TWSD
When opens hurt reputation
Podia has scraped the Word to the Wise blog and I’m currently receiving an ongoing drip campaign from them absolutely begging me to mention them in my blog post on cold emails.
Read MoreBad marketing automation, part deux
Back in April I wrote about some poor marketing automation that ended up spamming me with ‘cart abandonment’ emails when the issue was the company’s credit card processing went down. That post has now been scraped by the spammers Moosend and they keep sending me… poorly targeted automated spam.
Read MoreCAN SPAM says I can!

Saw a new disclaimer on mail sent to an address harvested off our website today:
Read MoreOpting out of “service” messages
A frequent question in a number of deliverability spaces is how to tell if a message is transactional or marketing. In most cases the decision is related to whether or not to respect an unsubscribe request. All too often companies decide that their messages are too important to allow someone to opt-out of. The problem is, in some cases, there is no longer a customer relationship to send notices about.
Read MoreSpam is never timely nor relevant
One of the ongoing recommendations to improve deliverability is to send email that is timely and relevant to the recipient. The idea being that if you send mail a recipient wants, they’re more likely to interact with it in a way that signals to the mailbox provider that the message is wanted. The baseline for that, at least whenever I’ve talked about timely and relevant, is that the recipient asked for mail from you in the first place.
Read MoreIt’s not marketing, it’s spam
There are times when I hesitate to call what marketers do “spam.” I can use the euphemisms with the best of ’em. “Cold emails” “Targeted Marketing” “B2B marketing.”
Read MoreHitting the ground running
We’ve landed in Dublin and are back at work. Blogging will pick up as I get back into the swing of things.
Read MoreUnsubscribe means unsubscribe
But, unfortunately, some senders don’t actually think unsubscribe means stop sending mail.
Today, for instance, the nice folks at The Container Store sent me an email with an “important update to my POP! account”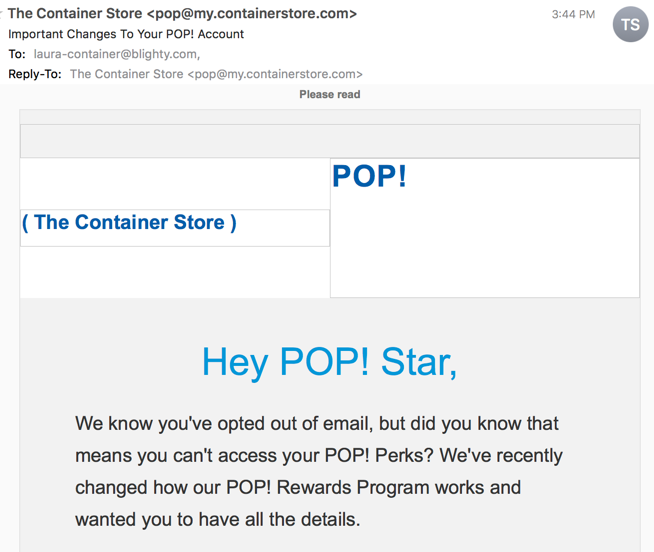
Yes, that’s an address I gave them. But I don’t have any record of setting up an account. I was on their mailing list for all of 4 emails back in November 2016 before unsubscribing. But, they’ve decided they can email me despite my unsubscribe request.
They’ve cloaked this as an “Important Account Update” about some account I don’t have. In fact, when I go to their website and try and see what this oh so important account is about they tell me: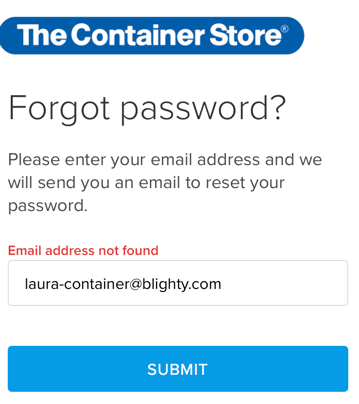
I understand legitimate account notifications might be an acceptable excuse to send mail even after the recipient opted out. This, however, was done extremely poorly. There is no record of the account that they are sending me information about. Neither the company nor I have any record of this account of mine.
At a minimum the emails should have only be sent to the folks that actually had an account. But, they weren’t.
I also have some issues with a company requiring recipients to accept email in order to continue using reward points. As a recipient, if I wanted what they were offering I might go ahead and continue receiving emails. But, I might not. It would all depend on how aggressive their email program is and how good the rewards are. As a deliverability consultant, this strikes me as a great way to create a mailing list full of unengaged users. Unengaged users lead to spam foldering and eventual failure of an email marketing program.
Whatever some executives think, and having been in this industry for a decade and I half I’m sure this is coming from the top down, this is not a good way to build an email program. You really can’t force folks to accept your email. ISPs are too protective of their users to make that a viable strategy.
Social media connections are not opt-ins
It seems silly to have to say this, but connecting on social media is not permission to add an address to your newsletter or mailing list or prospecting list or spam list. Back in 2016, I wrote:
Read MoreThat's not how you do it…
Got an email this morning from a company advertising their newest webinar “The Two Pillars of Effective Large-Scale Email: Security and Deliverability.” The message came to a tagged address, so clearly I’d given them one at some point. But I didn’t recognize the name or company or anything. I did a search to seen when I may have interacted with this company in the past.
Looking through my old emails, it appears I contacted this company through their support form back in 2007. They were blocking a client’s newsletter. This is what I sent:
The cycle goes on
Monday I published a blog post about the ongoing B2B spam and how annoying it is. I get so many of these they’re becoming an actual problem. 3, 4, 5 a day. And then there’s the ongoing “drip” messages at 4, 6, 8, 12 days. It is getting out of control. It’s spam. It’s annoying. And most of it’s breaking the law.
But, I can also use it as blog (and twitter!) fodder.
Appending in a nutshell
A few months ago a colleague sent me, and every other person on his overly large LinkedIn list, an email looking for some help hiring. It starts off with “Greetings LinkedI Connections” and ends with… an unsubscribe link.
Read MoreFraudulent signups or spam?
This morning I got spam from a major data broker / ESP / credit reporting agency claiming I’d signed up on some college website. In the UK. To check my credit score.
Uh. No. No I didn’t.
Of course, it’s very possible someone did use my email address when signing up for something at a UK university. They probably got a t-shirt or free pizza out of it. But that doesn’t really matter to me. A certain credit agency is spamming me with irrelevant and horribly targeted advertisements for their services and claiming the mail is opt in.
