ISPs
They Must Have Changed Something…
One of the most common refrains I hear from folks with delivery problems is that the filters must have changed because their mail suddenly started to go to the bulk folder. A few years ago, I posted about how even when there is no change in the sender’s behavior, reputation can slowly erode until mail suddenly goes to the Gmail bulk folder. Much of that still applies – although the comments on pixel loads (what other folks call ‘open rates’) are a bit outdated due to changes in Gmail behavior.
Read MoreIs email dead?
These last few years have been something, huh? Something had to give and, in my case, that something was blogging. There were a number of reasons I stopped writing here, many of them personal, some of them more global. I will admit, I was (and still am a little) burned out as it seemed I was saying and writing the same things I’d been saying and writing for more than a decade. Taking time off has helped a little bit, as much to focus on what I really want to talk about.
Read MoreHappy New Year
Well, it’s 2020. The start of a new year and a new decade, or not depending on what number theory you use to count decades. Personally, I think we, as pattern loving humans, just happen to love numbers that end with 0 and we’re going to consider it special whether or not it’s the actual end or start of a decade.
Read MoreTheir network, their rules
Much of the equipment and wires that the internet runs on is privately owned, nor is it a public utility in the traditional sense. The owners of the property have a lot of leeway to do what they like with that property. Yes, there are standards, but the standards are about interoperability. They describe things you have to do in order to exchange traffic with other entities. They do not dictate internal policies or processes.
Read MoreSuccessful sends on Black Friday
Last year a number of ISPs mentioned the Black Friday email volume was congesting their systems and causing delays. While anecdotally it seems that volume is up over last year I also haven’t heard any ISPs talking about congestion. Likewise, most of the delivery folks I’ve spoken too today and over the weekend are saying there were no major problems.
Read MoreThe inbox is a moving target
The more I look at the industry, the more convinced I am that we’re in the middle of a fundamental shift in how email is filtered. This shift will change how we handle email deliverability and what tools we have and what information we can use as senders to address challenges to getting to the inbox.
Read MoreWhat does mitigation really mean?
It is a regular occurrence that senders ask filters and ISPs for mitigation. But there seems to be some confusion as to what mitigation really means. I regularly hear from senders who seem to think that once they’ve asked for mitigation that they don’t have to worry about filtering or blocking at that ISP for a while. They’re surprised when a few weeks or even days after they asked for mitigation their mail is, one again, blocked or in the bulk folder.
Filters evolving
I started writing this blog post while sitting on a conference call with a bunch of senders discussing some industry wide problems folks are having with delivery. Of course the issue of Microsoft comes up. A lot of senders are struggling with reaching the inbox there and no one has any real, clear guidance on how to resolve it. And the MS employees who regularly answer questions and help folks have been quiet during this time.
In some ways the current situation with Microsoft reminds me of what most deliverability was like a decade ago. Receivers were consistently making changes and they weren’t interacting with senders. There weren’t FBLs really. There weren’t postmaster pages. The reason knowing someone at an ISP was so important was because there was no other way to get information about blocking.
These days, we have a lot more institutional knowledge in the industry. The ISPs realized it was better to invest in infrastructure so senders could resolve issues without having to know the right person. Thus we ended up with postmaster pages and a proliferation of FBLs and best practices and collaboration between senders and receivers and the whole industry benefited.
It is challenging to attempt to troubleshoot deliverability without the benefit of having a contact inside ISPs. But it is absolutely possible. Many ISP folks have moved on over the years; in many cases due to layoffs or having their positions eliminated. The result is ISPs where there often isn’t anyone to talk to about filters.
The lack of contacts doesn’t mean there’s no one there and working. For instance, in the conference call one person asked if we thought Microsoft was going to fix their systems or if this is the new normal. I think both things are actually true. I think Microsoft is discovering all sorts of interesting things about their mail system code now that it’s under full load. I think they’re addressing issues as they come up and as fast as they can. I also think this is some level of a new normal. These are modern filters that implement the lessons learned over the past 20 years of spam filtering without the corresponding cruft.
Overall, I do think we’re in a period of accelerating filter evolution. Address filtering problems has always been a moving target, but we’ve usually been building on known information. Now, we’re kinda starting over. I don’t have a crystal ball and I don’t know exactly what the future will bring. But I think the world of deliverability is going to get challenging again.
Cyber Monday volumes
Wow! Congrats to all the senders out there for sending So Much Volume that mail servers are full. I’ve even seen reports that STARTTLS connections are taking multiple seconds to establish at Gmail. The volume of mail that it takes to make Google slow down is impressive.
Of course, Gmail isn’t the only system exhibiting slow downs. Other major consumer webmail providers are also showing signs their servers are under heavy load. I’m seeing reports about both AOL and Microsoft accepting mail slowly. Oddly enough, I’ve not seen anything about Yahoo having issues. Maybe folks just never use yahoo.com addresses any more.
There may not be a fix for this. It is very possible receiving systems just do not have the capacity to handle the volume of mail folks want to send today. If senders have, collectively, decided to send more mail than max capacity there isn’t much that can be done. Maybe some very forward thinking ISPs have spare servers they can deploy, but it’s unlikely.
No major advice here, just a warning that receivers may not be able to access all the mail that’s currently being shoved at them. Nothing to do except retry, and perhaps hold off some “less urgent” sends until after normal business hours. Those of you who are sending Cyber Monday sales emails may just have to extend them to Tuesday in some cases.
EDIT: After I posted this, I saw problems with Yahoo (mail accepted but not making it to the inbox) and Earthlink as well.
Marketing automation plugins facilitate spam
There’s been an explosion of “Google plugins” that facilitate spam through Gmail and G Suite. They have a similar set of features. Most of these features act to protect the spammer from spam filtering and the poor reputation that comes from purchasing lists and incessantly spamming targets. Some of these plugins have all the features of a full fledged ESP, except a SMTP server and a compliance / deliverability team.
I’ll give the folks creating these programs credit. They identified that the marketers want a way to send mail to purchased lists. But ESPs with good deliverability and reputations don’t allow purchased lists. ESPs that do allow purchased lists often have horrible delivery problems. Enter the spam enabling programs.
From the outside, the folks creating these programs have a design goal to permit spam without the negatives. What do I mean? I mean that the program feature set creates an environment where users can send spam without affect the rest of their mail.
The primary way the software prevents spam blocking is using Google, Amazon or Office 365 as their outbound mail server. Let’s be frank, these systems carry enough real mail, they’re unlikely to be widely blocked. These ISPs are also not geared up to deal with compliance the same way ESPs or consumer providers are.
There seem to be more and more of these companies around. I first learned of them when I started getting a lot of spam from vaguely legitimate companies through google mail servers. Some of them were even kind enough to inform me they were using Gmail as their marketing strategy.
I didn’t realize quite how big this space was, though. And it does seem to be getting even bigger.
Then a vendor in the space reached out looking for delivery help for them and their customers. Seems they were having some challenges getting mail into some ISPs. I told them I couldn’t help. They did mention 3 or 4 names of their competitors, to help me understand their business model.
Last week, one of the companies selling this sort of software asked me if I’d provide quotes for a blog article they were writing. This blog article was about various blocklists and how their software makes it such that their customers don’t really have to worry about blocking. According to the article, even domain based blocking isn’t an issue because they recommend using a domain completely separate from their actual domain. I declined to participate. I did spend a little time on their website just to see what they were doing.
This morning a vendor in the space joined one of the email slack channels I participate in asking for feedback on their software. Again, they provide software so companies can send spam through google outbound IPs. Discussions with the vendor made it clear that they take zero responsibility for how their software is used.
I don’t actually expect that even naming and shaming these companies facilitating spam will do anything to change their minds. They don’t care about the email ecosystem or how annoying their customers are. About the best they could do is accept opt-out requests from those of us who really don’t want to be bothered by their customers. Even that won’t really help, even domain based opt-outs are ineffective.
What needs to happen is companies like Google, Amazon and Microsoft need to step up and enforce their anti-spam policies.
Reading between the lines
Reading between the lines an important skill in deliverability.
Why? Over the last few years there’s been an increasing amount of collaboration between deliverability folks at ESPs and ISPs. This is great. It’s a vast improvement on how things were 10 years ago. However, there are still ongoing complaints from both sides. There probably always will be. And it’s not like a blog post from me is going to fix anything. But I see value in talking a bit about how we can improve our ability to collaborate with one another.
Naming Names
One of the things that regularly happens at email conferences is a bunch of representatives from various ISPs and sometimes deliverability companies get up on stage and entertain questions from the audience about how to get email to the inbox. I’ve sat in many of these sessions – on both sides of the stage. The questions are completely predictable.
Almost invariably, someone asks if they can quote the ISP representative, because there is this belief that if you connect a statement with an employee name that will give the statement more weight. Except it doesn’t really. People who aren’t going to listen to the advice won’t listen to it even if there are names attached.
A lot of what I publish here is based on things the ISP reps have said. In some cases the reps actually review and comment on the post before I publish it. I don’t really believe attaching names to these posts will make them any more accurate. In fact, it will decrease the amount of information I can share and will increase the amount of time it takes to get posts out.
Last night I was joking with some folks that I should just make up names for attribution. Al did that many years ago, coining the pseudonym Barry for ISP reps. Even better, many of the ISP employees adopted Barry personas and used them to participate in different online spaces. Barry A. says X. Barry B. says Y. Barry C. says W. Barry D.
It doesn’t matter what names I attach.
I think I’m going to start adding this disclaimer to the appropriate blog posts:
Any resemblance to persons living or dead should be plainly apparent to them and those that know them. All events described herein actually happened, though on occasion the author has taken certain, very small, liberties with narrative.
Because, really.
Truth, myths and realities
For a long time it was a known fact that certain ISPs recycled abandoned addresses into spamtraps. There were long discussions by senders about this process and how it happened. Then at a conference a few years ago representatives of ISPs got up and announced that they do not recycle addresses. This led to quite a bit of consternation about how deliverability folks were making things up and were untrustworthy and deceptive.
In the early 2000’s ISPs were throwing a lot of things at the wall to deal with mail streams that were 80 – 90% bulk. They tried many different things to try and tame volumes that were overwhelming infrastructure. ISPs did try recycled traps. I know, absolutely know, two did. I am very sure that others did, too, but don’t have specific memories of talking to specific people about it.
At that time, a lot of deliverability knowledge was shared through word of mouth. That turned into a bit of an oral history. The problem with oral history is that context and details get lost. We can use the story of the ISP that did/did not recycle traps as an example.
