Reputation
Why Deliverability Depends
A common complaint about the advice or answers any deliverability person gives is that the generic answer to questions is: It Depends. This is frustrating for a lot of folks because they think they’re asking a simple question and so, clearly, there should be one, simple, clear answer.
Read More#ltdelivery: Maintaining reputation
At tomorrow’s #ltdelivery session we’ll continue talking about session: Maintaining and warming up reputations.
Read MoreLet’s Talk: Reputation
The next 3 or 4 Let’s Talk sessions are going to be all about reputation. We’ll start with a general overview of reputation and identity, then move on to specific kinds of reputation (IP, domain, URL, content), then we’ll talk about how to create, maintain and repair reputation. Still working on the outline, but I’m pretty convinced this will be at least 3 sessions.
Read MoreStop obsessing about open rates
In 2020:
- 250OK says open rates were much lower than ESPs report.
- The Only Influencers list hosts a discussion about the value and use of open rates.
- A potential client contacts me asking if I can get their open rates to a certain percentage.
- A client shows me evidence of 100% inboxing but wants to improve their open rate.
- An industry group runs sessions at multiple meetings discussing how inaccurate open rates are.
The industry needs to stop obsessing over open rates.
Read MoreDetails matter
I field a lot of delivery questions on various online fora. Often people try and anonymise what they’re asking about by abstracting out the question. The problem is that there are very few answers we can give in the abstract.
Read MoreRe-adding subscribers after reputation repair
A comment came in on Engagement and Deliverability and I thought it was a good question and deserved a discussion.
Read MoreMy domain reputation is bad, should I get a new domain?
Many companies have the occasional “oops” where they send email they probably shouldn’t have. This can often cause a decrease in reputation and subsequent delivery problems. Some companies rush to fix things by changing domains.
Read MoreWhat’s a suspicious domain?
The question came up on slack and I started bullet pointing what would make a domain suspicious. Seemed like a reasonable blog post. In no particular order, some features that make a domain suspicious to spam filters.
Read MoreReputation is in the eye of the beholder
A few years ago reputation was generally recognised as one thing. If a sending reputation or IP reputation was good in one place it was likely good in other places. Different entities mostly reputation using the same set of signals albeit slightly tweaked to meet their own needs. More recently there is a divergence in how reputation is measured, meaning delivery can be vastly different across entities.
Read MoreUpdating the filtering model
One thing I really like about going to conferences is they’re often one of the few times I get to sit and think about the bigger email picture. Hearing other people talk about their marketing experiences, their email experiences, and their blocking experiences usually triggers big picture style thoughts.
Earlier this week I was at Activate18, hosted by Iterable. The sessions I attended were interesting and insightful. Of course, I went to the deliverability session. While listening to the presentation, I realized my previous model of email filtering needed to be updated.
Warmup advice for Gmail
Getting to the Gmail inbox in concept is simple: send mail people want to receive. For a well established mail program with warm IPs and domains, getting to the inbox in practice is simple. Gmail uses recipient interaction with email to determine if an email is wanted or not. These interactions are easy when mail is delivered to the inbox, even if the user has tabs enabled.
When mail is in the bulk folder, even if it’s wanted, users are less likely to interact with the mail. Senders trying to change their reputation to get back to the inbox face an uphill battle. This doesn’t mean it’s impossible to get out of the bulk folder at Gmail, it’s absolutely possible. I have many clients who followed my advice and did it. Some of these clients were simply warming up new IPs and domains and needed to establish a reputation. Others were trying to repair a reputation. In both cases, the fixes are similar.
When I asked colleagues how they handled warmup at Gmail their answers were surprisingly similar to one another. They’re also very consistent with what I’ve seen work for clients.
Filtering by gestalt
One of those $5.00 words I learned in the lab was gestalt. We were studying fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS) and, at the time, there were no consistent measurements or numbers that would drive a diagnosis of FAS. Diagnosis was by gestalt – that is by the patient looking like someone who had FAS.
It’s a funny word to say, it’s a funny word to hear. But it’s a useful term to describe the future of spam filtering. And I think we need to get used to thinking about filtering acting on more than just the individual parts of an email.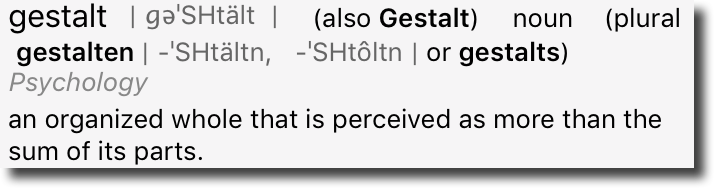
Filtering is not just IP reputation or domain reputation. It’s about the whole message. It’s mail from this IP with this authentication containing these URLs. Earlier this year, I wrote an article about Gmail filtering. The quote demonstrates the sum of the parts, but I didn’t really call it out at the time.
Are seed lists still relevant?
Those of you who have seen some of my talks have seen this model of email delivery before. The concept is that there are a host of factors that contribute to the reputation of a particular email, but that at many ISPs the email reputation is only one factor in email delivery. Recipient preferences drive whether an email ends up in the bulk folder or the inbox.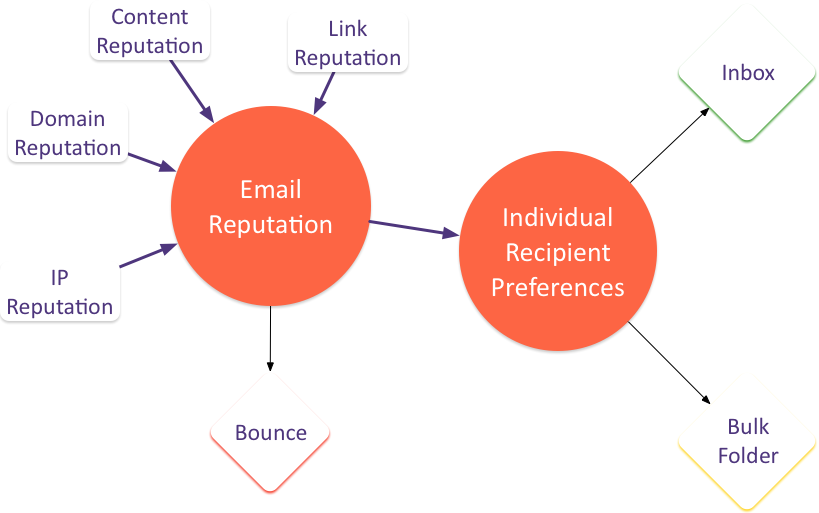
The individual recipient preferences can be explicit or implicit. Users who add a sender to their address book, or block a sender, or create a specific filter for an email are stating an explicit preference. Additionally, ISPs monitor some user behavior to determine how wanted an email is. A recipient who moves an email from the bulk folder to the inbox is stating a preference. A person who hits “this-is-spam” is stating a preference. Other actions are also measured to give a user specific reputation for a mail.
Seed accounts aren’t like normal accounts. They don’t send mail ever. They only download it. They don’t ever dig anything out of the junk folder, they never hit this is spam. They are different than a user account – and ISPs can track this.
This tells us we have to take inbox monitoring tools with a grain of salt. I believe, though, they’re still valuable tools in the deliverability arsenal. The best use of these tools is monitoring for changes. If seed lists show less than 100% inbox, but response rates are good, then it’s unlikely the seed boxes are correctly reporting delivery to actual recipients. But if seed lists show 100% inbox and then change and go down, then that’s the time to start looking harder at the overall program.
The other time seed lists are useful is when troubleshooting delivery. It’s nice to be able to see if changes are making a difference in delivery. Again, the results aren’t 100% accurate but they are the best we have right now.
Open subscription forms going away?
A few weeks ago, I got a call from a potential client. He was all angry and yelling because his ESP had kicked him off for spamming. “Only one person complained!! Do you know him? His name is Name. And I have signup data for him! He opted in! How can they kick me off for one complaint where I have opt-in data? Now they’re talking Spamhaus listings, Spamhaus can’t list me! I have opt-in data and IP addresses and everything.”
We talked briefly but decided that my involvement in this was not beneficial to either party. Not only do I know the complainant personally, I’ve also consulted with the ESP in question specifically to help them sort out their Spamhaus listings. I also know that if you run an open subscription form you are at risk for being a conduit for abuse.
This abuse is generally low level. A person might sign up someone else’s address in an effort to harass them. This is a problem for the victim, but doesn’t often result in any consequences for the sender. Last week’s SBL listings were a response to subscription abuse happening on a large scale.
Insight into Gmail filtering
Last week I posted a link to an article discussing how Gmail builds defenses to protect their users from malicious mail. One of the things I found very interesting in that article was the discussion about how Gmail deploys many changes at once, to prevent people from figuring out what the change was.
Let’s take a look at what Gmail said.