I know that address is widely sold in the UK to “legitimate” marketers. It’s very possible that it was purchased by the spammer in question. Or, I dunno, maybe they’re the ones selling it. As a victim, I don’t really care why a company is spamming me.
Part of a sender’s job to make sure their data is accurate. And they failed.
But for this particular company, that’s par for the course. When I posted about this over on Facebook, I had multiple friends pointing out that this company regularly spams and sells spamming services.
Spammers gonna spam.
Outreach or spam?
This showed up in my mailbox earlier today: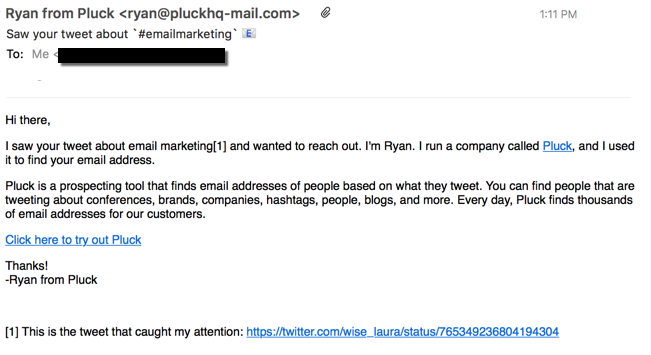
The tweet in question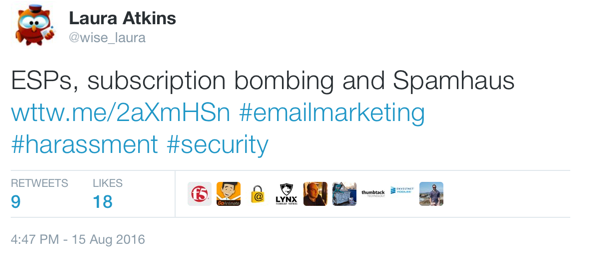
From Crunchbase: “Pluck is an email prospecting tool that gives you the email addresses of the people tweeting about subjects related to your business.”
Prospecting: another name for spamming. Look, I know that you want to sell you’re newest, greatest product to the world. But just because I tweet something with a # that you think is relevant to your product doesn’t mean that I want to get your spam. I also know it’s hard to get attention and find prospects; I’m a small business owner, too and I need to market my own services. But spamming isn’t a good idea. Ever.
There’s been a significant increase in this kind of spam “to help your business” lately. It’s a rare day I don’t get something from some company I’ve never heard of trying to sell me their newest product. It might be something if they tried a contact or two and then went away. But they’ll send mail for weeks or months without getting an answer. Look, silence IS an answer and it means you need to go away and leave your prospects alone.
Unfortunately, there are services out there that sell a product that let you “automatically follow up” with your prospects. Pluck up there uses one of them, as that’s who’s handling all the links in the message. In fact, if you go to the bare domain (qcml.io) they talk a good anti-spam game. “Die, spammers, die.” I reported the message to them. I’m not expecting them to actually do anything, and I’m not expecting a response.
It’s just spam under another name. There’s no pretense that it’s anything else. Even if it’s sent in a way that makes it look like a real person typed the message, like QuickMail offers. “All emails will come straight out of your personal inbox as though you typed them yourself.” As if you typed them yourself.
The worst part is there’s no real way to stop the mail. I can’t unsubscribe. The companies selling the software don’t provide any guidance to their customers about what the law requires. Take the message from Pluck that started the post. It violates CAN SPAM in multiple ways. Moreover, the address they used is not publicly associated with my twitter handle, which means they’re doing some harvesting somewhere. That means treble penalties under CAN SPAM.
I could reply and ask them to stop mailing me. I’ve done that a couple times with a message that says, “Please don’t email me any more.” I’ve got to tell you, some people get really mad when you ask them not to email you. Some just say yes, but others are really offended that you asked them to stop and get abusive. It’s gotten to the point where I don’t ask any more because of that one person who decides to harass, threaten and scream at me. Sure, it’s maybe 1 in 5, but I don’t have the time or energy to figure out who is going to be receptive and who isn’t. I don’t have time for that. No one has time for that.
I’m expecting that filters are going to catch up eventually and these types of mail will be easier to filter out. Until then, though, small business owners like myself are stuck in a place where we have to deal with spam distracting us from our business. At least I get blog content out of it.
Clickthrough forensics
When you click on a link in your mail, where does it go? Are you sure?
HTTP Redirects
In most bulk mail sent the links in the mail aren’t the same as the page the recipients browser ends up at when they click on it. Instead, the link in the mail goes to a “click tracker” run by the ESP that records that that recipient clicked on this link in this email, then redirects the recipients web browser to the link the mail’s author wanted. That’s how you get the reports on how many unique users clicked through on a campaign.
In the pay-per-click business that’s often still not the final destination, and the users browser may get redirected through several brokers before ending up at the final destination. I walked through some of this a few years ago, including how to follow link redirection by hand.
HTTP Forensics
Evil spammers sometimes deploy countermeasures against that approach, though – having links that will only work once or twice, or redirects that must be followed within a certain time, or javascript within an intermediate page or any of a bunch of other evasions. For those you need something that behaves more like a web browser.
For serious forensics I might use something like wireshark to passively record all the traffic while I interact with a link from inside a sandboxed browser. That’s not terribly user-friendly to use or set up, though, and usually overkill. It’s simpler and usually good enough to use a proxy to record the web traffic from the browser. There are all sorts of web proxies, used for many different things. What they have in common is that you configure a web browser to talk to a proxy and it’ll send all requests to the proxy instead of to the actual website, allowing the proxy to make any changes it wants as it forwards the requests on and the results back.
For investigating what a browser is doing the most useful proxies are those aimed at either web developers debugging web apps or crackers penetration testers compromising web apps. Some examples are Fiddler (Windows), Cellist (OS X, commercial), mitmdump (OS X, linux, Windows with a little work), Charles (anything, commercial) or ZAP (anything).
I’m going to use mitmdump and Firefox. You don’t want to use your main browser for this, as the proxy will record everything you do in that browser while you have it configured – and I want to keep writing this post in Safari as I work.
Mailbox preview and HTML content
I just received a slightly confusing email.
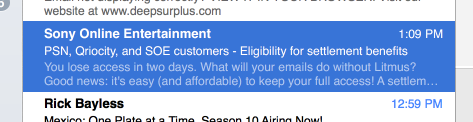
The From address and the Subject line are from Sony, but the content looks like it’s from email analytics firm Litmus. What’s going on here?