Deliverability folks talk about an ISP that recycles traps. They don’t mention how often it happens. Some folks make the assumption that this is an ongoing process. It’s not, but anyone who knows it’s not risks violating confidences if they correct it. Besides, if senders believe it’s an ongoing process maybe they’ll be better behaved. Eventually, the story becomes all ISPs recycle traps all the time. This is our “fact” that’s actually a myth.
Then an ISP employee goes to a conference an definitively states they don’t recycle traps. I believe he stated the truth as he knows it to be. That ISP moved on from recycled traps to other kinds of traps because there were better ways to monitor spam.
We were talking about this on one of the deliverability lists and I told another story.
[ISP] recycled addresses once – back when JD was there which must have been, oh, around 2005/6 or so. I heard this directly from JD. It wasn’t done again, but a whole bunch of people just assumed it was an ongoing thing. Since my knowledge was a private conversation between JD and me, I never felt comfortable sharing the information. Given the circumstances, I’ve decided it’s OK to start sharing that end of the story a little more freely.
No one set out to create a myth, it just happened. No one intended to mislead. But sometimes it happens.
iOS List Unsubscribe Functionality
Al did a great post over on Spamresource about the how the new list unsubscribe function in the default mail client from iOS10. What’s been interesting to me is how much I’m hearing from ESP folks about how their customers want it gone.
If you don’t know what we’re talking about, in the default mail client on iOS10, Apple is now offering a way to unsubscribe from list mail by placing an unsubscribe link at the top of the message.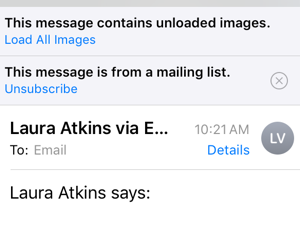
As you can see, this isn’t just for commercial mail, it’s in place for every mailing list that has a List-Unsubscribe header. (This is a screenshot from something I posted to OI this morning). For me, it’s somewhat intrusive. I’m on a lot of discussion lists – technical, marketing, business and even a couple social ones. Reading them on my phone has become a challenge, as every email in a thread contains the “unsubscribe” button now.
Luckily, you can dismiss the message for all posts to that mailing list by hitting the ⮾⮾⮾⮾x. Interestingly, once you’ve turned it off there seems to be no way to turn it back on for that list.
Senders have different complaints, however, they do not have to do with intrusiveness or usability issues.
I’ve heard complaints about placement and about how easy it makes it to unsubscribe. One person even stated that everyone knows the place for an unsubscribe is at the bottom of a message and it should never be at the top of a message. I find these arguments unpersuasive. Unsubscribing should be easy. Unsubscribing should be trivial. People should be able to stop getting mail on a whim. Particularly here in the US, where unsolicited mail is legal, being able to quickly opt-out is the only thing keeping some of our mailboxes useful.
I’ve also heard some concerns that are a little more understandable. One company was concerned that unsubscribes go directly to their ESP rather than directly to them. This is a somewhat more understandable concern. Good senders use unsubscribes as part of their KPIs and as part of their campaign metrics. They know how much an unsubscribe costs them and will use that as part of their metrics for defining a successful campaign. Still, though, it’s not that big a concern. ESPs are already handling these kinds of unsubscribes from providers like gmail and hotmail.
Almost 7 years ago I blogged about a sender who wanted an unsubscribe link in the email client. It was a bit of snark on my part. The interesting part, though, is that some senders want unsubscribe mediated in the client and others things it’s horrible. I think this tells me that there’s no universal right answer. It Depends might be the most hated statement in deliverability, but it is the absolutely the reality of the situation.
Purchased lists and ESPs: 9 months later
It was about 8 months ago I published a list of ESPs that prohibit the use of purchased lists. There have been a number of interesting responses to that post.
ESPs wanted to be added to the list
The first iteration of the list was crowdsourced from different ESP representatives. They shared the info they had with each other. With their permission, I put it together into a post and published it here. Since then, I’ve had a trickle of ESPs asking to be added to the list. I’m happy to add any ESP. The only requirement is a privacy policy (or AUP) that states no purchased lists.
People reference the list regularly
I’ve had a lot of ESP deliverability folks send thanks for writing this post. They tell me they reference it regularly when dealing with clients. It’s also been listed as “one of the best blog posts of 2015” by Pardot.
Some 2016 predictions build on the post
I’ve read multiple future predictions that talk about how the era of purchased lists is over. I don’t think they’re wrong. I think that purchased lists are going to be deliverability nightmares on an internet where users wanting a mail is a prime factor in inbox deliverability. They’re already difficult to deliver, but it’s going to get worse.
Not everyone thinks this is a good post. In fact, I just recently got an comment about how wrong I was, and… well, I’ll just share it because I don’t think my summary of it will do it any justice.
What do you think about these hot button issues?
 It’s been one of those weeks where blogging is a challenge. Not because I don’t have much to say, but because I don’t have much constructive to say. Rants can be entertaining, even to write. But they’re not very helpful in terms of what do we need to change and how do we move forward.
It’s been one of those weeks where blogging is a challenge. Not because I don’t have much to say, but because I don’t have much constructive to say. Rants can be entertaining, even to write. But they’re not very helpful in terms of what do we need to change and how do we move forward.
A few different things I read or saw brought out the rants this week. Some of these are issues I don’t have answers to, and some of them are issues where I just disagree with folks, but have nothing more useful to say than, “You’re wrong.” I don’t even always have an answer to why they’re wrong, they’re just wrong.
I thought today I’d bring up the issues that made me so ranty and list the two different points of views about them and see what readers think about them. (Those of you who follow me on Facebook probably know which ones my positions are, but I’m going to try and be neutral about my specific positions.)
Buying lists costs more than just money
 I’ve been talking to a lot of companies recently who are dealing with some major delivery challenges probably related to their practice of purchasing lists and then sending advertising to every address on the list. They assure me that their businesses would be non-viable if they didn’t purchase lists and it has to be that way.
I’ve been talking to a lot of companies recently who are dealing with some major delivery challenges probably related to their practice of purchasing lists and then sending advertising to every address on the list. They assure me that their businesses would be non-viable if they didn’t purchase lists and it has to be that way.
Maybe that’s true, maybe it is more cost effective to purchase lists and send mail to them. I know, though, that their delivery is pretty bad. And that a lot of the addresses they buy never see their email. And that they risk losing their ESP, or they risk being SBLed, or they risk being blocked at Gmail, or they risk bulk foldering at Hotmail. There are a lot of risks to using purchased lists.
The reality is it’s only getting harder to mail to purchased lists and it’s getting more expensive to mail purchased lists. Paying for the list is a small part of the cost of using them.
Other costs incurred by companies using purchased lists include:
1) Having multiple ESPs. There are certainly legitimate reasons for companies to use different ESPs but there is a cost associated with it. Not only do they have to pay for duplicate services, but they spend a lot of employee time moving lists and recipients around to see who might have the better delivery today.
2) Multiple domains and brand new websites for every send. Landing pages are good marketing and are normal. But some ISPs track the IPs of the landing sites, and those IPs can get their own poor reputation. To get around it, senders using purchased lists often have to create new websites on new IPs for every send.
3) Complicated sending schedules. Sending schedules aren’t dictated by internal needs, they’re dictated by what ISP is blocking their IPs or domains (or even ESP) right now.
All of these costs are hidden, though. The only cost on the actual bottom line is the money they spend for the addresses themselves and that’s peanuts. Because, fundamentally, the folks selling addresses have no incentive to take any care in collecting or verifying the data. In fact, any verification they do only cuts into their profit, as buyers won’t actually pay for the verification and data hygiene and it also reduces the size of the lists they can sell.
And, no, data hygiene companies that look for traps and bounces and “bad addresses” don’t take a bad list and make it good. They just take a bad list and make it a little less bad. If the recipients don’t want the mail, all the hygiene in the world isn’t going to get that message into the inbox.
Outsourcing address collection to list selling companies is more expensive than it looks on paper. That doesn’t stop anyone from building a business around purchased lists, though.
October 2015: The month in email

When you spend most of your day working on email and spam issues, it starts to cross into all aspects of your life. In October, I was amused by authors who find names in spam, SMTP-related t-shirts on camping trips, and spam that makes you laugh. Maybe I need a vacation?
We were quite busy with conference presentations and client work this month, but took time to note the things that captured our attention, as always. We highlighted a few things we enjoyed reading around the web: Brian Krebs’ Reddit AMA, the results of Jan Schaumann’s survey on ethics in internet operations, and a great post on Usenet from Joe St. Sauver.
In industry news, we covered a few glitches that are worth noting, in case you missed them: Yahoo FBL confirmation emails, Google postmaster tools, Network Solutions email, and weird Lashback listings. Even though these have mostly been resolved, it’s useful to keep track of the types and frequency of these sorts of issues, as they can significantly impact your deliverability and may be useful as your clients or business stakeholders raise questions about campaign performance.
Steve contributed a few key technical posts this month, including a short post on IPv6 authentication issues, following up on the issues he outlined back in July. He also noted Gmail’s upcoming move to DMARC p=reject, which is notable for the ways they are are looking to mitigate risks with their ARC proposal. Finally, he wrote that it’s worth looking at false positives every now and then, as it can reveal interesting patterns in the ESP landscape.
Finally, a good suggestion from the best practices file: engagement through confirming user names, and a not-so-good plan for an app that’s sure to invite abuse and harassment.
Are botnets really the spam problem?
Over the last few years I’ve been hearing some people claim that botnets are the real spam problem and that if you can find a sender then they’re not a problem. Much of this is said in the context of hating on Canada for passing a law that requires senders actually get permission before sending email.
Botnets are a problem online. They’re a problem in a lot of ways. They can be used for denial of service attacks. They can be used to mine bitcoins. They can be used to host viruses. They can be used to send spam. They are a problem and a lot of people spend a lot of time and money trying to take down botnets.
For the typical end user, though, botnets are a minor contributor to spam in the inbox. Major ISPs, throughout the world, have worked together to address botnets and minimize the spam traffic from them. Those actions have been effective and many users never see botnet spam in their inbox, either because it’s blocked during send or blocked during receipt.
Most of the spam end users have to deal with is coming from people who nominally follow CAN SPAM. They have a real address at the bottom of the email. They’re using real ISPs or ESPs. They have unsubscribe links. Probably some of the mail is going to opt-in recipients. This mail is tricky, and expensive, to block, so a lot more of it gets through.
