Hotmail
When you can’t get a response
I’ve seen a bunch of folks in different places looking for advice on what to do when they can’t get a response from a postmaster team, or a filtering company. I was all set to write yet another post about how silence is an answer. Digging through the archives, though, I see I’ve written about this twice already in the last 18 months.
Read MoreTroubleshooting and codes
Microsoft is still in the process of rolling out new mail servers. One thing that is new about these is some new codes on their error messages. This has led to questions and speculations as to what is going on.
Engagement filters for B2B mail
While I was doing some research for a client today I rediscovered Terry Zink’s blog. Terry is one of the MS email folks and he regularly blogs about the things MS is doing with Outlook.com and Office 365.
The post that caught my eye was discussing the Microsoft Spam Fighter program. The short version is that in order to train their spam filters, Microsoft asks a random cross-section of their users if the filters made the right decision about email. This data is fed back into the Microsoft machine learning engine.
As Terry explains it:
Another way Gmail is different
I was answering a question on Mailop earlier today and had one of those moments of clarity. I finally managed to articulate one of the things I’ve known about Gmail, but never been able to explain. See, Gmail has never really put a lot of their filtering on the SMTP transaction and IP reputation. Other ISPs do a lot of the heavy lifting with IP filters. But not Gmail.
While I was writing the answer I realized something. Gmail was a late entrant into the email space. AOL, Hotmail, Yahoo, even the cable companies, were providing email services in the 90s. When spam started to be a problem, they started with IP based blocking. As technology got better and content filtering became viable, improvements were layered on top of IP based blocking.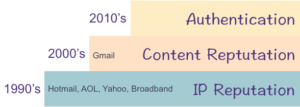
Gmail didn’t enter the mailbox market until the 2000’s. When they did, they had money, lots of hardware, and internal expertise to do content filtering. They didn’t start with IP based filtering, so their base is actually content filtering. Sure, there were some times when they’d push some mail away from the MTAs, but most of their filtering was done after the SMTP transaction. The short version of this is I never really pay any attention to IP reputation when dealing with Gmail. It’s just another factor. Unless you’re blocked and if you get blocked by Gmail, wow, you really screwed up.
Gmail does, of course, do some IP based blocking. But in my experience IP filters are really only turned against really egregious spam, phishing and malicious mail. Most email marketers reading my blog won’t ever see IP filters at Gmail because their mail is not that bad.
Other companies aren’t going to throw away filters that are working, so the base of their filters are IPs. But Google never had that base to work from. Their base is content filters, with some IP rep layered on top of that.
That’s a big reason Gmail filters are different from other filters.
Microsoft deprecating SmartScreen filters
At the beginning of the month Microsoft announced that they were deprecating the SmartScreen filters used by the desktop Microsoft mail clients. These are the filters used in Exchange and various version of Outlook mail. This is yet further consolidation of spam filtering between the Microsoft free webmail domains, Office365 hosted domains and self hosted Exchange servers. The online services (hotmail.com, outlook.com, Office365, live.com, etc) have been using these filters for a while. The big change now is that they’re being pushed down to Exchange and Outlook users not hosted on the Microsoft site.
EOP was developed for Outlook.com (and friends) as well as Office365 users. From Microsoft’s description, it sounds like the type of machine learning engine that many providers are moving to.
Microsoft has published quite a bit of information about these filters and how they work on their website. One of the best places to start is the Anti-spam Protection FAQ. Something senders should pay attention to is the final question on that page: “What are a set of best outbound mailing practices that will ensure that my mail is delivered?” Those are all things deliverability folks recommend for good inbox delivery.
Poking around looking at the links and descriptions, there is a host of great information about spam filtering at Microsoft and how it works.
A page of note is their Exchange Online Protection Overview. This describes the EOP process and how the filters work.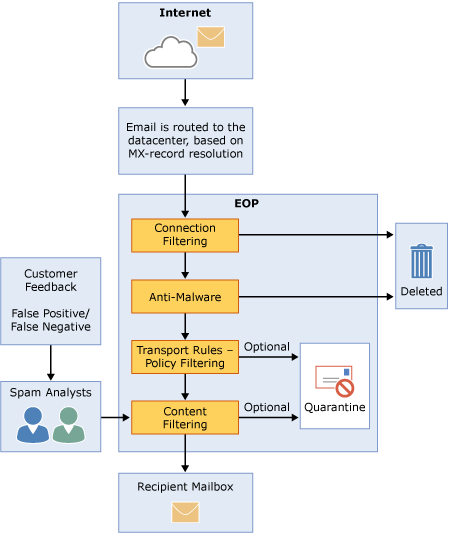
Hotmail having a bad day
Hotmail seems to be having a bad day, responding to a lot of delivery attempts with “554 Transaction failed” responses.