Opening the mail it looks like a fairly generic “Oops, we lost a class-action lawsuit, have $2 worth of worthless internet points!” email from Sony; no mention of Litmus at all. My first thought is that Mail.app has managed to scramble it’s summary database and it’s pulling summaries from the wrong email, as I am on a Litmus mailing list or two, but nothing else looks off.
Digging around inside the source of the mail I do find a bunch of tracking gifs from emltrk.com, which is a Litmus domain so there is a Litmus connection there somewhere. Curious.
Finally, about two pages in to the HTML part of the mail I find this:
What not to do when buying lists
Saturday morning I check my mail and notice multiple emails from the DMA. Yes, I got three copies of an email from the US Direct Marketing Association with the subject line Kick It Up A Notch With The DMA Career Center. It seems the DMA are buying addresses from various companies. Because I use tagged email addresses, this means their naive de-duping doesn’t realize that laura-x and laura-y are the same email address. Of course, they’ve also managed to send to an untagged email address, too. I have no idea where they got that particular address; I’m sure I’ve never handed that address over to the DMA for any reason.
Saturday afternoon, I check one of the professional filtering / anti-spam mailing list. Some subscribers are asking for copies of spam from 97.107.23.191 to .194. They’d seen a lot of mail to non-existent email addresses from that range and were looking to see what was going on and who was sending such bad mail. Multiple people on the list popped up with examples of the DMA mail.
Sunday morning, I checked the discussions wherein I discovered the DMA was added to the SBL (SBL 202218, SBL 202217, SBL 202216). It seems not only did they hit over a hundred Spamhaus spamtraps, they spammed Steve Linford himself.
No, I'm really not Christine
Got this to one of my accounts recently.
Congratulations and welcome to emailinform.
Read MoreTWSD: Mail known spam trap addresses
One of the things we all “know” is that if spammers get their hands on spamtrap addresses then they’ll stop sending mail to those addresses. This is true for a lot of spammers, but sadly it’s not true for all.
I don’t think it’s any secret that I consult for all types of mailers, from those who just need a little tune up to those who want me to help them avoid filters and blocking. During some of these consulting projects, I use my own spam folder as research and provide information on the spam that I am receiving from them.
A few years ago I was working with a company who hires a lot of different affiliates to send acquisition email. A few of their affiliates had really poor practices and they were trying to figure out which affiliates were the problem. I handed over a number of mails from my personal spam traps, in order to help them identify the problem affiliate.
I told them, and their affiliate, what my spamtrap addresses were. And, for many years I stopped receiving that particular spam. But, over the last few weeks I’ve seen a significant uptick in spam advertising my former client.
I’m certainly not trying to convince anyone that handing over spamtraps is a good thing. But there is at least some evidence out there that they’re not even competent enough to permanently remove traps. I really have to wonder at how sloppy some marketers are, too, that they’ll hire spammers and not at least hand over a list of addresses they know are bad addresses to mail.
I really thought spammers were smarter than that. I am, apparently, wrong.
EDIT: Of course, mailing this spamtrap gets them nothing but a little ranty blog post here. It doesn’t result in blocking, or disconnection from their ISP or their ESP or anything else. I suspect if there was actually an affect, like, say, I started forwarding this mail to Spamhaus or other filtering companies, they might stop mailing this address. Anyone want a 20 year old, slightly used spam trap?
TWSD: Hiding the opt-out
![]()
This is an actual opt-out link that came in a recent email. Sadly, this is a real company, listed on the NYSE sent by a major ESP.
A Spam Blast from the Past
A couple of days ago an ex-employee of Opt-In Inc., was kind enough to do a Reddit AMA answering questions about their experience working with Steve Hardigree in the “legitimate” email marketing industry, back in the early 2000s.
The whole thing is worth a read, but I thought I’d share some of his more interesting answers here.
Everyone knows everyone
TWSD: Adapt to filters
This morning the new Yahoo! CEO posted about changes to Yahoo! mail. I logged into one of my Yahoo accounts to check and see if I had access to the new Yahoo! mail client yet. I don’t, but I did notice that spammers have adapted to the new Yahoo model of disabling filters in the mail folder. Most of the mail in my inbox has, at the very top of the message “Click not spam to enable links!”
My favorite has to be the animated gif of how to click “not spam.”
Spammers spend so much time and energy compensating for filters, hopping IP addresses, rotating through domains, and specially creating mail for different ISPs. I have to wonder, though, if they would waste less time by sending opt-in mail.
Harvesting and forging email addresses
For the contact address on our website, Steve has set up a rotating set of addresses. This is to minimize the amount of spam we have to deal with coming from address harvesters. This has worked quite well. In fact it works so well I didn’t expect that publishing an email address for taking reader questions would generate a lot of spam.
Boy, was I wrong. That address has been on the website less than a month and I’m already getting lots of spam to it. Most of it is business related spam, but there’s a couple things that make me think that someone has been signing that address up to mailing lists.
One is the confirmation email I received from Yelp. I don’t actually believe Yelp harvested my address and tried to create me an email account. I was happy when I got the first mail from Yelp. It said “click here to confirm your account.” Yay! Yelp is actually using confirmations so I just have to ignore the mail and that will all go away.
At least I was happy about it, until I started getting Yelp newsletters to that address.
Yelp gets half a star for attempting to do COI, but loses half for sending newsletters to people who didn’t confirm their account.
I really didn’t believe that people would grab a clearly tagged address off the blog and subscribe it to mailing lists or networking sites. I simply didn’t believe this happened anymore. I know forge subscribing used to be common, but it does appear that someone forge signed me up for a Yelp account. Clearly there are more dumb idiots out there than I thought.
Of course, it’s not just malicious people signing the address up to lists. There are also spammers harvesting directly off the website.
I did expect that there would be some harvesting going on and that I would get spam to the address. I am very surprised at the volume and type of spam, though. I’m getting a lot of chinese language spam, a lot of “join our business organization” spam and mail claiming I subscribed to receive their offers.
Surprisingly, much of the spam to this address violates CAN SPAM in some way shape or form. And I can prove harvesting, which would net treble damages if I had the time or inclination to sue.
It’s been an interesting experience, putting an unfiltered address on the website. Unfortunately, I am at risk of losing your questions because of the amount of spam coming in. I don’t think I’ve missed any, yet, but losing real mail is always a risk when an address gets a lot of spam – whether or not the recipient runs filters.
I’m still pondering solutions, but for now the questions address will remain as it is.
Just Block It
I tend to go back and forth about reporting spam these days. On one level I know that it’s all a numbers game, and policy enforcement is more about the quantity of complaints than the quality. Knowing this I don’t often send in complaints. I do make a few exceptions: when I know the policy enforcement team or when it’s a current or former client.