Much of this mail is sent by companies using real ISP connections. Brian Krebs, who I’ve mentioned before, wrote an article about one hosting company who previously supported a number of legal spammers. This hosting company was making $150,000 a month by letting customers send CAN SPAM legal mail. But the mail was unwanted enough that AOL blocked all of the network IP space – not just the spammer space, but all the IP space.
It’s an easy decision to block botnet sources. The amount of real mail coming from botnet space is zero. It’s a much bigger and more difficult decision to block legitimate sources of emails because there’s so much garbage coming from nearby IPs. What AOL did is a last resort when it’s clear the ISP isn’t going to stop spam coming out from their space.
Botnets are a problem. But quasi legitimate spammers are a bigger problem for filter admins and end users. Quasi legitimate spammers tend to hide behind ISPs and innocent customers. Some send off shared pools at ESPs and hide their traffic in the midst of wanted mail. They’re a bigger problem because the mail is harder to filter. They are bigger problems because a small portion of their recipients actually do want their mail. They’re bigger problems because some ISPs take their money and look the other way.
Botnets are easy to block, which makes them a solved problem. Spam from fixed IPs is harder to deal with and a bigger problem for endusers and filters.
Gmail having issues
As of 7/22/15, 1:17 PM, Google reports the issue is resolved.
Over on the mailop list multiple people are reporting delivery problems to Gmail.
The Google status page confirms this:
When spam filters fail
Spam filters aren’t perfect. They sometimes catch mail they shouldn’t, although it happens less than some people think. They sometimes fail to catch mail they should.
One of the reason filters fail to catch mail they should is because some spammers invest a lot of time and energy in figuring out how to get past the filters. This is nothing new, 8 or 9 years ago I was in negotiations with a potential client. They told me they had people who started working at 5pm eastern. Their entire job was to craft mail that would get through Hotmail’s filters that day. As soon as they found a particular message that made it to the inbox, they’d blast to their list until the filters caught up. When the filters caught up, they’d start testing again. This went on all night or until the full list was sent.
Since then I’ve heard of a lot of other filter bypass techniques. Some spammers set up thousands of probe accounts at ISPs and would go through and “not spam” their mail to fool the filters (ISPs adapted). Some spammers set up thousands of IPs and rotate through them (ISPs adapted). Some spammers register new domains for every send (ISPs adapted). Some spammers used botnets (ISPs adapted)
I’m sure, even now, there are spammers who are creating new techniques to get through filters. And the ISPs will adapt.
Mythbusting deliverability and engagement
Yesterday I published an article talking about an engagement webinar hosted by the EEC and DMA. I made a couple predictions about what would be said.
Read MoreDelivery and engagement
Tomorrow is the webinar Mythbusters: Deliverability vs. Engagement. This webinar brings together the ISP speakers from EEC15, plus Matt from Comcast, to expand on their comments. There’s been some confusion about the impact of engagement on delivery and whether or not senders should care about recipient engagement.
My opinion on the matter is well known: recipient engagement drives delivery to the inbox at some providers. I expect tomorrow we’ll hear a couple things from the ISPs.
Engagement, ISPs and the EEC
There’s been some controversy over some of the things said by the ISPs at the recent EEC meeting. Different people interpret what was said by the ISPs in different ways. The EEC has set up a webinar for March 17 to clarify and explain what was meant by the ISPs.
Read MoreEmail filtering: not going away.
 I don’t do a whole lot of filtering of comments here. There are a couple people who are moderated, but generally if the comments contribute to a discussion they get to be posted. I do get the occasional angry or incoherent comment. And sometimes I get a comment that is triggers me to write an entire blog post pointing out the problems with the comment.
I don’t do a whole lot of filtering of comments here. There are a couple people who are moderated, but generally if the comments contribute to a discussion they get to be posted. I do get the occasional angry or incoherent comment. And sometimes I get a comment that is triggers me to write an entire blog post pointing out the problems with the comment.
Today a comment from Joe King showed up for The Myth of the Low Complaint Rate.
Dodging filters makes for effective spamming
Spam is still 80 – 90% of global email volume, depending on which study look at. Most of that spam doesn’t make it to the inbox; ISPs reject a lot of it during the SMTP transaction and put much of rest of it in the bulk folder. But as the volumes of spam have grown, ISPs and filters are relying more and more on automation. Gone are the days when a team of people could manually review spam and tune filters. There’s just too much of it out there for it to be cost effective to manually review filters.
In some ways, though, automatic filters are easier to avoid than manual filters. Take a spam that I received at multiple addresses today. It’s an advertisement for lists to “meet my marketing needs.” I started out looking at this mail to walk readers through all of the reasons I distrusted this mail. But some testing, the same sorts of testing I do for client mails, told me that this mail was making it to the inbox at major ISPs.
What told me this mail was spam? Let’s look at the evidence.
Top Commented Blog Posts on WttW in 2014
Here are the top 6 most commented on blog topics our Industry News & Analysis blog.
Read MoreEmail problems are costly
Last week Zulily released their quarterly earnings. Their earnings’ report was disappointing, resulting in a drop in their stock prices. The chairman of the company told reporters on a conference call that part of the reason for the drop in earnings were due to deliverability problems “at a large ISP.”
Read MoreWhat about the bots?
M3AAWG published a letter to the FCC addressing the implementation of CSRIC III Cybersecurity Best Practices (pdf link)
The takeaway is that of the ISPs that contribute data to M3AAWG (37M+ users), over 99% of infected users receive notification that they are infected.
I hear from senders occasionally that they are not the problem, bots are the problem and why isn’t anyone addressing bots. The answer is that people are addressing the bot problem.
ISP relations in a nutshell
Senders: You’re blocking our mail, why?
Receivers: Because you’re spamming, stop spamming and we won’t block you.
Senders: But we’re not spamming. What do you mean we’re spamming! How could we be spamming, we’re not sending spam!
Receivers: You’re doing all these things (generating complaints, sending to dead accounts, hitting spam traps, not bounce handling, etc) that makes your mail indistinguishable from spam.
Senders: But we can’t tell what we’re doing wrong unless you give us more data!
Receivers: OK, fine. Here are FBLs, postmaster pages, sender access to support people. Now, stop spamming.
time passes
Receivers: It’s costing us how much to provide support to senders?!?! And after years of giving them lots of data it’s still the same problems over and over again? We’re not a charity, we’re going to control our costs and stop providing so much personal support.
And that, readers, is why receivers are pulling back from providing the data they used to.
ISPs speak at M3AAWG
Last week at M3AAWG representatives from AOL, Yahoo, Gmail and Outlook spoke about their anti-spam technologies and what the organizations were looking for in email.
This session was question and answers, with the moderator asking the majority of the questions. These answers are paraphrased from my notes or the MAAWG twitter stream from the session.
What are your biggest frustrations?
AOL: When senders complain they can’t get mail in and we go look at their stats and complaints are high. Users just don’t love that mail. If complaints are high look at what you may have done differently, content does have an effect on complaints.
Outlook: When we tightened down filters 8 years ago we had to do it. Half of the mail in our users inbox was spam and we were losing a steady number of customers. The filter changes disrupted a lot of senders and caused a lot of pain. But these days only 0.5% of mail in the inbox is spam. Things happen so fast, though, that the stress can frustrate the team.
Gmail: Good senders do email badly sometimes and their mail gets bulked. Senders have to get the basic email hygiene practices right. Love your users and they’ll love you back.
What’s your philosophy and approach towards mail?
AOL: There is a balance that needs to be struck between good and bad mail. The postmaster team reminds the blocking team that not all mail is bad or malicious. They are the sender advocates inside AOL. But the blocking team deals with so much bad mail, they sometimes forget that some mail is good.
Yahoo: User experience. The user always comes first. We strive to protect them from malicious mail and provide them with the emails they want to see. Everything else is secondary.
Gmail: The faster we stop spam the less spam that gets sent overall. We have highly adaptive filters that can react extremely quickly to spam. This frustrates the spammers and they will give up.
Outlook: The core customer is the mailbox user and they are a priority. We think we have most of the hardcore spam under control, and now we’re focused on personalizing the inbox for each user. Everyone online should hold partners accountable and they should expect to be held accountable in turn. This isn’t just a sender / ESP thing, ISPs block each other if there are spam problems.
What are some of your most outrageous requests?
We’ve been threatened with lawsuits because senders just don’t want to do the work to fix things. Some senders try to extort us. Other senders go to the advertising execs and get the execs to yell at the filtering team.
Coming to MAAWG and getting cornered to talk about a particular sender problem. Some senders have even offered money just to get mail to the spam folder.
Senders who escalate through the wrong channels. We spent all this money and time creating channels where you can contact us, and then senders don’t use them.
Confusing business interests with product interests. These are separate things and we can’t change the product to match your business interest.
What are your recommendations for changing behaviors?
Outlook: We provide lots of tools to let you see what your recipients are doing. USE THE TOOLS. Pay attention to your recipient interaction with mail. Re-opt-in recipients periodically. Think about that mail that is never opened. Monitor how people interact with your mail. When you have a problem, use our webpages and our forms. Standard delivery problems have a play book. We’re going to follow that playbook and if you try to get personal attention it’s going to slow things down. If there’s a process problem, we are reachable and can handle them personally. But use the postmaster page for most things.
Gmail: Get your hygiene right. If you get your hygiene right, deliverability just works. If you’re seeing blocking, that’s because users are marking your mail as spam. Pay attention to what the major receivers publish on their postmaster pages. Don’t just follow the letter of the law, follow the spirit as well. Our responsibility, as an ISP, is to detect spam and not spam. Good mailers make that harder on us because they do thinks that look like spammers. This doesn’t get spammer mail in more, it gets legitimate mail in less. Use a real opt-in system, don’t just rely on an implied opt-in because someone made a purchase or something.
Yahoo: ESPs are pretty good about screening their customers, so pay attention to what your ESPs are saying. Send mail people want. Verify that the email addresses given to you actually belong to people who want your mail. Have better sender practices.
What do you think about seed accounts?
The panel wasn’t very happy about the use of seed accounts. Seeds are not that useful any longer, as the ISPs move to more and more personalized delivery. Too much time and too many cycles are used debugging seed accounts. The dynamic delivery works all ways.
When things go wrong what should we do?
AOL: Open a ticket. We know we’ve been lax recently, but have worked out of our backlog and are caught up to date. Using the ticketing system also justifies us getting more headcount and makes everyone’s experience better. Also, don’t continue what you’re doing. Pausing sending while you’re troubleshooting the issue. We won’t adjust a rep for you, but we may be able to help you.