It’s not you, it’s them. They’re aware of the issue.
Getting unblocked at Outlook.com
It’s been a crazy week here at M3AAWG. I have a lot of stuff to blog about, but I think one of the really important things to get out is the new unblock request page at Outlook / Hotmail.
https://sender.office.com
Submit your IPs and it will be reviewed.
(Apologies for the repeated bad links. I’m blaming con crud, lack of sleep and MSN/Hotmail/Office/Outlook for having so many domains I can’t keep them straight. I have finally gotten it right and tested it.)
Office365/EOP and Outlook.com/Hotmail will converge
Terry Zink posted two informative blog posts recently, the first being the change to unauthenticated mail sent over IPv6 to EOP and the second post about EOP (Office365 and Exchange Hosting) and Outlook.com/Hotmail infrastructure converging.
Exchange Online Protection (EOP) is the filtering system in place for Office 365 and hosted Exchange customers. Outlook.com/Hotmail utilized its own mail filtering system and provides SNDS/JMRP programs. EOP is setup for redundancy, failover, provides geo-region servers to serve customers, and has supported TLS for over a decade. Terry explains that Hotmail’s spam filtering technology is more advanced than EOP’s, but EOP’s backend platform is more advanced. The process to convert Outlook.com/Hotmail to use EOP’s filtering system started six months ago and is still a work in progress. Once completed, Outlook.com/Hotmail and Office365/EOP will share the same UX look and feel. The anti-spam technologies will be able to be shared between the two as they will share the same backend infrastructure.
Some of the challenges of merging the two systems include:
Thoughts on Hotmail filtering
One of the new bits of information to come out of the EEC15 deliverability discussions is how Hotmail is looking at engagement differently than other webmail providers.
Many webmail providers really do look at overall engagement with a mail when making delivery decisions. And this really impacts new subscribers the most. If there is a mailing where a lot of subscribers are engaged, then new subscribers will see the mail in their inbox. Based on what was said at the webinar earlier this week engagement has no effect at Hotmail outside of the individual user’s box.
I’ve certainly seen this with clients who’ve tried trimming subscriber lists but that doesn’t really help get mail moved from the Hotmail bulk folder to the inbox.
Instead of subscriber lists, Hotmail is really looking at bounces. They’re watching the number of nonexistent accounts senders are mailing to and they’re counting and a sender hits too many bad addresses and that is a major hit to their reputation.
All of this makes remediation at Hotmail challenging. Right now, we can remediate a bad reputation at a lot of ISPs and the filters catch up and mail starts flowing back to the inbox. Hotmail has set up a system that they say is “hard for spammers to game.” This seems to translate into hard for legitimate senders to fix their reputation.
Hotmail is, IMO, the current tough nut in terms of deliverability. Develop a bad reputation there and it’s difficult to fix it. I’m sure it’s possible, though.
Mythbusting deliverability and engagement
Yesterday I published an article talking about an engagement webinar hosted by the EEC and DMA. I made a couple predictions about what would be said.
Read MoreEmail predictions for 2015
Welcome to a whole new year. It seems the changing of the year brings out people predicting what they think will happen in the coming year. It’s something I’ve indulged in a couple times over my years of blogging, but email is a generally stable technology and it’s kind of boring to predict a new interface or a minor tweak to filters. Of course, many bloggers will go way out on a limb and predict the death of email, but I think that’s been way over done.
Even major technical advancements, like authentication protocols and the rise of IPv6, are not usually sudden. They’re discussed and refined through the IETF process. While some of these changes may seem “all of a sudden” to some end users, they’re usually the result of years of work from dedicated volunteers. The internet really doesn’t do flag days.
One major change in 2014, that had significant implications for email as a whole, was a free mail provider abruptly publishing a DMARC p=reject policy. This caused a lot of issues for some small business senders and for many individual users. Mailing list maintainers are still dealing with some of the fallout, and there are ongoing discussions about how best to mitigate the problems DMARC causes non-commercial email.