Read MoreThings Spammers Do
Much like every other day, I got some spam today. Here’s a lightly edited copy of it.
Let’s go through it and see what they did that makes it clear that it’s spam, which companies helped them out, and what you should avoid doing to avoid looking like these spammers…
You opted in
One thing I get in some of the comments here and in some of the discussions I have with email senders is that no commercial emailer ever sends unsolicited email. That, clearly, at some point the recipient opted in to receive mail and if that person doesn’t want mail they shouldn’t ever give out their email address.
I have an old yahoo address that’s used primarily as my Flickr account login. I don’t believe I’ve ever given out the address to anyone or opted in to anything. Anything’s possible, this address was created sometime in 2006 or 2007 and I may have tossed it into a form to test something. It’s certainly not an address I ever actually use.
Earlier this week I checked mail on the account. There were almost 700 messages in there. It was pretty amazing how much garbage this unused, unshared address collected. Notice the “clever” use of foreign alphabets and the number of legitimate companies who have acquired this address or hired people to mail me on their behalf. I’m sure some of it is phishing, too.
What not to do
There’s a London concert promoter that’s been spamming our old sales address for 5 or 6 years now. I’ve sent in complaints, I’ve tried to unsubscribe, and the mail still keeps coming. They managed to get through my filters, again, this morning. In a fit of frustration I tweeted about how frustrated I was that they would not stop spamming me.
Well, that got someone’s attention. The person managing their twitter account tweeted at me with an email address and a suggestion to send him my address so he could take care of it. I sent the mail as asked and even got a reply.
Unfortunately, the reply was “I clicked the unsubscribe link at the bottom of the message for you.”
I dunno, maybe his mouse is a magic mouse and, somehow, the click from that magic mouse will be more effective than a click from my not-magic mouse. I’m not holding out much hope, though. I have no doubt that my sales address will keep getting invited to raves in London long after I retire.
Spamming ESPs
In my mailbox there is a definite uptick in spam from ESPs advertising their services.
Today’s email was from a company that has the following in their anti-spam policy:
Does it look like you're spamming?
There are lots of terribly complicated rules in email marketing and retention. “Only send email to people who opted-in”, “Never use a pink background”[1], “Have a working unsubscription link”, “Don’t put FREE in the subject line”[1].
Another one should be “How does what you’re doing look to a typical recipient?”.
I’ve received several pieces of spam recently from senders who were ticking quite a lot of the “email best practices” checkboxes, but who completely blew it by not looking at it from the recipients point of view. The mistakes they’ve made, and the things to learn from them, and much the same, so I’ll just give one example.
“Likes Music” is not the same as “Likes Groupon Clones”
I’ve been a subscriber to our local radio station’s mailing list for years – promos KFOG is running, local gigs, that sort of thing, all in a newsletter sort of format. They recently sent out an ad for a Groupon clone called “SweetJack” – on it’s own, not as part of a newsletter. I’m not interested, and I think it’s a fairly poor pitch and won’t work well for their demographic, but fair enough. A couple of weeks later I start getting spam from SweetJack, thanking me for signing up – to the tagged email address I’d only given to KFOG. And no mention of KFOG at all.
Most recipients are just going to see this as spam out of the blue from SweetJack, and hammer on the “This is Spam” button until it goes away. That’s dreadful for SweetJack’s reputation, and is going to hurt their delivery.
Recipients paying more attention are going to notice that the first they heard of SweetJack was an out of the ordinary promo by KFOG, and then they start getting spam from SweetJack. They’re likely to assume that KFOG sold their email addresses to SweetJack – and that they’re sending their spam to an email address that only KFOG has in my case confirms that. That’s going to be dreadful for SweetJack’s reputation and going to damage the relationship between KFOG and their existing subscribers. A dreadful idea.
Digging down deeper, it seems that while KFOG being bought out by media behemoth Cumulus Media a few years back didn’t damage their on-air content, it did change the amount of respect they have for their subscribers. SweetJack is a new Groupon clone started by Cumulus Media. They did have legitimate access to the KFOG mailing lists, sorta. It’s probably not an AUP or privacy violation. It’s just the sort of thing an eager marketing guy at the corporate owners would think was a great idea, to leverage the value of their existing subscribers.
But it would have been a pretty bad idea had they carried it out perfectly, with clear messaging and transparency to the recipients. And they blew their one opportunity to do it well, and I’m betting that most of the recipients have SweetJack categorized as “spammers”, both mentally and in their mail clients.
1. Not a real email marketing rule.
Not lazy, just annoyed
I don’t usually send in spam reports, but I submitted a couple in the last few weeks. Somehow an address of mine is on a bunch of rave / club lists in London. You want to know what is happening at London clubs this week? It’s all there in my spam folder.
This mail finally hit my annoyance threshold, so I’ve been submitting reports and complaints to the senders the last few weeks. The mail, with full headers, goes with an explanation that the address that received it was harvested off a website more than 5 years ago and never opted in to receive any mail.
One of the ISPs I sent the report to has a web form where the complainant and the customer can see the report and both can comment on it. The customer replied to my complaint on it.
TWSD: I can haz ethix marketing
I’m getting slammed by spam advertising URLs at http://perfectdeliveries.com/ from
Ethix Marketing LLC
711 S. Carson Street Suite 4
Carson City, Nevada 89701
The kicker? They’re violating CAN SPAM while they’re doing it. Seriously, sending mail out through open relays and proxies with forged From: addresses is a violation of CAN SPAM. And they’re spamming for ambulance chasers.
Spammers, eh?
TWSD: lie about the source of address
A few months ago I got email from Staff of Norman Rockwell Museum of Vermont, to an addresses scraped off one of my websites. At the bottom it says:
Read MoreTWSD: SEO Spamming
It’s no secret that I get a lot of spam. It’s no secret that some catches my eye enough to actually write about it here. Today’s spam is an email that actually made me laugh, though. Somewhere, some gardening site paid a lot of money for search engine optimization and got ripped off.
We own the site samspade.org. It’s down now, victim of a major hardware crash, but this was a site with a number of tools for tracking spammers. This morning, I got email about SamSpade.
Would you buy a used car from that guy?
There are dozens of people and companies standing up and offering suggestions on best practices in email marketing. Unfortunately, many of those companies don’t actually practice what they preach in managing their own email accounts.
I got email today to an old work email address of mine from Strongmail. To be fair it was a technically correct email. Everything one would expect from a company handling large volumes of emails. It’s clear that time and energy was put into the technical setup of the send. If only they had put even half that effort into deciding who to send the email to. Sadly, they didn’t.