Glitchy Google Postmaster tools
A bunch of folks today mentioned they were seeing poor reputation for formerly good reputations on Google Postmaster Tools. I’m seeing a lot of screen shots that look like this one.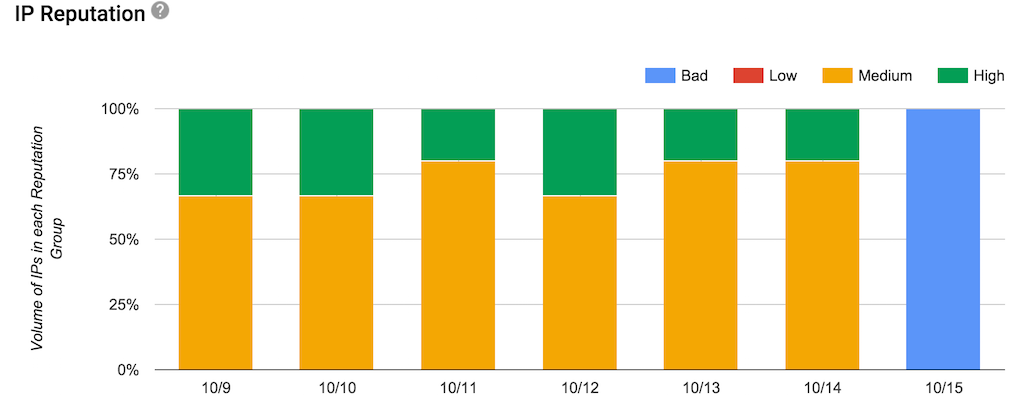
It looks like something is going on over there that has nothing to do with actual reputation. Could be a reporting bug, could be a filtering problem. I’m not seeing people mention delivery problems, just that the reputation monitor is showing bad reputation.
September 2015: The month in email
 September’s big adventure was our trip to Stockholm, where I gave the keynote address at the APSIS Conference (Look for a wrapup post with beautiful photos of palaces soon!) and had lots of interesting conversations about all things email-related.
September’s big adventure was our trip to Stockholm, where I gave the keynote address at the APSIS Conference (Look for a wrapup post with beautiful photos of palaces soon!) and had lots of interesting conversations about all things email-related.
Now that we’re back, we’re working with clients as they prepare for the holiday mailing season. We wrote a post on why it’s so important to make sure you’ve optimized your deliverability strategy and resolved any open issues well in advance of your sends. Steve covered some similar territory in his post “Outrunning the Bear”. If you haven’t started planning, start now. If you need some help, give us a call.
In that post, we talked a bit about the increased volumes of both marketing and transactional email during the holiday season, and I did a followup post this week about how transactional email is defined — or not — both by practice and by law. I also wrote a bit about reputation and once again emphasized that sending mail people actually want is really the only strategy that can work in the long term.
While we were gone, I got a lot of spam, including a depressing amount of what I call “legitimate spam” — not just porn and pharmaceuticals, but legitimate companies with appalling address acquisition and sending strategies. I also wrote about spamtraps again (bookmark this post if you need more information on spamtraps, as I linked to several previous discussions we’ve had on the subject) and how we need to start viewing them as symptoms of larger list problems, not something that, once eradicated, means a list is healthy. I also posted about Jan Schaumann’s survey on internet operations, and how this relates to the larger discussions we’ve had on the power of systems administrators to manage mail (see Meri’s excellent post here<).
I wrote about privacy and tracking online and how it’s shifted over the past two decades. With marketers collecting and tracking more and more data, including personally-identifiable information (PII), the risks of organizational doxxing are significant. Moreso than ever before, marketers need to be aware of security issues. On the topic of security and cybercrime, Steve posted about two factor authentication, and how companies might consider providing incentives for customers to adopt this model.
Outrunning the Bear

You’ve started to notice that your campaigns aren’t working as well as they used to. Your metrics suggest fewer people are clicking through, perhaps because more of your mail is ending up in junk folders. Maybe your outbound queues are bigger than they used to be.
You’ve not changed anything – you’re doing what’s worked well for years – and it’s not like you’ve suddenly had an influx of spamming customers (or, if you have, you’ve dealt with them much the same as you have in the past).
So what changed?
Everything else did. The email ecosystem is in a perpetual state of change.
There’s not a bright line that says “email must be this good to be delivered“. Instead, most email filtering practice is based on trying to identify mail that users want, or don’t want, and delivering based on that. There’s some easy stuff – mail that can be easily identified as unwanted (malware, phishing, botnet spew) and mail that can easily be identified as wanted (SPF/DKIM authenticated mail from senders with clean content and a consistent history of sending mail that customers interact with and never mark as spam).
Instead, most email filtering practice is based on trying to identify mail that users want, or don’t want, and delivering based on that. There’s some easy stuff – mail that can be easily identified as unwanted (malware, phishing, botnet spew) and mail that can easily be identified as wanted (SPF/DKIM authenticated mail from senders with clean content and a consistent history of sending mail that customers interact with and never mark as spam).
The hard bit is the greyer mail in the middle. Quite a lot of it may be wanted, but not easily identified as wanted mail. And a lot of it isn’t wanted, but not easily identified as spam. That’s where postmasters, filter vendors and reputation providers spend a lot of their effort on mitigation, monitoring recipient response to that mail and adapting their mail filtering to improve it.
Postmasters, and other filter operators, don’t really care about your political views or the products you’re trying to sell, nor do they make moral judgements about your legal content (some of the earliest adopters of best practices have been in the gambling and pornography space…). What they care about is making their recipients happy, making the best predictions they can about each incoming mail, based on the information they have. And one of the the most efficient ways to do that is to look at the grey area to see what mail is at the back of the pack, the least wanted, and focusing on blocking “mail like that”.
If you’re sending mail in that grey area – and as an ESP you probably are – you want to stay near the front or at least the middle of the grey area mailers, and definitely out of that “least wanted” back of the pack. Even if your mail isn’t great, competitors who are sending worse mail than you will probably feel more filtering pain and feel it sooner.
Some of those competitors are updating their practices for 2015, buying in to authentication, responding rapidly to complaints and feedback loop data, and preemptively terminating spammy customers – and by doing so they’re both sending mail that recipients want and making it easy for ISPs (and their postmasters and their machine learning systems) to recognize that they’re doing that.
Other competitors aren’t following this years best practices, have been lazy about providing customer-specific authentication, are letting new customers send spam with little oversight, and aren’t monitoring feedback and delivery to make sure they’re a good mail stream. They end up in the spam folder, their good customers migrate elsewhere because of “delivery issues” and bad actors move to them because they have a reputation for “not being picky about acquisition practices“. They risk spiraling into wholesale bulk foldering and becoming just a “bulletproof spam-friendly ESP”.
If you’re not improving your practices you’re probably being passed by your competitors who are, and you risk falling behind to the back of the pack.
And your competitors don’t need to outrun the bear, they just need to outrun you.
Reputation is about behavior

Reputation is calculated based on actions. Send mail people want and like and interact with and get a good reputation. Send mail people don’t want and don’t like and don’t interact with and get a bad reputation.
Reputation is not
… about who the sender is.
… about legitimacy.
… about speech.
… about message.
Reputation is
… about sender behavior.
… about recipient behavior.
… about how wanted a particular mail is forecast to be.
… based on facts.
Reputation isn’t really that complicated, but there are a lot of different beliefs about reputation that seem to make it complicated.
The reputation of a sender can be different at different receivers.
Senders sometimes target domains differently. That means one receiver may see acceptable behavior but another receiver may see a completely different behavior.
Receivers sometimes have different standards. These include standards for what bad behavior is and how it is measured. They may also have different thresholds for things like complaints and bounces.
What this means is that delivery at one receiver has no impact on delivery at another. Just because ISP A delivers a particular mail to the inbox doesn’t mean that ISP B will accept the same mail. Each receiver has their own standards and sometimes senders need to tune mail for a specific receiver. One of my clients, for instance, tunes engagement filters based on the webmail domain in the email address. Webmail domain A needs a different level of engagement than webmail domain B.
Public reputation measures are based on data feeds.
There are multiple public sources where senders can check their reputation. Most of these sources depend on data feeds from receiver partners. Sometimes they curate and maintain their own data sources, often in the form of spamtrap feeds. But these public sources are only as good as their data analysis. Sometimes, they can show a good reputation where there isn’t one, or a bad reputation where there isn’t one.
Email reputation is composed of lots of different reputations.
Email reputation determines delivery. Getting to the inbox doesn’t mean sending from an IP with a good reputation. IP reputation is combined with domain reputation and content reputation to get the email reputation. IP reputation is often treated as the only valuable reputation because of the prevalence of IP based blocking. But there are SMTP level blocks against domains as well, often for phishing or virus links. Good IP reputation is necessary but not sufficient for good email delivery.
Reputation is about what a sender does, not about who a sender is.