Still, DMARC as a protocol has been in development for a few years. A number of large brands and commercial organizations were publishing p=reject policies. The big mail providers were implementing DMARC checking, and rejection, on their inbound mail. In fact, this rollout is one of the reasons that the publishing of p=reject was a problem. With the flip of a switch, mail that was once deliverable became undeliverable.
Looking back through any of the 2014 predictions, I don’t think anyone predicted that two major mailbox providers would implement p=reject policies, causing widespread delivery failures across the Internet. I certainly wouldn’t have predicted it, all of my discussions with people about DMARC centered around business using DMARC to protect their brand. No one mentioned ISPs using it to force their customers away from 3rd party services and discussion lists.
I think the only constant in the world of email is change, and most of the time that change isn’t that massive or sudden, 2014 and the DMARC upheaval notwithstanding.
But, still, I have some thoughts on what might happen in the coming year. Mostly more of the same as we’ve seen over the last few years. But there are a couple areas I think we’ll see some progress made.
ISPs speak at M3AAWG
Last week at M3AAWG representatives from AOL, Yahoo, Gmail and Outlook spoke about their anti-spam technologies and what the organizations were looking for in email.
This session was question and answers, with the moderator asking the majority of the questions. These answers are paraphrased from my notes or the MAAWG twitter stream from the session.
What are your biggest frustrations?
AOL: When senders complain they can’t get mail in and we go look at their stats and complaints are high. Users just don’t love that mail. If complaints are high look at what you may have done differently, content does have an effect on complaints.
Outlook: When we tightened down filters 8 years ago we had to do it. Half of the mail in our users inbox was spam and we were losing a steady number of customers. The filter changes disrupted a lot of senders and caused a lot of pain. But these days only 0.5% of mail in the inbox is spam. Things happen so fast, though, that the stress can frustrate the team.
Gmail: Good senders do email badly sometimes and their mail gets bulked. Senders have to get the basic email hygiene practices right. Love your users and they’ll love you back.
What’s your philosophy and approach towards mail?
AOL: There is a balance that needs to be struck between good and bad mail. The postmaster team reminds the blocking team that not all mail is bad or malicious. They are the sender advocates inside AOL. But the blocking team deals with so much bad mail, they sometimes forget that some mail is good.
Yahoo: User experience. The user always comes first. We strive to protect them from malicious mail and provide them with the emails they want to see. Everything else is secondary.
Gmail: The faster we stop spam the less spam that gets sent overall. We have highly adaptive filters that can react extremely quickly to spam. This frustrates the spammers and they will give up.
Outlook: The core customer is the mailbox user and they are a priority. We think we have most of the hardcore spam under control, and now we’re focused on personalizing the inbox for each user. Everyone online should hold partners accountable and they should expect to be held accountable in turn. This isn’t just a sender / ESP thing, ISPs block each other if there are spam problems.
What are some of your most outrageous requests?
We’ve been threatened with lawsuits because senders just don’t want to do the work to fix things. Some senders try to extort us. Other senders go to the advertising execs and get the execs to yell at the filtering team.
Coming to MAAWG and getting cornered to talk about a particular sender problem. Some senders have even offered money just to get mail to the spam folder.
Senders who escalate through the wrong channels. We spent all this money and time creating channels where you can contact us, and then senders don’t use them.
Confusing business interests with product interests. These are separate things and we can’t change the product to match your business interest.
What are your recommendations for changing behaviors?
Outlook: We provide lots of tools to let you see what your recipients are doing. USE THE TOOLS. Pay attention to your recipient interaction with mail. Re-opt-in recipients periodically. Think about that mail that is never opened. Monitor how people interact with your mail. When you have a problem, use our webpages and our forms. Standard delivery problems have a play book. We’re going to follow that playbook and if you try to get personal attention it’s going to slow things down. If there’s a process problem, we are reachable and can handle them personally. But use the postmaster page for most things.
Gmail: Get your hygiene right. If you get your hygiene right, deliverability just works. If you’re seeing blocking, that’s because users are marking your mail as spam. Pay attention to what the major receivers publish on their postmaster pages. Don’t just follow the letter of the law, follow the spirit as well. Our responsibility, as an ISP, is to detect spam and not spam. Good mailers make that harder on us because they do thinks that look like spammers. This doesn’t get spammer mail in more, it gets legitimate mail in less. Use a real opt-in system, don’t just rely on an implied opt-in because someone made a purchase or something.