Gmail: Do not jump the gun and open a ticket on the first mail to the spam folder. Our filters are so dynamic, they update every few minutes in some cases. Be sure there is a problem. If you are sure you’re following the spirit and letter of the sender guidelines you can submit a ticket. We don’t respond to tickets, but we work every single one. When you’re opening a ticket provide complete information and full headers, and use the headers from your own email address not headers from a seed account. Give us a clear and concise description of the problem. Also, use the gmail product forum, it is monitored by employees and it’s our preferred way of getting information to the anti-abuse team. Common issues lots of senders are having will get addressed faster.
Outlook: Dig in and do your own troubleshooting, don’t rely on us to tell you what to fix. The support teams don’t have a lot of resources so use our public information. If you make our job harder, then it takes longer to get things done. But tell us what changes you’ve made. If you’ve fixed something, and tell us, our process is different than if you’re just asking for a delisting or asking for information. When you’ve fixed things we will respond faster.
How fast should users expect filters to respond after making changes?
Filters update continually so they should start seeing delivery changes almost immediately. What we find is people tell us they’ve made changes, but they haven’t made enough or made the right ones. If the filters don’t update, then you’ve not fixed the problem.
Engagement, it's not what you might think
Most delivery experts will tell you that ISPs measure recipient engagement as a part of their delivery. That’s absolutely true, but I think there’s a language difference that makes it hard for senders to understand what we mean by engagement.
ISPs, and other filtering companies, profile their user base. They know, for instance, who logs in and checks mail every day. They know who checks mail every 20 seconds. They know who gets a lot of spam. They know who hasn’t logged in for months. They know who accurately marks mail as spam and who is sloppy with the this-is-spam button. They know if certain recipients get the same mail, it’s likely to be spam.
Engagement at the ISPs is more about the recipient engaging with their email address and the mail in their mailbox then it is about the recipient engaging with specific emails.
Abuse it and lose it
Last week I blogged about the changes at ISPs that make “ISP Relations” harder for many senders. But it’s not just ISPs that are making it a little more difficult to get answers to questions, some spam filtering companies are pulling back on offering support to senders.
For instance, Cloudmark sent out an email to some ESPs late last week informing them that Cloudmark was changing their sender support policies. It’s not that they’re overwhelmed with delisting requests, but rather that many ESPs are asking for specific data about why the mail was blocked. In December, Spamcop informed some ESPs that they would stop providing data to those ESPs about specific blocks and spam trap hits.
These decisions make it harder for ESPs to identify specific customers and lists causing them to get blocked. But I understand why the filtering companies have had to take such a radical step.
Support for senders by filtering companies is a side issue. Their customers are the users of the filtering service and support teams are there to help paying customers. Many of the folks at the filtering companies are good people, though, and they’re willing to help blocked senders and ESPs to figure out the problem.
For them, providing information that helps a company clean up is a win. If an ESP has a spamming customer and the information from the filtering company is helping the ESP force the customer to stop spamming that’s a win and that’s why the filtering companies started providing that data to ESPs.
Unfortunately, there are people who take advantage of the filtering companies. I have dozens of stories about how people are taking advantage of the filtering companies. I won’t share specifics, but the summary is that some people and ESPs ask for the same data over and over and over again. The filtering company rep, in an effort to be helpful and improve the overall email ecosystem, answers their questions and sends the data. In some cases, the ESP acts on the data, the mail stream improves and everyone is happy (except maybe the spammer). In other cases, though, the filtering company sees no change in the mail stream. All the filtering company person gets is yet another request for the same data they sent yesterday.
Repetition is tedious. Repetition is frustrating. Repetition is disheartening. Repetition is annoying.
What we’re seeing from both Spamcop and Cloudmark is the logical result from their reps being tired of dealing with ESPs that aren’t visibly fixing their customer spam problems. Both companies are sending some ESPs to the back of the line when it comes to handling information requests, whether or not those ESPs have actually been part of the problem previously.
The Cloudmark letter makes it clear what they’re frustrated about.
SBCGlobal having a bad day
I’m seeing scattered reports of the SBCGlobal.net MTAs refusing connections. No current information about fixes.
ISP Relationships
Delivra has a new whitepaper written by Ken Magill talking about the value (or lack thereof) of relationships with ISPs. In Ken’s understated way, he calls baloney on ESPs that claim they have great delivery because they have good relationships with ISPs.
He’s right.
I get a lot of calls from potential clients and some calls from current clients asking me if I can contact an ISP on their behalf and “tell the ISP we’re really not a spammer”. My normal answer is that I can, but that there isn’t a place in the spam filtering process for “sender has hired Laura and she says they’re not a spammer.” I mean, it would be totally awesome if that was the case. But it’s not. It’s even the case where I’m close friends with folks inside the ISPs.
I’m pretty sure I’ve told the story before about being at a party with one of the Hotmail ISP folks. There was a sender that had hired me to deal with some Hotmail issues and I’d been working with Barry H. (name changed, and he’s not at Hotmail any more) to resolve it. During the course of the party, we started talking shop. Barry told me that he was sure that my client was sending opt-in mail, but that his users were not reacting well for it. He also told me there was no way he could override the filters because there wasn’t really a place for him to interfere in the filtering.
Even when folks inside the ISPs were willing and able to help me, they usually wouldn’t do so just because I asked. They might look at a sender on my request, but they wouldn’t adjust filters unless the sender met their standards.
These days? ISPs are cutting their non-income producing departments to the bone, and “sender services” is high up the list of departments to cut. Most of the folks I know have moved on from the ISP to the ESP side. Ken mentions one ISP rep that is now working for a sender. I actually know of 3, and those are just employees from the top few ISPs who are now at fairly major ESPs. I’m sure there are a lot more than that.
The reality is, you can have the best relationships in the world with ISPs, but that won’t get bad mail into the inbox. Filters don’t work that way anymore. That doesn’t mean relationships are useless, though. Having relationships at ISPs can get information that can shorten the process of fixing the issue. If an ISP says “you are blocked because you’re hitting spam traps” then we do data hygiene. If the ISP says “you’re sending mail linking to a blocked website” then we stop linking to that website.
I have a very minor quibble with one thing Ken said, though. He says “no one has a relationship with Spamhaus volunteer, they’re all anonymous.” This isn’t exactly true. Spamhaus volunteers do reveal themselves. Some of them go around openly at MAAWG with nametags and affiliations. A couple of them are colleagues from my early MAPS days. Other do keep their identities secret, but will reveal them to people they trust to keep those identities secret. Or who they think have already figured it out. There was one drunken evening at MAAWG where the nice gentleman I was joking with leaned over and says “You know I am elided from Spamhaus, right?” Uh. No? I didn’t. I do now!
But even though I have the semi-mythical personal relationship with folks from Spamhaus, it doesn’t mean my clients get preferential treatment. My clients get good advice, because I know what Spamhaus is looking for and can translate their requirements into solid action steps for the client to perform. But I can think of half a dozen ESP delivery folks that have the same sorts of relationships with Spamhaus volunteers.
Overall, relationships are valuable, but they are not sufficient to fix inbox delivery problems.
Hunting the Human Representative
Yesterday’s post was inspired by a number of questions I’ve fielded recently from people in the email industry. Some were clients, some were colleagues on mailing lists, but in most cases they’d found a delivery issue that they couldn’t solve and were looking for the elusive Human Representative of an ISP.
There was a time when having a contact inside an ISP was almost required to have good delivery. ISPs didn’t have very transparent systems and SMTP rejection messages weren’t very helpful to a sender. Only a very few ISPs even had postmaster pages, and the information there wasn’t always helpful.
More recently that’s changed. It’s no longer required to have a good relationship at the ISPs to get inbox delivery. I can point to a number of reasons this is the case.
ISPs have figured out that providing postmaster pages and more information in rejection messages lowers the cost of dealing with senders. As the economy has struggled ISPs have had to cut back on staff, much like every other business out there. Supporting senders turned into a money and personnel sink that they just couldn’t afford any longer.
Another big issue is the improvement in filters and processing power. Filters that relied on IP addresses and IP reputation did so for mostly technical reasons. IP addresses are the one thing that spammers couldn’t forge (mostly) and checking them could be done quickly so as not to bottleneck mail delivery. But modern fast processors allow more complex information analysis in short periods of time. Not only does this mean more granular filters, but filters can also be more dynamic. Filters block mail, but also self resolve in some set period of time. People don’t need to babysit the filters because if sender behaviour improves, then the filters automatically notice and fall off.
Then we have authentication and the protocols now being layered on top of that. This is a technology that is benefiting everyone, but has been strongly influenced by the ISPs and employees of the ISPs. This permits ISPs to filter on more than just IP reputation, but to include specific domain reputations as well.
Another factor in the removal of the human is that there are a lot of dishonest people out there. Some of those dishonest people send mail. Some of them even found contacts inside the ISPs. Yes, there are some bad people who lied and cheated their way into filtering exceptions. These people were bad enough and caused enough problems for the ISPs and the ISP employees who were lied to that systems started to have fewer and fewer places a human could override the automatic decisions.
All of this contributes to the fact that the Human Representative is becoming a more and more elusive target. In a way that’s good, though; it levels the playing field and doesn’t give con artists and scammers better access to the inbox than honest people. It means that smaller senders have a chance to get mail to the inbox, and it means that fewer people have to make judgement calls about the filters and what mail is worthy or not. All mail is subject to the same conditions.
The Human Representative is endangered. And I think this is a good thing for email.
Having the same conversation
This morning I was reading a blog post about the failure of the congressional super committee. The author commented
Read MoreNot lazy, just annoyed
I don’t usually send in spam reports, but I submitted a couple in the last few weeks. Somehow an address of mine is on a bunch of rave / club lists in London. You want to know what is happening at London clubs this week? It’s all there in my spam folder.
This mail finally hit my annoyance threshold, so I’ve been submitting reports and complaints to the senders the last few weeks. The mail, with full headers, goes with an explanation that the address that received it was harvested off a website more than 5 years ago and never opted in to receive any mail.
One of the ISPs I sent the report to has a web form where the complainant and the customer can see the report and both can comment on it. The customer replied to my complaint on it.
Blocklist changes
Late last year we wrote about the many problems with SORBS. One of the results of that series of posts was a discussion between a lot of industry professionals and GFI executives. A number of problems were identified with SORBS, some that we didn’t mention on the blog. There was an open and free discussion about solutions.
A few months ago, there were a bunch of rumors that GFI had divested themselves from SORBS. There were also rumors that SORBS was purchased by Proofpoint. Based on publicly available information many of us suspected that GFI was no longer involved in SORBS. Yet other information suggested that Proofpoint may truly have been the purchaser.