Just because a company is a household name doesn’t mean their practices are good enough to make it to the inbox. Email is a meritocracy. Send mail that merits the inbox and it will get to recipients. Send email that doesn’t, and suffer the repercussions.
Old Lists and RadioShack
RadioShack is putting their assets up for sale including more than 65 million customer records and 13 million email addresses. Many are up in arms about the sale of personal data including the Texas Attorney General and AT&T who both want the data destroyed.
Part of the controversy is that RadioShack’s privacy policy states the collected data will be only used by RadioShack and its affiliates and that they will not “sell or rent your personally identifiable information to anyone at any time”. Company acquisitions happen all the time and data like this is often sold to the new owner and the sale of customer data is common. The problem with RadioShack selling the customer data is that their privacy policy states they will never sell the information.
RadioShack was one of the first companies to ask for personal information at checkout, sometimes refusing a sale without providing it and the collection of data during checkout caught on quickly. Having demographic information for retargeting of customers is extremely valuable to marketers, but only if it’s valid data. With RadioShack, people often lie about their zip code and if they are giving incorrect zip codes I’m pretty sure their email address isn’t going to be valid either. Even Kramer asks why does RadioShack ask for your phone number…
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WgfaYKoQxzQ
If a client asked if this was a good investment and if the list had value, I would tell them no. Sending to this list will have poor delivery because the data is dirty and the lack of a clear opt-in is going to be problematic especially since a RadioShack customer is not expecting to receive mail from you. Many ESPs have policies prohibiting sending to a purchased list and doing so will hurt your relationship with the ESP.
If a client had already purchased the list and wanted to send to it, I would tell them their reputation is going to take a significant hit and I would discourage them from sending. The list is going to be full of domains that no longer exist and contain abandoned email addresses including ones that have been turned into spam traps.
When preparing to send to a new list of email addresses, I go through this process:
Updated M3AAWG Best Practices for Senders
M3AAWG has published a new version of the Senders Best Common Practices document and the contains a lot of new information since the original publication in 2008. The new document covers how to vet ESP customers, considerations when selecting a dedicated or share IP to send mail, and includes best practices on a number of technical processes.
The Senders Best Common Practices document is targeted at deliverability teams and email marketers. Any company that is sending marketing emails, using an Email Service Provider, or provides an email enabled platform, it’s always good to go back and periodically review your system to ensure nothing was missed and to stay up-to-date on all new recommendations.
A few of the recommendations include the use of the List-Unsubscribe header, publishing a clear WHOIS for domains used for sending mail, and how to process non-delivery report messages.
The List-Unsubscribe header provides an additional way for users to opt-out of email messages. Gmail and Outlook.com both use the presence of the list-unsubscribe header to provide a one-click button to allow the user to unsubscribe from the mailing list. Often enough, if a user cannot find an opt-out link, they’re marking the message as spam. Allowing a recipient to unsubscribe easily is critical to maintaining good delivery reputation.
A WHOIS is query to determine who is the registered user or assignee of a domain name. During a session at the most recent M3AAWG meeting, it was announced that spammers throw away 19 million domains per year. When a postmaster or abuse desk receive a complaint, they’ll often query to see who owns the domain the email was sent from or who owns the domains used in the hyperlinks. If the WHOIS record is out of date or set to private, this limits the ability for the postmaster or abuse desk to reach out to the owner of the domain.
Processing non-deliver reports is critical to maintaining a high delivery reputation. Many ESPs have an acceptable-use-policy that includes a bounce rate. Mailjet recommends a bounce rate of less than 8% and Mandrill recommends less than 5%. If a system is not in place to remove the hard bounces from your mailing list, the sender’s reputation will quickly deteriorate.
The Senders Best Common Practices document can be downloaded at M3AAWG.org.
Brief DBL false positive
A code glitch in a new DBL sub-zone known as 'Abused-Legit' caused the new Abused-Legit zone to list ".net." for 60 minutes from 08:35 UTC.
Read More
URL reputation and shorteners
A bit of a throwback post from Steve a few years ago. The problem has gotten a little better as some shortening companies are actually disabling spammed URLs, and blocking URLs with problematic content. I still don’t recommend using a public URL shortener in email messages, though.
Any time you put a URL in mail you send out, you’re sharing the reputation of everyone who uses URLs with that hostname. So if other people send unwanted email that has the same URL in it that can cause your mail to be blocked or sent to the bulk folder.
That has a bunch of implications. If you run an affiliate programme where your affiliates use your URLs then spam sent by your affiliates can cause your (clean, opt-in, transactional) email to be treated as spam. If you send a newsletter with advertisers URLs in it then bad behaviour by other senders with the same advertisers can cause your email to be spam foldered. And, as we discussed yesterday, if spammers use the same URL shortener you do, that can cause your mail to be marked as spam.
Even if the hostname you use for your URLs is unique to you, if it resolves to the same IP address as a URL that’s being used in spam, that can cause delivery problems for you.
What does this mean when it comes to using URL shorteners (such as bit.ly, tinyurl.com, etc.) in email you send out? That depends on why you’re using those URL shorteners.
The URLs in the text/html parts of my message are big and ugly
Unless the URL you’re using is, itself, part of your brand identity then you really don’t need to make the URL in the HTML part of the message visible at all. Instead of using ‘<a href=”long_ugly_url”> long_ugly_url </a>’ or ‘<a href=”shortened_url”> shortened_url </a>’ use ‘<a href=”long_ugly_url”> friendly phrase </a>’.
(Whatever you do, don’t use ‘<a href=”long_ugly_url”> different_url </a>’, though – that leads to you falling foul of phishing filters).
The URLs in the text/plain parts of my message are big and ugly
The best solution is to fix your web application so that the URLs are smaller and prettier. That will make you seem less dated and clunky both when you send email, and when your users copy and paste links to your site via email or IM or twitter or whatever. “Cool” or “friendly” URLs are great for a lot of reasons, and this is just one. Tim Berners-Lee has some good thoughts on this, and AListApart has two good articles on how to implement them.
If you can’t do that, then using your own, branded URL shortener is the next best thing. Your domain is part of your brand – you don’t want to hide it.
I want to use a catchy URL shortener to enhance my brand
That’s quite a good reason. But if you’re doing that, you’re probably planning to use your own domain for your URL shortener (Google uses goo.gl, Word to the Wise use wttw.me, etc). That will avoid many of the problems with using a generic URL shortener, whether you implement it yourself or use a third party service to run it.
I want to hide the destination URL from recipients and spam filters
Then you’re probably spamming. Stop doing that.
I want to be able to track clicks on the link, using bit.ly’s neat click track reporting
Bit.ly does have pretty slick reporting. But it’s very weak compared to even the most basic clickthrough reporting an ESP offers. An ESP can tell you not just how many clicks you got on a link, but also which recipients clicked and how many clicks there were for all the links in a particular email or email campaign, and how that correlates with “opens” (however you define that).
So bit.ly’s tracking is great if you’re doing ad-hoc posts to twitter, but if you’re sending bulk email you (or your ESP) can do so much better.
I want people to have a short URL to share on twitter
Almost all twitter clients will abbreviate a URL using some URL shortener automatically if it’s long. Unless you’re planning on using your own branded URL shortener, using someone else’s will just hide your brand. It’s all probably going to get rewritten as t.co/UgLy in the tweet itself anyway.
If your ESP offers their own URL shortener, integrating into their reporting system for URLs in email or on twitter that’s great – they’ll be policing users of that just the same as users of their email service, so you’re unlikely to be sharing it with bad spammers for long enough to matter.
All the cool kids are using bit.ly, so I need to to look cool
This one I can’t help with. You’ll need to decide whether bit.ly links really look cool to your recipient demographic (Spoiler: probably not) and, if so, whether it’s worth the delivery problems they risk causing.
And, remember, your domain is part of your brand. If you’re hiding your domain, you’re hiding your branding.
So… I really do need a URL shortener. Now what?
It’s cheap and easy to register a domain for just your own use as a URL shortener. Simply by having your own domain, you avoid most of the problems. You can run a URL shortener yourself – there are a bunch of freely available packages to do it, or it’s only a few hours work for a developer to create from scratch.
Or you can use a third-party provider to run it for you. (Using a third-party provider does mean that you’re sharing the same IP address as other URL shorteners – but everyone you’re sharing with are probably people like you, running a private URL shortener, so the risk is much, much smaller than using a freely available public URL shortener service.)
These are fairly simple fixes for a problem that’s here today, and is going to get worse in the future.
Domains need to be warmed, too
One thing that came out of the ISP session at M3AAWG is that domains need to be warmed up, too. I can’t remember exactly which ISP rep said it, but there was general nodding across the panel when this was said.
This isn’t just the domain in the reverse DNS of the sending IP, but also domains used in the Return Path (Envelope From) and visible from.