Yahoo: ESPs are pretty good about screening their customers, so pay attention to what your ESPs are saying. Send mail people want. Verify that the email addresses given to you actually belong to people who want your mail. Have better sender practices.
What do you think about seed accounts?
The panel wasn’t very happy about the use of seed accounts. Seeds are not that useful any longer, as the ISPs move to more and more personalized delivery. Too much time and too many cycles are used debugging seed accounts. The dynamic delivery works all ways.
When things go wrong what should we do?
AOL: Open a ticket. We know we’ve been lax recently, but have worked out of our backlog and are caught up to date. Using the ticketing system also justifies us getting more headcount and makes everyone’s experience better. Also, don’t continue what you’re doing. Pausing sending while you’re troubleshooting the issue. We won’t adjust a rep for you, but we may be able to help you.
Gmail: Do not jump the gun and open a ticket on the first mail to the spam folder. Our filters are so dynamic, they update every few minutes in some cases. Be sure there is a problem. If you are sure you’re following the spirit and letter of the sender guidelines you can submit a ticket. We don’t respond to tickets, but we work every single one. When you’re opening a ticket provide complete information and full headers, and use the headers from your own email address not headers from a seed account. Give us a clear and concise description of the problem. Also, use the gmail product forum, it is monitored by employees and it’s our preferred way of getting information to the anti-abuse team. Common issues lots of senders are having will get addressed faster.
Outlook: Dig in and do your own troubleshooting, don’t rely on us to tell you what to fix. The support teams don’t have a lot of resources so use our public information. If you make our job harder, then it takes longer to get things done. But tell us what changes you’ve made. If you’ve fixed something, and tell us, our process is different than if you’re just asking for a delisting or asking for information. When you’ve fixed things we will respond faster.
How fast should users expect filters to respond after making changes?
Filters update continually so they should start seeing delivery changes almost immediately. What we find is people tell us they’ve made changes, but they haven’t made enough or made the right ones. If the filters don’t update, then you’ve not fixed the problem.
Hotmail having a bad day
Looks like Hotmail / Microsoft is having a rather bad day. Their DNS seems to be intermittent. While they were down a while ago they were returning SERVFAIL for some DNS lookups, including MX lookups.
For senders who have the DNS data in their recursive resolvers, this will have no impact. For senders who either don’t have the data cached or who have the data expire before the servers come back online there may be a transient increase in the number of bounces at Microsoft domains (Hotmail, Outlook, MSN.com, office365.com and the Microsoft corporate domains including microsoft.com and their other domains like xboxone.com).
"Blocked for Bot-like Behavior"
An ESP asked about this error message from Hotmail and what to do about it.
“Bot-like” behaviour usually means the sending server is doing something that bots also do. It’s not always that they’re spamming, often it’s a technical issue. But the technical problems make the sending server look like a bot, so the ISP is not taking any chances and they’re going to stop accepting mail from that server.
If you’re an ESP what should you look for when tracking down what the problem is?
First make sure your server isn’t infected with anything and that you’re not running an open relay or proxy. Second, make sure your customers aren’t compromised or have had their accounts hijacked.
Then start looking at your configuration.
HELO/EHLO values
SNDS is back
For years now, Microsoft has maintained Smart Network Data Services (SNDS) for anyone sending mail to Hotmail/Outlook/Live.com. This is a great way for anyone responsible for an IP sending mail to hotmail to monitor what traffic Hotmail is seeing from that IP address.
This morning I got up to a number of people complaining that logins were failing on the website and the API was down. I contacted the person behind SNDS and they confirmed there was a problem and they were fixing it.
Sometime this afternoon it was possible to login to the SNDS interface again, so it looks like they did fix it.
A bit of a warning, though, don’t expect to see any of the data from the last few days. There seems to be something with SNDS that means that when the service is down data isn’t collected or available. In the past when there have been problems, older data was not populated when the service came back.
Hotmail issues
A number of people, both at ESPs and on the mailops mailing list, are reporting problems at Hotmail. The most common reports are senders getting
Read MoreHotmail moves to SPF authentication
Hotmail has recently stopped using Sender ID for email authentication and switched to authenticating with SPF. The protocol differences between SenderID and SPF were subtle and most senders who were getting a pass at Hotmail were already publishing SPF records.
From an email in my inbox from September:
Outlook.com
The big news in email today is Microsoft’s announcement of the next version of Hotmail: Outlook.com. This does appear to be an attempt to compete with a host of Google’s offerings. Not only does Outlook.com include Skype and access to social media accounts, but it also includes web app versions of Word, Excel and Powerpoint with 7GB of storage space.