My first thought, upon receiving the mail, was that some new, eager employee bought a very old and crufty list somewhere. Because Strongmail has a reputation for being responsible mailers, I sent them a copy of the email to abuse@. I figured they’d want to know that they had a new sales / marketing person who was doing some bad stuff.
I know how frustrating handling abuse@ can be, so I try to be short and sweet in my complaints. For this one, I simply said, “Someone at Strongmail has appended, harvested or otherwise acquired an old email address of mine. This has been added to your mailing list and I’m now receiving spam from you. ”
They respond with an email that starts with:
“Thank you for your thoughtful response to our opt-in request. On occasion, we provide members of our database with the opportunity to opt-in to receive email marketing communications from us.”
Wait. What? Members of our database? How did this address get into your database?
“I can’t be sure from our records but it looks like someone from StrongMail reached out to you several years ago. It’s helpful that you let us know to unsubscribe you. Thank you again.”
There you have it. According to the person answering email at abuse@ Strongmail they sent me a message because they had sent mail to me in the past. Is that really what you did? Send mail to very old email addresses because someone, at some point in the past, sent mail to that address? And you don’t know when, don’t know where the address came from, don’t know how it was acquired, but decided to reach out to me?
How many bad practices can you mix into a single send, Strongmail? Sending mail to addresses where you don’t know how you got them? Sending mail to addresses that you got at least 6 years ago? Sending mail to addresses that were never opted-in to any of your mail? And when people point out, gently and subtly, that maybe this is a bad idea, you just add them to your global suppression list?
Oh. Wait. I know what you’re going to tell me. All of your bad practices don’t count because this was an ‘opt-in’ request. People who didn’t want the mail didn’t have to do anything, therefore there is no reason not to spam them! They ignore it and they are dropped from your list. Except it doesn’t work that way. Double opt-in requests to someone has asked to be subscribed or is an active customer or prospect is one thing. Requests sent to addresses of unknown provenance are still spam.
Just for the record, I have a good idea of where they got my address. Many years ago Strongmail approached Word to the Wise to explore a potential partnership. We would work with and through Strongmail to provide delivery consulting and best practices advice for their customers. As part of this process we did exchange business cards with a number of Strongmail employees. I suspect those cards were left in a desk when the employees moved on. Whoever got that desk, or cleaned it out, found those cards and added them to the ‘member database.’
But wait! It gets even better. Strongmail was sending me this mail, so that they could get permission to send me email about Email and Social Media Marketing Best Practices. I’m almost tempted to sign up to provide me unending blog fodder for my new series entitled “Don’t do this!”
Content based filtering
A spam filter looks at many things when it’s deciding whether or not to deliver a message to the recipients inbox, usually divided into two broad categories – the behaviour of the sender and the content of the message.
When we talk about sender behaviour we’ll often dive headfirst into the technical details of how that’s monitored and tracked – history of mail from the same IP address, SPF records, good reverse DNS, send rates and ramping, polite SMTP level behaviour, DKIM and domain-based reputation and so on. If all of those are OK and the mail still doesn’t get delivered then you might throw up your hands, fall back on “it’s content-based filtering” and not leave it at that.
There’s just as much detail and scope for diagnosis in content-based filtering, though, it’s just a bit more complex, so some delivery folks tend to gloss over it. If you’re sending mail that people want to receive, you’re sure you’re sending the mail technically correctly and you have a decent reputation as a sender then it’s time to look at the content.
You want your mail to look just like wanted mail from reputable, competent senders and to look different to unwanted mail, viruses, phishing emails, botnet spoor and so on. And not just to mechanical spam filters – if a postmaster looks at your email, you want it to look clean, honest and competently put together to them too.
Some of the distinctive content differences between wanted and unwanted email are due to the content as written by the sender, some of them are due to senders of unwanted email trying to hide their identity or their content, but many of them are due to the different quality software used to send each sort of mail. Mail clients used by individuals, and content composition software used by high quality ESPs tends to be well written and complies with both the email and MIME RFCs, and the unwritten best common practices for email composition. The software used by spammers, botnets, viruses and low quality ESPs tends not to do so well.
Here’s a (partial) list of some of the things to consider:
Tagged Email Addresses
Sept 17, 2019: Shutting down comments on this post because we cannot help you recover any email account and I am concerned about the number of people who are providing PII (including phone numbers, credit card numbers!!! and email addresses) in the comments.
Read MoreYou might be a spammer if….
You feel the need to add
PLEASE NOTE THAT THIS IS NOT A SPAM OR AUTOMATED EMAIL, IT’S ONLY A REQUEST FOR A LINK EXCHANGE. YOUR EMAIL ADDRESS HAS NOT BEEN ADDED TO ANY LISTS, AND YOU WILL NOT BE CONTACTED AGAIN.IF YOU’D LIKE TO MAKE SURE WE DON’T CONTACT YOU AGAIN, PLEASE FILL IN THE FOLLOWING FORM: <link>
Read More
PLEASE ACCEPT OUR APOLOGIES FOR CONTACTING YOU.
Did anyone actually look at this email before sending?
I received spam advertising AARP recently. Yes, AARP. Oh, of course they didn’t send me spam, they hired someone who probably hired someone who contracted with an affiliate marketer to send mail.
The affiliates, while capable of bypassing spam filters, are incapable of actually sending readable mail.
The psychic and the not-really-opt-in
I’ve been getting a continual stream of spam from a psychic. I blogged about it a few months ago, and even had a call with the psychic’s ESP. None of that seemed to matter. Every few days I’d get another ad for psychic candles, or recording services or whatever. It wasn’t mail I could easily filter, and every time I’d get it I’d growl and dump it in my junk folder.
Yesterday, I received another mail from her. The subject line is “list opt-in verification.” Really? Could she really be actually confirming her list? Actually asking if I want to continue receiving mail?
When an open is not a sign of interest
A lot of people, including myself, are using opens as one of the measures of engagement. This, as a general rule, is not a bad measure. However, there are people who will open email not because they’re interested in it, but because they know it is spam.
Take, for instance, the email address I acquired in 1993. Yes, I still have this address. I stopped using it to sign up for lists in 1999 and stopped using it for most of the rest of my mail around 2001. This address, though, is on any number of spam mailing lists. The spam that gets through is usually sent by hard-core spammers. The ISP that hosts that mailbox uses Communigate Pro to filter mail, so much of the casual spam is filtered.