From the ISP’s perspective, this makes tons of sense. Some of the most prolific snowshoe spammers use new domains and new IPs for every send. They’re not trying to establish a reputation, rather they’re trying to avoid one. ISPs respond by distrusting any mail from a new IP with a new domain.
Is Amazon SES a reputable place to send mail from
On the first installment of our Wednesday question series, I chose a question from twitter.
Read MoreReputation is more complex than a single number
I checked our SenderScore earlier this month, as quite a few people mentioned that they’d seen SenderScore changes – likely due to changed algorithms and new data sources.
It sure looks like something changed. Our SenderScore was, for a while, zero out of a hundred. That’s as bad as it’s possible to get. I didn’t get a screenshot of the zero score, but I grabbed this a couple of days later:
Are ReturnPath wrong? No. Given what I know about the traffic from our server (very low traffic, particularly to major consumer domains, and a negligible amount of unavoidable backscatter due to our forwarding role addresses for a non-profit to final recipients on AOL) that’s not an unreasonable rating. And I’m fairly sure that as they get their new algorithms dialed in, and get more history, it’ll get closer. (Though I’m a bit surprised that less than 60 mails a day is considered a moderate volume.)
But all our mail is delivered fine. I’ve seen none of my mail bounce. It’s very rare someone mentions that our mail has ended up in a bulk folder. I’ve received the replies I’ve expected from all the mail I’ve sent. Recipient ISPs don’t seem to see any problems with our mail stream.
A low reputation number doesn’t mean you actually have a problem, it’s just one data point. And a metric that’s geared to model one particular sort of sender (very high-volume senders, for example) isn’t going to be quite as useful in modeling very different senders. You need to understand where a particular measure is coming from, and use it in combination with all the other information you have rather than focusing solely on one particular number.
Hunting the Human Representative
Yesterday’s post was inspired by a number of questions I’ve fielded recently from people in the email industry. Some were clients, some were colleagues on mailing lists, but in most cases they’d found a delivery issue that they couldn’t solve and were looking for the elusive Human Representative of an ISP.
There was a time when having a contact inside an ISP was almost required to have good delivery. ISPs didn’t have very transparent systems and SMTP rejection messages weren’t very helpful to a sender. Only a very few ISPs even had postmaster pages, and the information there wasn’t always helpful.
More recently that’s changed. It’s no longer required to have a good relationship at the ISPs to get inbox delivery. I can point to a number of reasons this is the case.
ISPs have figured out that providing postmaster pages and more information in rejection messages lowers the cost of dealing with senders. As the economy has struggled ISPs have had to cut back on staff, much like every other business out there. Supporting senders turned into a money and personnel sink that they just couldn’t afford any longer.
Another big issue is the improvement in filters and processing power. Filters that relied on IP addresses and IP reputation did so for mostly technical reasons. IP addresses are the one thing that spammers couldn’t forge (mostly) and checking them could be done quickly so as not to bottleneck mail delivery. But modern fast processors allow more complex information analysis in short periods of time. Not only does this mean more granular filters, but filters can also be more dynamic. Filters block mail, but also self resolve in some set period of time. People don’t need to babysit the filters because if sender behaviour improves, then the filters automatically notice and fall off.
Then we have authentication and the protocols now being layered on top of that. This is a technology that is benefiting everyone, but has been strongly influenced by the ISPs and employees of the ISPs. This permits ISPs to filter on more than just IP reputation, but to include specific domain reputations as well.
Another factor in the removal of the human is that there are a lot of dishonest people out there. Some of those dishonest people send mail. Some of them even found contacts inside the ISPs. Yes, there are some bad people who lied and cheated their way into filtering exceptions. These people were bad enough and caused enough problems for the ISPs and the ISP employees who were lied to that systems started to have fewer and fewer places a human could override the automatic decisions.
All of this contributes to the fact that the Human Representative is becoming a more and more elusive target. In a way that’s good, though; it levels the playing field and doesn’t give con artists and scammers better access to the inbox than honest people. It means that smaller senders have a chance to get mail to the inbox, and it means that fewer people have to make judgement calls about the filters and what mail is worthy or not. All mail is subject to the same conditions.
The Human Representative is endangered. And I think this is a good thing for email.
Delivery challenges increasing
Return Path published their most recent Global Deliverability report this morning. (Get the Report) This shows that inbox placement of mail has decreased 6% in the second half of 2011. This decrease is the largest decrease Return Path has seen in their years of doing this report.
To be honest, I’m not surprised at the decrease. Filters are getting more sophisticated. This means they’re not relying on simply IP reputation for inbox delivery any longer. IP reputation gets mail through the SMTP transaction, but after that mail is subject to content filters. Those content filters are getting a lot better at sorting out “wanted” from “unwanted” mail.
I’m also hearing a lot of anecdotal reports that bulk folder placements at a couple large ISPs increased in the first quarter of 2012. This is after the RP study was finished, and tells me increased bulk folder placement is more likely to be a trend and not a blip.
One of the other interesting things from the RP study is that the differences are not across all mail streams, but are concentrated in certain streams and they vary across different regions.
IP Address reputation primer
There has been a lot of recent discussion and questions about reputation, content and delivery. I started to answer some of them, and then realized there weren’t any basic reference documents I could refer to when explaining the interaction. So I decided to write some.
This first post is about IP address reputation with some background on why IPs are so important and why ISPs focus so heavily on the sending IP.
Looking towards the future
I had the opportunity to go to a seminar and networking event hosted by Return Path yesterday evening. The topic was “Email trends in 2012” and it was presented by Tom Sather.
If any of you get the opportunity to go to a talk presented by any of the Return Path folks I encourage you to do so. They know their stuff and their presentations are full of good information.
One of the trends mentioned is the increase in reliance on domain reputation. It’s something I’ve been thinking about more and more recently. I wrote a little bit about it recently, but have focused more on the whole realm of content filtering rather than just domain reputation.
Domain reputation is where delivery is going. And I think a lot of senders are going to struggle with delivery as they find that IP reputation is not enough to get into the inbox.
What matters for reputation?
There is a contingent of senders and companies that seems to believe that receiver ISPs and filtering companies aren’t measuring reputation correctly. Over and over again the discussion comes up where senders think they can improve on how reputation is measured.
One factor that is continually repeated is the size of the company. I’ve even seen a couple people suggest that corporate net worth should be included in the reputation calculation.
The problem with this suggestion is that just because a company is big or has a high net worth or is on the Fortune500 doesn’t mean that the mail they send isn’t spam. I’ve certainly received spam from large, name brand companies (and organizations). I’ve also consulted with a number of those companies who bought or appended a list and then had to deal with the fallout from a Spamhaus listing or upstream disconnection.
Sure, there is a certain logic to company size and prominence being a part of a reputation calculation. For instance, my experience suggests consumers who recognize a brand are less likely to treat mail as “spam” even if they didn’t sign up for the mail in the first place. Certainly there are large brands (Kraft, FTDDirect, 1-800–Flowers, OfficeDepot) that have been caught sending mail to people who never opted in to their lists.
Many people don’t realize that company size and prominence are already factored into the reputation scores. No ISPs don’t look at a mail and, if it’s authenticated, add in a little positive because it’s part of a giant, name brand company. Rather, the recipients change how they interact with the mail. Even recipients who didn’t sign for mail from Office Depot may click through and purchase from an offer. Some recipients recognizing the brand will hit delete instead of “this is spam.”
All of these things mean that big brands have recognition that takes into account that they are prominent brands. Elaborate processes and extra reputation points given to big brands don’t need to happen, they’re already an innate part of the system.
Setting expectations at the point of sale
In my consulting, I emphasize that senders must set recipient expectations correctly. Receiver sites spend a lot of time listening to their users and design filters to let wanted and expected mail through. Senders that treat recipients as partners in their success usually have much better email delivery than those senders that treat recipients as targets or marks.
Over the years I’ve heard just about every excuse as to why a particular client can’t set expectations well. One of the most common is that no one does it. My experience this weekend at a PetSmart indicates otherwise.
As I was checking out I showed my loyalty card to the cashier. He ran it through the machine and then started talking about the program.
Cashier: Did you give us your email address when you signed up for the program?
Me: I’m not sure, probably not. I get a lot of email already.
Cashier: Well, if you do give us an email address associated with the card every purchase will trigger coupons sent to your email address. These aren’t random, they’re based on your purchase. So if you purchase cat stuff we won’t send you coupons for horse supplies.
I have to admit, I was impressed. PetSmart has email address processes that I recommend to clients on a regular basis. No, they’re not a client so I can’t directly take credit. But whoever runs their email program knows recipients are an important part of email delivery. They’re investing time and training into making sure their floor staff communicate what the email address will be used for, what the emails will offer and how often they’ll arrive.