This week those rumors were confirmed.
Email filters
What makes the best email filter? There isn’t really a single answer to that question. Different people and different organizations have different tolerances for how false positives versus false negatives. For instance, we’re quite sensitive to false positives here, so we run extremely conservative filtering and don’t block very much at the MTA level. Other people I know are very sensitive to false negatives and run more aggressive filtering and block quite a bit of mail at the MTA level.
For the major ISPs, the people who plan, approve, design and monitor the filters usually want to maximize customer happiness. They want to deliver as much real mail as possible while blocking as much bad mail. Blocking real mail and letting through bad mail both result in unhappy customers and increase the ISP’s costs, either through customer churn or through support calls. And this is a process, filters are not static. ISPs roll out new filters all the time, sometimes they are an improvement and sometimes they’re not. When they’re not, they’re pulled out of production. This works both for positive filters like Return Path and negative filters like blocklists.
Then there is mail filtering that doesn’t have to do with spam. Business filters, for instance, often block non-business mail. Permission of the recipient often isn’t even a factor. Companies don’t often go out of their way to block personal mail, but if personal mail gets blocked (say the vacation plane ticket or the amazon receipt) they don’t often unblock it. But when you think about why a business provides email, it makes perfect sense. The business provides email to further its own business goals. Some personal usage is usually OK, but if someone notices and blocks personal email then it’s unlikely the business will unblock it, even if the employee opted in.
In the case of email filters, the free market does work. Different ISPs filter mail differently. Some people love Gmail’s filters. Other people think Hotmail has the best filtering. There are different standards for filtering, and that makes email stronger and more robust. Consumers have choices in their mail provider and spamfiltering.
Changes at Gmail
As I’ve said before, I can usually tell when some ISP changes their filtering algorithm because I start getting tons and tons of calls about delivery problems at that ISP. This past month it’s been Gmail.
There have been two symptoms I’ve been hearing about. One is an increase in bulk folder delivery for mail that previously was reliably hitting the inbox. The other is a bit more interesting. I’ve heard of 3 different mailers, with good reputations and very clean lists, that are seeing 4xx delays on some of their mail. The only consistency I, and my colleagues at some ESPs, have identified is that the mail is “bursty.”
The senders affected by this do send out mail daily, but the daily mail is primarily order confirmations or receipts or other transactional mails. They send bi-weekly newsletters, though, exploding their volume from a few tens of thousands up to hundreds of thousands. This seems to trigger Gmail to defer mail. It does get delivered eventually. It’s frustrating to try and deal with because neither side is really doing anything wrong, but good senders are seeing delivery delays.
For the bulk foldering, Bronto has a good blog post talking about the changes and offering some solid suggestions for how to deal with them. I’m also hearing from some folks who are reliable that Gmail may be rolling back some of the bulk foldering changes based on feedback from their users.
So if you’re seeing changes at Gmail, it’s not just you.
You can't always get what you want
It’s a problem anyone who has done any delivery work has faced. There’s a client who is having blocklist problems or ISP delivery problems and they won’t pay any attention to what you say. They insist that you talk to the blocklist or the ISP or hand over contacts directly so they can “dialog with” someone internally. They don’t like what they’re hearing, and they hope that the answer will be different if they find a new person to talk to.
The reality is many of the people at ISPs and blocklists don’t want to talk to these types of senders. They may answer a friendly question from someone they know and trust, but sometimes not even then.
Some very large ISPs and major blocklists don’t even take sender questions. They won’t communicate with anyone about any delivery issues.
I’ve had to tell more than a few clients recently that various ISPs and blocklists weren’t interested in helping those clients with their delivery problems. There are two classes of reactions I get from clients. Some clients focus on moving forward. “OK, now what? How can we identify the issue, what data do we have and how can we figure out what the problem is?”
Other clients continue to look for ways to talk to whomever is blocking their mail. They’re convinced if they can just “explain their business model” or be told what they’re doing wrong, that all their delivery problems will magically disappear.
Needless to say those clients who focus on moving forward and looking at the information they do have have much better success resolving their delivery problems. What many senders don’t understand is the wealth of data they have that will help them resolve the issue. And even if they know it’s buried in their files, they don’t always know where to start looking or even what they’re looking for.
But that is, of course, why you hire someone like me who understands spamfiltering and email. I help senders understand how email filters work and identify what parts of their programs are likely to be responsible for delivery issues. I often find the most valuable service I provide to clients is a fresh set of eyes that can see the forest. With my help, they manage to stop obsessing unproductively about one particular symptom and focus on the underlying problems.
Senders who think the holy grail of problem resolution is speaking to the right person at an ISP or blocklist generally are disappointed, even when they hire someone who knows all the right people at the ISPs. They can’t always get what they want. But I can often help them get what they need.
Turn it all the way up to 11
I made that joke the other night and most of the folks who heard it didn’t get the reference. It made me feel just a little bit old.
Anyhow, Mickey beat me to it and posted much of what I was going to say about Ken Magill’s response to a very small quote from Neil’s guest post on expiring email headers last week.
I, too, was at that meeting, and at many other meetings where marketers and the folks that run the ISP spam filters end up in the same room. I don’t think the marketers always understand what is happening inside the postmaster and filtering desks on a day to day basis at the ISPs. Legitimate marketing? It’s a small fraction of the mail they deal with. Ken claims that marketing pays the salaries of these employees and they’d be out of a job if marketing didn’t exist. Possibly, but only in the context that they are paid to keep their employers servers up and running so that the giant promises made by the marketing team of faster downloads and better online experiences actually happen.
If there wasn’t an internet and there weren’t servers to maintain, they’d have good jobs elsewhere. They’d be building trains or designing buildings or any of the thousands of other jobs that require smart technical people.
Ken has no idea what these folks running the filters and keeping your email alive deal with on a regular basis. They deal with the utter dregs and horrors of society. They are the people dealing with unrelenting spam and virus and phishing attacks bad enough to threaten to take down their networks and the networks of everyone else. They also end up dealing with law enforcement to deal with criminals. Some of what they do is deal with is unspeakable, abuse and mistreatment of children and animals. These are the folks who stand in front of the rest of us, and make the world better for all of us.
They should be thanked for doing their job, not chastised because they’re doing what the people who pay them expect them to be doing.
Yes, recipients want the mail they want. But, y’know, I bet they really don’t want all the bad stuff that the ISPs protect against. Ken took offense at a statement that he really shouldn’t have. ISPs do check their false positive rates on filtering, and those rates are generally less than 1% of all the email that they filter. Marketers should be glad they’re such a small part of the problem. They really don’t want to be a bigger part.
Email and law in the news
A couple things related to the intersection of email and law happened recently.
The 6th circuit court ruled that the government must have a search warrant before accessing email. The published opinion is interesting reading, not just because of the courts ruling on the law but also because of the defendant. Berkeley Premium Nutraceuticals toyed with spamming to advertise their product as a brief search of public reporting sites shows. The extent and effort they went to in order to stay below the thresholds for losing their merchant accounts is reminiscent of the effort some mailers go through to get mail through ISP filters.
The other bit of interesting reading is the Microsoft motion to dismiss the case brought against them by Holomaxx. It is a relatively short brief (33 pages) and 3 of those pages are simply a listing of the relevant cases demonstrating ISPs are allowed to filter mail as they see fit. 2 more pages are dedicated to listing the relevant Federal and State statutes. I strongly encourage anyone considering suing any large ISP to to read this pleading. These lawyers understand email law inside and out and they are not going to mess around. They also have both statute and case law on their side. They point this out before the end of page 1:
Going to MAAWG
Following on from last weeks post about MAAWG, I thought I’d write a bit about actually going to MAAWG. You’re an ESP and you’ve been accepted into the organization. Now you have some decisions to make.
Read MoreMAAWG: Not a Marketing Conference
There seems to be this great misunderstanding among a huge number of email marketers and delivery professionals that MAAWG is some sort of marketing or marketing related conference.
They’re wrong.
MAAWG is the Messaging Anti-Abuse Working Group. The intention of the group is to provide a setting where companies providing internet services can work together to stop abuse. Email is one of the major platforms talked about, but there are also discussions about other forms of messaging abuse.
This conference is unique both in its content and in the people who attend. For many ISP reps this is their sole opportunity to get together with peers, former co-workers and friends. Many of the ISP folks are actually low to mid-level employees who are working the front lines fighting abuse every day. MAAWG is a chance for them to work and socialize with people who understand their jobs and the challenges associated with handling abuse on a daily basis. It’s a place to look at the larger issues and blow off steam.
There are a number of folks who show up at the conference that don’t deal with abuse in any capacity, however. They don’t have to deal with rampant levels of spam heavy enough to take down a mailserver. They don’t have to deal with the horror that is child porn. They don’t have to deal with angry subscribers. They don’t have to deal with criminals.
In short, they’re not abuse desk folks. They are, at best, a delivery person but more often are some high level executive at a marketing firm. These folks treat MAAWG as a place to wheedle business cards and contacts from the ISP reps. Stop abuse? The only abuse they see is that their email isn’t instantly delivered to the inbox. Spam? That’s what other people send. Phishing? Child porn? Not important.
All too many of them are not even subtle or coy about the fact that their only concern is finding contacts. One ISP rep tells the story of some marketer that followed him into the bathroom and attempted to trade business cards while the ISP person was at the urinal. Make no mistake, this is not an isolated incident. The badgering is so bad that some ISP reps refuse to state who their employer is.
The ISP folks are there to actually spend time with their peers and y’know, do actual work. ISP reps are not there to get hassled by dozens of marketers.
To be fair, a number of ESPs send delivery folks who are actually working to stop abuse. They do chase spammers through their systems. They do deal with criminals. Unfortunately, because they are from ESPs they are prohibited from actually working with the ISPs.
Why? Because so many of the ESP reps aren’t actually there to stop abuse that MAAWG has had to draw firm lines between ESPs and ISPs to make the ISP reps feel comfortable. I can’t fault MAAWG for that even as I can see there are ESP reps who perform the exact same job functions as the ISP reps.
The ESPs have created this situation. Instead of sending folks on their side who deal with messaging abuse, they send high level executives and marketers. They send people who think that the ISPs owe them something. That believe the ISPs will let mail through just because they shared a beer at the conference. That believe there is some inner circle and if they join they can find out the secret sauce so they can get their mail through filters. They send people who think that ISPs should be forced to sit at a table and listen to marketers yell about “the false positive problem.”