Generally, if I open an email (and load images or click through) on that account it is only in order to track down a spammer. For instance, I’m getting a lot of spam there from affiliates offering me the opportunity to purchase printing services for a very low price. I have actually been opening the mail, and clicking through. But I’m not clicking through because I’m interested in purchasing. I’m clicking through to see if my reports to abuse@ printer are resulting in any action against the spammers. (They’re not).
The thing is, though, I know that by clicking through on ads, I’ve now been promoted by the spammer to the “clicks on emails! it’s a live address!” list. Which only means I’m going to get more spam from them. Lucky me.
Using clicks and opens as a measure of engagement isn’t necessarily bad. But when using them you have to understand the limitations of the measurement and that what you may think it’s telling you isn’t actually what it’s telling you.
You want to sell me a list?
Over the years, some of my clients have found it expedient to give me email addresses at their domains. These addresses forward mail addressed to laura@clientsite to my own mailbox. Generally these are so I can be added to internal mailing lists and have access to their internal tools.
It’s often amusing to see the spam that comes through to those addresses. Over the last few weeks I’ve received multiple spams advertising an email appending service.
Let the irony sink in. An email appending service is sending me an email at a client company offering the client company the opportunity to append email addresses. “See how accurate our appending is!”
How accurate can a service be if they can’t even target their own spam correctly?
In addition to the appalling targeting they’re also violating CAN SPAM (no physical postal address), their website is a collection of broken links and they don’t provide any company name or information in the email or on the website.
To top it all off, the mail says, “if you’re not the right person to act on this mail, please forward this to the right person.” Followed by a standard legal disclaimer that says, “The information contained in this e-mail message and any attachments is confidential information intended only for the use of individuals or entities named above. If the reader of this message is not the intended recipient you are hereby notified that any dissemination, distribution or copying of this communication is strictly prohibited. If you have received this communication in error, please notify us immediately by e-mail at the originating address.”
I wonder if blogging about the utter email incompetence about mail from David Williams, Business Development (phone number: 800-961-5127) violates the confidentiality clause?
Tagged.com's newest trick
I signed up a disposable address at tagged.com last summer, to see how their signup process went and how aggressive they were at marketing.
They mailed me maybe a dozen times over the course of a month and then the mail stopped.
Until today.
Today I got two messages from tagged.com, one from Sophia C (33) and one from Melinda E (27). The messages are identical except for the names and some of the advertising on the bottom.
I find it a bit coincidental that after all the recent news about Tagged that I start getting mail from them again. Mail that is not from anyone I know. Mail attempting to entice me into logging back into the tagged site.
Social network spam
I’ve been seeing more and more social network spam recently, mostly on twitter. In some ways it’s even more annoying than email spam. Here I am, happily having a conversation with a friend and then some spammer sticks their nose in and tweets “myproduct will solve your problem!”
It’s happened twice in the last week.
In most recent example, I was asking my twitter network for some advice on pasta making. I’ve made pasta a few times, but it’s never been exactly right. Not having an Italian grandmother to ask, I was looking for someone with experience in pasta making to answer a few questions. I was having an ongoing conversation with a friend who was helping me troubleshoot my problems. He gave me his recipe to try to see if that would work better. I thanked him profusely and replied that I would give it a try but probably not tomorrow because it was accounting day and those tend to run late. Someone replied to that tweet suggesting I try some random accounting software to make my accounting easier.
Just… No.
Interjecting product ads in a conversation may be the “acceptable” and “best practice” way to market through social networking. But, I can promise that you’re no better the guy who interrupts conversations at parties so he can hand out business cards for his affiliate program selling herbal male enhancement drugs.
Don’t be That Guy.
Update: Today’s twitter spam was from one of the email accreditation services attempting to sell me their email delivery services.
TWSD: Using FOIA requests for email addresses
Mickey has a good summary of what’s going on in Maine where the courts forced the Department of Inland Fisheries and Wildlife to sell the email addresses of license purchasers to a commercial company.
There isn’t permission associated with this and the commercial company has no pretense that the recipients want to receive mail from them. This is a bad idea and a bad way to get email addresses and is no better than spammers scraping addresses from every website mentioning “fishing” or “hunting.”
Spammers aren't who you think they are
Shady direct marketers exploit CAN SPAM to continue spamming but protect themselves from the law. This is something I’ve been talking about for a while (TWSD), and it’s nice to see the mainstream press noticing the same thing.
HT: Box of Meat
Important notification spammers break the law
I’m currently being inundated at multiple address with spam advertising spamming services. Most of these notices have the subject line: IMPORTANT NOTIFICATION. The text includes:
Read MoreThe good, the typical and the ugly
In the theme of the ongoing discussions about ESPs and their role in the email ecosystem, I thought I’d present some examples of how different ESPs work.
The good ESPs are those that set and enforce higher standards than the ISPs. They invest money and time in both proactive and reactive policy enforcement. On Monday I’ll talk about these standards, and the benefits of implementing these policies.
The typical ESPs are those that have standards equivalent to those of the ISPs. They suspend or disconnect customers when the customers generate problems at the ISPs. They have some proactive policy enforcement, but most of their enforcement is reactive. On Tuesday I’ll talk about these standards and how they’re perceived by the ISPs and spam filtering companies.
The ugly ESPs are those that have low standards and few enforcement policies. They let customers send mail without permission. Some of the ugly ESPs even abuse other ESPs to send some of their mail, thus sharing their bad reputations across the industry. On Wednesday I’ll look at some of their practices and discuss how they affect other players in the industry.
TWSD: keep spamming even when they say they'll stop
About a month ago I posted about receiving spam from a psychic attempting to sell me candles and stuff. The spammer was sending mail from a company called “Garden of Sound” using an ESP called OnLetterhead. A brief investigation led me to believe that unsubscribing from the mail was not going to do anything.
The post prompted an email from Scott B. the VP of Marketing of the company that is responsible for OnLetterhead. I replied to his email, pointing out a number of things he was doing that made his business look like an ESP front for spammers.
After he received my mail he called me to talk to me about the content of my post and the email and to assure me they were immediately implementing one of my suggestion (that they not put a generic “here’s how to unsubscribe” link on their 1000+ link domains, instead have those actually point to their AUP and corporate pages). He also assured me they took my complaint seriously and I would no longer be receiving email.
Guess what?
Garden of Sound is still spamming me from OnLetterhead. They’ve not even managed to implement the changes they pledged would be rolled out the same week as my blog post. Sure, the domain I’m getting spam from is different, the physical postal address is different, the product is different, the friendly from is different. But the preheader still says “this mail sent by Garden of Sound.” It’s all the same list, it’s all the same company, it’s all the same group of spammers.