I’m not sure how actively people will be grabbing Outlook.com addresses, as you can use hotmail.com addresses with the Outlook.com interface. Only time will tell, though, how this affects email marketing and spam filtering.
Email marketing OF THE FUTURE!
ISPs are continually developing tools for their users. Some of the newer tools are automatic filters that help users organize the volumes of mail they’re getting. Gmail released Priority Inbox over a year ago. Hotmail announced new filters as part of Wave 5 back in October.
All of these announcements cause much consternation in the email marketing industry. Just today there was a long discussion on the Only Influencers list about the new Hotmail filtering. There was even some discussion about why the ISPs were doing this.
I think it’s pretty simple why they’re creating new tools: users are asking for them. The core of these new filters is ISPs reacting to consumer demand. They wouldn’t put the energy into development if their users didn’t want it. And many users do and will use priority inbox or the new Hotmail filtering.
Some people are concerned that marketing email will be less effective if mail is not in the inbox.
Hotmail fights greymail
I’ve heard a lot of marketers complaining about people like me who advocate actually purging addresses from marketing lists if those addresses are non-responsive over a long period of time. They have any number of reasons this advice is poor. Some of them can even demonstrate that they get significant revenue from mailing folks who haven’t opened an email in years.
They also point out that there isn’t a clear delivery hit to leaving those abandoned addresses on their list. It’s not like bounces or complaints. There isn’t a clear way to measure the dead addresses and even if you could there aren’t clear threshold guidelines published by the ISPs.
Nevertheless, I am seeing more and more data that convinces me the ISPs do care about companies sending mail that users never open or never read or never do anything with.
The most recent confirmation was the announcement that Hotmail was deploying more tools to help users manage “greymail.” I briefly mentioned the announcement last week. Hotmail has their own blog post up about the changes.
It seems my initial claim that these changes this won’t affect delivery may have been premature. In fact, these changes are all about making it easier for Hotmail users to deal with the onslaught of legitimate but unwanted mail.
Changes at Hotmail
Microsoft announced a number of changes to the Hotmail interface today. It doesn’t look like this will affect how mail is received, but will affect how users can interact with it.
As always, the best advice I can give you is send mail people want and like.
Holomaxx v. Yahoo and MS: The hearing
I visited Judge Fogel’s courtroom this morning to listen to the oral motions in the Holomaxx cases. This is a general impression, based on my notes. Nothing here is to be taken as direct quotes from any participant. Any errors are solely my own. With that disclaimer in mind, let’s go.
The judge is treating these two cases as basically a single case. When it came time for arguments, the cases were called together and both Yahoo and Microsoft’s lawyers were at the defendant’s table.
Oral arguments centered on the question of CDA immunity and to a lesser extent if there is an objective industry standard for blocking and dealing with blocks. Nothing at all was mentioned about the wiretapping arguments.
The judge opened the hearing with a quick summary of the case so far and what he wanted to hear from the lawyers.
Judge Fogel pointed out that current case law suggests that the CDA provides a robust immunity to ISPs to block mail. The plaintiff can’t just say that the blocks were done in bad faith, there has to be actual evidence to show bad faith. The law does permit subjective decisions by the ISPs. Also, that it is currently hard to see any proof of bad faith by the defendants.
The judge asked the plaintiff’s attorney for his “absolute best argument” as to the bad faith exhibited by the defendants.
The plaintiff responded that they are a competitor who is being stonewalled by the defendants. That their email is not spam (as it is CAN SPAM compliant) and it is wanted email. The defendants are not following the “objective industry standard” as defined by MAAWG.
The judge responded clarifying that the plaintiff really claimed he didn’t need to present any evidence. “Yes.” Judge Fogel mentioned the Towmbly standard which says that a plaintiff must have enough facts to make their allegations plausible, not just possible.
Yahoo!’s lawyer pointed out that both case law and the statutes require a robust showing to invalidate claims under the CDA. And that the purpose of the CDA is to protect ISPs from second guessing. She started to bring up the absolute numbers of emails, but was interrupted and told the numbers weren’t relevant. My notes don’t say if that was the judge or Holomaxx’s lawyer that interrupted, and the numbers discussion did come up again.
Yahoo continued that the CAN SPAM compliance is not a litmus test for what is spam. The decision for what is and is not spam is left to the subjective judgement of the ISP. She also pointed out that the numbers are important. She defined the amount of spam as a tax on the network and a tax on users.