It’s certainly possible PetSmart has the occasional email delivery problem despite this, but I expect they’re as close to 100% inbox delivery as anyone else out there.
Permission-ish based marketing
My Mum flew in to visit last week, and over dinner one evening the talk turned to email.
Read MoreEmail marketing ulcers for the holiday
I’ve mentioned here before that I can usually tell when the big ISPs are making changes to their spam filtering as that ISP dominates my discussions with current and potential clients and many discussions on delivery mailing lists.
The last two weeks the culprit has been Yahoo. They seem to be making a lot of changes to their filtering schemes right at the busiest email marketing time of the year. Senders are increasing their volume trying to extract that last little bit of cash out of holiday shoppers, but they’re seeing unpredictable delivery results. What worked to get mail into the inbox a month ago isn’t working, or isn’t working as well, now.
Some of this could be holiday volume related. Many marketers have drastically increased their mail volume over the last few weeks. But I don’t think the whole issue is simply that there is more email marketing flowing into our mailboxes.
As I’ve been talking with folks, I have started to see a pattern and have some ideas of what may be happening. It seems a lot of the issue revolves around bulk foldering. Getting mail accepted by the MXs seems to be no different than it has been. The change seems to be based on the reputation of the URLs and domains in the email.
Have a domain with a poor reputation? Bulk. Have a URL seen in mail people aren’t interested in? Bulk. Have a URL pointing to a website with problematic content? Bulk.
In the past IPs that were whitelisted or had very good reputations could improve delivery of email with neutral or even borderline poor reputations. It seems that is no longer an effect senders can rely on. It may even be that Yahoo, and other ISPs, are going to start splitting IP reputation from content reputation. IP reputation is critical for getting mail in the door, and without a good IP reputation you’ll see slow delivery. But once the mail has been accepted, there’s a whole other level of filtering, most of it on the content and generally unaffected by the IP reputation.
I don’t think the changes are going to go away any time soon. I think they may be refined, but I do think that reputation on email content (particularly domains and URLs and target IP addresses) is going to play a bigger and bigger role in email delivery.
What, specifically, is going to happen at Yahoo? Only they can tell you and I’m not sure I have enough of a feel for the pattern to speculate about the future. I do think that it’s going to take a few weeks for things to settle down and be consistent enough that we can start to poke the black box and map how it works.
Beware the TINS Army
When consulting with clients, I spend a lot of time trying to help them better understand the concept of sender reputation. Spam reports, feedback loops, and other data that comes from a collection of positive and negative reputational feedback about a company sending email.
Certainly, the “This is not spam” action – moving an email from the spam folder to the inbox, or clicking the “not spam” button in a web mail’s interface, is a strong positive reputational action. Some webmail providers use this data to decide which bulked senders deserve being let out of the penalty box – which should have their mail once again delivered to the inbox.
A client recently theorized that a great solution to their delivery problems would be to do this “en masse.” Sign up for hundreds or thousands of webmail accounts, send my mail to them, and click on the “not spam” button for each of my own emails. That’ll greatly improve my sending reputation, right?
NO! ISPs have already thought of this. They watch for this. They’re really good at picking up on things like this. I know for a fact that Yahoo and Hotmail and AOL notice stuff like this, and I strongly suspect other webmail providers notice it as well.
What happens when Yahoo or Hotmail pick up on this type of unwanted activity? Well, if it’s at Yahoo, they’re likely to block all mail from you, 100%, forever. I’ve seen it happen more than once. Yahoo might even identify all of your netblocks, ones beyond the ones sending today’s mail or originating today’s activity. And good luck trying to convince them that you’re not a spammer – you have a better chance of winning the lottery two weeks in a row.
As for Hotmail – what would Hotmail do? Ask Boris Mizhen. Microsoft is currently suing him, alleging that he and/or his agents or associates engaged in this very practice.
Reputation monitoring sites
There are a number of sites online that provide public information about reputation of an IP address or domain name.
Read MorePublic reputation data
IP based reputation is a measure of the quality of the mail coming from a particular IP address. Because of how reputation data is collected and evaluated it is difficult for third parties to provide a reputation score for a particular IP address. The data has to be collected in real time, or as close to real time as possible. Reputation is also very specific to the source of the data. I have seen cases where a client has a high reputation at one ISP and a low reputation at another.
All this means is that there are a limited number of public sources of reputation data. Some ISPs provide ways that senders can check reputation at that ISP. But if a sender wants to check a broader reputation across multiple ISPs where can they go?
There are multiple public sources of data that I use to check reputation of client IP addresses.
Blocklists provide negative reputation data for IP addresses and domain names. There are a wide range of blocklists with differing listing criteria and different levels of trust in the industry. Generally the more widely used a list the more accurate and relevant it is. Generally I check the Spamhaus lists and URIBL/SURBL when investigating a client. I find these lists are good sources for discovering real issues or problems.
For an overall view into the reputation of an IP address, both positive and negative, I check with senderbase.org provided by Ironport and senderscore.org provided by ReturnPath.
All reputation sources have limitations. The primary limitation is they are only as good as their source data, and their source data is kept confidential. Another major limitation is reputation sources are only as good as the reputation of the maintainer. If the maintainer doesn’t behave with integrity then there is no reason for me to trust their data.
I use a number of criteria to evaluate reputation providers.
Reputation and "the cloud"
As Reddit recently learned it’s not a great idea to use the Amazon EC2 cloud to host mailservers. There are a number of reasons for this, most of them related to the reputation of mail coming from EC2 servers.
When you’re using machines in the cloud, changing IP addresses is as simple as initializing a new server. Spammers discovered this almost as soon as the EC2 cloud became public. They would set up a mailserver and send spam through that server until it was blocked. Then they’d just start another instance to avoid the block and keep spamming. They had an almost unlimited number of IP addresses to abuse and moving around was easy to do. Amazon did little to stop the spam coming from the cloud so many ISPs and spam filtering companies blocked email from the entire range of IP addresses allocated to the EC2 cloud.
Blocking large swathes of network space that are consistent sources of abuse is well accepted as a method of dealing with spam. Yes, this form of blocking has inconvenienced legitimate companies who aren’t actually doing anything wrong. But when a service provider doesn’t take sufficient action to stop customers from spamming through their networks, then ISPs will implement countermeasures.
Reddit and email
Ben over at Mailchimp writes about Reddit discovering a lot of their mail was being blocked because they were sending from the Amazon EC2 cloud.
Read MoreReputation
It used to be that every potential client that called me up to ask me to help them with their delivery issues would tell me they weren’t a spammer. Over the last year or so that’s changed to telling me that they have a good reputation and don’t understand why they’re having delivery problems.
This leads me to believe that there is some confusion about what reputation is and what reputation is not.
Reputation is a shorthand term for a complex formula measuring the history of email from an IP address. Some reputation schemes measure the history of email containing a particular URL or domain.
Recipient domains measure a lot of things and use them at various points during the email transaction. Some measurements are integrated into a single value that is queried during the SMTP transaction. If the measurement is too bad, the email is rejected or rate limited. Other measurements are queried after the email is accepted by the ISP, and those values determine if an email is delivered to the inbox or the bulk folder.
There are a couple important things to remember about reputation.
Truths and myths about email
Seven myths and two truths about email
My favorite:
[myth] Engagement is the new reputation. Actually, reputation metrics have always been about engagement, which is what complaint data and sender reputation reflect.Read More
What makes a good ESP?
There are a number of things that make a responsible ESP, including setting and enforcing standards higher than those set by the ISPs.
One of the responsible ESPs is Mailchimp. (Full disclaimer, I do consult for Mailchimp.) This ESP focuses on businesses with small to medium sized lists. They screen new customers for source of permission as well as mail content.
As well as putting a human in the loop and identifying problem customers manually, they have also developed an automated process that predicts the likelihood that a certain customer will violate their standards. This process is very similar to the reputation process in place at many ISPs. Customers that are flagged as potential problems are reviewed by staff members who contact the customer for further clarification.
What’s the benefit of this process? A good reputation, a clean customer base and positive notice by the ISPs. In fact, just recently I was contacted by one of the very large consumer ISPs, confirming that Mailchimp is one of my clients. He informed me that he’d noticed a few of the Mailchimp IPs had a really high reputation but weren’t whitelisted. He asked me to send him all of their IPs so he could make sure all their IPs were whitelisted.
Proactive auditing of customers and predictive modeling of mailing results is working for Mailchimp and their customers.
Some ESPs have aggressive cancellation policies, which helps them police their networks and their customers. I often encounter former customers of these ESPs, either as direct clients or as customers of my ESP clients. In one case, I was asking around about a new client at their old ESP. “They tell me they left you under their own power and there was no spam issue involved, can you comment?” The policy person would not comment specifically about that client, but did comment that “95% of our former customers were disconnected for cause.”
