Inbox Delivery
Never 100% inbox
No matter how great an email program deliverability is, no one can guarantee that 100% of the email sent will reach the recipient’s inbox. Why? Recipients can make decisions about where mail goes in their own inbox. Every mail client has a way for users to control where mail is delivered.
Read MoreBack to the office!
I’m back in the office after a busy June. The 2 continent, 3 city tour was unexpectedly extended to a 4th city thus I was out most of last week as well.
What was I doing? We spent a week in Dublin, which is an awesome and amazing city and I love it a little bit more every time we visit. After Dublin I jetted off to Chicago, where I spoke at ActiveCampaign’s first user conference.
The talk I did for ActiveCampaign was about how we’re in the middle of a fundamental shift in how email is filtered, particularly at the consumer ISPs. In order reach the inbox. we need to think beyond IP or domain reputation. We need to stop thinking of filters as a way of sorting good mail from bad mail. I touched a little on these concepts in my What kind of mail do filters target? blog post.
The shift in filtering is changing how email reaches the inbox and what we can and should be monitoring. At the same time, the amount of data we can get back from the ISPs is decreasing. This means we’re looking at a situation when our primary delivery fixes can’t be based on feedback from the filters. This is, I think, going to be an ongoing theme of blog posts over the next few months.
The next trip was to spend 2 days onsite at a client’s office. These types of onsite training are intense but I do enjoy them. As this was mostly client specific, there isn’t much I can share. They did describe it as a masterclass in deliverability, so I think it was also intense for them.
That was the planned 2 continent, 3 city tour. The last city was a late addition of a more personal nature. We headed downstate to join my cousin and her family in saying goodbye to my uncle. He was an amazing man. A larger than life, literal hero (underwater EOD, awarded the silver star) whom I wish I had known better. Most of what I remember is how much he loved and adored my aunt.
I’ll be getting back into the swing of blogging over the next few days. It’s good to be back and not looking at traveling in the short term.
Updating the filtering model
One thing I really like about going to conferences is they’re often one of the few times I get to sit and think about the bigger email picture. Hearing other people talk about their marketing experiences, their email experiences, and their blocking experiences usually triggers big picture style thoughts.
Earlier this week I was at Activate18, hosted by Iterable. The sessions I attended were interesting and insightful. Of course, I went to the deliverability session. While listening to the presentation, I realized my previous model of email filtering needed to be updated.
Following CAN SPAM isn't enough to reach the inbox
One of the top entries on the list of things deliverability folks hear all the time is, “But my mail is all CAN SPAM compliant!” The thing is… no one handling inbound mail really cares. Seriously. CAN SPAM is a law that is little more than don’t lie, don’t hide, and heed the no. Even more importantly, the law itself states that there is no obligation for ISPs to deliver CAN SPAM compliant mail.
Read MoreDid the algorithm change?
When faced with unexplained deliverability changes one of the first questions many folks ask is “Did the algorithm change.” In many ways this is an meaningless question. Why? Because there are two obvious answers to the question.
A1: Of course it didn’t.
A2: Of course it did.
Both answers are correct, but they’re answering different underlying questions. When we understand how two diametrically opposed answers are both correct, we understand much more about filtering.
Collecting email addresses
One of the primary ways to collect email addresses is from website visitors, and it’s actually a pretty good way to collect addresses. One of the more popular, and effective, techniques is through a pop-up window, asking for an address. Users need to provide an address or click a “no thanks” link or close the window. I’ve noticed, though, that many companies drop something passive aggressive in their “no thanks” button. “No, thanks, I don’t want to save money.” “I don’t need workout advice.”
Read MoreStill with the Microsoft problems
We took a quick trip to Dublin last week. I had every intention of blogging while on the trip, but… oops. I did get to meet with some clients, and had a great dinner while discussing email and delivery.
Coming back, I see a lot of folks still reporting delivery problems to Microsoft properties. I’ve been operating under the assumption this was temporary as kinks were worked out after the migration. I’m still pretty convinced not all of the problems are intentional. Even the best tested code can have issues that only show up under real load with real users. Reading between-some-lines tells me that the tech team is hard at work identifying and fixing issues. There will be changes and things will continue to improve.