Despite Scott’s attempt to convince me he wasn’t a spammer, it seems my initial impression was right. OnLetterhead is simply are a company attempting to look like they’re legitimate without actually taking any responsibility for the email going out from their network. They can’t even manage the bare minimum.
It’s companies like this that give the rest of ESPs a bad name.
I don't have a "this is spam" button
Here at Word to the Wise we have some unique requirements for mail. For instance, I need to be able to receive examples of emails that are being blocked elsewhere in order to do my job. This means not only do we not outsource mail to someone else, we also run limited spam filtering on the server side. It does mean I have to wade through a bit more spam than others do, but that’s generally not a problem. My client side filters do a decent job at keeping most of the crud out of my mailboxes.
My work account gets very little spam in the folder I use as my inbox. I’m not even sure exactly why this is, but it’s true. One of the exceptions is a psychic (no, really) who has a copy of one of my work email addresses and she regularly spams me offering her spiritual guidance and the opportunity to buy her stuff in order to make peace within my world. I’ve received these before, usually I just delete them and move on.
Occasionally, though, I long for the ease of a “this is spam” button. Just to be able to hit a single button, no work, no effort and know that I have registered my frustration with a spammer. Today was one of those days. I really don’t want this psychic spam in my mailbox. It seems reasonably professionally done, though, so I check the headers to see if it’s being send from any ESP I know and if it’s worth my time to send in a “hey, didn’t sign up for this, and no, I didn’t forget, either” email.
I visited the website belonging to the domain sending the mail.
TWSD: Privacy protection for commercial domains
One of my major pet peeves is supposedly legitimate companies hiding behind privacy protection in their whois records. There is absolutely no reason for a legitimate company to do this. There are lots of reasons a non-legitimate company might want to hide behind privacy services, but I have never heard a good reason for legitimate companies to hide.
Look, a company sending any commercial email is required by law to provide a physical postal address in every email they send. What point is there, then, to hiding addresses in whois records? The only thing it does is make a sender look like a spammer. If a sender is a business, then they need to have a real business address anyway, and that address should be available in their domain registration.
It may seem like a trivial point, it may seem minor, but spammers use domain privacy services to hide the various tendrils of their businesses. They don’t want anyone to be able to tell that domain A is related to domain B is related to domain C. Proxy services let them trivially hide their identities. This is the major business use of privacy protection. Real companies don’t need to hide behind privacy services.
Using domain privacy services make senders look like spammers. One trivial thing that ISPs can do is stop providing FBLs or whitelistings to domains behind privacy services. This will weed out spammers without doing harm to real senders. Certification services can refuse to certify companies that hide their identity. My small contribution to the cause is to refuse to represent any company to an ISP if their domain is behind a privacy service.
Just to be clear, I have no problem with personal, non-business domains using privacy services. There are valid reasons individuals may want to hide their physical location. But businesses? Step up and quit hiding.
On the subject of privacy services, Mickey recently reviewed a court ruling that commented on the legality of using privacy services. The court says:
Who are you and why are you mailing me?
I’ve mentioned here before that I use tagged addresses whenever I sign up for. This does help me mentally sort out what’s real spam and what’s just mail I’ve forgotten I’ve signed up for.
Yesterday, I received and email from e-fense.com thanking me for my interest in their new product. The mail came to a tagged address, but not a tag that I would have given to e-fense.com. Their opening paragraph said:
TWSD: My lunch is not spam
My ISP information page occasionally gets trackback pings from various blog posts. This week one of the trackbacks was from a blog post titled “One man’s Spam is another man’s lunch.” The theme of the blog post was that email marketers are poor, put upon business people that have to contend with all sorts of horrible responses from recipients, spam filtering companies and ISPs.
Since the poster took the time to link to my blog, I thought I’d take the time to look in detail at his post and talk about how likely it is to work.
You might be a spammer if…
… the best thing you have to say about your email practices is “They’re CAN SPAM compliant.”
… text to .gif is a vital part of your email generation process
… you have to mail from multiple ESPs in order to get good delivery
Please contribute your own in the comments.
I’d also like to thank Al for guest posting 2 days this week. Thanks, Al!
TWSD: Dumb and dumber
I recently received a spam offering to get one of my personal websites listed in foreign search engines. Harvesting addresses off websites is dumb. Even dumber is sending a followup a week later with a notice at the top.
Read MoreTWSD: Run, hide and obfuscate
Spammers and spamming companies have elevated obfuscating their corporate identities to an artform. Some of the more dedicated, but just this side of legal, spammers set up 3 or 4 different front companies: one to sell advertising, one or more to actually send mail, one to get connectivity and one as a backup for when the first three fail. Because they use rotating domain names and IP addresses all hidden behind fake names or “privacy protection services”, the actual spammer can be impossible to track without court documents.
One example of this is Ken Magill’s ongoing series of reports about EmailAppenders.
Aug 5, 2008 Ouch: A List-Purchase Nighmare
Sept 9, 2008 Umm… About EmailAppenders’ NYC Office
Sept 15, 2008 E-mail Appending Plot Thickens
Nov 11, 2008 EmailAppenders Hawking Bogus List, Claims Publisher
Dec 23, 2008 Internet Retailer Sues EmailAppenders
Feb 1, 2009 EmailAppenders Update
Mar 10, 2009 Another Bogus E-mail List Claimed
April 14, 2009 EmailAppenders a Court No-Show, Says Internet Retailer
April 21, 2009 EmailAppenders Gone? New Firm Surfaces
May 5, 2009 EmailAppenders Back with New Web Site, New Name
Their actions, chronicled in his posts, are exactly what I see list providers, list brokers and “affiliate marketers” do every day. They hide, they lie, they cheat and they obfuscate. When someone finally decides to sue, they dissolve one company and start another. Every new article demonstrates what spammers do in order to stay one step ahead of their victims.
While Ken has chronicled one example of this, there are dozens of similar scammers. Many of them don’t have a persistent reporter documenting all the company changes, so normal due diligence searches fail to turn up any of the truth. Companies looking for affiliates or list sources often fall victim to scammers and spammers, and suffer delivery and reputation problems as a result.
Companies that insist on using list sellers, lead generation companies and affilates must protect themselves from these sorts of scammers. Due diligence can be a challenge, because of the many names, domains and businesses these companies hide behind. Those tasked with investigating affiliates, address sources or or mailing partners can use some of the same investigative techniques Ken did to identify potential problems.