These are two examples of ESPs that are working hard to minimize the amount of unwanted mail going through their network. They have invested time and energy into tools and staff to monitor the network. Staff is empowered to make decisions about customers and management believes no customer is “to big to disconnect.”
Tomorrow we’ll look at typical ESPs and their normal practices.
The coming changes
Yesterday I talked about how I’m hearing warnings of a coming paradigm shift in the email industry. While these changes will affect all sender, ESPs in particular are going to need to change how they interact with both ISPs and their customers.
Currently, ESPs are able to act as “routine conveyers.” The traffic going across their network is generated by their customers and the ESP only handles technical issues. Responsible ESPs do enforce standards on their customers and expect mailings to meet certain targets. They monitor complaints and unknown users, they monitor blocks and reputation. If customers get out of line, then the ESP steps in and forces their customer to improve their practices. If the customer refuses, then the ESP disconnects them.
Currently standards for email are mostly dictated by the ISPs. Many ESPs take the stance that if any mail that is not blocked by the ISPs then it is acceptable. But just because a certain customer isn’t blocked doesn’t mean they’re sending mail that is wanted by the recipients.
It seems this reactive approach to customer policing may no longer be enough. In fact, one of the large spam filter providers has recently offered their customers the ability to block mail from all ESPs with a single click. This may become a more common response if the ESPs don’t start proactively policing their networks.
Why is this happening? ISPs and filtering companies are seeing increasing percentages of spam coming out of ESP netspace. Current processes for policing customers are extremely reactive and there are many ESPs that are allowing their customers to send measurable percentages of spam. This situation is untenable for the filtering companies or the ISPs and they’re sending out warnings that the ESPs need to stop letting so much spam leave their networks.
Unsurprisingly, there are many members of the ESP community that don’t like this and think the ISPs are overreacting and being overly mean. They do not think the ISPs or filtering companies should be blocking all an ESPs customers just because some of the customers are sending unwanted mail. Paraphrased, some of the things I’ve heard include:
AOL EWL: low complaints no longer enough
This morning AOL announced some changes to their Enhanced White List. Given I’ve not talked very much about the AOL EWL in the past, this is as good a time as any to talk about it.
The AOL Enhanced Whitelist is for those senders that have very good practices. Senders on the EWL not only get their mail delivered to the inbox, but also have links and images enabled by default. Placement on the EWL is done solely on the basis of mail performance and only the best senders get on the list.
The new announcement this morning says that AOL will take more into account than just complaints. Previously, senders with the lowest complaint rates qualified for the EWL. Now, senders must also have a good reputation in addition to the low complaint rates. Good reputation is a measure of user engagement with a particular sender.
This change only reinforces what I and many other delivery experts have been saying: The secret to good delivery is to send mail recipients want. ISPs are making delivery decisions based on those measurements. Send mail that recipients want, and there are few delivery problems.
For a long time good delivery was tied closely to complaint rates, so senders focused on complaints. Spammers focused on complaints too, thus managing to actually get some of their spam delivered. ISPs noticed and started looking at other ways to distinguish wanted mail from spam. One of the better ways to separate spam from wanted mail is to look at user engagement. And the ISPs are measuring engagement and using that measurement as part of their decision making process. Send so much mail users don’t read it, and your reputation goes down followed by your delivery rates.
I need IP addresses for reputation
Number one of seven in our occasional series on why ESPs need, or don’t need, lots of IP addresses to send mail properly.
Read MoreRescuing reputation
One of the more challenging things I do is work with companies who have poor reputations that they’re trying to repair. These companies have been getting by with poor practices for a while, but finally the daily delivery falls below their pain threshold and they decide they need to fix things.
That’s when they call me in, usually asking me if I can go to the ISPs and tell the ISPs that they’re not spammers, they’re doing everything right and will the ISP please stop unfairly blocking them. Usually I will agree to talk to the ISPs, if fixing the underlying problems doesn’t improve their delivery on its own. But before we can talk to the ISPs, we have to try to fix things and at least have some visible changes in behavior to take to them. Once they have externally visible changes, then we can ask the ISPs for a little slack.
With these clients there isn’t just one thing they’ve done to create their bad reputation. Often nothing they’re doing is really evil, it’s just a combination of sorta-bad practices that makes their overall reputation really bad. The struggle is fixing the reputation requires more than one change and no single change is going to necessarily make an immediate improvement on their reputation.
This is a struggle for the customer, because they have to start thinking about email differently. Things have to be done differently from how they’ve always been done. This is a struggle for me because I can’t guarantee if they do this one thing that it will have improved delivery. I can’t guarantee that any one thing will fix their delivery, because ISPs measure and weight dozens of things as part of their delivery making decisions. But what I can guarantee is that if they make the small improvements I recommend then their overall reputation and delivery will improve.
What small improvement have you made today?
How reputation and content interact
Recently, one of my clients had a new employee make a mistake and ended up sending newsletters to people in their database that had not subscribed to those particular newsletters. This resulted in their recipients getting 3 extra emails from them. These things happen, people fat-finger database queries or aren’t as careful with segmentation as they should be.
My clients were predictably unhappy about sending mail their users hadn’t signed up for and asked me what to do to fix their reputation. I advised they not do anything other than make sure they don’t do that again. The first send after their screw-up had their standard 100% inbox delivery. The second send had a significant problem with bulk foldering at Hotmail and Yahoo. The third send had their standard 100% inbox delivery.
So what happened on the second send? It appears that on that send they had a link or other content that “filled the bucket.” Generally, their IP reputation is high enough that content isn’t sufficient to send their mail into the bulk folder. However, their reputation dipped based on the mistake last week, and thus the marginal content caused the bulk foldering.
Overall, these are senders with a good reputation. Their screw up wasn’t enough to damage their delivery itself, but may have contributed to all their mail going into the bulk folder the other day. I expect that their reputation will rebound quickly and they will be able to send the same content they did and see it in the inbox.
Technology does not trump policy when it comes to delivery
Recently Ken Magill wrote an article looking at how an ESP was attempting to sell him services based on the ESPs ‘high deliverability rates.’ I commented that Ken was right, and I still think he is.
Ken has a followup article today. In the first part he thanks Matt Blumberg from Return Path for posting a thoughtful blog post on the piece. Matt did have a very thoughtful article, pointing out that the vast majority of things affecting delivery are under the control of the list owner, not under the control of the ESP. As they are both right, I clearly agree with them. I’ve also posted about reputation and delivery regularly.
Hidden cost of email blasts
Seth Godin has a post up today talking about how friction, that is the cost of sending marketing, is good for marketing. With more friction, marketers make choices about sending instead of sending to everyone.
The post touches on a point I’ve certainly tried to explain to clients and senders in general.
Winning friends and removing blocks
I do a lot of negotiating with blocklists and ISPs on behalf of my clients and recently was dealing with two incidents. What made this so interesting to me was how differently the clients approached the negotiations.
In one case, a client had a spammer slip onto their system. As a result the client was added to the SBL. The client disconnected the customer, got their IP delisted from the SBL and all was good until the spammer managed to sweet talk the new abuse rep into turning his account back on. Predictably, he started spamming again and the SBL relisted the IP.
My client contacted me and asked me to intercede with Spamhaus. I received a detailed analysis of what happened, how it happened and how they were addressing the issue to prevent it happening in the future. I relayed the info to Spamhaus, the block was lifted and things are all back to normal.
Contrast that with another client dealing with widespread blocking due to a reputation problem. Their approach was to ask the blocking entity which clients they needed to disconnect in order to fix the problem. When the blocking entity responded, the customer disconnected the clients and considered the issue closed. They didn’t look at the underlying issues that caused the reputation problems, nor did they look at how they could prevent this in the future. They didn’t evaluate the customers they disconnected to identify where their processes failed.
The first client took responsibility for their problems, looked at the issues and resolved things without relying on Spamhaus to tell them how to fix things. Even though they had a problem, and is statistically going to have the occasional problem in the future, this interaction was very positive for them. Their reputation with the Spamhaus volunteers is improved because of their actions.
The second client didn’t do any of that. And the people they were dealing with at the blocking entity know it. Their reputation with the people behind the blocking entity was not improved by their actions.
These two clients are quite representative of what I’ve seen over the years. Some senders see blocking as a sign that somehow, somewhere there is a flaw in their process and a sign they need to figure out how to fix it. Others see blocking as an inconvenience. Their only involvement is finding out the minimum they need to do to get unblocked, doing it and then returning to business as usual. Unsurprisingly, the first type of client has a much better delivery rate than the second.
Confirmed opt-in
I spent the morning in multiple venues correcting mis-understandings of confirmed opt-in. The misunderstandings weren’t so much that people didn’t understand how COI works, but more they didn’t understand all the implications.