This isn’t to say ESPs and marketing companies shouldn’t join MAAWG and go to conferences. There’s a lot of abuse that both groups have to deal with. But MAAWG isn’t a marketing conference. Sending only marketers or executives to the conference not only misses the point of the organization, it actively sabotages it.
Comments on Holomaxx post
I’m putting together a longer analysis of the Holomaxx case that will look at the claims against the various defendants. There’s some deep mis-understanding of how various things works (hint: wiretapping? not so much).
There was one comment from “The Other Barry” about complaints that I think bears highlighting.
More information on arrests
Terry Zink has a more detailed post on some of the spammer arrests and takedowns that have happened recently.
In addition to the events I mentioned yesterday, authorities arrested an Armenian man suspected of running the Bredolab botnet. Unfortunately, the arrest has not stopped the spam with the malware payload.
These are issues that many ISP abuse and postmaster desks deal with on a daily basis. Their filtering schemes and policies are in place to protect customers from the mob, and criminals. I don’t think enough marketers and senders understand exactly how much the ISPs are dealing with and why many ISPs don’t really care that “mail is taking 12 hours to get to the inbox.” They are dealing with much more important things.
We're gonna party like it's 1996!
Over on deliverability.com Dela Quist has a long blog post up talking about how changes to Hotmail and Gmail’s priority inbox are a class action suit waiting to happen.
All I can say is that it’s all been tried before. Cyberpromotions v. AOL started the ball rolling when they tried to use the First Amendment to force AOL to accept their unsolicited email. The courts said No.
Time goes on and things change. No one argues Sanford wasn’t spamming, he even admitted as much in his court documents. He was attempting to force AOL to accept his unsolicited commercial email for their users. Dela’s arguments center around solicited mail, though.
Do I really think that minor difference in terminology going to change things?
No.
First off “solicited” has a very squishy meaning when looking at any company, particularly large national brands. “We bought a list” and “This person made a purchase from us” are more common than any email marketer wants to admit to. Buying, selling and assuming permission are par for the course in the “legitimate” email marketing world. Just because the marketer tells me that I solicited their email does not actually mean I solicited their email.
Secondly, email marketers don’t get to dictate what recipients do and do not want. Do ISPs occasionally make boneheaded filtering decisions? I’d be a fool to say no. But more often than not when an ISP blocks your mail or filters it into the bulk folder they are doing it because the recipients don’t want that mail and don’t care that it’s in the bulk folder. Sorry, much of the incredibly important marketing mail isn’t actually that important to the recipient.
Dela mentions things like bank statements and bills. Does he really think that recipients are too stupid to add the from address to their address books? Or create specific filters so they can get the mail they want? People do this regularly and if they really want mail they have the tools, provided by the ISP, to make the mail they want get to where they want it.
Finally, there is this little law that protects ISPs. 47 USC 230 states:
Gmail and SenderScore
Return Path discusses that a high (>80) SenderScore is correlated with inbox delivery at Gmail.
Read MoreBotnets and viruses and phishing, oh my!
MessageLabs released their monthly report on email threats yesterday. Many media outlets picked up and reported that 41% of spam was from a the Rustock botnet.
Other highlights from the report include:
Freemail opens
Justin Coffey commented on my check your assumptions post pointing out his data on opens related to ISPs. He says:
Read MoreLycos delivery problems
Lycos has had some ongoing problems this week. Their alert on the issue says:
Read MoreGetting removed from an ISP block
A question came up on a mailing list about how long it typically took to resolve a spam block at an ISP. I don’t think that question actually has a single answer, as each ISP has their own, special, process.
ISPA takes 5 minutes. You fill out a form, it runs through their automated system and you’re usually delisted.
ISPB asks a lot of questions in their form, so it takes about 15 minutes to collect all the data they want and 10 minutes to fill out their form. Then, using very, very short words you keep repeating what you need to the tier 1 person who initially responded. That person eventually figures out they can’t blow you off and throws your request to tier 2, who handles it immediately.
ISPC has a different, somewhat long form. Again, you spend time collecting all the data and then fill out the somewhat obscure form. You get a response, but it’s a boilerplate totally unrelated to the initial request, so you keep answering until you find a tier 1 rep who can read and do what you initially asked.
ISPD has a form that takes about 2 minutes to fill out. Unfortunately, it goes to an outsourced postmaster team in the Far East and response times are ranging from days to months right now.
ISPE has an email address and if you catch them on a good day, they’re very helpful. Sometimes there’s no response, though.
ISPF has a troubleshooting page and accept requests to fix things, but never respond in any visible manner.
ISPG they tells you to talk to Spamfiltering Company H.
Spamfiltering company H answers their email in a prompt and friendly manner. OK, sometimes the answers are just “wow, your client/customer/IP range is sending lots of spam,” but hey, it’s an answer.
Spamfiltering company I is a useless bag of protoplasm and don’t even answer the email address they give you on their webpages. In a fit of fairness, I have heard they will occasionally respond, but usually that response is to tell you to go pay some apparently unrelated company a bribe to get delisted.
Spamfiltering company J doesn’t have a lot of ways to contact them, but have a lot of folks that participate in various semi-public arenas so if you’re even slightly part of the community, you can email them and they’re very helpful.
Spamfiltering company K is totally useless, but will tell you to have recipients whitelist you.
Delivery consulting: it's all about the credibility
A few months ago I found a great blog post written by an ER doctor about how to convince other doctors to come in and deal with a patient in the middle of the night. There are quite few similarities between his advice and the advice I would give delivery experts, ISP relations folks and ESP representatives when dealing with ISPs and spam filtering companies.
Read MoreThe importance of data hygiene
Over the weekend, one of the major ISPs purged a lot of abandoned accounts from their system. This has resulted in a massive increase in 550 user unknown bounces at that ISP. This ISP is one of those that uses bounces to feed into their reputation system and the purge may cause otherwise good senders to be blocked temporarily.
Talking to clients and other industry folks, it looks like the addresses that have newly bounced off had zero activity for at least 6 months. Nothing. Nada. No clicks. No opens. No interaction.
This is why data hygiene is so critical. Just because the emails are being accepted at the ISP, and even showing inbox placement at the mailbox monitoring companies does not mean that there is actually someone reading your email. Failure to look at overall data means that when an ISP bulk deletes abandoned accounts then bounces will increase. While I don’t expect this to have any real, long term effect on sender reputation I do expect that some senders with a lot of cruft on their list will see some short term delivery problems.
Companies that run re-engagement campaigns saw a whole lot less bouncing and even less blocking as a result of the purge. They were removing addresses that were non-responsive all along and thus didn’t have major deadwood on their list.
Ongoing data hygiene shows you what your list really is, not your list plus abandoned accounts. The addresses that the ISP purged? They were not valuable anyway. No one was reading that mail for at least 6 months.
If you did see a spike in bounces this weekend at a major ISP, you should really look at engagement. If some percentage of recipients at one ISP are actually non-existent, then it’s likely that about that same number are non-existent at other major ISPs as well. What are you going to do to identify and remove those dead addresses from your lists?
Delivery problems are not all spam related
Not every delivery failure is due to poor reputation or spam. Sometimes ISPs just have problems on their mailservers and so mail doesn’t get through. It’s often hard for delivery experts (and their bosses and their customers and their clients) to watch email delays or rejections without being able to do anything about it.
Sometimes, though, there is nothing to do. The rejections are because something broke at the ISP and they have to sort through it. Just this week there’s been a lot of twitter traffic about problems at a major cable company. They are rate limiting senders with very good reputations. They have admitted there is a problem, but they don’t have a fix or an ETA. From what I’ve heard it they’re working with their hardware vendor to fix the problem.
Hardware breaks and backhoes eat fiber. Yes, ISPs should (and all of the large ones do) have backups and redundancies. But those backups and redundancies can’t always handle the firehose worth of mail coming to the ISPs. As a result, the ISPs start rejecting some percentage of mail from everyone. Yahoo even has a specific error message to distinguish between “we’re blocking just you” from “we’re shedding load and temp failing everyone.”
This is why the ISPs throw up their hands at senders
I recently saw a question from an ESP rep asking if anyone had a personal contact at a particular ISP. The problem was that they had a rejection from the ISP saying: 571 5.7.1 too many recipients this session. The ESP was looking for someone at the ISP in order to ask what the problem was.
This is exactly the kind of behaviour that drives ISPs bonkers about senders. The ISP has sent a perfectly understandable rejection: “5.7.1: too many recipients this session.” And instead of spending some time and energy on the sender side troubleshooting, instead of spending some of their own money to work out what’s going on, they fall back on asking the ISPs to explain what they should do differently.
What, exactly, should you do differently? Stop sending so many recipients in a single session. This is not rocket science. The ISP tells you exactly what you need to do differently, and your first reaction is to attempt to mail postmaster@ the ISP and then, when that bounces, your next step is to look for a personal contact?
No. No. No.
Look, connections and addresses per connections is one of the absolute easiest things to troubleshoot. Fire up a shell, telnet to port 25 on the recipient server, and do a hand SMTP session, count the number of receipts. Sure, in some corporate situations it can be a PITA to do, sometimes you’re going to need to get it done from a particular IP which may be an interface on an appliance and doesn’t have telnet or whatever. But, y’know what? That Is Your Job. If your company isn’t able to do it, well, please tell me so I can stop recommending that as an ESP. Companies have to be able to test and troubleshoot their own networks.
Senders have been begging ISPs for years “just tell us what you want and we’ll bother you less.” In this case the ISP was extremely clear about what they want: they want fewer recipients per connection. But the ESP delivery person is still looking for a contact so they can talk to the ISP to understand it better.
This is why the ISPs get so annoyed with senders. They’re tired of having to do the sender’s job.
Return Path Changes certification standards
Return Path recently announced changes to their certification program. They will no longer be certifying 3rd party mailers.
Read MoreDelivery resources
I’m working on a few projects designed to help provide mentoring for other delivery people and to bridge the communication gap between the various groups active in email. One of those projects is collecting, linking to, and publishing more delivery resources. Some will be linked to directly from the blog, others will be linked to from the wiki. While I’m reasonably familiar with what’s out there, it is impossible for me to know about all the useful resources available. So I ask you readers:
Read MoreState of the Industry
Over the last few weeks I’ve had a series of posts on the blog from various authors who are active in the email space.
I posted A very young industry commenting on the lack of experience among email marketers. I think that some of the conflict between ISPs and ESPs and receivers and marketers can be traced back to this lack of longevity and experience. Often there is only a single delivery expert at a company. These people often have delivery responsibilities dropped on them without any real training or warning. They have to rely on outside resources to figure out how to do their job and often that means leaning on ISPs for training.