With all that being said, I think it’s important to realize that delivering to the new system is not the same as delivering to the old system. This is a major overhaul of their email handling code, representing multiple years worth of planning and development inside Microsoft. It’s very likely that not all of the current delivery problems are the result of deployment. Some of the problems are likely a result of new standards and thresholds for reaching the inbox. What worked a year ago to get into the inbox just doesn’t any more.
Thinking about deliverability
I was chatting with folks over on one of the email slack channels today. The discussion was about an ESP not wanting to implement a particular change as it would hurt deliverability. It led me down a path of thinking about how we think of deliverability and how that informs how we approach email.
The biggest problem I see is the black and white thinking.
There’s an underlying belief in the deliverability, receiving, and filtering communities that the only way to affect sending behavior is to block (or threaten to block) mail.
This was true back in the ancient times (the late 90’s). We didn’t have sophisticated tools and fast CPUs. There weren’t a lot of ways to handle bad mail other than to block. Now the landscape is different. We have many more tools and the computing capacity to quickly sort large streams of data.
At most places these days, blocking is an escalation, not a warning shot. Many places rate limit and bulk folder questionable mail as a first strike against problem mail. Sometimes the mail is bad enough to result in a block. Other times, it’s not bad enough to block, so it disappears into the bulk folder.
There’s a corresponding belief in the sending community that if their behavior doesn’t result in blocking then they’re acting acceptably. This isn’t true either. There are a lot of things you can do (or not do) that don’t help delivery, but will actively harm delivery. Likewise, there are things you can do that don’t actively harm delivery, but will help. All of these things add up to reaching the inbox.
Looking forward
I had a number of very good talks with folks at the Email Innovations Summit earlier this week. I’m still digesting it all. It’s clear that getting to the inbox isn’t a solved problem. Around a decade ago I figured that the explosion of complaint feedback loops would make my job obsolete. That more data would mean anyone could manage delivery. That’s not the case for a couple reasons. The biggest is that filters don’t look just at complaints and there aren’t FBLs for all the other factors.
For whatever reason, many companies are still struggling with delivery.
Even more interesting is how changes in filters and inboxes are making it harder to measure delivery. In some ways I feel like we’re losing ground on inbox measurement. Filters changes and will keep changing, both to address emerging threats and to meet the needs and wants of subscribers. Gone are the days where Panels have their problems. Seed lists have their problems. There’s a longer blog post here, but it’s nearly the weekend and I’ve had a long week.
Hope you have something great planned.
It's not fair
In the delivery space, stuff comes in cycles. We’re currently in a cycle where people are unhappy with spam filters. There are two reasons they’re unhappy: false positives and false negatives.
False positives are emails that the user doesn’t think is spam but goes into the bulk folder anyway.
Fales negatives are emails that the user does thing is spam but is delivered to the inbox.
I’ve sat on multiple calls over the course of my career, with clients and potential clients, where the question I cannot answer comes up. “Why do I still get spam?”
I have a lot of thoughts about this question and what it means for a discussion, how it should be answered and what the next steps are. But it’s important to understand that I, and most of my deliverability colleagues, hate this question. Yet we get it all the time. ISPs get it, too.
A big part of the answer is because spammers spend inordinate amounts of time and money trying to figure out how to break filters. In fact, back in 2006 the FTC fined a company almost a million dollars for using deceptive techniques to try and get into filters. One of the things this company did would be to have folks manually create emails to test filters. Once they found a piece of text that would get into the inbox, they’d spam until the filters caught up. Then, they’d start testing content again to see what would get past the filters. Repeat.
This wasn’t some fly by night company. They had beautiful offices in San Francisco with conference rooms overlooking Treasure Island. They were profitable. They were spammers. Of course, not long after the FTC fined them, they filed bankruptcy and disappeared.
Other spammers create and cultivate vast networks of IP addresses and domains to be used in snowshoeing operations. Still other spammers create criminal acts to hijack reputation of legitimate senders to make it to the inbox.