In one venue, the conversation centered around how small a portion of deliverability the initial subscription process affects. Sure, sending unwanted, unexpected email can and does cause reputation problems, but merely using COI as a subscription methodolgy doesn’t automatically give a sender a good reputation or good delivery. Senders using COI as a subscription practice need to also need to send relevant and engaging mail that their recipients expect to receive. They need to handle their bounces well and purge or re-engage inactive subscribers. They need to keep their complaints low and their responses high.
How you manage subscriptions is only one factor in reputation schemes, and even if the subscription method is COI other factors can negate any bonus involved.
The second conversation involved Ken challenging me on the comment I left on his quiz yesterday. I said COI wasn’t foolproof and he challenged me to explain how. I did, and he’ll be following up next week.
Reputation as measured by the ISPs
Part 3 in an ongoing series on campaign stats and measurements. In this installment, I will look a little closer at what other people are measuring about your email and how that affects your reputation at the ISPs.
Part 1: Campaign Stats and Measurements
Part 2: Measuring Open Rate
Reputation at the ISPs is an overall measure of how responsive recipients are to your email. ISPs also look at how much valid email you are sending. Anything the ISP can measure and use to distinguish good mail from bad is used in calculating reputation.
Some of the major metrics ISPs use include the following.
Invalid Address Rates
The ISPs count how much mail from any particular IP address is hitting non-existent addresses. If you are mailing a large number of email addresses that do not exist (550 user unknown), this is a suggestion that your address collection techniques are not very good. Responsible mailers do have the occasional bad address, including typos, expired/abandoned addresses, but the percentage in comparison to the number of real email addresses is low. How low is low? Public numbers suggest problems start at 10% user unknowns, but conversations with ISP employees show they consider lower levels a hint there may be a problem.
To calculate bounce rate ISPs take the total number of addresses that were for invalid accounts and divide that by the total number of addresses that the sender attempted to send mail to. Rates above 10% may cause significant delivery issues on their own, rates lower that 10% may still contribute to poor delivery through poor reputation scores.
Spamtraps
ISPs pay a lot of attention to how much mail is hitting their “trap” or “bait” accounts. There are a number of different sources of these trap accounts: old abandoned email addresses, addresses that never existed or even role accounts. Hits to a trap account tells the ISP there are addresses on your list that did not opt-in to receive mail. And if there are some addresses they know about that did not opt-in, it is likely that there are other addresses that did not opt in.
Spamtraps tend to be treated as an absolute number, not as a percentage of emails. Even a single spamtrap on a list can significantly harm delivery. According to the ReturnPath Benchmark report lists with a single spamtrap had nearly 20% worse delivery than lists without spamtraps.
This is spam clicks (FBL complaints)
Complaints from users are heavily used by ISPs. This tells them directly how many people are objecting to your email. In this case, permission is removed from the equation. Even if a sender has permission to send email, the recipient can say “no, I don’t want this, it is spam.” The ISPs put more weight on what their users tell them than on what the senders tell them.
TWSD: Lying and Hiding
Another installment in my ongoing series: That’s What Spammers Do. In today’s installment we take a look at a company deceiving recipients and hiding their real identity.
One of my disposable addresses has been getting heavily spammed from mylife.com. The subject lines are not just deceptive, they are provably lies. The mail is coming from random domains like urlprotect.com or choosefrequency.com or winnernotice.com advertising links at safetyurl.com or childsafeblogging.com or usakidprotect.com.
The spam all claims someone is “searching for…” at their website. The only thing is, the email address is associated with a fake name I gave while testing a website on behalf of a client. I know what website received the data and I know what other data was provided during the signup process. I also know that the privacy policy at the time said that my data would not be shared and that only the company I gave the information to would be sending me email.
Just more proof that privacy policies aren’t worth the paper they’re written on. But that’s not my real issue here.
The real issue is that I am receiving mail that is clearly deceptive. The subject lines of the emails up until yesterday were “(1) New Message – Someone Searching for You, Find Out…” Yesterday, I actually clicked through one of the messages to confirm that the emails were ending up at mylife.com. After that, the subject lines of the emails changed to “(1) New Person is Searching for You.” I don’t know for sure that my click has caused the change in subject lines, but the timing seems a bit coincidental.
It’s not that someone, somewhere gave mylife.com bad data, or that someone typed a name into the mylife.com search engine and the mylife.com database showed that name and my email address were the same. Neither this name or this email address show up in a google search and I can say with certainty that this is a unique address and name combination given to a specific website. Therefore, the subject lines are clearly and demonstrably lies.
The spams are also coming from different domains and advertising links in different domains. The content is identical, the CAN SPAM addresses are identical. While the court may not rule this is deceptive under the rules of CAN SPAM, it certainly is an attempt to avoid domain level spam filters.
Who are mylife.com? Well, their website and the CAN SPAM address on their spam claims they are the company formerly known as reunion.com. I’ve talked about reunion.com here before. They have a history of harvesting addresses from users address books. They were sued for deceptive email practices under California law, but won the case just recently. They seem to think that the court case was permission to send deceptive email and have thus ramped up their deceptive practices.
If you are a legitimate email marketer, there are a couple take home messages here.
1) Spammers send mail with different domains, from different IP addresses, that contain identical content, landing pages and CAN SPAM addresses. Legitimate marketers should not rotate content and sends through different domains or different IP addresses. Pick your domain, pick your IP and stick with it.
1a) Spammers use randomly chosen domain names and cycle through domains frequently. Legitimate marketers must not use unrelated domains in marketing. Use a domain name that relates to your product, your industry or you.
2) Spammers send mail with deceptive subject lines. Legitimate marketers should make sure their subject lines are clear and truthful.
3) Spammers send mail in violation of the privacy policy under which information was collected. Legitimate marketers should be very careful to handle data in accordance with their privacy policies.
That’s what spammers do. Is that what you do?
Monitoring customers at ESPs
In the past I’ve talked about vetting clients, and what best effort encompasses when ESPS try to keep bad actors out of their systems. But what does an ESP do to monitor clients ongoing? Al Iverson from ExactTarget says that they:
Read MoreAOL talks about reputation
Over at the AOL postmaster blog, Christine posts about reputation and AOL.
Read MoreReputation: part 2
Yesterday, I posted about reputation as a combination of measurable statistics, like bounce rates and complaint rates and spamtrap hits. But some mailers who meet those reputation numbers are still seeing some delivery problems. When they ask places, like AOL, why their mail is being put into the bulk folder or blocked they are told that the issue is their reputation. This leads to confusion on the part of those senders because, to them, their reputation is fine. Their numbers are exactly where they were a few weeks ago when their delivery was fine.
What appears to have changed is how reputation is being calculated. AOL has actually been hinting for a while that they are looking at reputation, and even published a best practices document back in April. Based on what people are saying some of that change has started to become sender visible.
We know that AOL and other ISPs look at engagement, and that they can actually measure engagement a lot more accurately than sender can. Senders rely on clicks and image loading to determine if a user opened an email. ISPs, particularly those who manage the email interface, can measure the user actively opening the email.
We also know that ISPs measure clicks. Not just “this is spam” or “this is not spam” clicks in the interface, but they know when a link in an email has been clicked as well.
I expect that both these measures are now a more formal and important part of the AOL reputation magic.
In addition to the clicks, I would speculate that AOL is now also looking at the number of dead addresses on a list. It is even possible they are doing something tricky like looking at the number of people who have a particular from address in their address book.
All ISPs know what percentage of a list is delivered to inactive accounts. After a long enough period of time of inactivity, mail to those accounts will be rejected. However for some period of time the accounts will be accepting mail. Sending a lot of mail to a lot of dead accounts is a sign of a mailer who is not paying attention to recipient engagement.
All ISPs with bulk folders have to know how many people have the from address in their address book. Otherwise, the mail would get delivered incorrectly. In this way, ISPs can monitor the “generic” recipient’s view of the email. Think of it as a similar to hitting the “this is not spam” button preemptively.
This change in reputation at the ISPs is going to force senders to change how they think of reputation, too. No longer is reputation all about complaints, it is about sending engaging and relevant email. The ISPs are now measuring engagement. They are measuring relevancy. They are measuring better than many senders are.
Senders cannot continue to accrete addresses on lists and continue sending email into the empty hole of an abandoned account while not taking a hit on their reputation. That empty hole is starting to hurt reputation much more than it helps reputation.
Reputation
Reputation is the buzzword in delivery these days. Everyone talks about building a good reputation and how to do it. Makes sense, the ISPs are always hammering on reputation and how critical reputation is. The more I talk with delivery folks on the ESP side of thing, the move I realize that there is a fundamental disconnect between what the ESPs mean when they say reputation and what the ISPs mean when they say reputation.
Many people handling delivery think that the bulk of reputation is wrapped up in complaint rates and bounce rates. I think they know the ISPs measure more than just complaints and bounces (spamtraps!) but really believe that most of developing a good reputation is all about keeping those complaints low.
