventually, AOL made the decision to share that data with some senders and ISPs. The lawyers made the decision to redact the “To:” address, but not make any other changes to the message because they believe they should not be sharing subscriber email addresses with third parties. As some people correctly point out, the lawyers are not interested in hearing from non lawyers about changing this. It is possible that another lawyer may be able to put together a position paper and convince them this stance is overly cautious. I am pretty sure, though, that no one without a legal degree will be given any audience from them.
Given the success of the AOL FBL and the demand from both ESPs and ISPs for FBLs, other ISPs started offering FBLs as well. Many of them also redacted the To: address, either just following AOL’s lead or under advice of their own counsel.
That means, as senders, we are in a situation where we really cannot make the ISPs change what they’re doing. We can either adapt our own mailing practices to cope with them or we can forego the data provided by the FBL. One of the challenges in choosing to shun the whitelist at AOL that in order to qualify for whitelisting, you have to accept a FBL. For ISPs, who want to whitelist their outgoing MTAs, but have customers sending mail, maybe running small mailing lists, or who are forwarding mail to their ISP account, this can be a problem. However, any ISP needs some sort of abuse desk automation, and this automation should be able to handle FBLs. This can also be a problem for small ESPs or companies doing in-house email marketing. They buy something off the shelf to handle mail (or install mailman) that does not do VERP or otherwise enter the specific address in the email. When faced with a redacted email they cannot do anything with the complaint.
What does the FBL email tell the FBL recipient?
This really depends on what role the FBL recipient plays in the mail transport system. Bandwidth and network service providers use the FBL as an aggregate tool. They really only deal with FBL complaints if there is a change in complaint volume about an IP, they don’t treat each complaint as a valuable source of information. Typically what happens is that an ISP abuse desk notices a spike in complaints. After investigation, they may discover that a customer machine is compromised. They then notify the customer, the customer patches or disconnects the machine and the problem is fixed.
ESPs tend treat the FBL as an unsubscribe mechanism as well as a way to monitor customers. A few FBL complaints are not necessarily a sign that the sender is spamming, but once a threshold is reached the ESP delivery / abuse team addresses the issue. Spammers can get FBLs and often use them as a way to clean lists of complainants. Some really dirty spammers even suppress those complainants from all their lists.
Is a FBL useful?
This is really something that someone else cannot tell you. Some companies find FBLs to be extremely useful, even after they have had to make investments in software (either off the shelf or custom) to send mail that will survive the FBL redaction process and to handle the actual FBL email. Some companies find the FBLs to be more trouble than they are worth. The question, however, is really one only the sender can answer.
Overall, I think FBLs are more helpful than they are harmful. They do require investment on both sides of the transaction, but does encourage senders and receivers to cooperate with one another.
FBL updates
Roadrunner shifted the release date for their new FBL to December 14th.
Despite rumors, the Yahoo FBL is not actually accepting new participants.
Bad Idea
My mailbox and IM windows have been swamped with messages about an ISP sending out mail to participants in their FBL program. It seems this particular ISP could use some delivery consulting.
See, this ISP sent out emails with blocks of 50 – 75 email addresses in the To: line. Bad idea. Delivery wise, I do not expect that they had many delivery problems. In the copy I saw, most of the addresses started with “support” and those addresses often have fewer blocks on them than other addresses. I also do not think this ISP will see subscriber emails blocked because of this.
However, it is very, very bad practice to do what they did. And the fact that the ISP can get away with it does not mean that any other mailer can get away with it.
RoadRunner FBL changes
RoadRunner announced changes to their FBL this morning. Everyone who is currently getting a FBL should have received an email. Important dates to remember include the following.
August 28: Existing RR FBL will be frozen. No changes to existing loops will be accepted and no new FBL applications will be processed. All current FBLs will continue to work.
November 17 (tentative): The new FBL will go live. Existing FBLs will not be converted from the old FBL to the new one. Everyone wishing to be a part of the new FBL will be required to re-enroll in the program beginning on this date.
December 31 (tentative): The old FBL ceases to exist.
More information about the migration is available at http://postmaster.rr.com/FBL.html
Yahoo update
It has been quite a while since I have had the opportunity to share information about Yahoo here on the blog, but there is new information to share.
Yesterday, Mark Risher from Yahoo spent some time talking with people about all things spam over at Yahoo. Matt from EmailKarma posted the transcripts as well as some excerpts from the talk. The really interesting bit, for me, was confirmation that Yahoo will be bringing back their FBL in the next few weeks. I have been hearing rumors about the return of the FBL for a while now, and it seems the general timeline (fall-ish) is accurate.
Speaking of the feedback loop, there have also been rumors that Yahoo is not accepting any changes to existing feedback loops. This does not seem to be the case. According to an internal person, companies who are currently in the beta FBL program can make changes to the program by contacting the postmaster team.