Why do you still get spam? That’s a bit like asking why people speed or run red lights. You still get spam because spammers invest a lot of money and time into sending you spam. They’re OK with only a small percentage of emails getting through filters, they’ll just make it up in volume.
Spam still exists because spammers still exist.
5 Simple Tricks to Reach the Inbox
I saw a post over on LinkedIn today. It was from an ESP, talking about their simple tips and tricks for getting into the inbox. The laughable bit was half the “tricks” had nothing to do with getting to the inbox, but rather were about enticing people to open the mail once it’s gotten to the inbox.
There are no “tricks” to getting to the inbox. There used to be some tricks. But the ISPs figured them out and protect against them.
Content is the new volume!
I’m having a great time here at #EEC16. Today is my visit and go to sessions day, since tomorrow I’m speaking at 2 different sessions.
I was lucky enough to get into the Customer Experience session presented by Carey Kegel of SmartPak and Loren McDonald of IBM Marketing Cloud. It was an interesting session.
If you don’t know, SmartPak is a brand focused on selling horse tack and supplements. They initially started off by creating packs of supplements for your horse. This is great for horse owners, as it means the barn staff just needs to add one pack to your horse’s feed. No measuring, no confusion, it’s simple and means your horse gets what they need.
First they started talking about the volume of email sent by SmartPak. Their mails aren’t that consistent, but they mail between 25 and 30 emails a month. Some months last year they mailed every day.
What they started seeing, though, is that the volume of marketing mail drove list churn. The biggest reason users gave for unsubscribing was “too much volume.” The more mail they sent, the more unsubscribes they saw. Even worse, more volume did not translate into revenue. As email volume went up, email performance decreased.
They tested adding content to emails. Just a block on the side of the email with links to content on their website. Adding the content links increased click through rates by 9% and revenue per email by 15%.
These results don’t require the content be in the emails. Using emails to drive recipients to already existing content on the website, including videos and surveys.
The session didn’t specifically discuss deliverability directly, but I think there were some clear deliverability benefits to content marketing. In fact, an email with no call to action, simply a post-purchase “what to expect” email had an open rate of 33%. These types of open rates help improve overall reputation and lead to more inbox deliveries.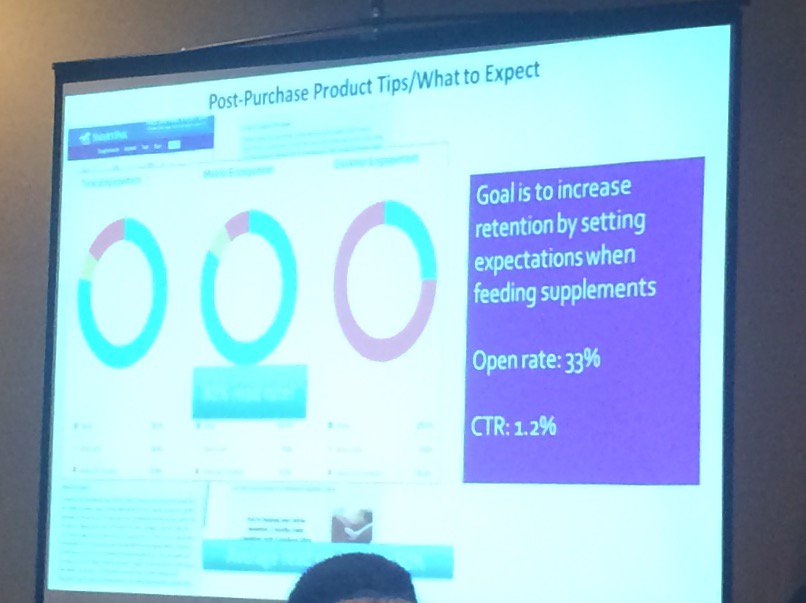
The session really drove home how valuable content marketing is. One thing that was continually repeated during the session is that most marketers have the content already. Use email to drive users to the content you already have. Include that content in marketing mails. Meet the recipient’s needs and wants.
There are a couple takeaways I got from the session.