TWSD: Lying and Hiding
Another installment in my ongoing series: That’s What Spammers Do. In today’s installment we take a look at a company deceiving recipients and hiding their real identity.
One of my disposable addresses has been getting heavily spammed from mylife.com. The subject lines are not just deceptive, they are provably lies. The mail is coming from random domains like urlprotect.com or choosefrequency.com or winnernotice.com advertising links at safetyurl.com or childsafeblogging.com or usakidprotect.com.
The spam all claims someone is “searching for…” at their website. The only thing is, the email address is associated with a fake name I gave while testing a website on behalf of a client. I know what website received the data and I know what other data was provided during the signup process. I also know that the privacy policy at the time said that my data would not be shared and that only the company I gave the information to would be sending me email.
Just more proof that privacy policies aren’t worth the paper they’re written on. But that’s not my real issue here.
The real issue is that I am receiving mail that is clearly deceptive. The subject lines of the emails up until yesterday were “(1) New Message – Someone Searching for You, Find Out…” Yesterday, I actually clicked through one of the messages to confirm that the emails were ending up at mylife.com. After that, the subject lines of the emails changed to “(1) New Person is Searching for You.” I don’t know for sure that my click has caused the change in subject lines, but the timing seems a bit coincidental.
It’s not that someone, somewhere gave mylife.com bad data, or that someone typed a name into the mylife.com search engine and the mylife.com database showed that name and my email address were the same. Neither this name or this email address show up in a google search and I can say with certainty that this is a unique address and name combination given to a specific website. Therefore, the subject lines are clearly and demonstrably lies.
The spams are also coming from different domains and advertising links in different domains. The content is identical, the CAN SPAM addresses are identical. While the court may not rule this is deceptive under the rules of CAN SPAM, it certainly is an attempt to avoid domain level spam filters.
Who are mylife.com? Well, their website and the CAN SPAM address on their spam claims they are the company formerly known as reunion.com. I’ve talked about reunion.com here before. They have a history of harvesting addresses from users address books. They were sued for deceptive email practices under California law, but won the case just recently. They seem to think that the court case was permission to send deceptive email and have thus ramped up their deceptive practices.
If you are a legitimate email marketer, there are a couple take home messages here.
1) Spammers send mail with different domains, from different IP addresses, that contain identical content, landing pages and CAN SPAM addresses. Legitimate marketers should not rotate content and sends through different domains or different IP addresses. Pick your domain, pick your IP and stick with it.
1a) Spammers use randomly chosen domain names and cycle through domains frequently. Legitimate marketers must not use unrelated domains in marketing. Use a domain name that relates to your product, your industry or you.
2) Spammers send mail with deceptive subject lines. Legitimate marketers should make sure their subject lines are clear and truthful.
3) Spammers send mail in violation of the privacy policy under which information was collected. Legitimate marketers should be very careful to handle data in accordance with their privacy policies.
That’s what spammers do. Is that what you do?
Buying lists and other stupid marketing tricks
Back in November, I commented on Zoominfo and that they were selling senders very bad lists. At that time, Zoominfo did not have my current information. They have since rectified that problem and are now selling my information to people.
This morning, I received an email that said:
How to devalue your mailing lists
This morning I got spam about college basketball – Subject: Inside: your ESPN Tourney Guide. That’s anything but unusual, but this spam got through my spam filters and into my inbox. That’s a rare enough event that I’m already annoyed before I click on the mail in order to mark it as spam.
Wait a second, the spam claims to be from Adobe. And it’s sent to a tagged address that I only gave to Adobe. Sure enough, it’s Adobe and ESPN co-branded spam about college basketball sent to an Adobe list.
Down at the bottom of the email there’s a blob of tiny illegible text, in very pale grey on white. Buried in there is an opt-out link: “If you’d prefer not to receive e-mail like this from Adobe in the future, please click here to unsusbscribe“.
I’d prefer not to receive college sports spam from anyone, including Adobe, so I click on it and find a big empty white webpage with this in the middle of it:
Who is Julia and why won't she leave me alone?
There seems to be some new spam software in use. Julia <random last name> keeps telling me about her new webcam, how much she wants to date me and wants to know when I want to visit. These spams started February 1. I’ve had 179 caught by my MUA filters, and 152 caught by spamassassin (SA score >7 are filtered to a special account).
This is exactly the type of pattern that causes people to write filters that years later people look at and ask why someone thought this was a reasonable marker for spam.
The good folks over at MailChimp have examined some of the scoring rules that their clients trigger. They found some “Julia” type markers. Some oddities they reported on:
But that's what spammers do!
A few weeks ago I was asked my opinion about a delivery situation. It seems that a sender wanted to mail to a purchased email list. They asked what I thought about getting fresh IP addresses and domains to use to send mail to the purchased list. “We know we’re going to get complaints, probably hit spamtraps and generally have problems with the first few sends of the list. We want to do this without harming our reputation. We figure if we move over to different domains and different IP addresses than we can send this mail and not suffer a reputation hit.”
Uh. Yeah. That’s what spammers do. They split off their mail into discrete sets so that they can spam with impunity and still have one or two ranges that have a good reputation and decent delivery. Some spammers have taken the discrete companies to extremes, and have a series of companies. They purchase a new list and send it through their companies one by one. At each step, they aggressively purge off bounces and complainers. Gradually, they move the list through their steps, resulting in a list that generates few complaints that they can send through their high reputation companies with few delivery problems.
Sure, legitimate mailers can do the same type of thing. But how legitimate can a sender be if they are using spammer tactics? And these are not mailers unwittingly doing something that spammers also do, these are mailers who are using spammer tactics for exactly the same reason spammers do it. They are trying to send mail people do not want, but send it in a way that does not negatively affect their bottom line.
Spammers hide and try to avoid their bad reputation. Legitimate mailers do not.
TWSD: breaking the law
I tell my clients that they should comply with CAN SPAM (physical postal address and unsubscribe option) even if the mail they are sending is technically exempt. The bar for legality is so low, there is no reason not to.
Sure, there is a lot of spam out there that does not comply with CAN SPAM. Everything you see from botnets and proxies is in violation, although many of those mails do actually meet the postal address and unsubscribe requirements.
One of my spams recently caught my eye today with their disclaimer on the bottom: “This email message is CAN SPAM ACT of 2003 Compliant.” The really funny bit is that it does not actually comply with the law. Even better, the address it was sent to is not published anywhere, so the company could also be nailed for a dictionary attack and face enhanced penalties.
It reminds me of the old spams that claimed they complied with S.1618.