This perspective may have been true in the past, but is becoming less true as time goes on. There are a lot of very smart people managing incoming mail at the ISPs and they are constantly looking for ways to better meet the desires of their customers. Lest we forget, their customers are not the senders, their customers are the end users. Their customers are not senders.
Part of meeting the needs of end users means actually giving them a way to provide feedback. AOL started the trend with the this-is-spam button, and other ISPs (ones that controlled the user interface at least) followed suit. For a very long time, reputation was dominated by complaint percentages, with modifiers for number of spamtrap addresses and number of non-existent users.
The problem is, these numbers were easy to game. Spammers could modify their metrics such that their email would end up in the inbox. In response, the ISPs started measuring things other than complaints, bounces and spamtraps. These other measurements are strong modifiers to complaints, such that mailers with what used to be acceptable complaint rates are seeing their mail end up bulked or even rejected.
Recently, AOL seems to have made some subtle modifications to their reputation scores. The result is mailers who have previously acceptable complaint rates are seeing delivery problems. When asked, AOL is only saying that it is a reputation issue. Lots of senders are trying to figure out what it is that is more important than complaints.
Tomorrow, I will talk about what I think AOL could be measuring.
The Question
Mark Brownlow has a list of 12 questions every email marketer should ask about their marketing program. Buried in the middle is the most important question for delivery.
Read MoreAppropriating reputation
One of the thing savvy spammers are doing these days is appropriating the reputation of someone else. Reputation appropriate takes many forms. Some spammers hijack windows machines, turn them into bots and send spam through major ISP smarthosts. “Legitimate email marketers” buy service from mainstream ESPs to send their permission-challenged email that they cannot get delivered through their own IP space.
There are different strategies for companies to prevent bad groups from appropriating their reputation. For the ESP, the prime defense against reputation appropriation is screening new customers and new lists.
When screening potential customers, there are three broad categories that customers fall into. One is the legit prospect that is exactly whom they represent to you, these are the easy guys. Another is the naive mailer, who really does not have any clue about email but wants to move into the digital age. This mailer is often extremely small, but knows nothing about email. The final category is the subversive prospect. This is the company who knows exactly what they are doing, and who is actively working to hide their practices from the ESP. They are attempting to subvert the process.
Over the coming weeks I will be talking more about screening new customers and how to distinguish the naive customer from the subversive one.
How not to handle unsubscribes
On the heels of my unsubscribe experience last week where an ESP overreacted and unsubscribed addresses that did not belong to me, I encountered another deeply broken unsubscribe process. This one is the opposite, there is no way to unsubscribe from marketing mail at all. Representatives of PayPal have only been able to suggest that if I do not want their mail, that I block PayPal in my email client.
I had a PayPal account years and years ago. They made some extensive privacy policy changes back in 2003 and when I did not actively agree to the new policies, they closed the account. That account closure seemed to take, I heard nothing from PayPal. In early 2008, I made a purchase at a vendor that only accepted credit cards through PayPal. Normally, I do not do business with vendors who only accept payment through PayPal, but there appeared to be a way to make the payment without establishing a PayPal account, so I went ahead and made the purchase.
The receipt from that purchase came from PayPal, and mentioned that I had an existing PayPal account. I figured that because the address was the same as the 2003 account that the boilerplate did not understand ‘closed accounts’. I brushed off the notice and did not worry about it.
On June 23, I received marketing email from PayPal. The mail offered 10% off my first eBay purchase, if I set up an eBay account using the same address on my PayPal account. Yay. Spam. Oh, well, no big deal, there was an unsub link at the bottom of the email. It is PayPal, they are a legitimate company, they will honor an unsubscribe. It will all be fine.
Or. Not.
Clicking on the unsubscribe link in the email takes me to a webpage that tells me I had to login to my account to unsubscribe. But I do not have an account!
They clearly think I have an account linked to the email address they mailed. I decide to see if I can recover the account and then unsubscribe. I put in the email address they sent the marketing email to, the password I probably would have used had I actually set up this account and hit “submit.” PayPal now asks me to set up 3 questions to use to recover my account in case I forget the login in the future. Uh. What? No. I do not want to set up an account, I want them to stop sending me email. I abandon that webpage.
I then attempt to recover the password to the account. Put in the email address that PayPal is sending email to and hit “forgot password”. PayPal, as expected, sends me an email. Click this magic link to recover your account. PayPal then asks me to input the full number of the credit card associated with the account – the credit card number I do not have. What account? What credit card number? Is this from my 2003 subscription that was closed? Is this from the purchase I made in February? I abandon that webpage.
The recover password email helpfully lists a phone number I can call for assistance so I call. In order to be able to talk to someone I have to enter my phone number. And the credit card number associated with my account. I resorted to randomly pounding on “0” and telling the voice recognition software I wanted help. Eventually, it got so confused it transfered me to a real human.
Tragically, the voicemail system was actually more helpful than the real human on the other end. Distilling down hours of sitting on the phone with them, I am told the following:
Those addresses are costing you
Mark Brownlow has a post up about the hidden costs of bad email marketing. These center around brand damage, but there are other costs to poor email marketing strategies.
Previously, having old and non-responsive email addresses on a mailing list did not hurt and may have helped a reputation at an ISP. In some cases, these addresses may have even helped a reputation by increasing the number of emails delivered thus lowering the overall percentage of complaints.
More recently, some ISPs have started looking at the characteristics of recipients as part of the reputation score of a sender. If a sender is mailing a lot of abandoned email addresses, these ISPs can detect that fact. This counts against a senders reputation and may result in email ending up in the bulk folder or being blocked at the transaction.
Many senders are extremely resistant to removing old addresses from their lists. Some of the more numbers driven ones have even followed the statistics and can tell me exactly how many people ignore their email for 12 months or 18 months, and then come back and make a large purchase. This is true, sometimes people will ignore email for a long time and then come back. Keeping these people on a list may be beneficial.
However, in those recipients who ignore email (no opens, no clicks) for a long time are some addresses that have been abandoned. While these addresses are not spamtraps, repeatedly sending email to large numbers of abandoned addresses will lower the sender’s reputation over time.
All senders should have a process for dealing with non-active addresses. Allowing cruft to accumulate on a list does negatively affect reputation.
Disposable or Temporary Addresses
Mark Brownlow has a really good post up today about disposable and temporary addresses and how they affect marketers trying to build an opt-in list.
I use tagged addresses for all my signups, and have for more than 10 years now. It lets me track who I gave an address to and if this mail is contrary to what I signed up for or the address has leaked, I can shut down mail to that address entirely.
Tagged addresses also have another function. One of our local brew pubs has a rewards program, spend money there, get points. As part of the signup process, they requested an email address. All the email I have received from them has been clearly branded, well designed, they are an example of how to use email right. That is until last week. Last week I received an email to the tagged address from some survey company. The survey company provided no branding, nothing.
Botnets
Terry Zink has been posting articles about botnets as traced by Hotmail. I do not often talk about botnets as they are outside my area of expertise. They are not something I deal with, as no one who uses botnets is welcome as a client here.
My clients and I, however, do have to deal with the fallout from botnets. Because of botnets, receiver ISPs are extremely suspicious of mail from any IP address that they have not seen mail from previously. Mail from new IPs is, more often than not, a newly infected Windows machine. This results in mail from new IPs not starting with a reputation of zero but starting with a negative reputation.
Botnets are another example of spammers making it more difficult for mailers with permission to use email.
Email non-viable for acquisition
Chris Marriott over at iMediaConnection talks about all the reasons email is a non-starter as a replacement for direct mail. This is something I have been telling clients for a while now. Chris mentions a number of reasons for why email is not an acquisition tool.
Read MoreReport spam button broken
Q Interactive and Marketing Sherpa published a press release today about how fundamentally broken the “report spam” button is. They call for ISPs to make changes to fix the problem. I think the study on recipient perceptions is useful and timely. There is an ongoing fundamental paradigm shift in how ISPs are handling email filters. ISPs are learning how to measure a senders collective reputation with end users, and, more importantly integrate that reputation into the equation used to determine how to filter and deliver incoming email.
Q Interactive and Marketing Sherpa acknowledge this change in the report:
DKIM "i=" vs "d=" and Reputation
This really should be part seven of a twelve part series or some such as it deals with an aspect of DKIM that’s really important, but is way down in the details of implementation. (dkim.org is a reasonable place to start for a general overview of DKIM).
There’s an apparently endless thread on the DKIM-SSP spec development mailing list at the moment about the differences between two fields in a DKIM signature that could be used to tie a senders reputation to. Several ESP delivery folks asked me to explain what everyone was talking about, and this post is a first cut at that.
“i=” vs “d=”
There are two possible fields in a DKIM signature that could be used to identify the sender of a message, and so to tie a sender history and reputation record to. They are the so-called “i=” and “d=” field, from the syntax used to include them in the signature.