She also addressed the anti-competitive claim. Even if Holomaxx is right, and neither defendant was conceding the point, and it is doubtful that the anti-competitive point can be proven, competition alone cannot establish bad faith. What evidence is there that either defendant exhibited bad faith? In Yahoo’s case there is zero advertiser overlap and in the Microsoft case Holomaxx showed one shared customer.
She then pointed out that the MAAWG document was a stitched collection of experiences from desks. That the document itself says it is not a set of best practices. She also pointed out that there was nothing in the document about how to make spam blocking decisions. That it was solely a recommendation on how to handle people who complain.
According to Yahoo!’s lawyer the plaintiffs brought this suit because they disagreed with the ISPs’ standards for blocking and they were upset about how they were treated. That the worst Holomaxx can say is the MS and Y! had bad customer service.
At this point there was some discussion between the judge and lawyers about how they were currently in a “grey area” between Rule 9(b) and Rule 12(b)6. I am not totally sure what this was about (one of my lawyer readers can help me out?) but there was also mention of using these rules in the context of the ISPs’ robust immunity under the CDA.
Finally, the judge asked Microsoft’s lawyer if he had anything more to add. He reiterated that the MAAWG document was not a standard, it was a collection of options. He also brought up the volume issue again, asserting that even if it is a true standard that the volume of unwanted mail sent by Holomaxx does not mean ISPs need to follow it.
Judge Fogle asked him if he meant there was no legal obligation for the ISPs to be warm and fuzzy.
The judge and defendant lawyers talked around a few general ideas about the MAAWG document. First that there was no obligation to tell senders enough information so that senders could reverse engineer spam filters. Microsoft also brought up the volume issue again, saying that the volume of unwanted 3rd party mail that the plaintiff was sending was, in itself, proof that the mail was bad.
Holomaxx interrupted claiming that the volume is a red herring. Judge Fogel countered with “but the gross number of unwanted emails is a huge number of emails.” Holomaxx’s lawyer argued that both Yahoo and Microsoft had large, robust networks, and the volume is irrelevant. I thought this was funny, given how often both of them have outages due to volume. However, the Holomaxx lawyer did have a point. Facebook sends billions of emails a day and both Yahoo and Hotmail can cope with that volume of mail and that volume dwarfs what Holomaxx sends.
The judge asked if he should look at the percentage of complaints about the mail rather than the gross number. Holomaxx replied that both were just a drop in the bucket and neither number was relevant.
Holomaxx then claimed again that MAAWG was a standard. The judge pointed out it was a standard for customer service, not a standard for blocking. Holomaxx disagreed and said that the MAAWG document was a standard for both how to block and how to deal with blocks afterwards.
The judge asked Holomaxx if there was any actual evidence of their claims. He talked about a case he heard a few years ago. Some company was suing Google because their search results were not on the front page of Google results. That company didn’t prevail because they never offered any actual evidence that Google was deliberately singling them out. He asked Holomaxx how they were being singled out.
Holomaxx replied there was no industry standard to measure against.
The judge wrapped up the hearing by pointing out that he was being asked to show where the exceptions to the CDA were and that he had to consider the implications of his ruling. He agreed that bad faith was clearly an exception to CDA protection, but what was the burden of proof required to identify actual bad faith. He seemed to think this was the most important point and one that would take some deliberation.
Overall, the hearing took about 15 minutes, which seemed in line with the case immediately before this one.
My impression was that the judge was looking for Holomaxx to argue something, anything with facts rather than assertion. But, I am scientist enough to see that may be my own biases at work. But the judge gave Holomaxx the opportunity to show their absolute best evidence, and Holomaxx provided exactly zero, instead falling back to it’s true because we said it’s true.
The judge will issue a written ruling, I’ll keep an eye out for it and post it when it’s out.
Holomaxx doubles down
Holomaxx has, as expected, filed a motion in opposition to the motion to dismiss filed by both Yahoo (opposition to Yahoo motion and Hotmail (opposition to Microsoft motion). To my mind they still don’t have much of an argument, but seem to believe that they can continue with this.
They are continuing to claim that Microsoft is scanning email before the email gets to Microsoft (or Yahoo) owned hardware.