JD Falk described how many at ISPs feel about this in his post With great wisdom…
Yahoo and Goodmail
The industry has been abuzz the last few days with the news that of Feb 1, Yahoo will no longer be supporting Goodmail in their interface. I did get a chance to get a response from someone at Yahoo, but didn’t get a chance to talk to anyone from Goodmail. Look for a post next week discussing the breakup, what impact it has on the industry and what this may mean for other ISPs.
Read MoreIt doesn't matter what you say
“What should we tell the ISP?” is a frequent question from my customers. The answer is pretty simple. It doesn’t usually matter what you tell the ISP. What matters are your actions.
If a sender is having delivery problems then the solution is not to call the ISP and talk to them about why the sender’s mail should not be delivered to the bulk folder. Instead, the solution is to evaluate the email and the address acquisition process and the list hygiene process. Identify where potential problems are and then resolve those problems.
Typically, the ISPs won’t need to be contacted. The changes to the email will register and delivery will improve. In some cases, particularly when there’s been some major mistake, contacting the ISP and explaining the mistake and what steps have been taken to stop the mistake from happening in the future may help resolve the issue faster. But if nothing has changed, then there’s no reason for the ISP to expect anything to change.
It doesn’t matter what you say. It matters what you do.
Bad year coming for sloppy marketers
MediaPost had an article written by George Bilbrey talking about how 2010 could be a difficult year for marketers with marginal practices. George starts off the article by noticing that his contact at ISPs are talking up how legitimate companies with bad practices are causing them problems and are showing up on the radar.
This is something I talked about a few weeks ago, in a series of blog posts looking at the changes in 2010. The signs are out there, and companies with marginal practices are going to see delivery get a lot more difficult. George lists some practices that he sees as problems.
AOL layoffs and postmaster changes
As most of you probably know, AOL went through a serious round of layoffs yesterday. Unlike previous layoffs this one did hit the postmaster team pretty hard. Anna posted this morning that she was the only non-programming member of the postmaster team left in the US. This means there are a number of experienced folks looking for work with experience managing delivery for a large outfit. More info is on her blog.
While I don’t have any firm data, I expect that this is going to significantly affect the support that senders see from AOL. I know many of us have held up AOL as the poster child for how ISPs should interact with senders. That era is drawing to a close.
These layoffs come as AOL has migrated to a new mail system and a lot of senders are seeing new and different error messages. I do believe the folks handling the mail system and the migration are still there and are feverishly working to resolve problems caused by the migration. Right now things are in flux and senders should probably expect delays in getting support from AOL for delivery problems.
UPDATE: Matt Vernhout has a list of suggestions for how to deal with AOL delivery issues.
Resource hogging
Today on SFGate there was an article talking about how some Bay Area coffee houses were struggling to deal with workers who purchase one cup of coffee and then camp out all day using the free wifi. The final paragraph quoted one of the campers.
Read MoreLessons from the good, the typical and the ugly
What can smart ESPs learn from my recent series The good, The typical and The ugly?
Read MoreA series of warnings
Over the last month there have been a number of people sounding warnings about coming changes that ESPs are going to have to deal with. There has been mixed reaction from various people, many people who hear these predictions start arguing with the speaker. Some argue that our predictions are wrong, others argue that if our predictions are right then the senders will just start acting more like spammers.
I have put together a collection of links from recent blog posts looking towards the future and how things may be changing.
How to fix delivery
For all of you that are asking “What do the ISPs want from us” Annalivia has posted a list of specifics that you can do to improve delivery.
Read MoreBlocking of ESPs
There’s been quite a bit of discussion on my post about upcoming changes that ESPs will be facing in the future. One thing some people read into the post is the idea that ISPs will be blocking ESPs wholesale without any regard for the quality of the mail from that company.
The idea that ESPs are at risk for blocking simply because they are ESPs has been floating around the industry based on comments by an employee at a spam filter vendor at a recent industry conference.
I talked to the company to get some clarification on what that spam filtering company is doing and hopefully to calm some of the concerns that people have.
First off, and probably most important, is that the spam filtering company in question primarily targets their service to enterprises. Filtering is an important part of this service, but it also handles email archiving, URL filtering and employee monitoring. The target market for the company is very different than the ISP market.
The ISPs are not talking about blocking indiscriminately, they are talking about blocking based on bad behavior.
Secondly, this option was driven by customer request. The customers of the spam filtering appliance were complaining about “legitimate” mail from various ESPs. Despite being reasonable targeted the mail was unrequested by the recipient. While ESPs use FBLs and other sources of complaints to clean complainers off rented or epended lists at ISPs, the option is not available for mail sent to corporations. Enterprises don’t, nor should they have to, create and support FBLs. Nor should employees be expected to unsubscribe from mail they never requested.
This option is the direct result of ESPs allowing customers to send spam.
Thirdly, this option is offered to those customers who ask for it. It is not done automatically for everyone. The option is also configurable down to the end user.
While I haven’t seen the options, nor which ESPs are affected, I expect that the ones on the list are the ones that the filtering vendor receives complaints about. If you are not allowing your customers to send spam, and are stopping them from buying lists or epending, then you probably have not come to the attention of the filtering company and are not on the list of ESPs to block.
The coming changes
Yesterday I talked about how I’m hearing warnings of a coming paradigm shift in the email industry. While these changes will affect all sender, ESPs in particular are going to need to change how they interact with both ISPs and their customers.
Currently, ESPs are able to act as “routine conveyers.” The traffic going across their network is generated by their customers and the ESP only handles technical issues. Responsible ESPs do enforce standards on their customers and expect mailings to meet certain targets. They monitor complaints and unknown users, they monitor blocks and reputation. If customers get out of line, then the ESP steps in and forces their customer to improve their practices. If the customer refuses, then the ESP disconnects them.
Currently standards for email are mostly dictated by the ISPs. Many ESPs take the stance that if any mail that is not blocked by the ISPs then it is acceptable. But just because a certain customer isn’t blocked doesn’t mean they’re sending mail that is wanted by the recipients.
It seems this reactive approach to customer policing may no longer be enough. In fact, one of the large spam filter providers has recently offered their customers the ability to block mail from all ESPs with a single click. This may become a more common response if the ESPs don’t start proactively policing their networks.
Why is this happening? ISPs and filtering companies are seeing increasing percentages of spam coming out of ESP netspace. Current processes for policing customers are extremely reactive and there are many ESPs that are allowing their customers to send measurable percentages of spam. This situation is untenable for the filtering companies or the ISPs and they’re sending out warnings that the ESPs need to stop letting so much spam leave their networks.
Unsurprisingly, there are many members of the ESP community that don’t like this and think the ISPs are overreacting and being overly mean. They do not think the ISPs or filtering companies should be blocking all an ESPs customers just because some of the customers are sending unwanted mail. Paraphrased, some of the things I’ve heard include:
Tribes
Earlier Laura talked about a communication gap between ESPs and ISPs.
My take on it is that it’s something more than just a difficulty in communicating, rather it’s a division due to differences in personality and approach of those individuals whose primary interest is themselves and those whose primary interest is the health of the overall email ecosystem.
The former group (who I mentally refer to using the shorthand “frat boys“) want to make everything all about them, and their companies revenue, and their visibility in the industry, and their ego resume. Broad generalizations with little need for understanding are adequate to raise their visibility and keep them employed. Details aren’t that important to them. Dominating the conversation is. (Lest that sound negative, these are exactly the individuals who can thrive in sales, customer relations, bizdev and marketing environments.)
The latter (shorthand “utilitarians“) instinctively want to make email work well and to be useful for everyone. They want email to be a healthy, useful system and tend to believe that that means optimizing for the greatest good for the greatest number. (If you’ve any philosophy background, think “felicific calculus as applied to email”). They tend to understand the system in much more detail than the frat boys, though maybe less than the mechanics. And they tend to be better at working together – as they’re more interested in hearing other peoples data in order to get better at what they do, rather than being there to convince others of their pre-decided agenda.
(There’s a third group I think of as “mechanics” who take more joy in the details of keeping the system running smoothly on a small scale, without much interest in the broader system, whether that be in a technical or business role. They tend not to be very interactive in public, though, so don’t have much impact at the level of conversations I’m thinking about).
While I hate the broad terms “senders” and “receivers” used to (falsely) divide the industry into two disjoint halves, I’m painting with a fairly broad brush here, so I’m going to stick with them.
There are quite a few of all three types of people at both senders and receivers – but their power and visibility varies.
At senders there’s a mix of frat boys and utilitarians in operational and policy making positions, but the frat boys tend to have a lot more public visibility – they’re the ones who are trying to be visible, to dominate the conversation, and they’re the people you tend to see doing all the talking and less of the listening, whether it be on industry mailing lists or at the microphone at a conference. Because of their greater visibility, they’re who you think of when you think of senders, and typically they’ll be the ones you end up interacting with most in any random mix of individuals from senders.
At receivers the operational (as opposed to policy) level is where the real decision making power is as far as email is concerned, and it’s heavily dominated by the utilitarians. (In fact, the more visible frat boys I can think of who were in influential positions at receivers are mostly now working on behalf of senders).
Frat boys are very, very bad at communicating with utilitarians. And utilitarians find it very hard to discuss issues they consider serious with frat boys at anything deeper than a superficial level.
Mechanics aren’t great at communicating with strangers in anything other than a fairly friendly environment, but manage best with other mechanics or with utilitarians.
If you’re a C level manager at a sender, and you’re deciding which of your staff are well suited to collaborate with typical receiver staff that’s something important to consider. The public face of the recievers are probably utilitarians. Frat boys are the worst representatives to send out to talk to them.
The delivery communication gap
There seems to be a general uptick in the number of specific questions that ESPs and commercial senders are asking recently. I’m getting them from clients, and I’m hearing similar stories from my various contacts over on the ISP side. The questions cover a wide range of areas in email delivery, but the underlying issue is really that there are no real fixed rules about email delivery anymore. The only rule is “send mail users want to receive” and there are no specific guidelines to how to do that.
This is frustrating for a lot of people. They want to know exactly how many complaints they need to stay under. They want to know what “engagement” means and how exactly the ISPs are measuring it. They want to know all of the metrics they need to meet in order to get mail to the inbox.
There is a lot of frustration among senders because they’re not getting the answers they think they need and they feel like the ISPs aren’t listening to them.
Likewise there is a lot of frustration among ISPs because they’re giving answers but they feel like they’re not being heard.
Some of the problem is truly a language difference. A lot of delivery people on the ESP side are marketers first and technologists second. They don’t have operational experience. They don’t have that any feel for the technology behind email and can’t map different failure modes onto their causes. Some of them don’t have any idea how email works under the covers. Likewise, a lot of postmaster people are technologists. They deeply understand their customers and their email servers and don’t speak marketing.
The other issue is the necessary secrecy. Postmasters have been burned in the past and so they have to be vague about what variables they are measuring and how they are weighting them.
All of this leads to a very adversarial environment.
I’ve been talking with a lot of people about this and none of us have any real answers to the solution. Senders say the ISPs should spend more time explaining to the senders what they need to do. ISPs say the senders should stop sending spam.
Am I quite off base here? Is there no communication gap? Am I just cynical and missing some obvious solution? Anyone have any suggestions on how to solve the issue?
Delivery delays due to congestion
Now that we’re deep in the middle of the Christmas shopping season, I’m seeing more and more complaints about delays at ISPs. Mickey talked about everything the ISPs have to consider when making hardware and buildout decisions in his post The hard truth about email on Spamtacular. When, like on cyber Monday, there’s a sharp increase in the volume of email, sometimes ISPs don’t have the capacity to accept all the email that is thrown at them.
Read MoreLegitimate email marketers need to take a stand
I was reading an article on Virus Rants and the opening paragraph really stood out.
Read MoreSenders need to take responsibility
Having just returned home from another conference, my head is full of new ideas, new thoughts and new projects. I enjoy seeing old friends, making new contacts and sharing ideas. One thing I don’t enjoy, though, is listening to senders and marketers complaining about how hard it is to be a sender because the ISPs will not tell them what standards they need to meet.
If the ISPs would just tell us what they want us to do, we’ll do it.
The ISPs have told senders what they want them to do. They want senders to stop sending mail that their users don’t want. It is a very simple statement.
Stop sending spam.
For many senders, however, it’s not enough. “Tell us exactly what we need to do to stop sending spam. What complaint rates must we be under? What bounce rates do we have to be under? How do you want us to do this?” By this point in the conversation the ISP person is mentally rolling their eyes and looking for a way to escape the conversation.
The ISPs don’t want to tell senders how to behave, they want senders to start behaving. Stop sending spam should be all they need to tell senders.
Senders who ask for ISPs to tell them how to stop sending mail recipients think is spam are looking for specific thresholds they can stay under. They’re not really interested in actually sending wanted mail, they’re interested in sending good-enough mail, where good-enough mail is simply mail that gets to the inbox.
Want to know why ISPs don’t think much of many senders? Because the senders are not visibly taking any stand against abuse. I know there are a lot of senders out there who stop a lot of spam from ever leaving their systems, but there’s also a lot of unwanted mail that goes out, too. Some of that mail is even spam by any definition of the word. All the ISPs can see is the spam that gets through, and then they hear just tell us what to do and we’ll do it. From an ISP perspective, this means the senders only care about the thresholds and getting in under the ISPs’ radars.
Senders need to take more responsibility for the mail that goes out over their networks.
What do I mean by this? I mean senders need to stop waiting for the ISPs to define good practices. Senders need to implement standards and good practices just because they’re good practices, not because the ISPs are dictating the practices. Senders need to stop customers from doing bad things, and dump them if they won’t stop. Senders need to stop relying on ISPs for specific answers to why mail is being blocked. Senders need to take responsibility for the mail going across their networks.
It’s time for senders to grow up and stop relying on others for guidance. They shouldn’t implement good practices just because the ISPs tell them to, but instead should implement good practices because they are good practices.
Problems at Cox: Resolved
People mailing to Cox in the wee hours of this morning may have received a rejection message citing the Invaluement DNSBL.
554 IMP a.b.c.d blocked. IPBL100 – Refer to Error Codes section at http://postmaster.cox.net for more information.
I spoke with one of the folks at Cox and they said there was an error in the implementation causing non-listed IPs to be rejected erroneously between about 4am to 8am (Eastern) this morning. The problem has been resolved as of 8am, and all traffic is flowing normally. The also stated that attempts to resend any blocked messages will succeed. They do apologize for any problems this may have caused.
For those of you with aggressive bounce handling, removing addresses after a single 550 bounce, you will also want to re-enable any cox.net subscribers that bounced off during this configuration problem.
They are all Barry. Listen to Barry
Al has a guest post up from an ISP rep (now universally referred to as Barry) about senders contacting ISPs. It lists things senders do that Barry Don’t Like.
Listen to Barry.
There are also comments from various other Barrys in the comments. Those are worth reading, too.
Rescuing reputation
One of the more challenging things I do is work with companies who have poor reputations that they’re trying to repair. These companies have been getting by with poor practices for a while, but finally the daily delivery falls below their pain threshold and they decide they need to fix things.
That’s when they call me in, usually asking me if I can go to the ISPs and tell the ISPs that they’re not spammers, they’re doing everything right and will the ISP please stop unfairly blocking them. Usually I will agree to talk to the ISPs, if fixing the underlying problems doesn’t improve their delivery on its own. But before we can talk to the ISPs, we have to try to fix things and at least have some visible changes in behavior to take to them. Once they have externally visible changes, then we can ask the ISPs for a little slack.
With these clients there isn’t just one thing they’ve done to create their bad reputation. Often nothing they’re doing is really evil, it’s just a combination of sorta-bad practices that makes their overall reputation really bad. The struggle is fixing the reputation requires more than one change and no single change is going to necessarily make an immediate improvement on their reputation.
This is a struggle for the customer, because they have to start thinking about email differently. Things have to be done differently from how they’ve always been done. This is a struggle for me because I can’t guarantee if they do this one thing that it will have improved delivery. I can’t guarantee that any one thing will fix their delivery, because ISPs measure and weight dozens of things as part of their delivery making decisions. But what I can guarantee is that if they make the small improvements I recommend then their overall reputation and delivery will improve.
What small improvement have you made today?
Overusing ISP contacts
I’ve written frequently about personal contacts at ISPs and how the vast majority of delivery problems can be solved without picking up the “Bat Phone” and having someone at the ISP do something. Al touches on the same subject today, blogging about his recent experiences having to contact “Barry” multiple times for many different issues.
Al resolves
The secret to dealing with ISPs
What is the secret to dealing with ISPs?
The short answer is: Don’t do it if at all possible. Talking to ISP reps generally isn’t going to magically improve your reptuation. There is no place in the reputation systems where delivery can be modified because the delivery specialist knows or is liked by the postmaster at an ISP.
With my clients, I work through delivery issues and can solve 80 – 90% of the issues without ever having to contact anyone at the ISPs. 90% of the remaining issues can be handled using the publicly available contacts and websites provided by the ISPs.
In the remaining cases, the “secret” to getting useful and prompt replies is to:
Problems at Excite
I’ve been chasing an intermittent and inconsistent delivery problem at Excite for a week or so. Excite is accepting email, but mail is not getting to the recipient’s inbox or bulk folder. Al tweeted he’s seeing a similar problem with his customers’ mail and had contacted Excite.
Excite does appear to be aware of the issue, but I have no ETA on a fix.
EDIT: Comments are closed
Deliverability versus delivery
Deliverability is a term so many people use every day, but what do we really mean when we use it? Is there an accepted definition of deliverability? Is the concept different than delivery?
At a recent conference I was running a session talking about email delivery, senders and the roles senders play in the email industry and at that particular organization. The discussion went on for a while, and the subject of deliverability versus delivery came up. J.D. Falk had a comment about the difference that resonated with me. Paraphrased, he said:
ISP Information pages
I have posted a ISP Information Page. Right now it contains links to Postmaster pages, Whitelist signup pages and FBL signup pages. I have some ideas on what information would be helpful to add, but would like to hear what types of info people would like to have easy access to.
What do you think I should add to the page?
Personal Contacts at ISPs: Part 2
I’ve talked quite a bit recently about working with ISPs and personal contacts. Today I have an example of what not to do.
One of my ISP friends informed me that another blogger published correspondence from an individual at that ISP, including the individual’s full contact information. The correspondence wasn’t a big deal, the blogger was assigned an IP address by their ISP that was previously used by a spammer. The ISP had a block on the address and he was contacting them to get the block removed. It was totally a misunderstanding on the blogger’s part and the blogger removed the info when the ISP contacted him. Still, once something is out on the net, it’s out there forever.
Don’t do that. Really. When someone at an ISP helps you, don’t go publishing their information on a blog somewhere. They will find out, even if it’s just because their mailbox explodes or their phone starts ringing off the hook with multiple calls about an “emergency” situation. It hurts the person who helped you, who now has to deal with a major increase in volume and work load, and they’re never going to help you again.
This also hurts the rest of us, as ISP employees retreat farther and farther away from contact with senders. Even those of us who are careful with contact information may find it hard to get responses when others in the field are spreading info around.
I know some ISPs can be difficult to get any information from. That’s part of my reason for publishing the ISP information page was to help people find the right contact information. I think it’s extremely important for delivery professionals to understand that you don’t need a personal contact at an ISP to resolve most issues. What you do need is a deep understanding of SMTP, a smattering of knowledge about DNS and HTTP, a firm grasp of privacy issues and an understanding of the dynamics of email.
ISP Postmaster Pages
I’ve been working on some reference information about ISPs for my own internal use as well as sharing with clients. There doesn’t seem to be any public reference site for postmaster sites, so I decided to publish what I’ve collected.
Read MoreWhen the script doesn't work
DJ asks in the comments of Friday’s post:
As Seth said, great reminder. For those that have great processes/channels in place, I’ve found incredible success. However, sometimes I’ve found my answer on Twitter (i.e., @godaddyguy). Also, there have been times where I’ve gone through the script (i.e., shaw.ca) and have never heard back. What then?
Read More
Getting whitelisted by endusers
One of the best ways to ensure mail is delivered to a recipients inbox is to encourage the recipient to add the senders from: address to their address book. In cases where an ISP might otherwise bulk folder the email, they will instead put the email into the inbox.
Senders are changing their practices to get recipients to add from addresses to address books. There are a number of companies reminding users to add addresses on the webpage at the time of signup. Most emails have recommendations in each email. Recently, there have been multiple reports of companies who send specific email campaigns to encourage recipients to whitelist the sender.
Cool Email Idea: Customized Whitelisting Instructions from ReturnPath.
How & Why You Need to be Added to Your Recipient’s Address Book from VerticalResponse.
In addition to the direct benefit to the recipient that whitelists the individual sender, there are some hints that ISPs are looking at individual whitelisting as part of their internal sender reputation scoring.