Holomaxx status
Just for completeness sake, Holomaxx did also file an amended complaint against Microsoft. Same sloppy legal work, they left in all the stuff about Return Path even though Return Path has been dropped from the suit. They point to a MAAWG document as a objective industry standard when the MAAWG document was merely a record of a round table discussion, not actually a standards document. I didn’t read it as closely as I did the Yahoo complaint, as it’s just cut and paste with some (badly done) word replacement.
So what’s the status of both cases?
The Yahoo case is going to arbitration sometime in July. Yahoo also has until May 20 to respond to the 1st amended complaint.
The Microsoft case is not going to arbitration, but they also have a response deadline of May 20.
I’m not a legal expert, but I don’t think that what Holomaxx has written fixes the deficits that the judge pointed out in his dismissal. We’ll see what the Y! and MSFT responses say a month from today.
Filtering adjustments at Hotmail
I’ve been seeing a lot of discussion on various fora recently about increased delivery issues at Hotmail. Some senders are seeing more deferrals, some senders are seeing more mail in the bulk folder. Some senders aren’t seeing any changes.
This leads me to believe that Hotmail made some adjustments to their filtering recently. Given some senders are unaffected, this appears to be a threshold change or a calculation change, tightening up their standards. The changes have been around for long enough now it does look like the filtering is working as intended and Hotmail is not going to roll these changes back.
So what can you do to fix delivery of mail that was good enough at Hotmail a few weeks ago and now isn’t?
Reputation monitoring sites
There are a number of sites online that provide public information about reputation of an IP address or domain name.
Read MoreSPF records: not really all that important
I’ve been working through some Hotmail issues with a client over the last few months. One of the things that has become clear to me is how little Hotmail actually does with SPF records. In fact, Hotmail completely ignored my client’s SPF record and continued to deliver email into the inbox.
This isn’t just a sender that had a “well, we think most of our email will come from these IPs but aren’t telling you to throw away email that doesn’t” record. In fact, this client specifically said “if email doesn’t come from this /28 range of email addresses, then it is unauthorized and should be thrown away.” The email was being sent from an IP outside of the range listed in the SPF record.
As part of the process involved in fixing the delivery problems, I had the client update their SPF record and then I enrolled their domain in the SenderID program at Hotmail. This didn’t have any effect, though. Hotmail is still not checking SPF for this client. When I asked Hotmail what was going on they said, “We do not do lookups on every sender’s mail.”
So, there you have it folks. The last bastion of SPF/SenderID has abandoned the technology. Even a totally invalid SPF record doesn’t matter, mail can still reach the inbox at Hotmail.
Link roundup June 18, 2010
Hotmail has released a new version of their software with some changes. Return Path discusses the changes in depth, but there are a couple that senders may find helpful.
Read MoreMicrosoft delivery partnerships
Last week John Scarrow from Microsoft made a public statement on Deliverability.com about Microsoft’s approach to using available products in the email industry.
Read MoreBreaking through the script
In handling day to day issues I use the ISP designated channels. This means I frequently get dragged into long conversations with people, probably outsourced to the far east, who can do nothing beyond send me a boilerplate.
This can be a frustrating experience when the issue you’re trying to deal with is not handled by the script. Generally, by the time someone has come to me for help, they are “off script” and I do need to actually talk to a human to get resolution.
With Hotmail, I’ve found that persistent repeating of very simple phrases will eventually get the issue kicked up to someone who can respond with something beyond another boilerplate. This can take days, but it is possible.
I’ve recently run into a Yahoo issue where I am trying to punch through the script, but have so far been unable to.
One of the services Word to the Wise offers is whitelisting. I collect info from customers, verify that what they’re doing will get them whitelisted at the ISPs that offer it, and then submit the information to the ISPs. Yahoo has recently moved to an online submission form for their whitelisting process, which is great for me. No more creating a giant document and then cutting and pasting the document into an email and then mailing it off.
The problem is, there seems to be a minor problem with the Yahoo Whitelisting submission form. When submitting an online application to Yahoo, they respond with a message that says “this application is not complete.”
I’ve been attempting to break through the script in order to find out what about the application is not complete. The webform has data checking, and you cannot submit a form while leaving any of the questions blank. Asking “what is wrong” when the application is kicked back has resulted in me having multiple copies of the whitelisting submission form.
It’s gotten so frustrating that I’ve escalated to personal contacts, but they can’t explain what’s not complete about the application as submitted online, either.
Has anyone had any success breaking through the Yahoo script? Has anyone managed to get IP addresses whitelisted through Yahoo using the online form?
